Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce Book Keeping & Accountancy Solutions Chapter 2 Accounts of ‘Not for Profit’ Concerns Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Book Keeping & Accountancy Solutions Chapter 2 Accounts of ‘Not for Profit’ Concerns
1. Objective Type Questions:
A. Select the most appropriate alternatives from the following and rewrite the sentences:
Question 1.
Not for Profit concern renders ___________ services to public at large.
(a) commercial
(b) social
(c) individual
(d) group
Answer:
(b) social
Question 2.
Donation for Scholarship Fund is ___________
(a) Capital Receipt
(b) Revenue Receipt
(c) Capital Expenditure
(d) Revenue Expenditure
Answer:
(a) Capital Receipt
![]()
Question 3.
Income and Expenditure Account is a ___________ Account.
(a) Capital
(b) Real
(c) Personal
(d) Nominal
Answer:
(d) Nominal
Question 4.
Outstanding subscription at the end of the Accounting Year represents ___________
(a) Liability
(b) an Expenditure
(c) an Asset
(d) Capital Fund
Answer:
(c) an Asset
Question 5.
Subscription received in advance during the accounting year is ___________
(a) an Income
(b) an Expense
(c) an Asset
(d) a Liability
Answer:
(d) a Liability
Question 6.
Excess of Income over Expenditure is termed as ___________
(a) Deficit
(b) Profit
(c) Surplus
(d) Loss
Answer:
(c) Surplus
Question 7.
Not for Profit concern prepares ___________ Account instead of Profit and Loss Account to know the result.
(a) Trading
(b) Income and Expenditure
(c) Cash
(d) Receipt and Payments
Answer:
(b) Income and Expenditure
![]()
Question 8.
The closing balance of Receipts and Payments Account usually represent ___________
(a) Closing stock
(b) Cash and Bank Balance
(c) Surplus
(d) Deficit
Answer:
(b) Cash and Bank Balance
Question 9.
Not for Profit organization is also called ___________ organization.
(a) service
(b) trading
(c) profit-making
(d) commercial
Answer:
(a) service
Question 10.
Expenditure on Purchase of Building is a ___________ Expenditure.
(a) Capital
(b) Revenue
(c) General
(d) Recurring
Answer:
(a) Capital
B. Write the Word/Phrase/Term, which can substitute each of the following Statements.
Question 1.
The Form of Organization providing services to the society only.
Answer:
Not for Profit concern
Question 2.
An account which is prepared by Not for Profit concern instead of Profit and Loss Account.
Answer:
Income and Expenditure Account
Question 3.
Donations are received for a specific purpose.
Answer:
Specific donation/Capital Receipt
Question 4.
The Receipts are not recurring in nature.
Answer:
Capital Receipt
![]()
Question 5.
An Account that records only revenue items in case of Not a for-profit concern.
Answer:
Income and Expenditure Account
Question 6.
Accounts which records only cash transactions in case of Not for Profit concerns.
Answer:
Receipts and Payments Account
Question 7.
The income is earned during the year but not received during the year.
Answer:
Outstanding income
Question 8.
The credit balance of Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer:
Surplus
Question 9.
To excess of total assets over total liabilities of a Not for Profit concern.
Answer:
Capital Fund
![]()
Question 10.
All such receipts are non-recurring in nature and not forming a part of a regular flow of income.
Answer:
Capital Receipts
C. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons.
Question 1.
Not for Profit concerns do not have a profit motive.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Not for profit concerns, the main aim is to give services to its members or to the society at large. They do not carry any Trading activity or Manufacturing activity so there is no question of having a profit motive for ‘Not for Profit’ concerns.
Question 2.
Charitable Institutions prepare Profit and Loss Accounts at the end of every financial year.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Charitable Institutions, Not for Profit concerns, do not undertake any trading activities and hence instead of Profit and Loss Account prepare Income-Expenditure Account to record all revenue expenses/losses and revenue incomes/gains of the current year.
Question 3.
There is no difference between Receipts and Payments Account and Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
In the Receipts and Payments Account, all receipts and payments transactions in cash or through the bank are recorded irrespective of the current year, previous year, or next year while in Income-Expenditure Account, only the current year’s incomes and expenses (Revenue) are recorded.
![]()
Question 4.
Income and Expenditure Account represents either surplus or deficit.
Answer:
This statement is True.
In the Income and Expenditure Account, all revenue incomes and expenses are recorded and at the end of the specified period, the difference is found out which is known as ‘Surplus’ (Revenue incomes are more than Revenue expenses) or ‘Deficit’ (Revenue expenses are more than Revenue incomes).
Question 5.
Receipts and Payments Accounts do not have any opening balance.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Receipts and Payments Account is just like a cash book of trading concern and opening balance (Cash or Bank or Cash and Bank) must be there to start recording of transactions.
Question 6.
Not for Profit concerns do not prepare a Balance Sheet.
Answer:
This statement is False.
To know the financial position of the organization, at the end of the particular period, Not for Profit concerns prepare Balance Sheet.
Question 7.
Purchases of Sports Equipments is a Capital Expenditure.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Generally, the life span of sports equipment is more than one year, so the purchase of sports equipment is considered a capital expenditure.
Question 8.
Income and Expenditure Account is a Real Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
In the Income and Expenditure Account, all the revenue incomes and revenue expenses are recorded and therefore it is a Nominal Account and not a Real Account.
![]()
Question 9.
The Receipts and Payments Account contains only the transactions relating to the current year.
Answer:
This statement is False.
In the Receipts and Payments Account, transactions of not only the current year but of the previous year or of the next year are also recorded.
Question 10.
Excess of Assets over liabilities is called Capital Fund.
Answer:
This statement is True.
For ‘Not for Profit’ concerns in the Balance Sheet, when a total of Assets is more than the total of Liabilities, the difference of amount is considered as ‘Capital Fund’.
D. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
Not for Profit organization is never engaged in ___________ activities.
Answer:
trading
Question 2.
Not for Profit organization is called ___________ organization.
Answer:
service
Question 3.
Receipts and Payments Account falls under the category of ___________ Account.
Answer:
Real
Question 4.
In Receipts and Payment Account the summary of ___________ transactions are recorded.
Answer:
cash
![]()
Question 5.
Income and Expenditure Account is similar to the ___________ Account of Trading concern.
Answer:
Profit and Loss
Question 6.
Credit side of Receipts and Payments Account shows cash ___________
Answer:
payments
Question 7.
Income and Expenditure Account is a ___________ Account.
Answer:
Nominal
Question 8.
Mumbai University prepares ___________ Account instead of a Profit and Loss account.
Answer:
Income and Expenditure
Question 9.
Subscription received from the members is considered as ___________ receipts.
Answer:
revenue
Question 10.
The transactions recorded in the Income and Expenditure Account related only to the ___________ year.
Answer:
current
E. Answer in one sentence only.
Question 1.
What do you mean by ‘Not for Profit’ Concern?
Answer:
A concern or organization which is formed and established to serve its members and society or the general public by undertaking various activities without any profit motive is called a ‘Not for Profit’ concern.
Question 2.
Which organizations prepare Income and Expenditure Account?
Answer:
‘Not for profit’ concern prepares Income and Expenditure Account.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Receipts and Payments Account?
Answer:
An account that is prepared by a ‘Not for Profit Concern’ to record a summary of all types of cash receipts and cash payments inclusive of bank transactions is called Receipts and Payments Account.
Question 4.
Why Income and Expenditure Account is prepared?
Answer:
Income and Expenditure Account is prepared to ascertain, whether the concern has sufficient income to meet its expenses, or not.
Question 5.
What is Capital Fund?
Answer:
Excess of Assets over Liabilities is known as Capital Fund which also consists of contributions, subscription, entrance fees, surplus income, etc.
Question 6.
What is a Subscription?
Answer:
Subscription is the periodical payment made by the members to the ‘Not for Profit’ concern for maintaining their membership.
Question 7.
What is ’Legacy’?
Answer:
Any asset, property, or amount of cash which ‘Not for Profit’ concern receives as per the provisions made in the will of the donor after his death is called Legacy.
![]()
Question 8.
What is Surplus?
Answer:
Excess of income over expenditure shown by Income and Expenditure Account represents Surplus for the financial year.
Question 9.
What do you mean by Non-recurring Expenses?
Answer:
Non-recurring expenses are the expenses that are made for the acquisition of fixed assets that gives benefits for a long period.
Question 10.
To which account ‘Surplus’ or ‘Deficit’ is transferred?
Answer:
‘Surplus’ or ‘Deficit’ is transferred to the Balance Sheet by adding it or subtracting it from Capital Fund.
F. I. Complete the Table:
Question 1.
| Sr. No. | Income (₹) | Expenditure (₹) | Surplus/Deficit (₹) |
| 1 | 10,000 | ? | 5,000 (Deficit) |
| 2 | 8,000 | ? | 4,000 (Surplus) |
| 3 | ? | 15,000 | 8,000 (Surplus) |
| 4 | 7,500 | 9,000 | ? |
| 5 | 15,000 | 11,300 | ? |
Solution:
| Sr.No. | Income (₹) | Expenditure (₹) | Surplus/Deficit (₹) |
| 1 | 10,000 | 15,000 | 5,000 (Deficit) |
| 2 | 8,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 (Surplus) |
| 3 | 23,000 | 15,000 | 8,000 (Surplus) |
| 4 | 7,500 | 9,000 | 1,500 (Deficit) |
| 5 | 15,000 | 11,300 | 3,700 (Surplus) |
II. Salaries paid during the year:
Question 1.
| Sr.No. | Total (₹) | Prepaid/Outstanding | ₹ | Expenditure for the year |
| 1 | 1,100 | Prepaid | 100 | ? |
| 2 | 2,700 | Prepaid | ? | 2,000 |
| 3 | 8,250 | Prepaid | ? | 6,650 |
| 4 | 1,200 | Outstanding | 200 | ? |
| 5 | ? | Outstanding | 600 | 5,100 |
| 6 | 1,800 | Outstanding | ? | 2,200 |
Solution:
| Sr. No. | Total (₹) | Prepaid/Outstanding | ₹ | Expenditure for the year |
| 1 | 1,100 | Prepaid | 100 | 1,000 |
| 2 | 2,700 | Prepaid | 700 | 2,000 |
| 3 | 8,250 | Prepaid | 1,600 | 6,650 |
| 4 | 1,200 | Outstanding | 200 | 1,400 |
| 5 | 4,500 | Outstanding | 600 | 5,100 |
| 6 | 1,800 | Outstanding | 400 | 2,200 |
III. Rent received during the year:
Question 1.
| Sr.No. | Total Received (₹) | Rent Received in Advance/Accrued | ₹ | Income for the year (₹) |
| 1 | 1,300 | Received in Advance | 200 | ? |
| 2 | ? | Received in Advance | 400 | 1,400 |
| 3 | 2,650 | Received in Advance | ? | 2,000 |
| 4 | ? | Accrued | 290 | 3,190 |
| 5 | 1,700 | Accrued | ? | 2,150 |
| 6 | 2,600 | Accrued | 500 | ? |
Solution:
| Sr.No. | Total Received (₹) | Rent received in Advance/Accrued | ₹ | Income for the year (₹) |
| 1 | 1,300 | Received in Advance | 200 | 1,100 |
| 2 | 1,800 | Received in Advance | 400 | 1,400 |
| 3 | 2,650 | Received in Advance | 650 | 2,000 |
| 4 | 2,900 | Accrued | 290 | 3,190 |
| 5 | 1,700 | Accrued | 450 | 2,150 |
| 6 | 2,600 | Accrued | 500 | 3,100 |
G. Calculate the following:
Question 1.
10 % p.a. Depreciation on Furniture ₹ 50,000 (for three months)
Solutions:
Depreciation = Cost of Asset × Rate × Period
= 50,000 × \(\frac{10}{100}\) × \(\frac{3}{12}\)
= ₹ 1250 Depr. for 3 months
Thus, Depreciation on furniture @ 10 % on ₹ 50,000 for 3 months = ₹ 1250.
![]()
Question 2.
12 % p.a. Interest on Bank loan ₹ 80,000 for 1 year.
