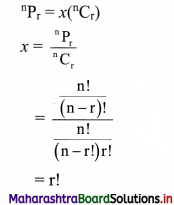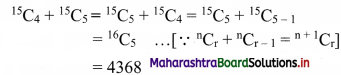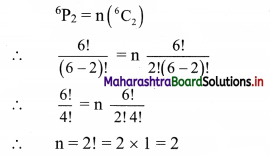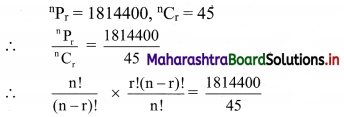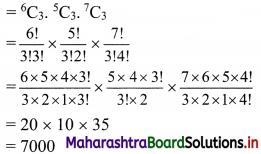Balbharati Maharashtra State Board 11th Commerce Maths Solution Book Pdf Chapter 6 Permutations and Combinations Miscellaneous Exercise 6 Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Commerce Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Permutations and Combinations Miscellaneous Exercise 6
Question 1.
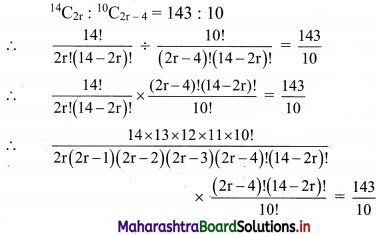
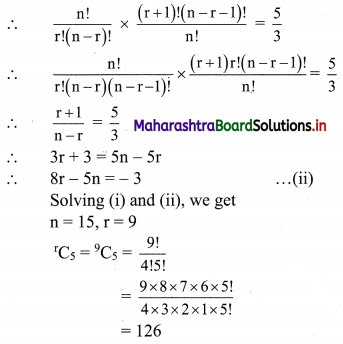
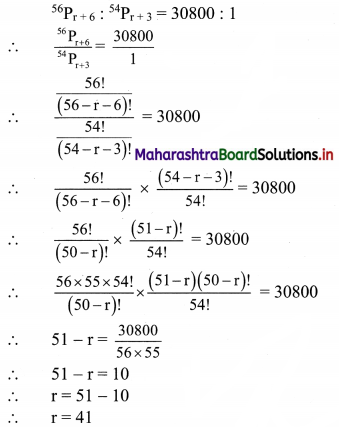
Find the value of r if 56Cr+6 : 54Pr-1 = 30800 : 1
Solution:
Question 2.
How many words can be formed by writing letters in the word CROWN in a different order?
Solution:
Five Letters of the word CROWN are to be permuted.
Number of different words = 5! = 120
Question 3.
Find the number of words that can be formed by using all the letters in the word REMAIN. If these words are written in dictionary order, what will be the 40th word?
Solution:
There are 6 letters A, E, I, M, N, R
The number of words starting with A = 5!
The number of words starting with E = 5!
The number of words starting with I = 5!
The number of words starting with M = 5!
The number of words starting with N = 5!
The number of words starting with R = 5!
Total number of words = 6 × 5! = 720
Number of words starting with AE = 4! = 24
Number of words starting with AIE = 3! = 6
Number of words starting with AIM = 3! = 6
The number of words starting with AINE = 2!
Total words = 24 + 6 + 6 + 2 = 38
39th word is AINMER
40th word is AINMRE
Question 4.
Find the number of ways of distributing n balls in n cells. What will be the number of ways if each cell must be occupied?
Solution:
There are n balls and n cells
(i) Every ball can be put in any of the n cells.
Number of distributions = n × n × …… × n = (n)n
(ii) For filling the first cell, n balls are available.
The first cell is filled in n ways.
The second cell is filled in (n – 1) ways
The third cell is filled in (n – 2) ways and so on.
the nth cell is tilled in one way.
Required number = n(n – 1)(n – 2) …… 1 = n!
Question 5.
Thane is the 20th station from C.S.T. If a passenger can purchase a ticket from any station to any other station, how many different tickets must be available at the booking window?
