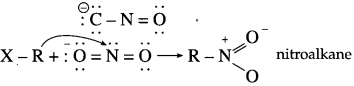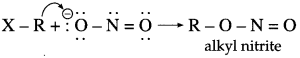Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 1 Living world Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 1 Living World
Question 1.
What are the basic principles of life?
Answer:
The basic principles of life are as follows:
- Metabolism: Metabolism is breaking of molecules (catabolism) and making of new molecules (anabolism). An organism performs metabolism in order to obtain energy and various chemical molecules essential for survival.
- Growth and development: Organisms tend to grow and develop in a well-orchestrated process from birth onwards.
- Ageing: It is the process during which molecules, organs and systems begin to lose their effective working and become old.
- Reproduction: For continuity of race (species), organisms reproduce (asexually or sexually) to produce young ones like themselves. However, mules and worker bees do not reproduce, yet are living.
- Death: As the body loses its capacity to perform metabolism, an organism dies.
- Responsiveness: Living organisms respond to thermal, chemical or biological changes in their surroundings.
![]()
Question 2.
Enlist the characters of living organisms.
Answer:
The basic principles of life are as follows:
- Metabolism: Metabolism is breaking of molecules (catabolism) and making of new molecules (anabolism). An organism performs metabolism in order to obtain energy and various chemical molecules essential for survival.
- Growth and development: Organisms tend to grow and develop in a well-orchestrated process from birth onwards.
- Ageing: It is the process during which molecules, organs and systems begin to lose their effective working and become old.
- Reproduction: For continuity of race (species), organisms reproduce (asexually or sexually) to produce young ones like themselves. However, mules and worker bees do not reproduce, yet are living.
- Death: As the body loses its capacity to perform metabolism, an organism dies.
- Responsiveness: Living organisms respond to thermal, chemical or biological changes in their surroundings.
Question 3.
What are taxonomical aids? Give examples.
Answer:
Taxonomical aids are used to study biodiversity, e.g. Herbaria, botanical gardens, museums, biodiversity parks, etc.
Question 4.
What is a herbarium?
Answer:
Herbarium is a dried plant specimen that is pressed, treated and mounted on a standard size sheet in order to preserve it.
[Note: Herbarium is a collection of dried, pressed and labelled plant specimens arranged by a classification system.]
![]()
Question 5.
What information is mentioned in the label of a plant specimen preserved in herbarium?
Answer:
It is also essential to record the date, place of collection along with detailed classification and highlighting with its ecological peculiarities, characters of the plant on a sheet. Local names of plant specimens and name of the collector may be added. This information is given at lower right comer of sheet and is called ‘label’.
Question 6.
What are botanical gardens?
Answer:
Botanical gardens are places where plants of different varieties collected from different parts of the world are grown in vivo in a scientific and systematic manner.
Question 7.
Define biodiversity.
Answer:
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms in an ecosystem.
Question 8.
Define conservation.
Answer:
Conservation involves attempting to slow down, stop or even reverse the loss in the natural habitat of an organism.
Question 9.
What is a museum? What are the various specimens found in a museum?
Answer:
1. Museums are places where collections of preserved plant and animal specimens are kept.
2. The different types of specimens found in a museum include;
(a) Plant and animal specimens preserved in formalin (10% to 40% formaldehyde) in transparent jars.
(b) Larger animals like birds and mammals, usually stuffed and preserved.
(c) Certain specimens in dried forms are also kept in a museum.
(d) Systematic collections of shells, skeletons of animals and insect boxes are also found in museums.
![]()
Question 10.
What is taxidermy?
Answer:
Taxidermy is a science in which larger animals like birds and mammals are usually stuffed and preserved.
Question 11.
Write a note on zoological park.
Answer:
- Zoological park (zoo) is a place where wild animals are kept in captivity.
- Wild animals are kept in a protected environment and care is taken to provide conditions similar to their natural habitat.
- It is a form of ex situ conservation of species i.e. away from their natural habitat.
- A naturalist can study the food habits and behaviour of animals in a zoological park.