Answer:
I = \(\frac{\mathrm{PRN}}{100}\)
= 80,000 × \(\frac{12}{100}\) × 1
= ₹ 9600.
Thus, interest on a Bank loan ₹ 80,000 for 1 year = ₹ 9600.
Question 3.
Opening stock of stationery ₹ 5,000, purchases of stationery ₹ 7000, outstanding stationery bill ₹ 12,000, closing stock ₹ 1000. What is the amount of stationery consumed?
Answer:

Question 4.
Salary ₹ 10,000, outstanding salary ₹ 5,000. Calculate the salary to be debited to the Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer:
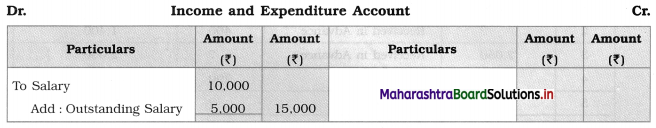
Question 5.
Library Books ₹ ……………? Less 10% Depreciation ₹ 5,000 = ₹ 45,000.
Answer:
Library books ₹ 50,000. Less 10% Depreciation ₹ 5,000 = ? 45,000

H. Find odd one:
Question 1.
Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account, Receipts and Payments Account, Balance Sheet.
Answer:
Receipts and Payments Account
Question 2.
Machinery, Furniture, Computers, Salaries.
Answer:
Salaries
Question 3.
Subscription, Stationery, Interest Received, Locker Rent received.
Answer:
Stationery
![]()
Question 4.