Solution:
Taking CST as the first station and Thane as 20th,
Let us name CST as A0 next station as A1 and so on, Thane is A20
From station A0, 20 different journeys are possible
From station A1, 20 different journeys are possible.
From station A20, 20 different journeys are possible.
Total number of different tickets of different journeys = 21 × 20 = 420
Question 6.
English alphabet has 11 symmetric letters that appear the same when looked at in a mirror. These letters are A, H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W, X, and Y. How many symmetric three letters passwords can be formed using these letters?
Solution:
Number of 3 Letter passwords = 11P3
= 11 × 10 × 9
= 990
Question 7.
How many numbers formed using the digits 3, 2, 0, 4, 3, 2, 3 exceed one million?
Solution:
A number that exceeds one million is to be formed from the digits 3, 2, 0, 4, 3, 2, 3.
Then the numbers should be any number of 7 digits which can be formed from these digits.
Also among the given numbers 2 repeats twice and 3 repeats thrice.
∴ Required number of numbers = Total number of arrangements possible among these digits – number of arrangements of 7 digits which begin with 0.
= \(\frac{7 !}{2 ! 3 !}-\frac{6 !}{2 ! 3 !}\)
= \(\frac{7 \times 6 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 !}{2 \times 3 !}-\frac{6 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 !}{2 \times 3 !}\)
= 7 × 6 × 5 × 2 – 6 × 5 × 2
= 6 × 5 × 2(7 – 1)
= 60 × 6
= 360
∴ 360 numbers that exceed one million can be formed with the digits 3, 2, 0, 4, 3, 2, 3.
Question 8.
Ten students are to be selected for a project from a class of 30 students. There are 4 students who want to be together either in the project or not in the project. Find the number of possible selections.
Solution:
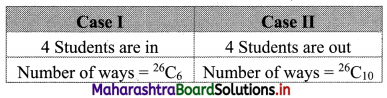
Required number = 26C6 + 26C10
Question 9.
A student finds 7 books of his interest but can borrow only three books. He wants to borrow the Chemistry part II book only if Chemistry Part I can also be borrowed. Find the number of ways he can choose three books that he wants to borrow.
Solution:
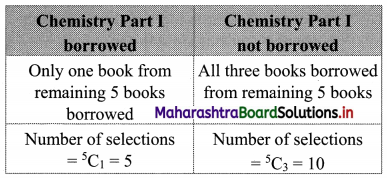
Required Number = 5 + 10 = 15
Question 10.
30 objects are to be divided into three groups containing 7, 10, 13 objects. Find the number of distinct ways of doing so. Solution:
Required number = 30C7 × 23C10 × 13C13
Question 11.
A student passes an examination if he secures a minimum in each of the 7 subjects. Find the number of ways a student can fail.
Solution:
Every subject a student may pass or fail.
∴ Total number of outcomes = 27 = 128
This number includes one case when the student passes in all subjects.
∴ Required number = 128 – 1 = 127
Question 12.
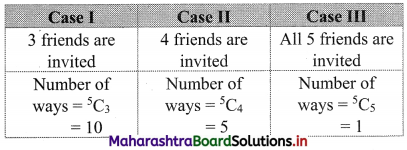
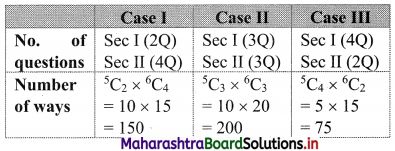
Nine friends decide to go for a picnic in two groups. One group decides to go by car and the other group decides to go by train. Find the number of different ways of doing so if there must be at least 3 friends in each group.
Solution:
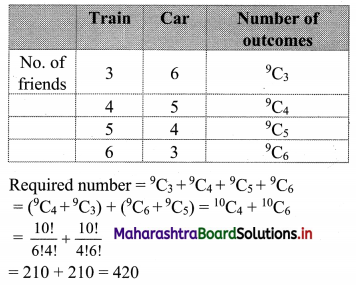
Question 13.