Question 12.
Mention some tools of maintaining biodiversity records.
Answer:
Flora, manuals, monographs and catalogues are some tools of maintaining biodiversity records.
Question 13.
Explain the different tools used for maintaining biodiversity records.
Answer:
The different tools used for maintaining biodiversity records are as follows:
- Flora: It is the plant life occurring in a particular area at a particular time.
- Monograph: It describes any one selected biological group.
- Manual: It provides information and keys about identification of species found in a particular area.
![]()
Question 14.
Define biodiversity park.
Answer:
Biodiversity park is an ecological assemblage of species that form self-sustaining communities on degraded/ barren landscape, e.g. Uttamrao Patil Biodiversity Park, Gureghar, Mahabaleshwar.
Question 15.
Write a note on ‘key’ used as a taxonomical aid.
Answer:
- Key is a taxonomical aid used in the classification of plants and animals.
- Keys are based on contrasting characters. One of the contrasting characters gets accepted and the other gets rejected.
- The statement in a key is called a lead.
- Normally keys are analytical in nature.
Question 16.
Name the following.
- A collection of dried plant specimen that are pressed, treated and mounted on a standard size sheet in order to preserve it.
- Places where collections of preserved plant and animal specimens are kept.
- Taxonomical aid used for classification of plants and animals which is based on contrasting characters.
Answer:
- Herbarium
- Museum
- Key
Question 17.
Fill in the blanks:
- The extent of complexity and density of ________ can be regarded as a measure of health of an ecosystem.
- In a museum, plant and animal specimens are preserved in _________ in transparent jars.
- A naturalist can study food habits and behaviour of animals in a ___________.
- Study of _________ is a must, to understand interrelations between organisms and maintain harmony on planet earth.
- The statement in a key is called a _________.
Answer:
- biodiversity
- formalin
- zoo/ zoological park
- biodiversity
- lead
![]()
Question 18.
Rakesh went for a study tour to the nearest national park. There he found some different plant species. He was not aware about their names and family. He wanted to bring that plants to his college and keep them for longer period of time, so that he can study them thoroughly. What should he do in such a situation?
Answer:
1. Rakesh can press and mount the plant specimen on the herbarium sheet and can preserve the dried plant material.
2. He can also write any information he knows about the plant on herbarium sheet, which can be used for further studies.
Question 19.
While doing his Ph.D. in Plant Taxonomy your friend has come across a plant, which he feels is a new species. How can he confirm the same?
Answer:
1. The newly discovered plant can be identified with the help of taxonomic keys, monographs, floras, herbaria and preserved plant specimens.
2. A separate taxonomic key is available for each taxonomic category.
3. The individual would have to study the morphological and anatomical features of the plant and compare it with the existing information available in the scientific literature.
Conservation of Biodiversity
Question 20.
Quick Review:
Answer:


Question 21.
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Which one of the following aspects is an inclusive characteristic of living things?
(A) Isolated metabolic reactions occurring in vitro
(B) Reproduction
(C) Irritability
(D) Increase in mass by accumulation of material on surface
Answer:
(C) Irritability
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following property is shown by both living and non-living things?
(A) Growth
(B) Consciousness
(C) Ageing
(D) Metabolism
Answer:
(A) Growth
Question 3.
Herbarium is
(A) a collection of living plants which are medicinally important
(B) a place where plants collected from different parts of the world are grown
(C) a garden where herbs are cultivated
(D) a collection of dried and preserved plants
Answer:
(D) a collection of dried and preserved plants
Question 4.
A zoological park does not
(A) have wild animals in captivity under human care.
(B) provide conditions similar to their natural habitat of animals.
(C) have a systematic collection of shells and skeletons of animals
(D) enable naturalists to study the food habits and behaviour of wild animals.
Answer:
(C) have a systematic collection of shells and skeletons of animals
![]()
Question 5.
A naturalist can study food habits and behaviour of animals in a
(A) museum
(B) zoological park
(C) botanical garden
(D) herbarium
Answer:
(B) zoological park
Question 6.