Reliance Industries, Venna Vidya Mandir, Laxmi Hospital, Manoj Sports club.
Answer:
Reliance Industries
Question 5.
Surplus, Deficit, Net Profit, Capital fund.
Answer:
Net Profit
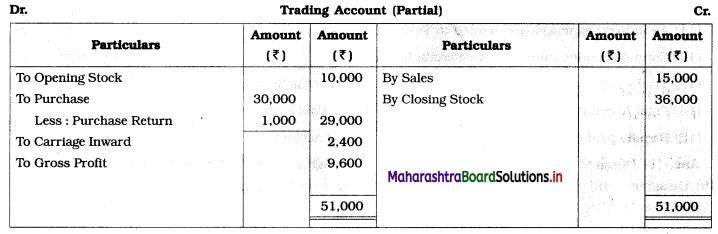
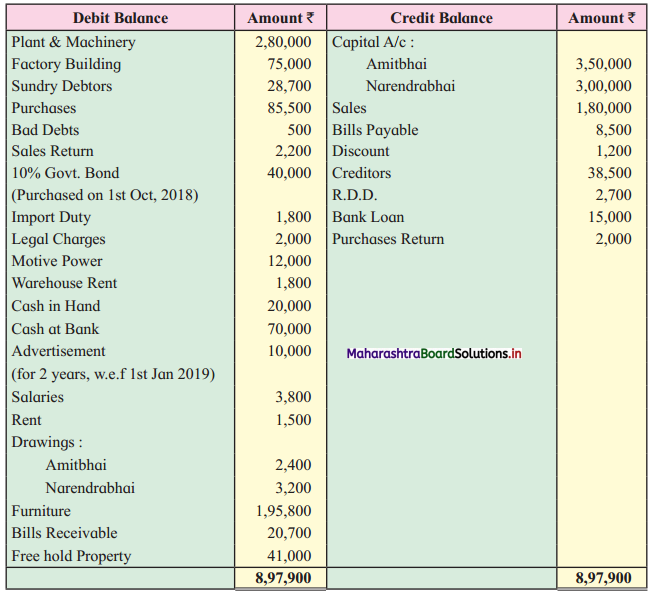
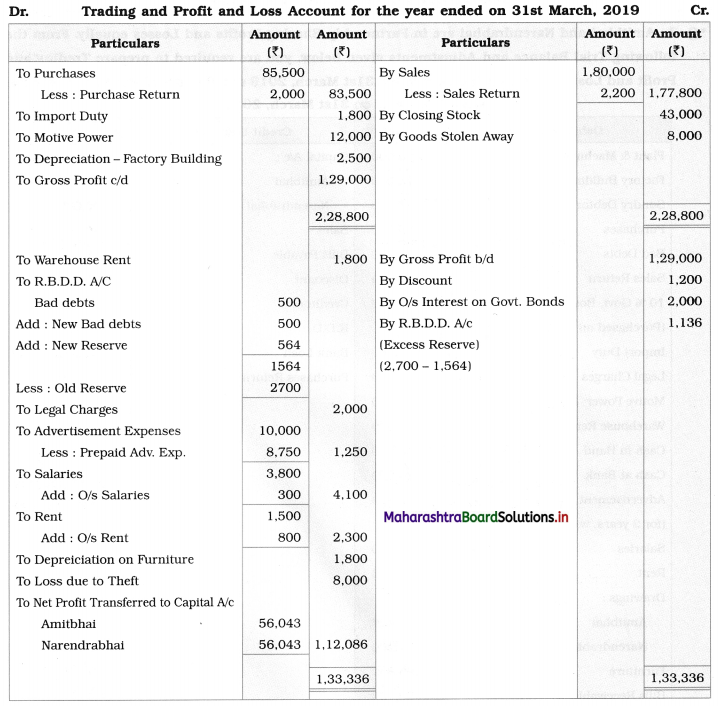
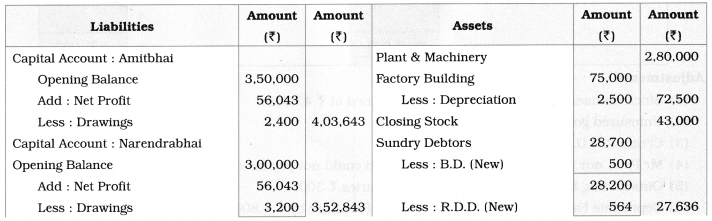
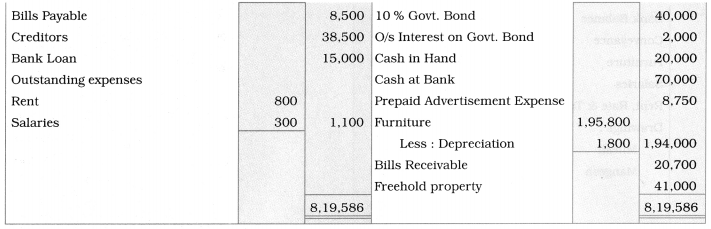
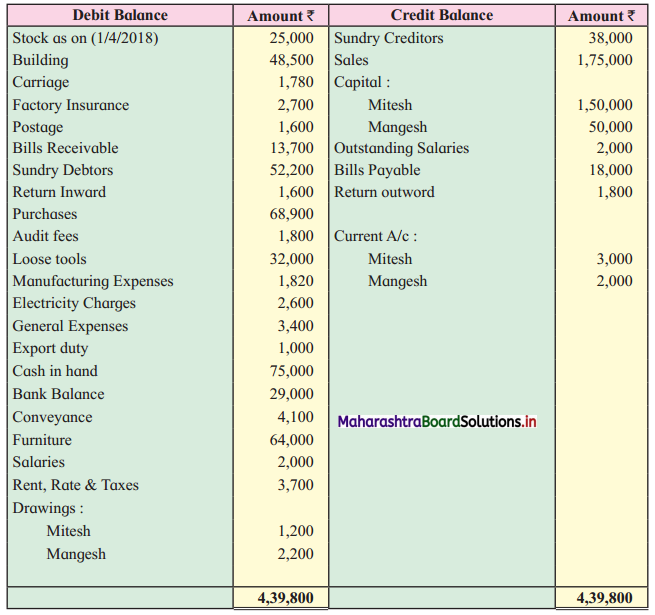
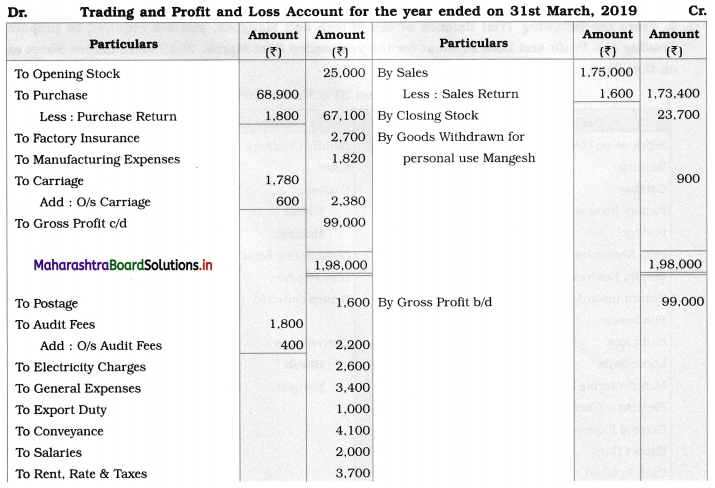
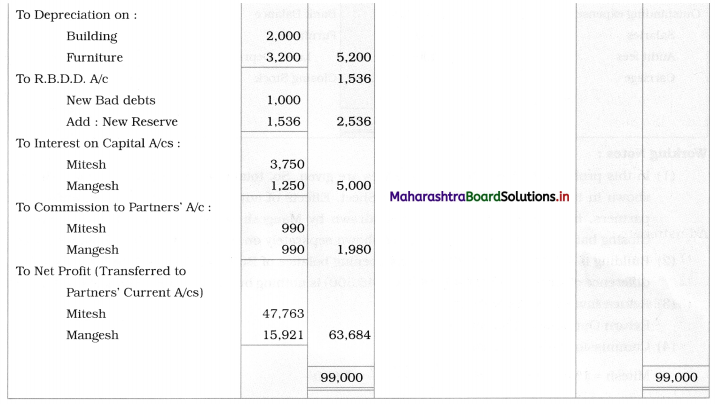
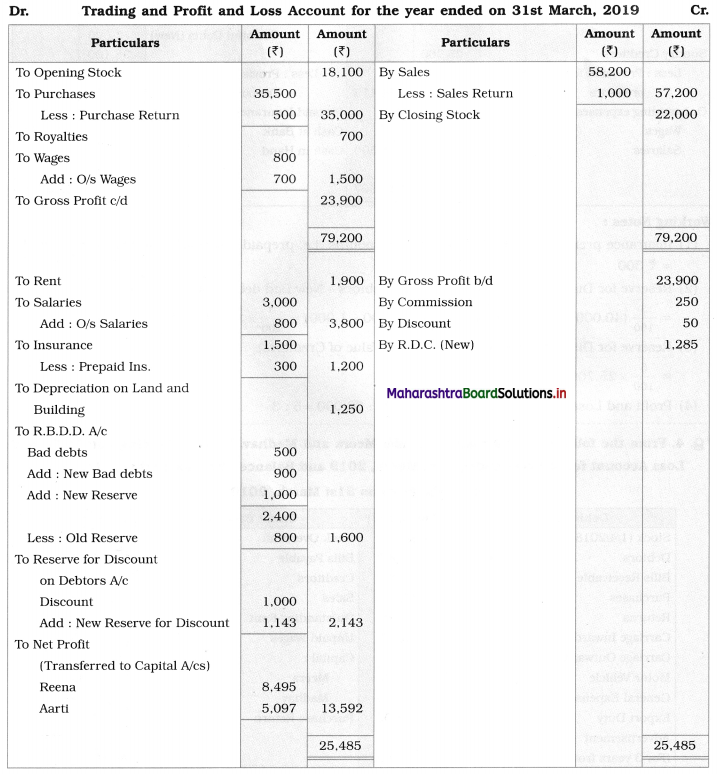
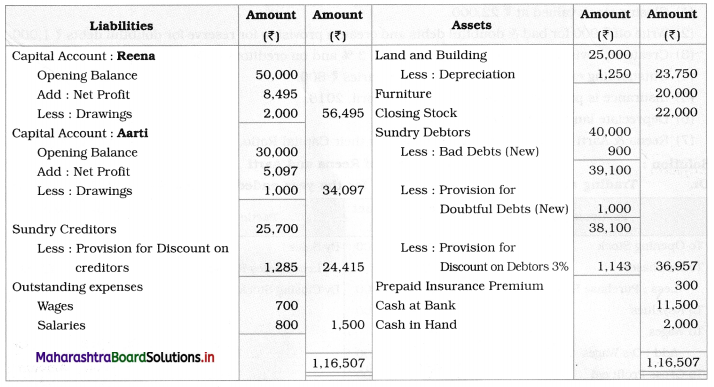
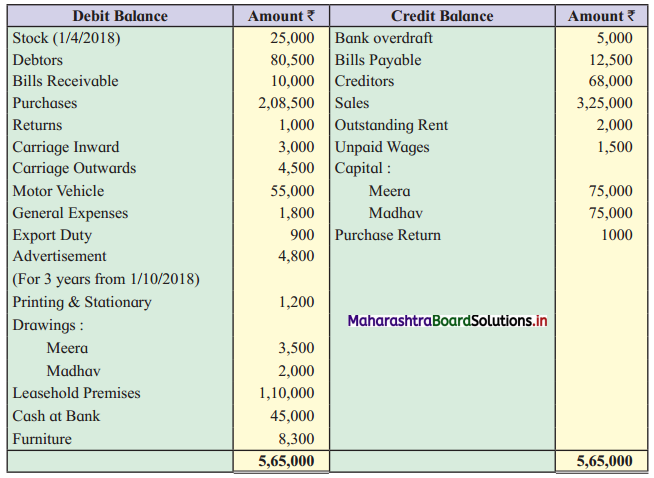
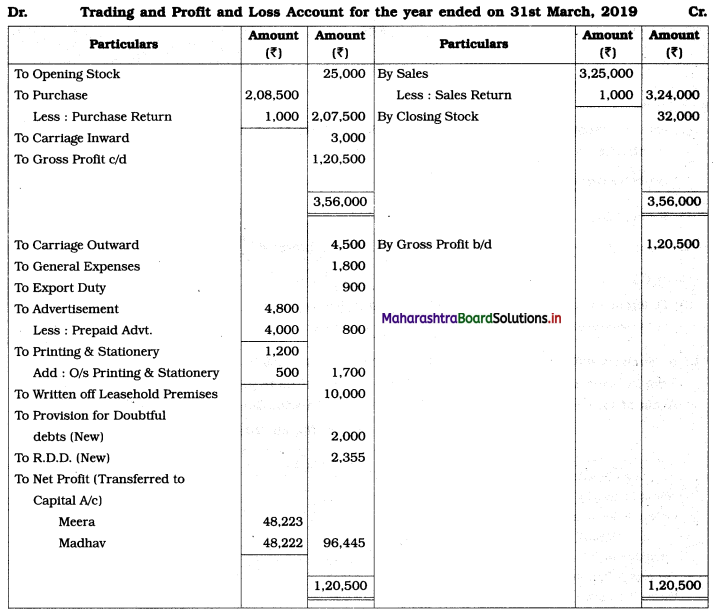
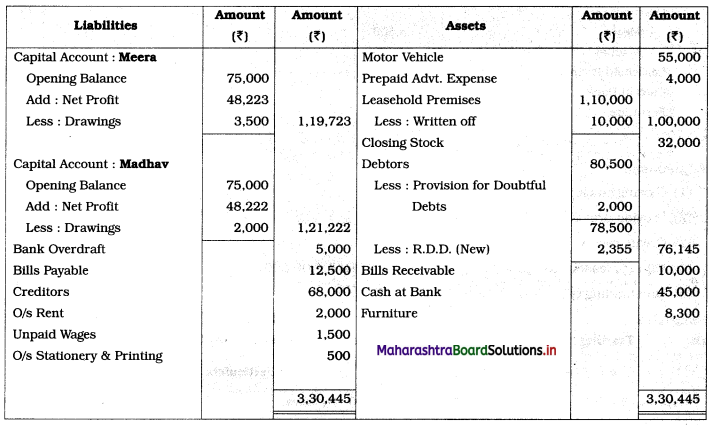
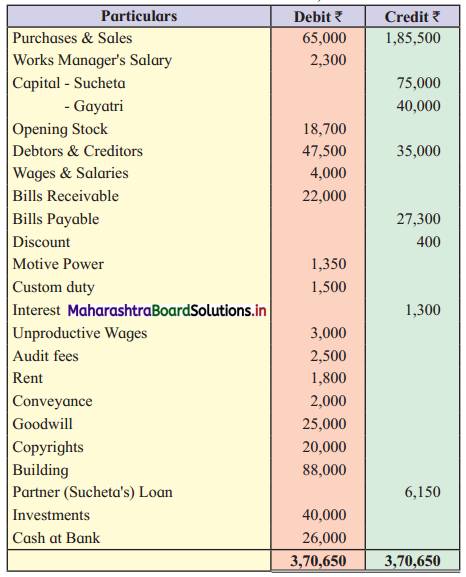
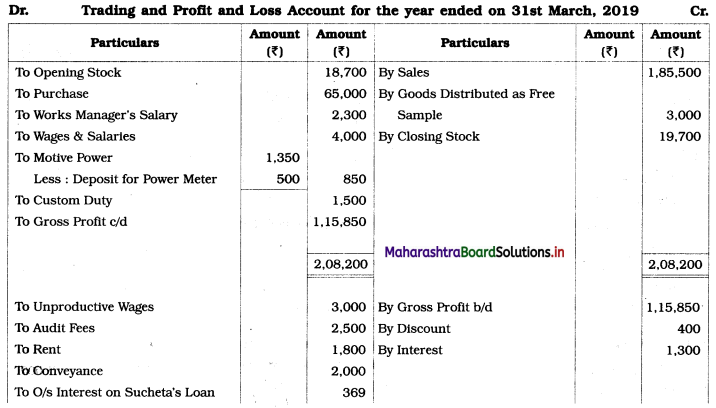
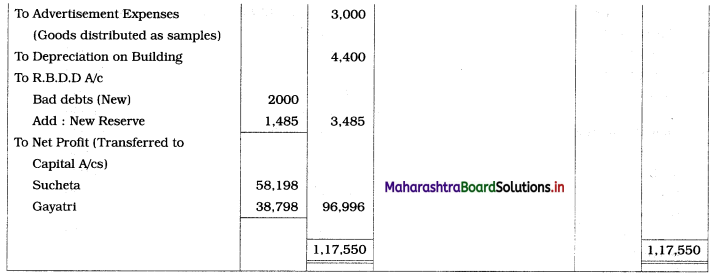
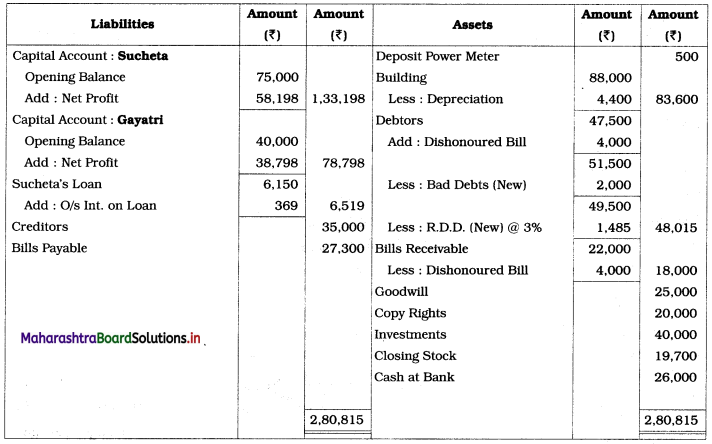
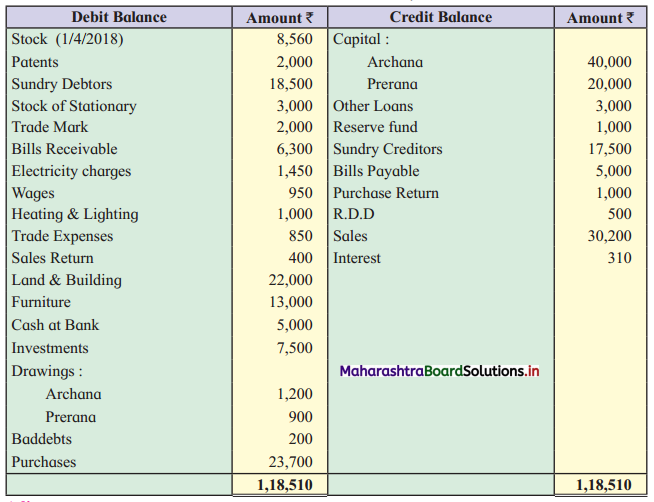
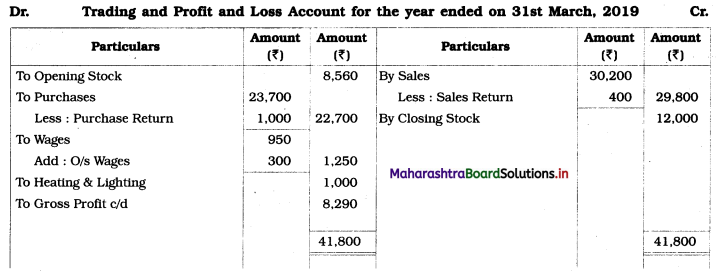
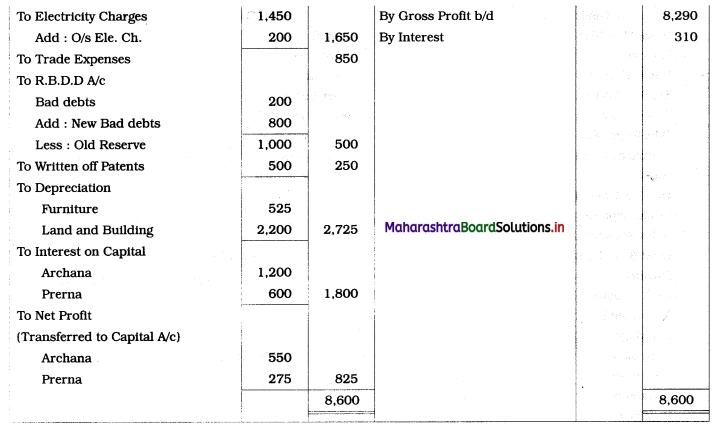
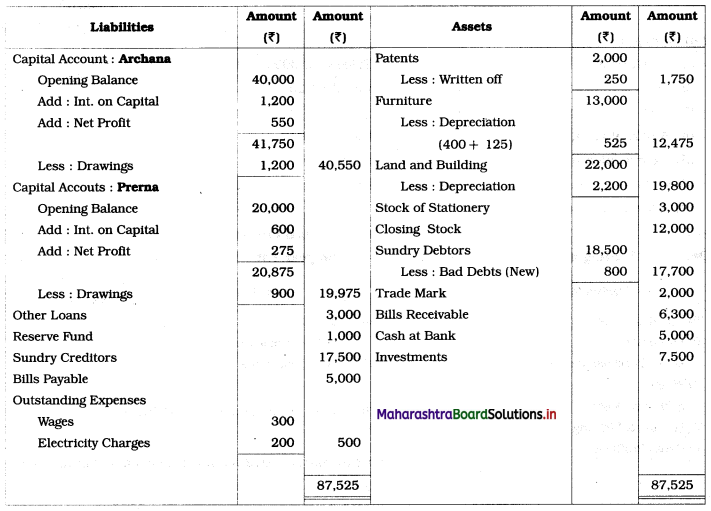
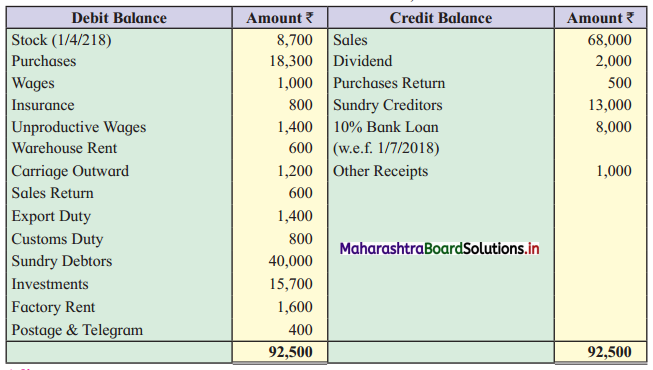
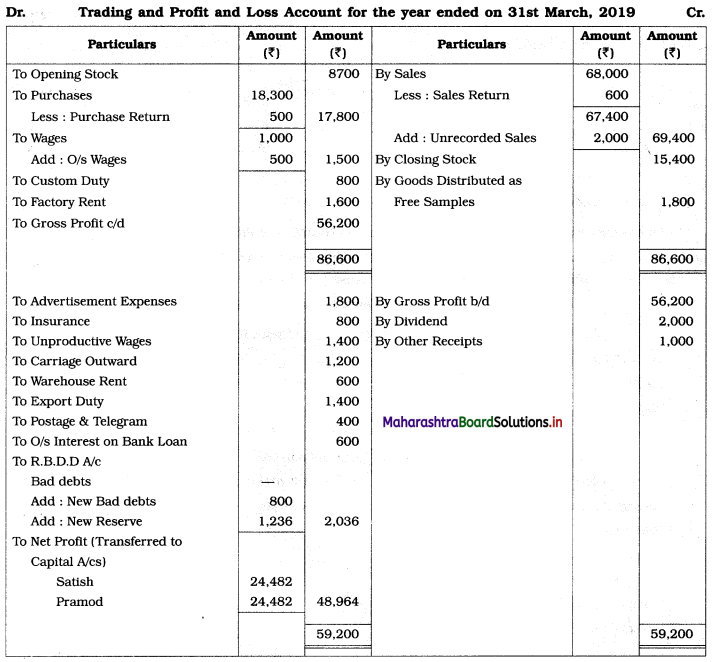
