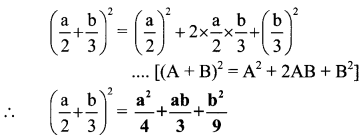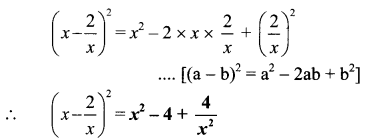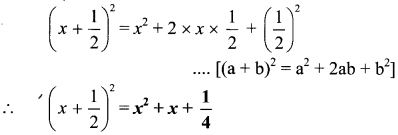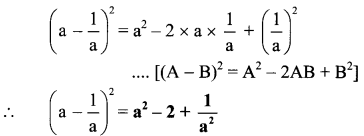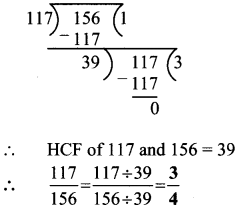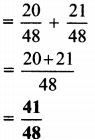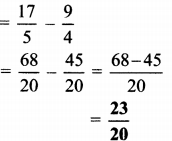Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Geography Solutions Chapter 2 The Sun, the Moon and the Earth Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Geography Solutions Chapter 2 The Sun, the Moon and the Earth
Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 The Sun, the Moon and the Earth Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Correct the wrong statements. Write down the corrected ones.
Question 1.
The moon revolves around the sun.
Answer:
Wrong – The moon revolves around the earth.
Question 2.
On a full moon day, the moon, the sun and the earth are positioned in this sequence.
Answer:
Wrong – On a full moon day, the sun, the earth and the moon are positioned in this sequence.
Question 3.
The revolutionary orbits of the earth and the moon are in the same plane.
Answer:
Wrong – The revolutionary orbits of the earth and the moon are not in the same plane. The moon’s revolutionary orbit makes an angle of about 5° with that the earth.
![]()
Question 4.
In one revolution of the moon, its orbit intersects the earth’s orbit only once.
Answer:
Wrong – In one revolution of the moon, its orbit intersects the earth’s orbit twice.
Question 5.
It is alright to observe a solar eclipse without protecting the eyes.
Answer:
Wrong – It is necessary to view the sun disc through dark glasses or through special goggles made for that purpose, otherwise the intense light of the sun can be harmful to the naked eye.
Question 6.
An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon is in the perigee position.
Answer:
Wrong – An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon is in the apogee position.
2. Select the correct option.
Question 1.
Solar eclipse

Answer:
(b)
Question 2.
The shape of sun disc at the time of annular solar eclipse.

Answer:
(a)
![]()
Question 3.
Apogee position of the moon.

Answer:
(c)
3. Complete the following table.
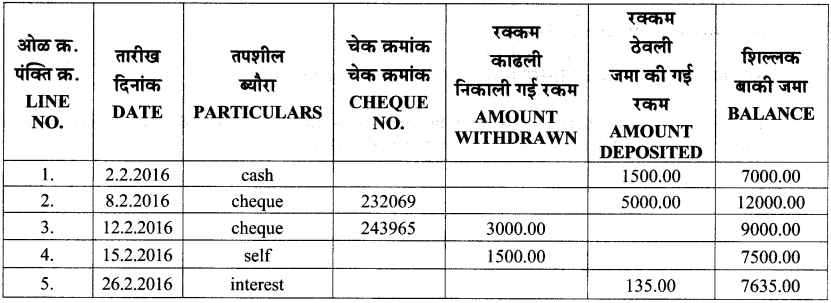
| Details | Lunar Eclipse | Solar Eclipse |
| Phase of the moon | ………… | ……………. |
| Sequence | Moon-Earth- Sun | …………. |
| Type of Eclipse | …………. | ………….. |
| Maximum duration of total eclipse | 107 minutes | ……………. |
Answer:
| Details | Lunar Eclipse | Solar Eclipse |
| Phase of the moon | Full Moon Day | New Moon Day |
| Sequence | Moon-Earth-Sun | Moon-Earth-Sun |
| Type of Eclipse | Total and Partial | Total, Partial, Annular |
| Maximum duration of total eclipse | 107 minutes | 440 Seconds |
4. Draw and label the diagrams.
Question 1.
Total and partial solar eclipse:
Answer:

Question 2.
Total and partial lunar eclipse:
Answer:

5. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Why do the sun, the moon and the earth not lie in one and the same line on every full moon and new moon day?
Answer:
(i) The orbital path of the earth and that of moon are not in the same plane.
(i) The moon’s revolutionary orbit makes an angle of about 5° with that of the earth.
(iii) On each new moon day, the lines joining the earth and the sun and the moon make an angle of 0° whereas on each full moon day, this angle is 180°.
(iv) So, the sun, the earth and the moon may not be in one straight line in the same plane on every new moon or full moon day.
Question 2.
When a total solar eclipse occurs why is the partial eclipse also seen from the earth?
Answer:
(i) On a new moon day if the sun, the moon & the earth fall in one line & are in the same plane, the shadow of the moon falls on the earth
(ii) This shadow is of two types – the central portion of the shadow is darker & the periphery is light.
(iii) In the area where the dark shadow falls, the sun becomes completely invisible. Such an area experiences a total solar eclipse.
(iv) However during the same period, at the places where the shadow is lighter, the sun disc appears partially covered. Such an area experience partial solar eclipse. Thus when a total solar eclipse occurs a partial eclipse is also seen from the earth.
![]()
Question 3.
Suggest measures that can be taken to eradicate the superstitions related to the eclipses.
Answer:
The following measures can be taken to eradicate superstition related to eclipses:
- Use of media to create awareness.
- Parental guidance to help think logically.
- Teachers guidance to help students develop a scientific outlook.
- Campaigns, public meetings and lectures especially in rural areas to eradicate superstitions.
Question 4.
What precautions should we take while observing a solar eclipse?
Answer:
The precautions to be taken while observing a solar eclipse are:
- We should not observe a solar eclipse with naked eyes as the intense light of the sun can harm them.
- We must use dark glasses or goggles that are specially designed for viewing the solar eclipse.
Question 5.
What types of Solar eclipses will occur in perigee conditions?
Answer:
Total and Partial solar eclipse will occur in perigee condition.
(1) Total solar eclipse :
- On a new moon day, the sun, the moon the earth are in a straight line & the shadow of the moon falls on the earth
- The area of dark shadow falls on the earth, the sun becomes completely invisible. This condition is known as total solar eclipse.
(2) Partial solar eclipse:
- However during the same period at places where the shadow is lighter, the sun disc appears partially covered,
- This condition is described as partial solar eclipse.
Activities:
- Collect paper cuttings about eclipses and paste them in a notebook.
- Write a note on an eclipse that you have seen.
- Using the internet, ‘Panchanga’ and calendar collect information about the eclipses that are likely to occur this year.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 The Sun, the Moon and the Earth InText Questions and Answers
Use your brain power:
Question 1.
On the day of solar eclipse, in which part of the earth will it not be seen?
Answer:
Solar eclipse will not be seen where there is night.
Question 2.
Can we see total and annular solar eclipses on the same occasion?
Answer:
No, total and annular solar eclipses cannot be seen on the same occasion.
Question 3.
Why is an annular lunar eclipse not seen?
Answer:
An annular lunar eclipse cannot be seen because:
- The size of the earth is bigger than that of the moon.
- As compared to the sun, the moon is close to the earth.
- Therefore, it is not possible that a dark shadow of the earth is cast in space & does not reach the moon.
Question 4.
Which eclipses will you see from the moon?
Answer:
Solar eclipses can be seen from the moon.
![]()
Question 5.
Why are solar eclipses caused by the other planets not seen from the earth?
Answer:
(i) A Solar eclipse occurs when the moon comes in between the sun & the earth & all of them are in the same plane & fall in one line on a new moon day.
(ii) Similarly, when Venus & Mercury come in between the earth & the sun, they make a small speck against the surface of the sun as they are too far away.
(iii) The other planets have orbits outside the earth’s & cannot fall in line between the earth & the sun.
(iv) Hence, the solar eclipse caused by other planets are not seen from the earth.
Think about it:
Question 1.
Figure shows positions of the moon as seen from the space and as seen from the earth. How will you identify which are which?