Which of the following is NOT a tool of maintaining biodiversity records?
(A) Flora
(B) Monograph
(C) Fauna
(D) Manual
Answer:
(C) Fauna
Question 7.
Which of the following tools provides information for identification of names of species found in a particular area?
(A) Catalogues
(B) Manuals
(C) Flora
(D) Monographs
Answer:
(B) Manuals
Question 8.
Keys are taxonomical aids that
(A) are used to identify plants and animals based on similarities and dissimilarities.
(B) contains the account of habitat and distribution of plants in a given area.
(C) provides an index to the plant species found in a particular area.
(D) provide information for identification of species found in an area.
Answer:
(A) are used to identify plants and animals based on similarities and dissimilarities.
![]()
Question 22.
Competitive Corner:
Question 1.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below: [NEET (UG) 2018]
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Herbarium | (a) It is a place having a collection of preserved plants and animals |
| 2. Key | (b) A list that enumerates methodically all the species found in an area with brief description aiding identification |
| 3. Museum | (c) It is a place where dried and pressed plant specimens mounted on sheets are kept |
| 4. Catalogue | (d) A booklet containing a list of characters and their alternates which are helpful in identification of various taxa. |
(A) i-b, ii-d, iii-c, iv-a
(B) i-c, ii-b, iii-a, iv-d
(C) i-a, ii-d, iii-c, iv-b
(D) i-c, ii-d, iii-a, iv-b
Answer:
(D) i-c, ii-d, iii-a, iv-b
Question 2.
The label of a herbarium sheet does not carry information on
(A) height of the plant
(B) date of collection
(C) name of collector
(D) local names
Answer:
(A) height of the plant
Question 3.
Which one of the following is NOT a correct statement? [NEET 2013]
(A) Herbarium houses dried, pressed and preserved plant specimens.
(B) Botanical gardens have collection of living plants for reference.
(C) A museum has collection of photographs of plants and animals.
(D) Key is a taxonomic aid for identification of specimens.
Answer:
(C) A museum has collection of photographs of plants and animals.
![]()
Question 23.
Basic Principles of Life
Question 1.
Define metabolism.
Answer:
Metabolism: Metabolism is breaking of molecules (catabolism) and making of new molecules (anabolism). An organism performs metabolism in order to obtain energy and various chemical molecules essential for survival.
Question 2.
Enlist the basic principles of life.
Answer:
The basic principles of life are as follows:
(i) Metabolism: Metabolism is breaking of molecules (catabolism) and making of new molecules (anabolism). An organism performs metabolism in order to obtain energy and various chemical molecules essential for survival.
(ii) Growth and development: Organisms tend to grow and develop in a well-orchestrated process from birth onwards.
(iii) Ageing: It is the process during which molecules, organs and systems begin to lose their effective working and become old.
(iv) Reproduction: For continuity of race (species), organisms reproduce (asexually or sexually) to produce young ones like themselves. However, mules and worker bees do not reproduce, yet are living.
(v) Death: As the body loses its capacity to perform metabolism, an organism dies.
(vi) Responsiveness: Living organisms respond to thermal, chemical or biological changes in their surroundings.
Question 3.
Reproduction is not an inclusive character of life. Explain.
Answer:
No, we cannot call reproduction as an inclusive character of life. Certain organisms like mules and worker bees do not reproduce and are still living. Thus, reproduction cannot be considered as an all inclusive defining characteristic of living organisms.
Question 4.
Define taxonomical aids and give two examples
Answer:
Taxonomical aids are used to study biodiversity, e.g. Herbaria, botanical gardens, museums, biodiversity parks, etc.
Question 5.
1. Define herbarium.
2. Mention any four essentials of a good herbarium.
Answer:
1. Herbarium is a dried plant specimen that is pressed, treated and mounted on a standard size sheet in order to preserve it.
[Note: Herbarium is a collection of dried, pressed and labelled plant specimens arranged by a classification system.]