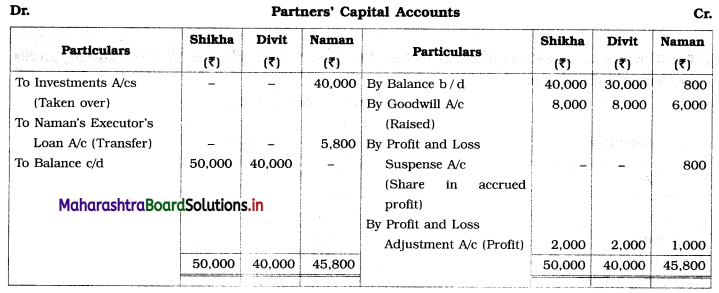
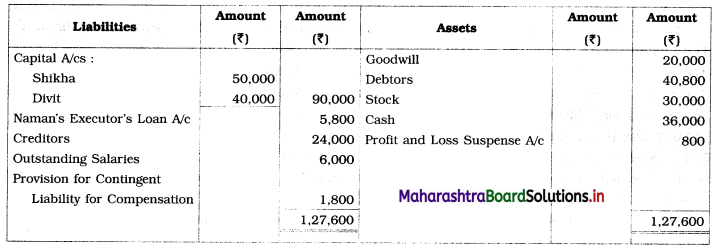
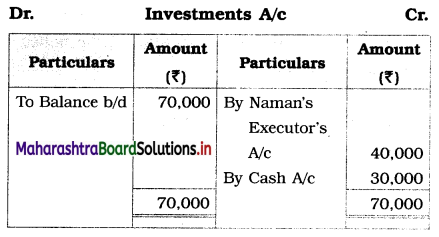
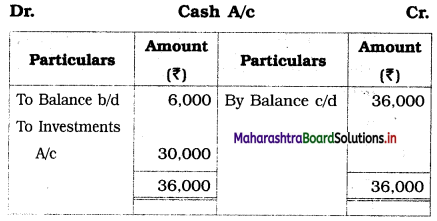
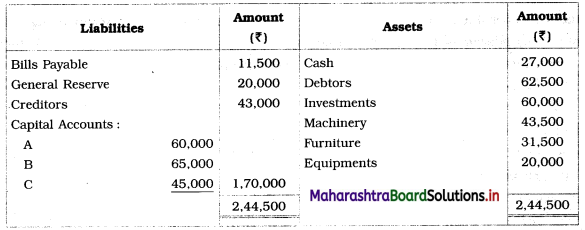
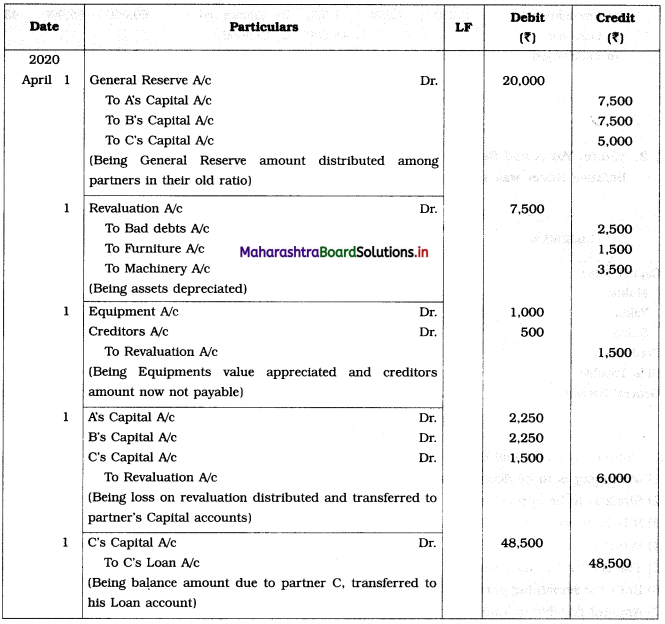
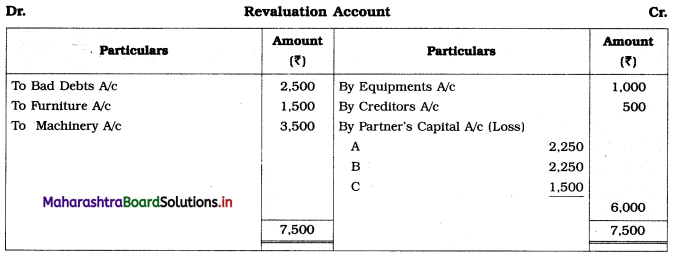
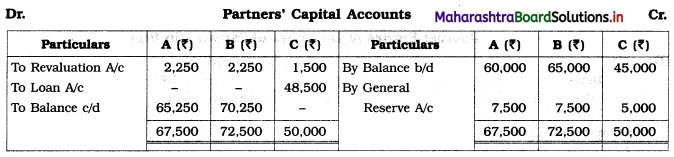
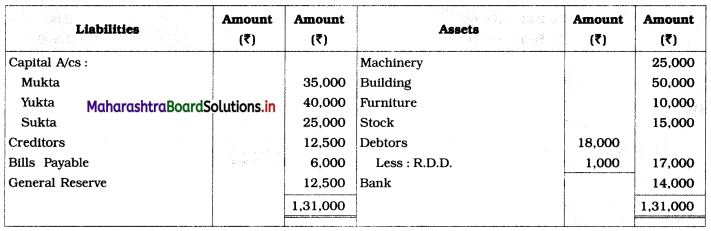
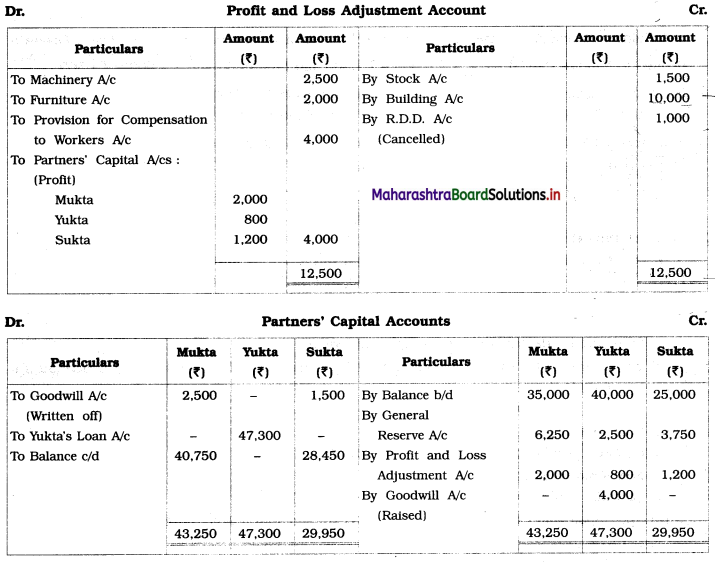
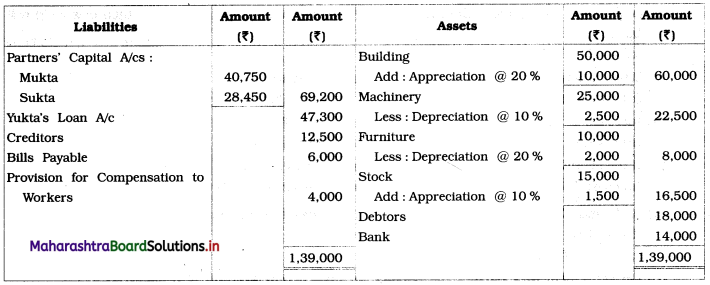
Practical Problems
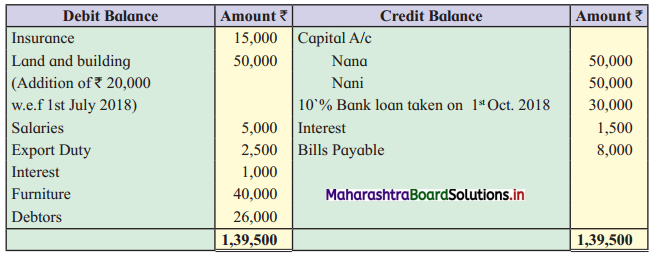
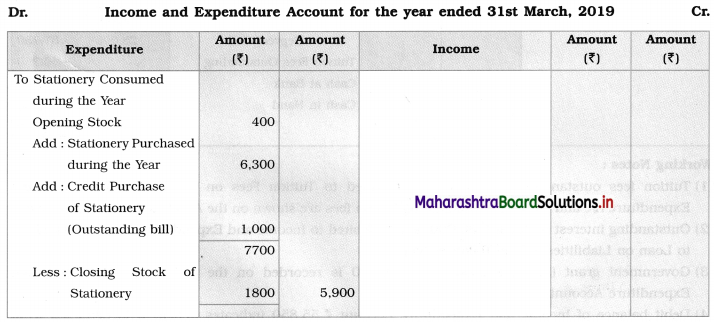
Question 1.
Calculation of stationery consumed during the year
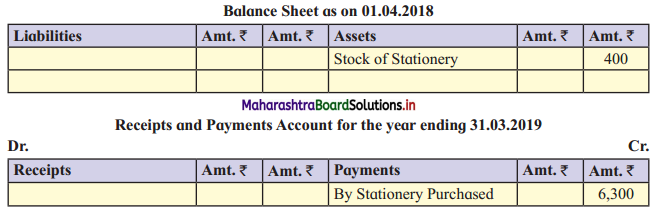
Adjustments:
1. ₹ 1,000 outstanding for the stationery bill.
2. Stock of Stationery as of 31 – 03 – 2019 was valued at ₹ 1,800.
With the above information, calculate the amount of Stationery consumed during the year and show its presence in final Accounts of a concern.
Solution:
In the books of ___________________
Balance Sheet as of 31 – 03 – 2019

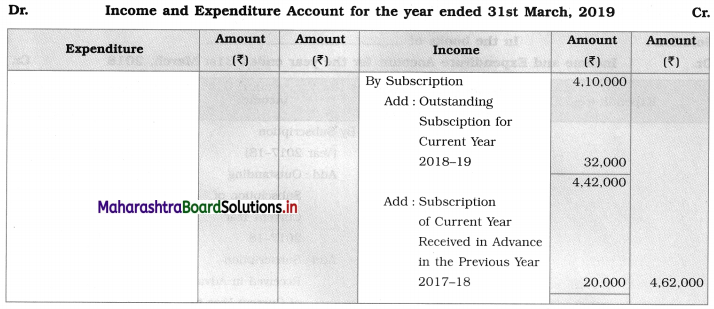
Question 2.