Answer:
Half of the moon’s portion is illuminated by the sun, and the other half remains dark. However, only some part of this illuminated portion of the moon can be seen from the earth. The position of the moon from the Earth is as follows:
- New moon
- Waxing crescent
- 1st Quarter
- Waxing Gibbous
- Full moon
- Waning Gibbous
- Last quarter
- Waning crescent
Question 2.
Like sunlight and moonlight, is there anything called the earth light? If yes, where do you think it is found?
Answer:
Yes, Earthlight is the partial illumination of the dark portion of the moon’s surface by light reflected from the earth’s airglow.
Question 3.
When solar eclipses do not occur on a new moon day, does it mean that the moon does not have any shadow at all?
Answer:
The moon casts a shadow on every new moon day, but solar eclipse occurs only when the moon’s shadow falls on the earth.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 The Sun, the Moon and the Earth Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct options from the brackets:
Question 1.
The shape of the moon’s orbit is _________. (round, elliptical, square)
Answer:
elliptical
Question 2.
The moon has _____ and ______ motions. (axial, orbital, elliptical)
Answer:
axial, orbital
Question 3.
When the moon is closest to the earth it is said to be in ________. (apogee, perigee, orbit)
Answer:
perigee
Question 4.
When the moon is farthest to the earth it is said to be in ______. (apogee, perigee, arial)
(round, elliptical, square)
Answer:
apogee
Question 5.
Solar Eclipse occurs on the _______ day. (full moon, new moon, quarter moon)
Answer:
new moon
Question 6.
Lunar Eclipse occurs on the ______ day. (full moon, new moon, quarter)
Answer:
full moon
Question 7.
_______ solar eclipse is a rare phenomenon. (Total, Partial, Annular)
Answer:
Annular
![]()
Question 8.
When the shadow of the moon on the central portion of the earth is darker while the periphery is lighter it is known as a _______ solar eclipse.
(partial, total, lunar)
Answer:
total
Question 9.
When the shadow of the moon on the central portion of the earth is lighter and the sun disc appears to be partially covered, it is known _________ solar eclipse.
(total, partial, solar)
Answer:
partial
Question 10.
The moon is ________ when the earth, the moon and the sun make an angle of 90°. (full, semicircular, crescent)
Answer:
semicircular
Question 11.
Occultation occurs with reference to the _____. (sun, moon, earth)
Answer:
moon
Question 12.
Transit is associated with the _______ .(sun, moon, earth)
Answer:
sun
Question 13.
During the period of _______ eclipse, a large number of birds and animals get confused. (solar, lunar, annular)
Answer:
solar
Correct the wrong statements. Write down the correct ones:
Question 1.
When the moon is closest to the earth it is said to be in apogee and when it is the farthest, the position is called perigee.
Answer:
Wrong – When the moon is closest to the earth it is said to be in perigee and when it is the farthest, the position is called apogee.
Question 2.
The moon wanes from the new moon day to the full moon day and waxes from the full moon to the new moon day.
Answer:
Wrong – The moon waxes from the new moon day to the full moon day and wanes from the full moon to the new moon day.
Select the correct options:
Question 1.

Answer:
(c)
Question 2.