2. The essentials of a good herbarium are as follows:
(i) It is essential to identify and label the collected specimen correctly.
(ii) Specimens should be stored in a dry place.
(iii) The plants are usually pressed and mounted on the sheet of paper known as herbarium sheets. Some plants are not suitable for pressing or mounting, like succulents, seeds, cones, etc. They need to be preserved in suitable liquid like formaldehyde, acetic alcohol, etc.
(iv) In order to preserve the specimen for longer durations, acid-free paper, special glues and inks must be used to mount the specimen so that the specimen does not deteriorate.
![]()
Question 6.
Shanaya found a unfamiliar plant on her visit to Tamil Nadu. She wants to study the plant thoroughly in her laboratory? How can she do so?
Answer:
1. Riya can press and mount the plant specimen on a herbarium sheet and preserve the dried plant material, until she returns back from her visit.
2. She can also write any available information regarding the collected specimen on the herbarium sheet, which can be useful for further studies with her biology teacher.
3. Various taxonomical aids can be useful to get information about this peculiar plant.
[Note: In order to conserve the local flora, Riya can collect photographs ofplant and describe it’s structure to her teacher.]
Question 7.
Manas wants to prepare a herbarium of plants.
1. What is a herbarium?
2. What are the essentials he should keep in mind to prepare a good herbarium?
3. What information should be added on the label of a herbarium?
Answer:
1. Herbarium is a dried plant specimen that is pressed, treated and mounted on a standard size sheet in order to preserve it.
[Note: Herbarium is a collection of dried, pressed and labelled plant specimens arranged by a classification system.]
2. (i) It is essential to identify and label the collected specimen correctly.
(ii) Specimens should be stored in a dry place.
(iii) The plants are usually pressed and mounted on the sheet of paper known as herbarium sheets. Some plants are not suitable for pressing or mounting, like succulents, seeds, cones, etc. They need to be preserved in suitable liquid like formaldehyde, acetic alcohol, etc.
(iv) In order to preserve the specimen for longer durations, acid-free paper, special glues and inks must be used to mount the specimen so that the specimen does not deteriorate.
(v) The specimens should be dried well before preparing a herbarium in order to prevent rotting of specimen.
3. It is also essential to record the date, place of collection along with detailed classification and highlighting with its ecological peculiarities, characters of the plant on a sheet. Local names of plant specimens and name of the collector may be added. This information is given at lower right comer of sheet and is called ‘label’.
![]()
Question 8.
Can humans help in conservation of biodiversity? Explain your answer.
Answer:
- Due to rapid increase in human population and industrialization, humans have over utilized natural resources; leading to degradation of the environment and hence only humans can help conserve the ecosystem.
- Humans are capable of conserving and improving the quality of nature and thus, can play a major role in biodiversity conservation.
- In order to conserve biodiversity and its environmental resources, humans must use the resources rationally and avoid excessive degradation of environment.
- Human beings are stakeholders of the environment and need to come together to overcome pollution and improve the environment quality in order to conserve biodiversity.
E.g. Ban or limit on use of harmful products (plastic, chemicals, etc.) that are toxic to various birds, animals, etc. Human beings also play a role in conservation of biodiversity by establishment of various sites for in situ (national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves) and ex situ (botanical gardens, culture collections and zoological parks) conservation.
Question 9.
Write a note on botanical gardens.
Answer:
Botanical gardens are places where plants of different varieties collected from different parts of the world are grown in vivo in a scientific and systematic manner.
The importance of botanical gardens is as follows:
- It is a place where there is an assemblage of living plants maintained for botanical teaching and research purpose.
- Botanical gardens are important for their records of local flora.
- Botanical gardens provide facilities for the collection of living plant materials for botanical studies.
- Botanical gardens also supply seeds and material for botanical investigations.
- The development of botanical gardens in any country is associated with its history of civilization, culture, heritage, science, art, literature and various other social and religious expressions.
- Botanical gardens besides possessing an outdoor garden may contain herbaria, research laboratory, greenhouses and library.