Presentation of Subscription only
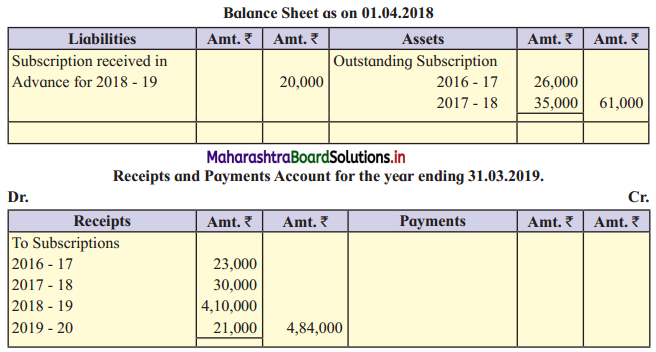
Adjustments:
The outstanding subscription for 2018-19 is ₹ 32,000.
With the above information, present the item Subscription in Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31 -03-2019 and Balance Sheet as on the date.
Solution:
In the books of ___________________
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
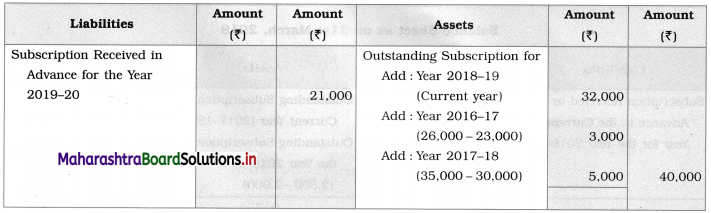
Working Note:
Outstanding subs, given in the balance sheet as on 01-04-2018 are ₹ 26,000 (for 2016-17) and ₹ 35,000 (for 2017-18). Against that, as shown in Receipt – Payment A/c ₹ 23,000 and ₹ 30,000 are received respectively. Means ₹ 3,000 and ₹ 5,000 are still outstanding which are known in the current year balance sheet.
![]()
Question 3.
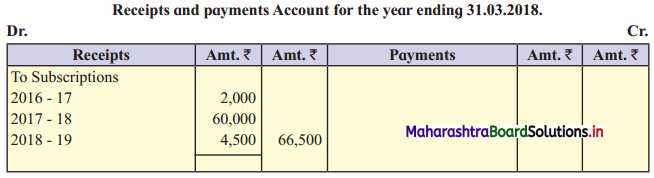
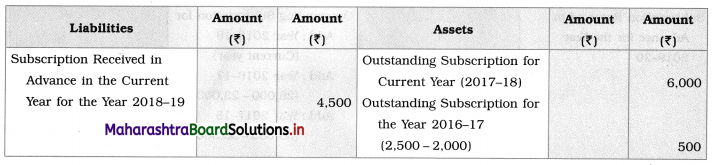
Adjustments:
Subscription outstanding for the year 2017-18 is ₹ 6,000.
During the previous year subscription received in advance for 2017-18 is ₹ 2,000.
The outstanding subscription of 2016-17 is ₹ 2,500.
With the help of the above information present the item Subscription in Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31-03-2018 and Balance Sheet as on that date.
Solution:
In the books of ___________________
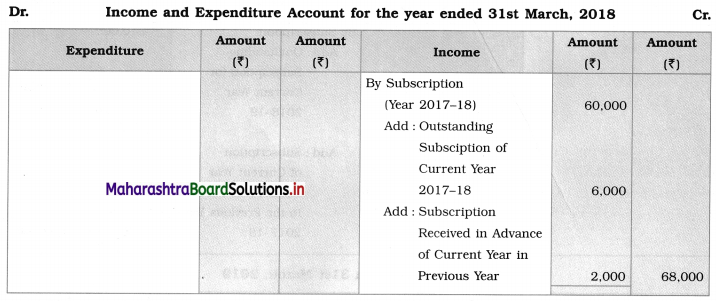
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2018
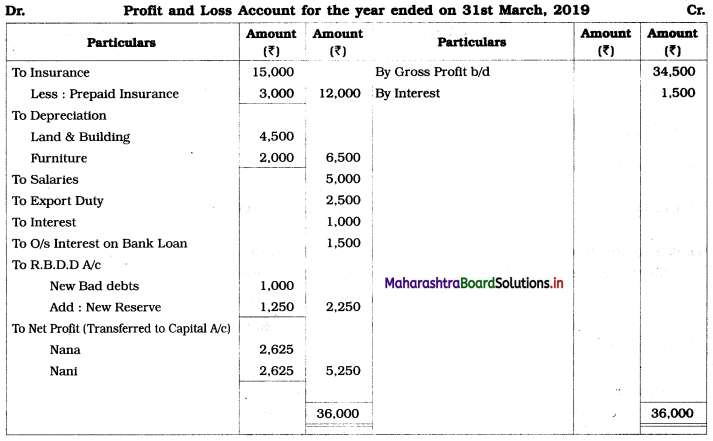
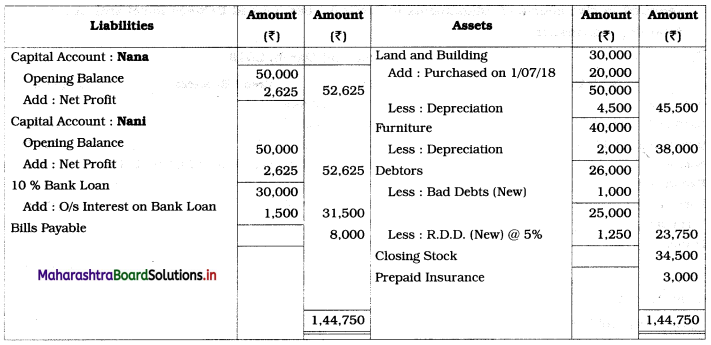
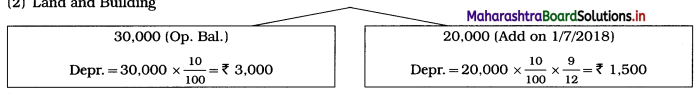
Question 4.
Preparation of Income and Expenditure Account only
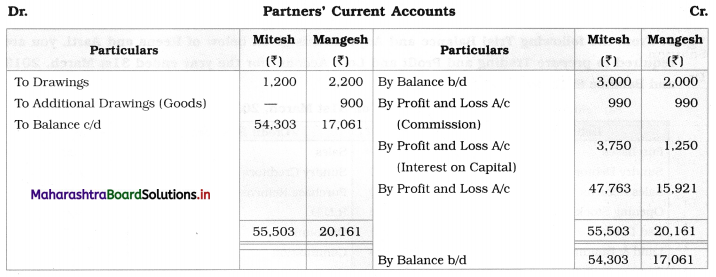
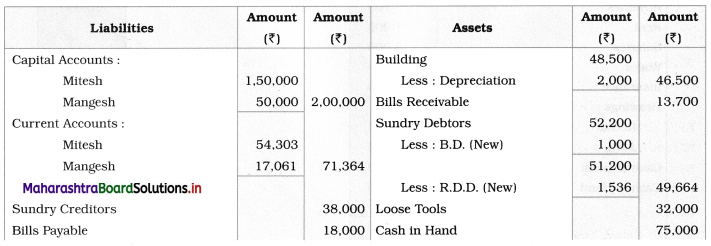
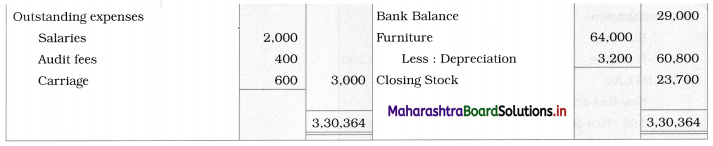
Following is the Receipts and Payments Account of “Satara Sports Club” Satara.
Prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31-03-2019.
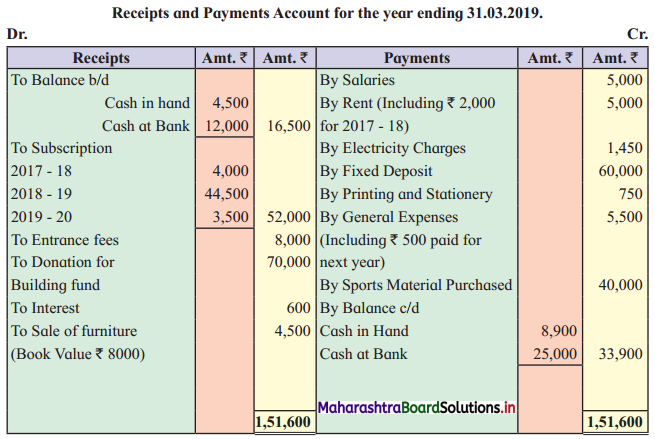
Adjustments:
1. Outstanding subscription for the current year is ₹ 4,500.
2. Outstanding rent for the current year amounted to ₹ 1,000.
3. Entrance fees are to be treated as Revenue Income.
4. Stock of sports material as of 01-04-2018 ₹ 6,000 and on 31 – 03 – 2019 ₹ 14,000.
Solution:
In the books of ‘Satara Sports Club’ Satara
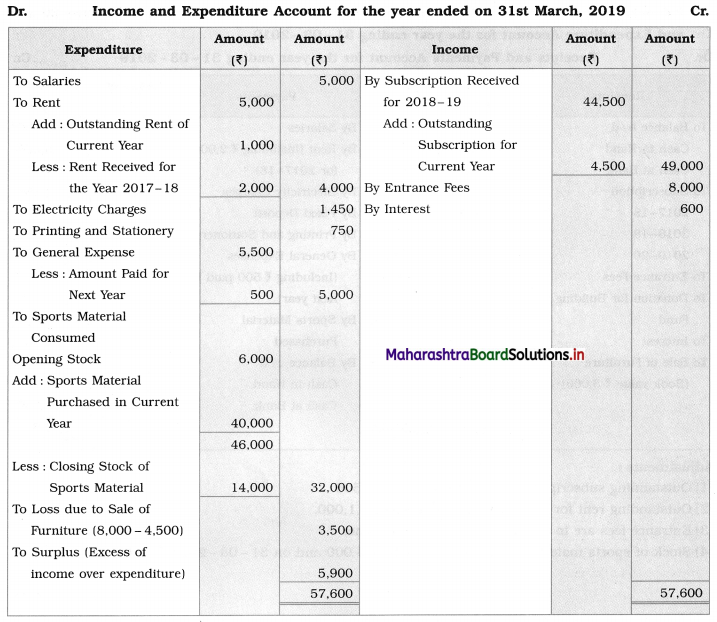
Working Notes:
1. Entrance fees are to be treated as Revenue income. Therefore entire amount is recorded on the income side.
2. Since the selling price of Furniture ₹ 4,500 is lower than its cost price of ₹ 8,000, there is a Loss in the sale of furniture.
It is calculated as follows:
Loss on sale of furniture = Book value (cost) – Selling price
= 8,000 – 4,500
= ₹ 3,500
It is debited to Income and Expenditure A/c.
![]()
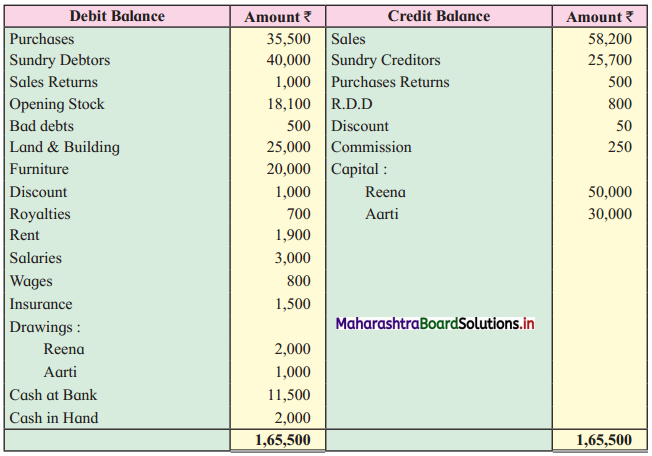
Question 5.
“Bhartiya Kala Kendra”, Solapur gives you the following information for the year ended on 31-03-2018. Prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31-03-2018.