Answer:
(c)
![]()
Complete the following table:
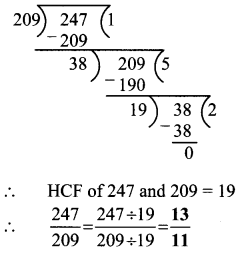
Question 1.
| Details | Numerical facts |
| 1. Perigee distance | ………. |
| 2. Apogee distance | ………. |
| 3. Angular distance between the moon’s and the earth’s orbit | ……….. |
| 4. Maximum duration of a total solar eclipse | ………. |
| 5. Maximum duration of a total lunar eclipse | ………… |
| 6. Number of solar eclipse (types) | …………. |
| 7. Number of lunar eclipse (types) | …………… |
Answer:
| Details | Numerical facts |
| 1. Perigee distance | 3,56,000 km |
| 2. Apogee distance | 4,07,000 km |
| 3. Angular distance between the moon’s and the earth’s orbit | 5° |
| 4. Maximum duration of a total solar eclipse | 7 minutes 20 seconds |
| 5. Maximum duration of a total lunar eclipse | 107 minutes |
| 6. Number of solar eclipse (types) | 3 |
| 7. Number of lunar eclipse (types) | 2 |
Name the following:
Question 1.
Motions of the moon.
Answer:
Axial and orbital motion.
Question 2.
Types of solar eclipse.
Answer:
Total solar eclipse, Partial solar eclipse, Annular solar eclipse.
Question 3.
Types of lunar eclipse.
Answer:
Total lunar eclipse and Partial lunar eclipse.
Question 4.
Eclipse that confuses animals and birds.
Answer:
Solar eclipse.
Question 5.
An example of occultation.
Answer:
Total solar eclipse.
Question 6.
The event of the occurrence of solar eclipse or lunar eclipse.
Answer:
Astronomical event.
![]()
Define the following:
Question 1.
Perigee:
Answer:
When the moon is the closest to the earth in its orbit, it is perigee.
Question 2.
Apogee:
Answer:
When the moon is at the farthest from the earth in its orbit, it is apogee.
Question 3.
Occultation:
Answer:
The moon revolves around the earth. While doing so, it obscures1 a star or a planet and that celestial2 body appears to hide behind the moon. This is called occultation.
Question 4.
Transit:
Answer:
If an inner planet like Mercury or Venus comes in between the line of the earth and the sun, a transit occurs. At that time a small dot appears to move across the sun’s disc.
Question 5.
Phases of the moon:
Answer:
The illuminated portion of the moon disc observed from the earth that keeps on changing every day within a lunar month are called the phases of the moon.
Question 6.
Solar Eclipse:
Answer:
If the moon comes between the earth and the sun in a straight line on new moon day, the shadow of the moon falls on the earth and the sun becomes totally or partially invisible in the shadow zone. This phenomenon is called the solar eclipse.
Question 7.
Lunar Eclipse:
Answer:
On a full moon day, the . moon’s path of revolution passes through the thick shadow of the earth and the moon becomes totally or partially invisible. This phenomenon is called lunar eclipse.
Question 8.
Annular Solar eclipse
Answer:
Sometimes when the moon is in apogee position, a deep shadow of the moon is cast in space & does not reach the earth. From a very small region of the earth, only an illuminated edge of the sun disc is seen in the form of a ring. This is called annular solar eclipse.
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
What is the period of waxing moon?
Answer:
The period of waxing moon is the fortnight from new moon to full moon in which the illuminated part of the moon from the earth keeps on increasing (waxing)
Question 2.
What is the period of waning moon?
Answer:
The period of waning moon is the fortnight from full moon to new moon in which the illuminated part of the moon seen from the earth keeps on decreasing (waning)
Question 3.
Why can we see the phases of the moon from the earth?
Answer:
We can see the phases of the moon from the earth due to the sunlight reflected from the moon.
![]()
Question 4.
When does the moon appear semi-circular in shape in the sky?
Answer:
On the first and the third quarter days, the moon, the earth & the sun make an angle of 90° due to which we see half the portion of the illuminated moon in a semi-circular shape in the sky.
Question 5.
What types of solar eclipses occur in perigee position?
Answer:
Total & Partial Solar eclipses occur in perigee position.
Question 6.
When does a lunar eclipse occur?
Answer:
A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon enters the shadow of the earth while revolving around it.
Give geographical reasons for the following statements:
Question 1.
We constantly see only one and the same side of the moon.
Answer:
- The time, the moon takes to make one revolution around the earth and one rotation around itself is the same.
- As the axial and the orbital motions of the moon are almost of the same duration, only one, the same side of the moon faces the earth.
- Therefore, we constantly see only one and the same side of the moon.
Question 2.
The distance between the moon and the earth keeps on changing.
Answer:
- The moon’s orbit of the revolution is elliptical to that of the earth.
- Hence the distance of the moon from the earth is not the same everywhere along its orbit while revolving.
- When it is the closest to the earth it is said to be in perigee and when it is at the farthest, the position is called apogee.
Question 3.
Eclipses do not occur on each new moon or full moon day.
Answer:
- The orbital path of the earth and that of the moon are not in the same plane.
- The moon’s revolutionary orbit makes an angle of about 5° with that of the earth.
- So, the sun, the earth and the moon may not be in one straight line in the same plane on every new moon or full moon day.
- Hence, eclipses do not occur on each new moon or full moon day.
Question 4.