- Botanical gardens are not only important for botanical studies, but also to develop tourism in the country.
![]()
Question 10.
Botanical gardens are important in botanical studies. Justify.
Answer:
Metabolism can be considered as an all-inclusive (defining) feature of life since it is exhibited by all living organisms and does not take place in non-living things. Another all-inclusive characteristic of life is responsiveness or irritability. This is a unique property of living beings since all living beings are conscious of their surroundings.
Question 11.
Suggest any three measures you can take to prevent loss of biodiversity.
Answer:
The essentials of a good herbarium are as follows:
- It is essential to identify and label the collected specimen correctly.
- Specimens should be stored in a dry place.
- The plants are usually pressed and mounted on the sheet of paper known as herbarium sheets. Some plants are not suitable for pressing or mounting, like succulents, seeds, cones, etc. They need to be preserved in suitable liquid like formaldehyde, acetic alcohol, etc.
- In order to preserve the specimen for longer durations, acid-free paper, special glues and inks must be used to mount the specimen so that the specimen does not deteriorate.
- The specimens should be dried well before preparing a herbarium in order to prevent rotting of specimen.
- It is also essential to record the date, place of collection along with detailed classification and highlighting with its ecological peculiarities, characters of the plant on a sheet.
Local names of plant specimens and name of the collector may be added. This information is given at lower right comer of sheet and is called ‘label’.
Question 12.
1. Define biodiversity.
2. How does loss of biodiversity affect the ecosystem?
Answer:
1. Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms in an ecosystem.
2. (i) The loss of biodiversity is an moral and ethical issue.
(ii) Biodiversity helps to maintain stability in an ecosystem.
(iii) Humans share the environment with various other organisms and harm to these species can result in loss of biodiversity.
(iv) The loss of even one variety of organisms can affect the entire ecosystem.
Hence, due to all these reasons, loss of biodiversity matters.
![]()
Question 13.
Define botanical garden and write a note on importance of greenhouses in botanical gardens.
Answer:
Botanical gardens are places where plants of different varieties collected from different parts of the world are grown in vivo in a scientific and systematic manner.
- Greenhouse is a structure with suitable walls and a roof in which plants are grown under regulated climatic conditions.
- Most botanical gardens exhibit ornamental plants which require stringent/ optimum climatic conditions for their growth and/or flowering.
- The greenhouse associated with botanical gardens are also used to grow and propagate those plants that may not survive seasonal changes.
Question 14.
Which science is used to animals at museums? preserve larger
Answer:
Taxidermy is a science in which larger animals like birds and mammals are usually stuffed and preserved.
Question 15.
What is a museum?
Answer:
Museums are places where collections of preserved plant and animal specimens are kept.
Question 16.
What chemical is used to preserve plant and animal specimens in transparent jars at museums?
Answer:
Plant and animal specimens preserved in formalin (10% to 40% formaldehyde) in transparent jars.
![]()
Question 17.
Define the following terms:
1. Flora
2. Monograph
3. Manual
Answer:
The different tools used for maintaining biodiversity records are as follows:
1. Flora: It is the plant life occurring in a particular area at a particular time.
2. Monograph: It describes any one selected biological group.
3. Manual: It provides information and keys about identification of species found in a particular area.
Question 18.
Define the following terms:
- Botanical garden
- Zoological parks
- Biodiversity parks
- Museum
- Herbarium
Answer:
- Botanical gardens are places where plants of different varieties collected from different parts of the world are grown in vivo in a scientific and systematic manner.
- Zoological park (zoo) is a place where wild animals are kept in captivity.
- Biodiversity park is an ecological assemblage of species that form self-sustaining communities on degraded/ barren landscape, e.g. Uttamrao Patil Biodiversity Park, Gureghar, Mahabaleshwar.
- Museums are places where collections of preserved plant and animal specimens are kept.
- Herbarium is a dried plant specimen that is pressed, treated and mounted on a standard size sheet in order to preserve it.
[Note: Herbarium is a collection of dried, pressed and labelled plant specimens arranged by a classification system.]