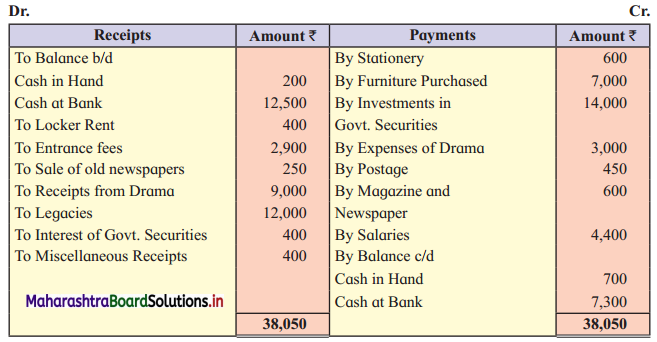
Additional Information:
1. Legacies are to be capitalized.
2. Outstanding salary ₹ 200.
3. 50% of Entrance fees are to be capitalized.
Solution:
In the books of Bhartiya Kala Kendra, Solapur
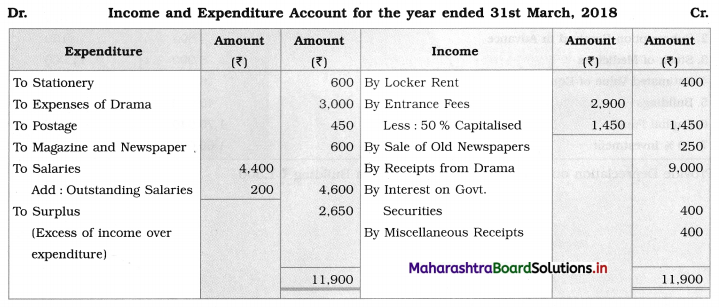
Question 6.
Accounts of a Charitable Hospital
From the following particulars relating to “Radha-Krishna Charitable Hospital”, Pune.
Prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31-03-2020 and Balance Sheet as of that date.
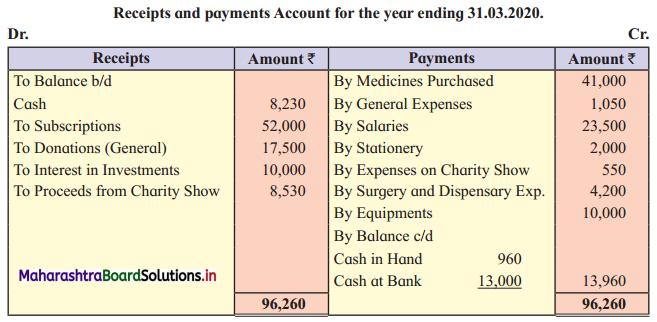
Additional Information:
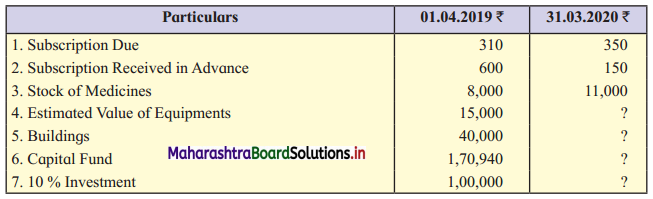
Provide Depreciation on Equipments ₹ 1,900 and on Building ₹ 1,500.
Solution:
In the Books of Radha-Krishna Charitable Hospital, Pune
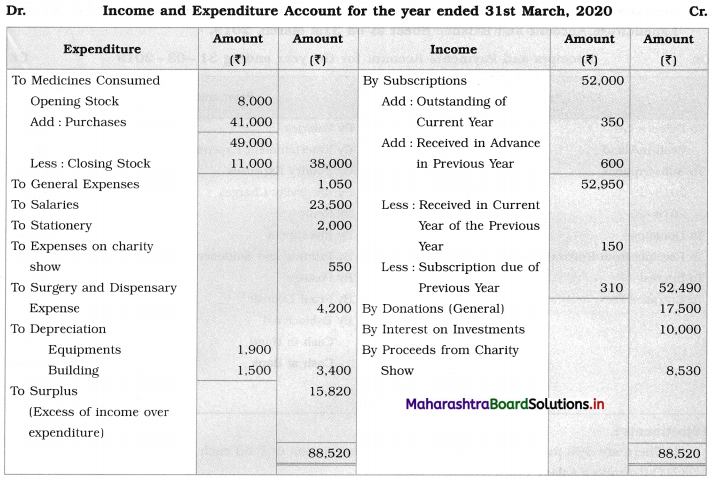
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2020
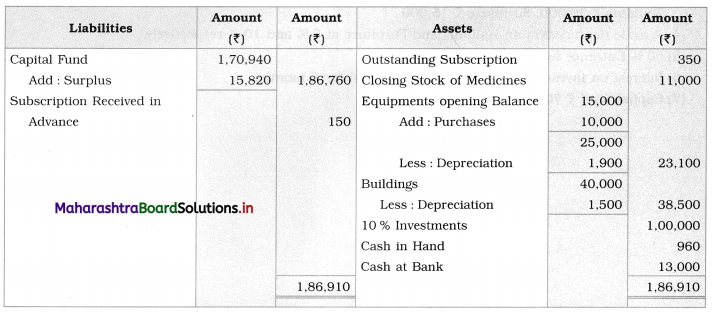
Working Notes:
1. To find medicines consumed, here in the opening stock, purchases are added and the closing stock of medicine is subtracted.
2. For equipment, in opening balance, add equipment purchased during the year and subtract depreciation to get the closing balance of equipment.
3. Interest ₹ 10,000 is received on 10% investments means there is no outstanding interest.
![]()
Question 7.
From the following transactions of Receipts and Payments Account of “Pavan-putra Hanuman Vyayamshala”, Parbhani and the adjustments are given, you are required to prepare Income and Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019.
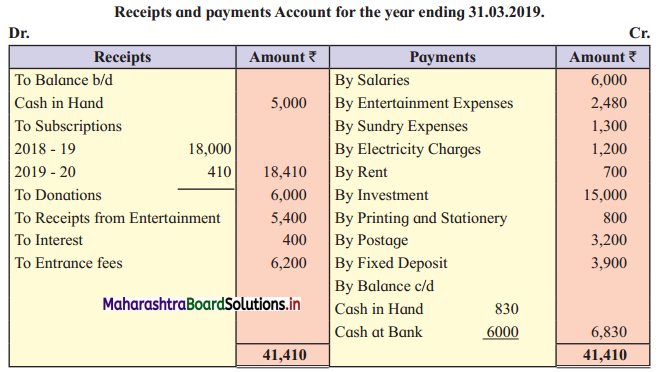
Adjustments:
1. There are 500 members paying an annual subscription of ₹ 50 each.
2. Outstanding salary was ₹ 1,200.
3. The Assets on 01-04-2018 were as follows:
Building ₹ 50,000, Furniture ₹ 15,000
4. Provide depreciation on Building and Furniture at 5% and 10% respectively.
5. 50% Entrance fees are to be capitalized.
6. Interest on investment at 5% p.a. has accrued for 6 months.
7. Capital fund ₹ 70,000 on 01-04-2018.
Solution:
In the Books of Pavan-putra Hanuman Vyayamshala, Parbhani
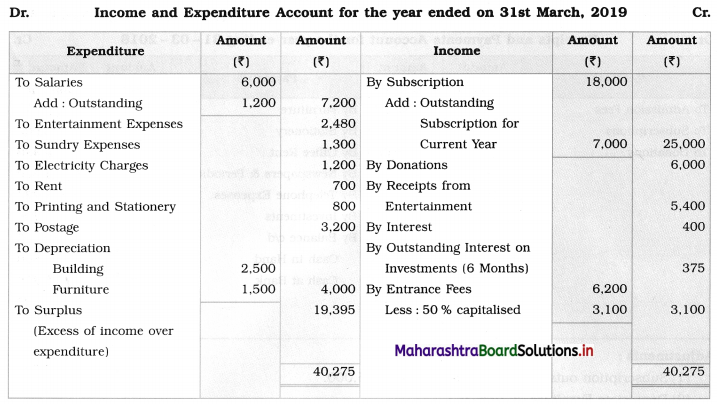
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
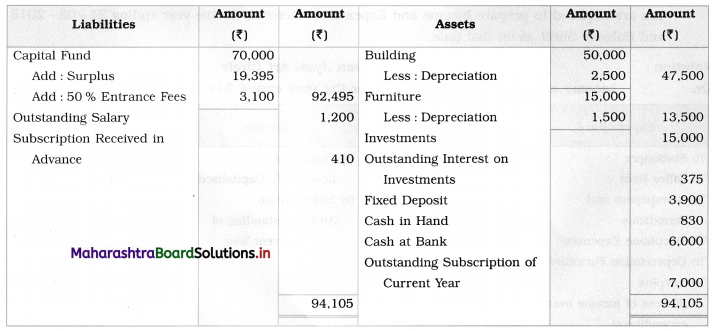
Working Notes:
1. Interest on investment is receivable for 6 months:
I = \(\frac{\text { PRN }}{100}\)
= 15,000 × \(\frac{5}{100} \times \frac{6}{12}\)
= ₹ 375 (outstanding interest on investment)
2. 50 % of entrance fees (i.e. \(\frac{6200}{2}\) = ₹ 310o) is to be capitalised means add it to capital fund.
3. Total subscription of current year = 500 members × ₹ 50 = ₹ 25,000
But actual subscription received = ₹ 18,000
means difference (25,000 – 18,000) of ₹ 7,000 is outstanding subscription.
Question 8.
Newly Started Art Circle
“Jeevan Jyoti Art Circle” a newly established concern has presented the following information:
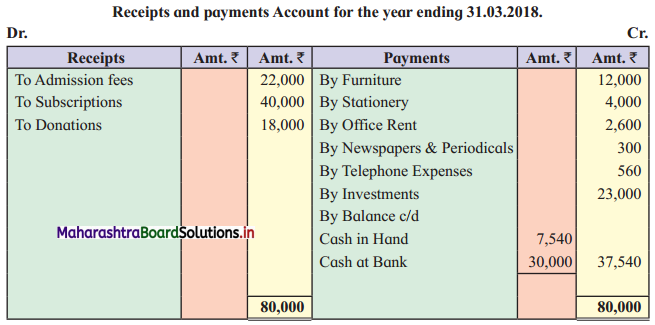
Adjustments:
1. Subscription outstanding for the year was ₹ 5,000.
2. Depreciate Furniture @ 10% p.a.
3. Full amount of admission fees and 50% donations are to be capitalized.
You are required to prepare an Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31-03-2018 and a Balance Sheet as of that date.
Solution:
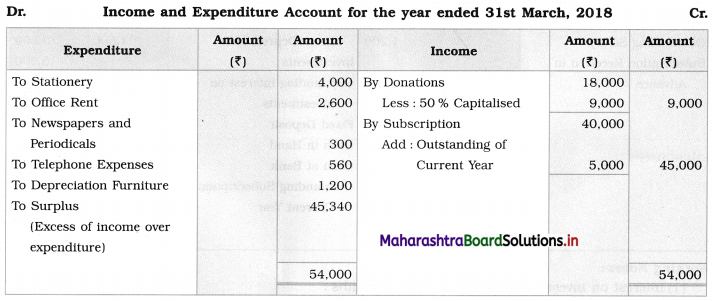
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2018
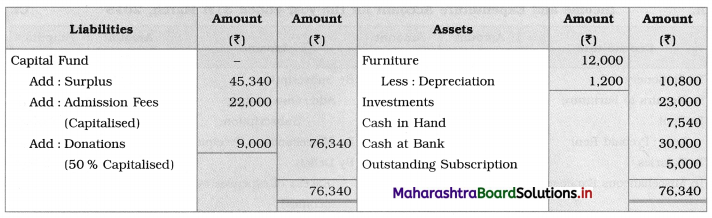
Working Notes:
The full amount of admission fees and 50% of donations are added to the surplus amount to get capital funds. (Opening balance of the capital fund is not given.)
![]()
Question 9.
Given below is the Receipts and Payments Account of “Vithai Mahila Mandat”, Pandharpur for the year ending 31-03-2018. Prepare an Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31-03-2018 and Balance Sheet as of that date.