The Annular solar eclipse is rarely seen.
Answer:
The Annular solar eclipse is rarely seen because
- The moon is in apogee position.
- The deep shadow of the moon is cast in space and does not reach the earth.
- From a very small region of the earth, only an illuminated edge of the sun disc is seen in the form of a ring.
Question 5.
Birds and animals are confused during the solar eclipse.
Answer:
Birds and animals are confused during the solar eclipse because –
- Untimely darkness sets in.
- The event does not suit their biological clock.
- Their response to the event is also unusual.
Question 6.
On the first and third quarter days, the moon appears semicircular in shape.
Answer:
- On the first and third quarter days, the moon, the earth and the sun make an angle of 90°
- At these positions, we see half the portion of an illuminated moon.
- Hence, in the sky, the moon appears semi-circular in shape.
Answer the following:
Question 1.
What precautions should we take while observing a solar eclipse?
Answer:
The precautions to be taken while observing a solar eclipse are:
- We should not observe a solar eclipse with naked eyes as the intense light of the sun can harm them.
- We must use dark glasses or goggles that are specially designed for viewing the solar eclipse.
![]()
Question 2.
What types of Solar eclipses will occur in perigee condition?
Answer:
Total and Partial solar eclipse will occur in perigee condition.
(i) Total solar eclipse :
- On a new moon day, the sun, the moon the earth are in a straight line & the shadow of the moon falls on the earth
- The area of dark shadow falls on the earth, the sun becomes completely invisible. This condition is known as total solar eclipse.
(ii) Partial solar eclipse:
- However during the same period at places where the shadow is lighter, the sun disc appears partially covered,
- This condition is described as partial solar eclipse.
Question 3.
How are lunar eclipses formed?
Answer:
(i) A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon enters the shadow of the earth while revolving around it.
(ii) On a full moon day if the sun, the earth & the moon, are in a straight line, the orbital path of the moon passes through the dark shadow of the earth.
(iii) If the moon is totally hidden within the shadow, a total lunar eclipse is seen & if only a part of the moon is in the shadow, a partial lunar eclipse is seen.
Write short notes on:
Question 1.
Characteristics of solar eclipse.
Answer:
- A solar eclipse occurs on a new moon day, but not on every new moon day.
- If and only if, the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same plane and fall in one line, the solar eclipses occur.
- The maximum duration of a total solar eclipse is 7 minutes and 20 seconds Question 40 seconds).
Question 2.
Characteristics of lunar eclipse.
Answer:
- A lunar eclipse occurs on a full moon day, but not on every full moon day.
- A lunar eclipse occurs if and only if the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same plane and fall in one line.
- The maximum duration of a total lunar eclipse is 107 minutes.
Question 3.
Occupation.
Answer:
- This is a typical event occurring in space.
- The moon revolves around the earth, while doing so, it obscures a star or a planet and that celestial body appears to hide behind the moon. This is called occultation.
Question 4.
What is a Transit?
Answer:
- If an inner planet like a Mercury or Venus comes in between the line of the earth and the sun, a transit occurs.
- At that time, a small dot appears to move across the sun’s disc.
- Transit is a type of solar eclipse.
![]()
Distinguish between the following:
Question 1.
Solar eclipse and Lunar eclipse :
Answer:
| Solar eclipse | Lunar eclipse |
| (i) A solar eclipse occurs on a new moon day. (ii) If and only if the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same plane and fall in one line, the solar eclipse occurs. (iii) The maximum duration of total solar eclipse | (i) A lunar eclipse occurs on a full moon day. (ii) A lunar eclipse occurs if and only if the sun, the earth and the moon are in the same plane and fall in one line. (iii) The maximum duration of a total lunar eclipse is 107 minutes. |
Question 2.
Total Solar eclipse and Annular Solar eclipse.
Answer:
| Total Solar eclipse | Annular Solar eclipse |
| (i) When the moon is between the sun and the earth all the three celestial objects are on the same plane and fall in one line. | (i) moon is in apogee position. This means it is farthest from the earth. |
| (ii) The central portion of the shadow of the moon is darker and the periphery is light. | (ii) A deep shadow of the moon is cast in space and does not reach the earth. |
| (iii) In the area of dark shadow on the earth, the sun becomes completely invisible. This condition is known as total solar eclipse | (iii) From a very small region of the earth, only an illuminated edge of the sun as a disc is seen in the form of a ring. This is called an annular eclipse. |
Draw and label the diagrams:
Question 1.
Moon’s Positions:
Answer:

Question 2.
Angle between the planes of orbit.
Answer:

Question 3.
Consider the relative positions of the sun, the moon, and the earth on the new moon day and both the quarters. What will be the angle between the lines joining the earth and the moon as well as the earth and the sun? How many times will this angle be formed in a month?
Answer:
The angle between the lines joining the earth and the moon as well as the earth and the sun is 90°. This angle will be formed twice a month.