![]()
Question 19.
On what characters is the ‘key’ based on? taxonomical aid
Answer:
- Key is a taxonomical aid used in the classification of plants and animals.
- Keys are based on contrasting characters. One of the contrasting characters gets accepted and the other gets rejected.
- The statement in a key is called a lead.
- Normally keys are analytical in nature.




























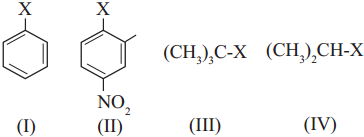



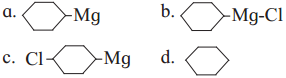


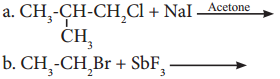




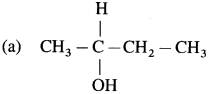
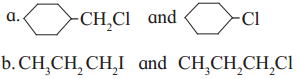
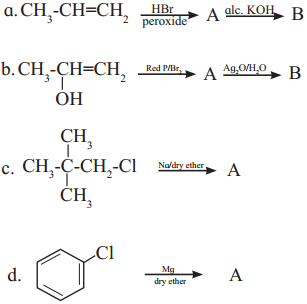
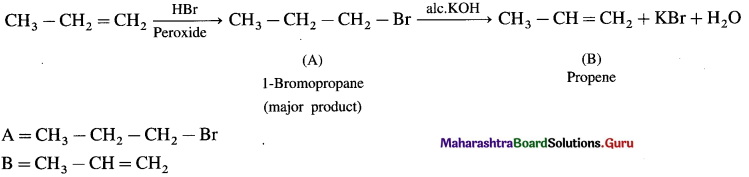
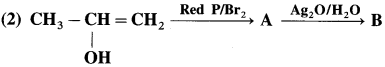
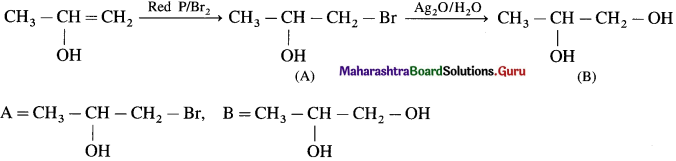
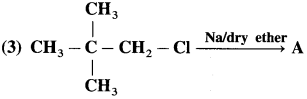
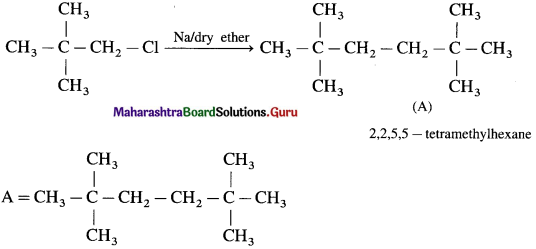
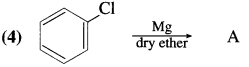

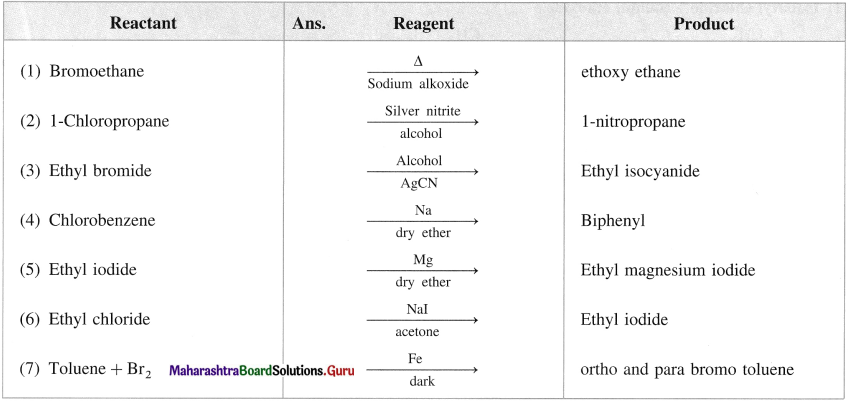

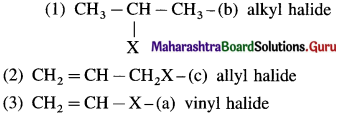




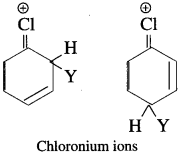
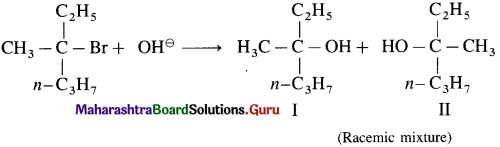
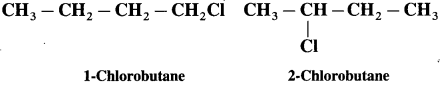
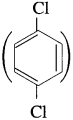 has mp. higher than those of o-and rn-isomers.