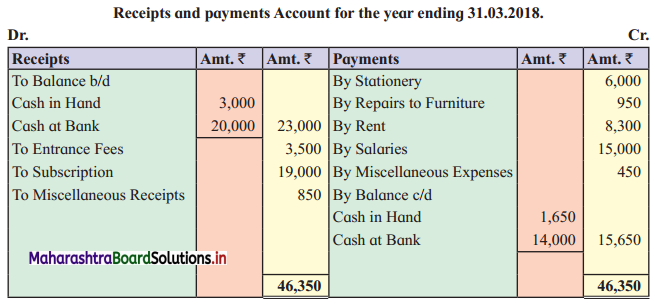
Adjustments:
1. Capital fund on 01-04-2017 was ₹ 90,000.
2. Outstanding subscription ₹ 4,000.
3. Entrance fees are to be capitalized.
4. Rent paid includes ₹ 800 paid for April 2018.
5. They have the following Assets and Liabilities as of 01-04-2017:
Furniture ₹ 9,000, Building ₹ 70,000, and Outstanding Expenses ₹ 12,000.
Solution:
In the books of Vithai Mahila Mandal, Pandharpur
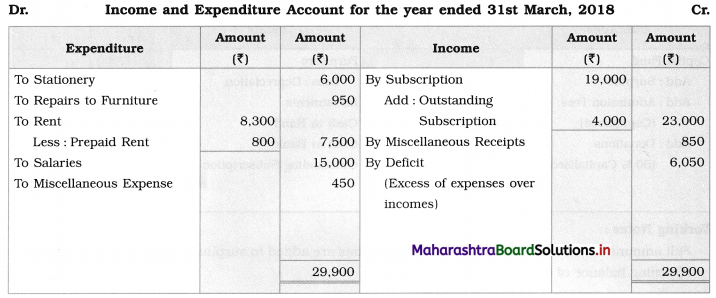
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2018
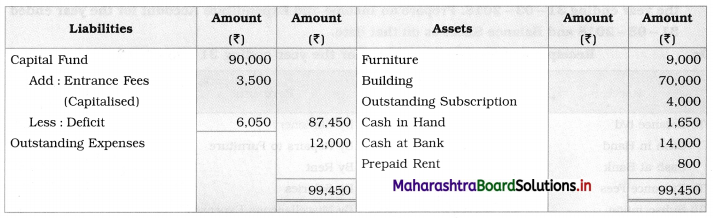
Working Notes:
1. Outstanding subscription of ₹ 4,000 is first added to subscription received on the credit side of Income and Expenditure A/c and then it is shown on the Assets side of Balance Sheet.
2. Entire amount of entrance fees ₹ 3,500 is added to the capital fund.
3. Prepaid ₹ 800 is first deducted from rent paid on the debit side of Income & Expenditure A/c and then shown on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
4. Outstanding expenses ₹ 12,000 is directly shown on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
Question 10.
From the following Receipts and Payments Account “K.B.P. Engineering College”, Nashik for the year ending on 31 – 03 – 2019 and additional information, prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31-03-2019 and Balance Sheet as on that date.
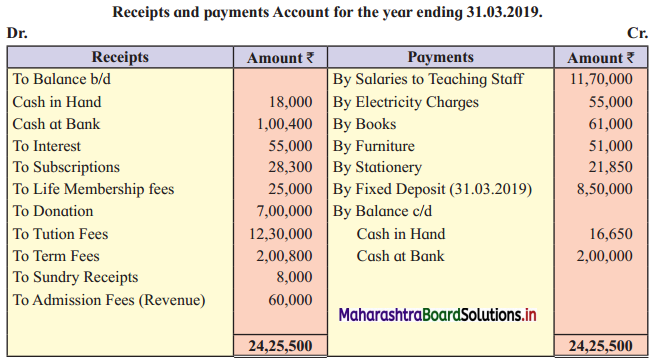
Additional Information:
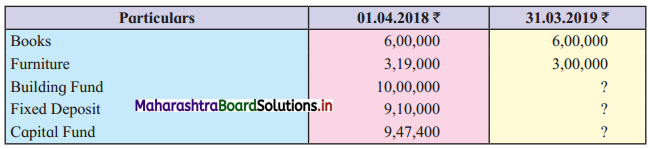
1. 50% of donations are for the Building funds and the balance is to be treated as Revenue income.
2. Outstanding subscription ₹ 5,300.
3. Life membership fees are to capitalize.
Solution:
In the books of K.B.P. Engineering College, Nashik
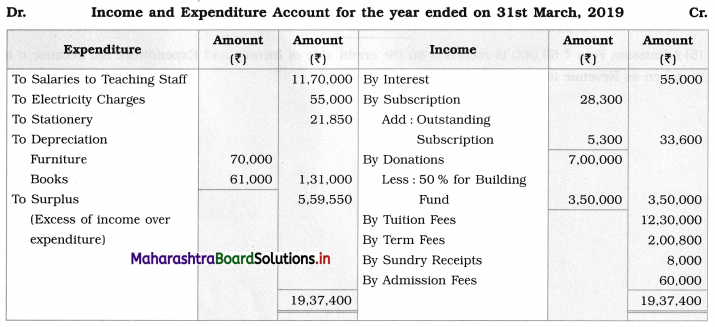
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
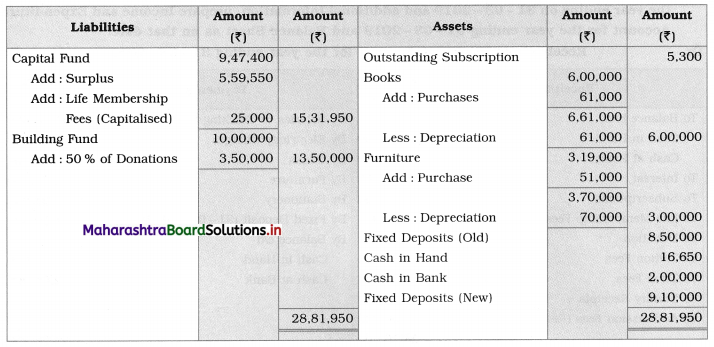
Working Notes:
1. Life membership fees are to be capitalized, which means add the entire amount to the capital fund.
2. 50% of Donations of ₹ 7,00,000 i.e., ₹ 3,50,000 is to be added to the Building Fund, and the remaining amount of donation i.e., ₹ 3,50,000 is credited to Income and Expenditure A/c.
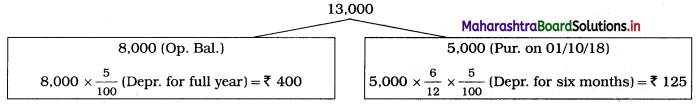
3. The depreciation on Fixed assets is calculated by using the following formula:
Depreciation = Opening balance + Purchases – Closing value
∴ Depreciation on Books = 6,00,000 + 61,000 – 6,00,000
= 6,61,000 – 6,00,000
= ₹ 61,000
∴ Depreciation on Furniture = 3,19,000 + 51,000 – 3,00,000
= 3,70,000 – 3,00,000
= ₹ 70,000
4. Fixed deposit: Opening balance given = ₹ 9,10,000
Fixed deposit (31-03-2019) = ₹ 8,50,000
(Newly purchased)
∴ Total fixed deposits = ₹ 17,50,000
5. Admission Fees ₹ 60,000 are recorded on the credit side of Income and Expenditure A/c because it is taken as Revenue income.
![]()
Question 11.
Account of a School
From the following Balance Sheet and Receipts and Payments Account of “New English School”, Barshi, prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31 – 03 – 2020 and a Balance Sheet as on that date.
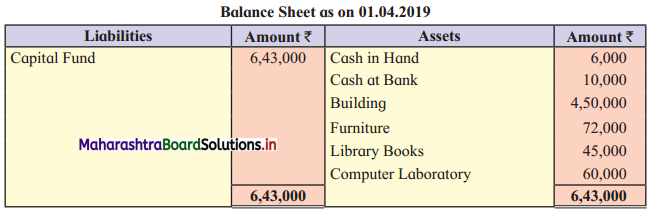
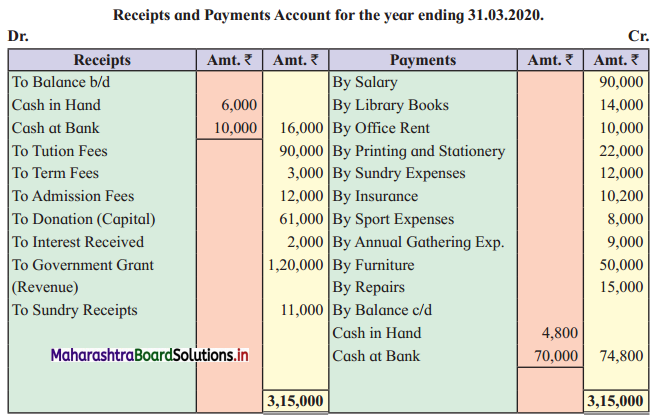
Additional Information:
1. Outstanding salary of ₹ 9,000.
2. Outstanding tuition fees ₹ 15,000.
3. Depreciate library books by ₹ 9,000 and Furniture by ₹ 10,000.
Solution:
In the books of New English School, Barshi
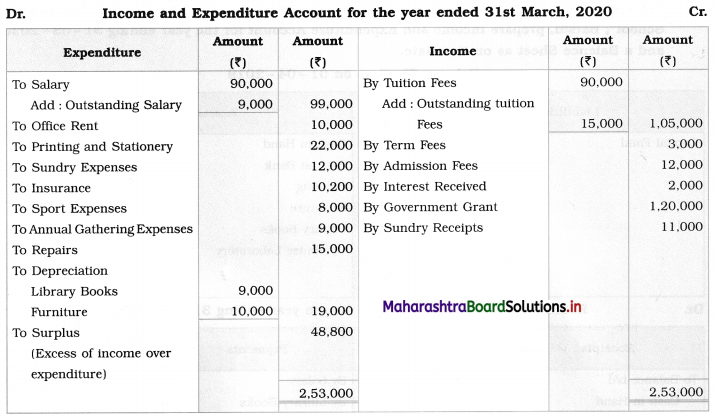
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2020
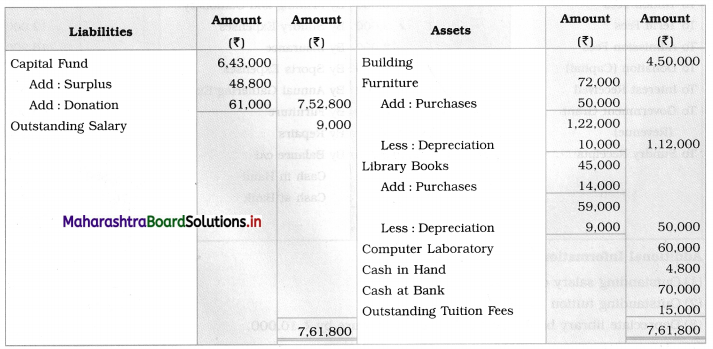
Working Notes:
1. Donation (Capital) is added to the Capital fund.
2. Government Grant ₹ 1,20,000 is recorded on the credit side of Income & Expenditure A/c because it is the revenue income of the organization.
3. Outstanding tuition fees ₹ 15,000 and outstanding salary ₹ 9,000 are added to the respective head of Account and then they are shown separately on the Assets side and Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet respectively.
Question 12.
Account of a Library
Following is the Receipts Payments Account of “Dhananjay Library”, Mumbai for the year ending 31-03-2020.
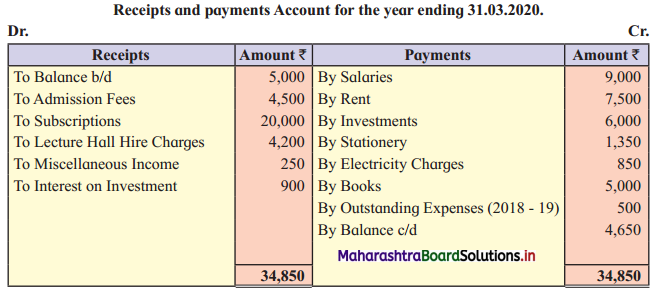
You are required to prepare an Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31-03-2020 and a Balance Sheet as of that day.