Five balls are to be placed in three boxes, where each box can contain upto five balls. Find the number of ways if no box is to remain empty.
Solution:
Let boxes be named as I, II, III
Let sets A, B, C represent cases in which boxes I, II, III remain empty
Then A ∪ B ∪ C represent the cases in which at least one box remains empty.
Then we use method of indirect counting
Required number = Total number of distributions – n(A ∪ B ∪ C) …..(i)
n(A ∪ B ∪ C) represent the number of undesirable cases
Total number of distributions = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 35 = 243 …….(ii)
n(A ∪ B ∪ C) = n(A) + n(B) + n(C) – n(A ∩ B) – n(B ∩ C) – n(C ∩ A) + n(A ∩ B ∩ C) …..(iii)
In box I is empty then every ball has two places (boxes) to go.
Similarly for box II and III.
∴ n(A) + n(B) + n(C) = 3 × 25 ……(iv)
If boxes I and II remain empty then all balls go to box III
Similarly we would have two more cases.
∴ n(A ∩ B) + n(B ∩ C) + n(C ∩ A) = 3 × 15 ……(v)
∴ n(A ∩ B ∩ C) = 0 …….(vi) [as all boxes cannot be empty]
Substitute from (iv), (v), (vi) to (iii) to get
n(A ∪ B ∪ C) = 3 × 25 – 3 × 15
= 96 – 3
= 93
Substitute n(A ∪ B ∪ C) and from (ii) to (i), we get
Required number = 243 – 93 = 150
Question 14.
A hall has 12 lamps and every lamp can be switched on independently. Find the number of ways of illuminating the hall.
Solution:
Every lamp is either ON or OFF.
There are 12 lamps
Number of instances = 212
This number includes the case in which all 12 lamps are OFF.
∴ Required Number = 212 – 1 = 4095
Question 15.
How many quadratic equations can be formed using numbers from 0, 2, 4, 5 as coefficients if a coefficient can be repeated in an equation?
Solution:
Let the quadratic equation be ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0
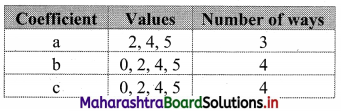
∴ Required number = 3 × 4 × 4 = 48
Question 16.
How many six-digit telephone numbers can be formed if the first two digits are 45 and no digit can appear more than once?
Solution:
Let the telephone number be 45abcd
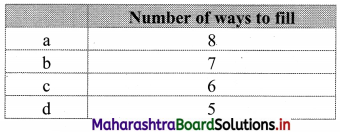
∴ Required number = 8P4 = 1680
Question 17.
A question paper has 6 questions. How many ways does a student have if he wants to solve at least one question?
Solution:
Every question is ‘SOLVED’ or ‘NOT SOLVED’.
There are 6 question.
Number of outcomes = 26
This number includes the case when the student solves NONE of the question.
Required number = 26 – 1
= 64 – 1
= 63
Question 18.
Find the number of ways of dividing 20 objects in three groups of sizes 8, 7 and 5.
Solution:
Select 8 objects out of 20 in 20C8 ways
Select 7 objects from the remaining 12 in 12C7 ways and 5 objects from the remaining 5 in 5C5 ways
Required number is = 20C8 × 12C7 × 5C5
Question 19.
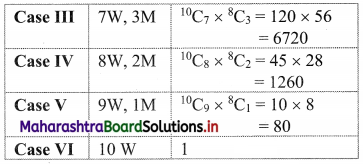
There are 8 doctors and 4 lawyers in a panel. Find the number of ways for selecting a team of 6 if at least one doctor must be in the team.
Solution:
There are 8 doctors and 4 lawyers.
We need to select a team of 6 which contains at least one doctor.
Since there are only 4 lawyers any team of 6 will contain at least two doctors.
Required number = 12C6 = 924
Question 20.
Four parallel lines intersect another set of five parallel lines. Find the number of distinct parallelograms that can be formed.
Solution:
We need 2 lines from each set.
Required number = 4C2 × 5C2
= 6 × 10
= 60