has mp. higher than those of o-and rn-isomers.
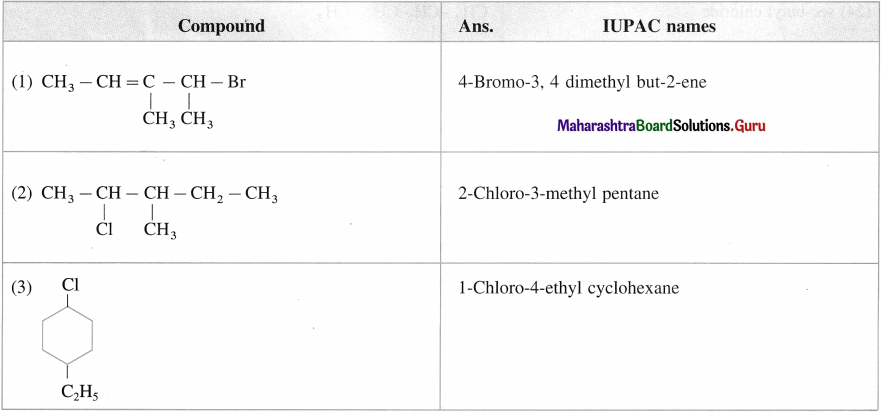
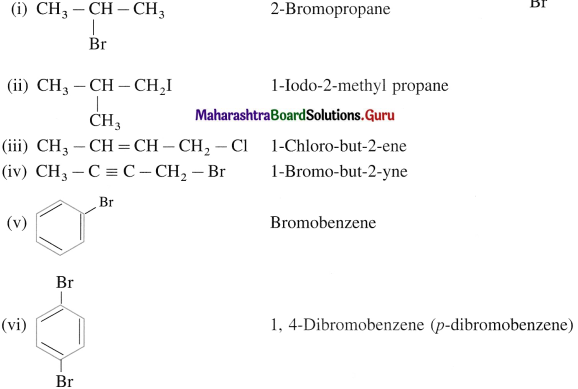
 carbon atom (the starred carbon atom) which is attached to four different groups, i.e., ethyl (-CH2 – CH3), methyl (CH3), chloro (Cl) and hydrogen (H) groups.
carbon atom (the starred carbon atom) which is attached to four different groups, i.e., ethyl (-CH2 – CH3), methyl (CH3), chloro (Cl) and hydrogen (H) groups.