The following information is also made available to you.
1. On 31 -03-2019, the library had the following Assets also; Books ₹ 50,000, Furniture ₹ 6,500, and Machinery of ₹ 30,000.
2. Subscription received in advance amounted to ₹ 500.
3. Outstanding salaries ₹ 1300 and Rent ₹ 950.
4. 50% of the admission fees should be capitalized.
5. Furniture to be depreciated at 10% p.a.
6. Library books were purchased on 1st April 2019 charge depreciation at 10% p.a.
7. The Investments were purchased on 01-04-2019 and they carry interest at 20% p.a.
Solution:
In the books of Dhananjay Library, Mumbai
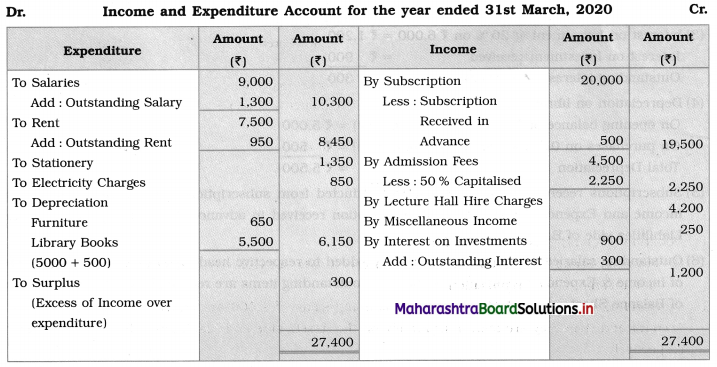
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2020
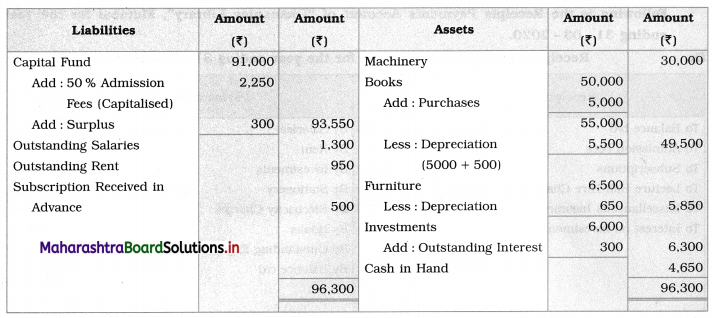
Working Notes:
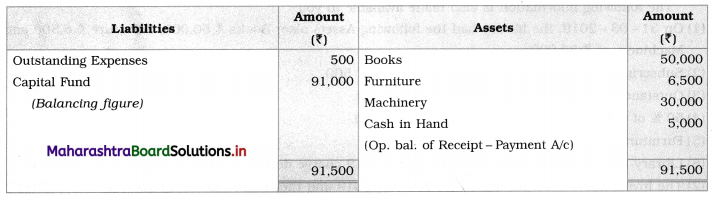
1. Opening Balance Sheet is prepared to find out opening capital fund:
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
2. Outstanding expenses of the previous year, paid in the current year so no entry for outstanding expenses (2018-19)
3. Interest on Investment @ 20% on ₹ 6,000 = ₹ 1,200
Interest on Investment received = ₹ 900
Outstanding interest on investment = ₹ 300
4. Depreciation on library books at 10% p.a.
On opening balance of ₹ 50,000 (for whole year) = ₹ 5,000
On purchases on 01-04-2019 (for whole year) = ₹ 500
Total Depreciation = ₹ 5,500
![]()
5. Subscriptions received in advance ₹ 500 is deducted from subscription received on the credit side of Income and Expenditure A/c and then subscription received in advance is shown separately on the Liabilities side of Balance Sheet.
6. Outstanding salaries and outstanding rent are added to the respective head of Account on the debit side of the Income & Expenditure Account and both the outstanding items are recorded on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
Question 13.
Outstanding Expenses and Prepaid Expenses
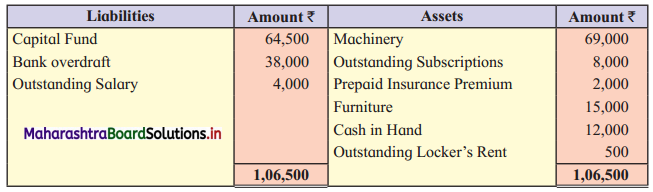
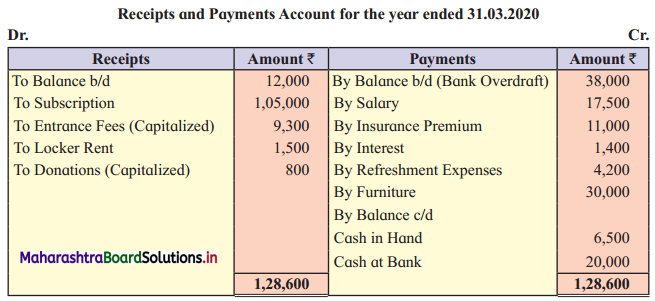
From the following information supplied to you, prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31-03-2020 and Balance Sheet as on that date for “Morya Sports Club”, Thane.
Balance Sheet as on 01-04-2019
Adjustments:
1. Subscription received includes ₹ 3,000 for 2018-19 and outstanding subscription for 2019-20 was ₹ 14,000.
2. On 31-03-2020, the Prepaid insurance premium was ₹ 2,500.
3. Depreciate Furniture by ₹ 3,000.
4. Locker rent outstanding for 2019-20 is ₹ 400.
Answer:
In the books of ‘Morya Sports Club’ Thane
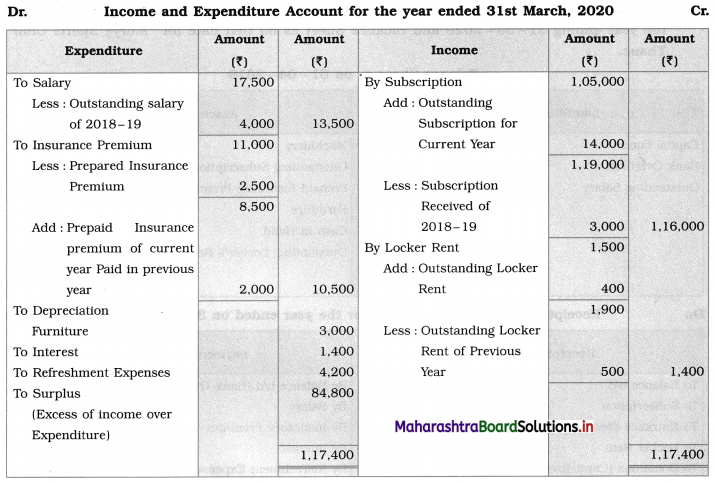
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2020
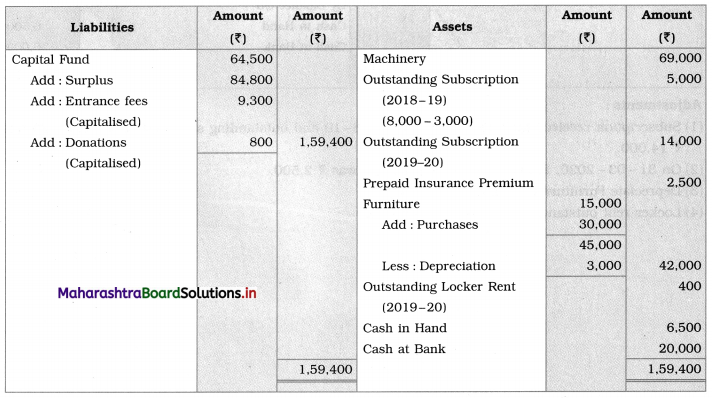
Working Notes:
1. Outstanding subscription (2018-19) ₹ 8,000 given in b/s against that ₹ 3,000 received in 2019-20.
Means still receivable subscription = ₹ 5,000 (8,000 – 3,000).
2. Prepaid insurance premium (2018-19) ₹ 2,000 is for the current year. Therefore, in the current year’s insurance premium, ₹ 2,000 is to be added and then subtract the current year’s prepaid insurance premium.
3. Outstanding salary of (2018-19), ₹ 4,000 of the previous year is to be subtracted from current year’s salary.
4. Total amount of donations and entrance fees are to be capitalized so add the entire amount of both the items to Capital fund.
5. Outstanding locker’s rent (2018-19) ₹ 500 is given in the Balance Sheet. It is to be subtracted from the current year’s locker’s rent and then adds the current year’s outstanding locker rent.
Question 14.
Charitable Hospital
Following information has been provided by “Vivekanand Charitable Hospital”, Latur. You are required to prepare an Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31-03-2019 and the Balance Sheet as of that date.
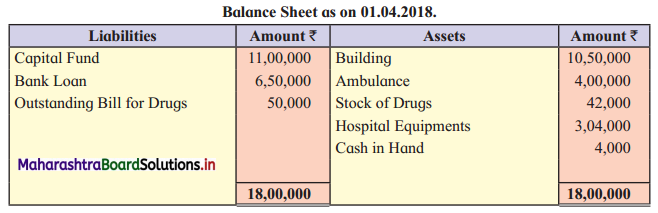
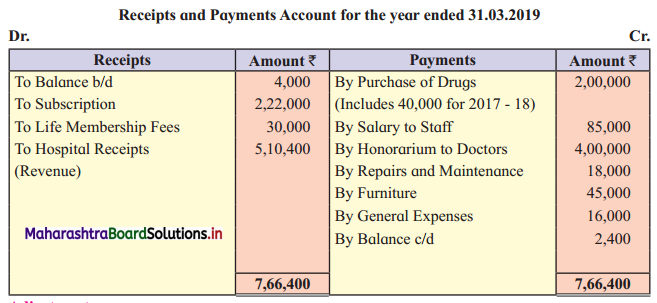
Adjustments:
1. On 31-03-2019 stock of drugs was valued at ₹ 22,000.
2. Depreciation on Building at 5% p.a. and on Ambulance ₹ 30,000.
3. Life membership fees are to be capitalized.
Answer:
In the books of Vivekanand Charitable Hospital, Latur
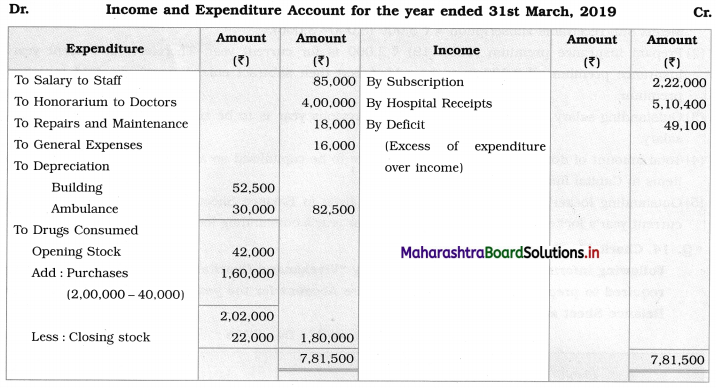
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
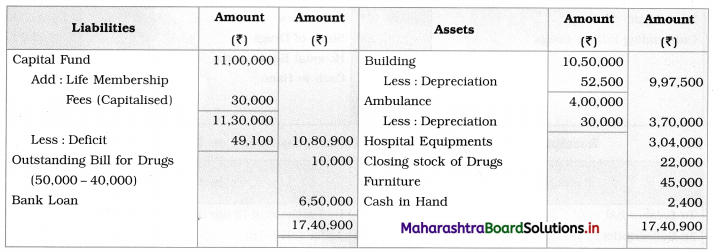
Working Notes:
1. Purchase of drugs ₹ 2,00,000 includes ₹ 40,000 of 2017-18 and in the Balance Sheet of 2017-18, the outstanding bill of drugs is ₹ 50,000 given. So, ₹ 10,000 is still outstanding.
![]()
2. Consumption of drugs:
Opening stock (2017-18) = ₹ 42,000
Add: Purchase of drugs = ₹ 1,60,000
Total = 1,60,000 + 42,000 = ₹ 2,02,000
Less: Closing stock of drugs = ₹ 22,000
Consumption of drugs = 1,80,000