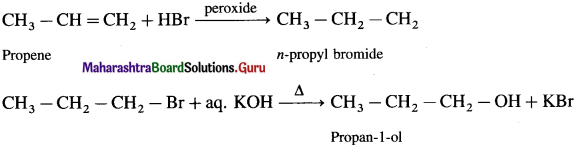


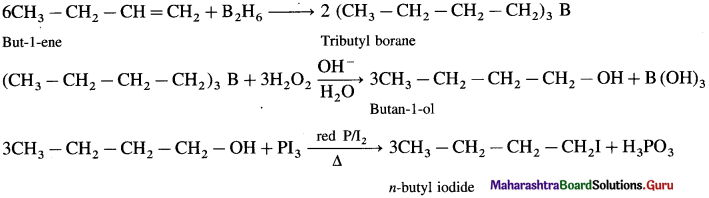
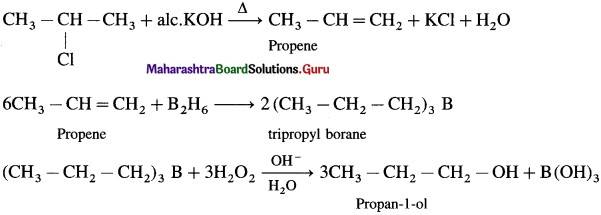


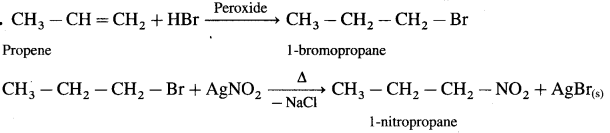


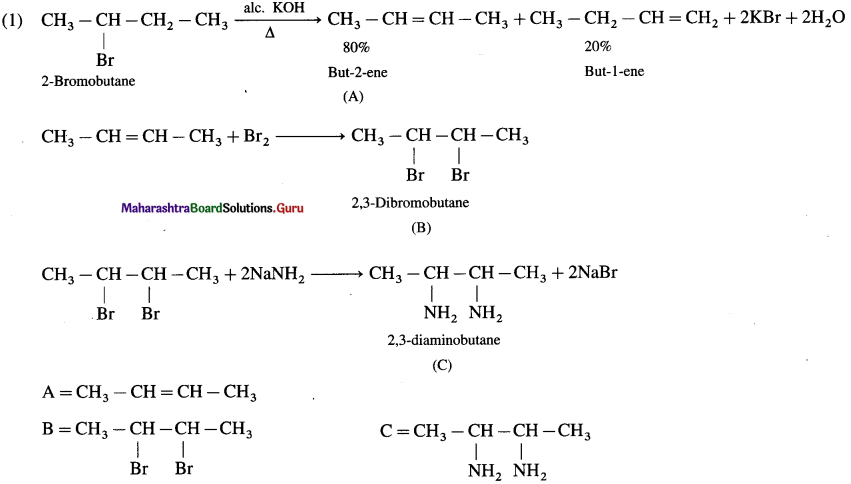
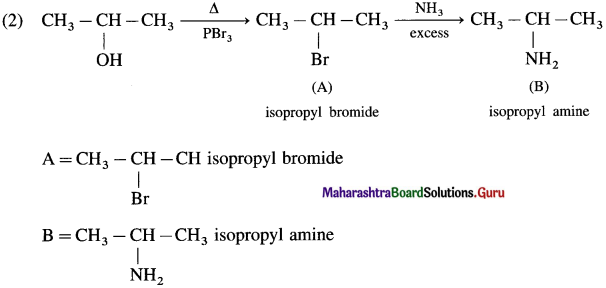






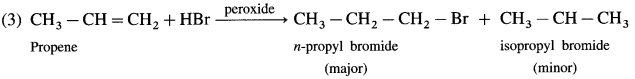
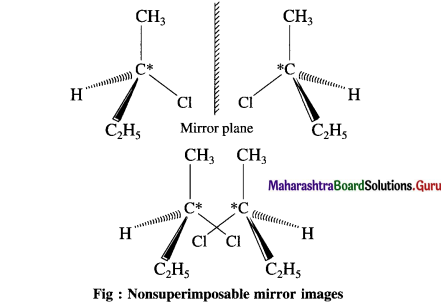
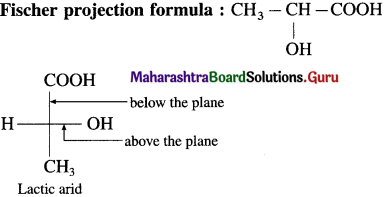
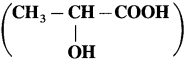 using Fischer projection formulae.
using Fischer projection formulae.