Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce Book Keeping & Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Analysis of Financial Statements Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce BK Important Questions Chapter 9 Analysis of Financial Statements
Objective Questions
A. Select the most appropriate alternative from those given below and rewrite the sentences:
Question 1.
The methodical classification of financial statement is called ____________
(a) an interpretation
(b) an analysis
(c) ratio
(d) Profit and Loss A/c
Answer:
(b) an analysis
Question 2.
The short-term deposits are ____________
(a) net cash
(b) cash equivalent
(c) cashflow
(d) cash outflow
Answer:
(b) cash equivalent
Question 3.
Cash proceeds from issue of debentures is a ____________ activity.
(a) financial
(b) non-financial
(c) operating
(d) trading
Answer:
(a) financial
![]()
Question 4.
The relationship between net profit before tax, interest and dividend and capital employed is known from ____________
(a) Current ratio
(b) Quick ratio
(c) ROI
(d) ROCE
Answer:
(c) ROI
Question 5.
Bills receivable is ____________
(a) Liquid asset
(b) Net profit
(c) Current asset
(d) Net loss
Answer:
(c) Current asset
Question 6.
ROCE should be ____________ than ROI.
(a) less
(b) higher
(c) equal
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) higher
Question 7.
Ideally liquid ratio/quick ratio should be ____________
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 1 : 1
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 1 : 3
Answer:
(b) 1 : 1
![]()
Question 8.
Gross/Net profit ratio expressed in ____________
(a) number
(b) ratio
(c) percentage
(d) words
Answer:
(c) percentage
B. Give one word/term/phrase for each of the following statements.
Question 1.
The tool for analysis of financial statement where individual figures of Balance Sheet are converted into a percentage.
Answer:
Common Size Balance Sheet
Question 2.
The type of activity in cash flow analysis, involving the purchase of fixed assets.
Answer:
Investing Activity
Question 3.
The ratio measures the efficiency of the production department.
Answer:
Gross Profit Ratio
Question 4.
The ratio measures the overall efficiency of the business.
Answer:
Net Profit Ratio
Question 5.
The ratio shows the operational efficiency of the business.
Answer:
Operating Profit Ratio
![]()
Question 6.
The ratio is computed to measure the overall efficiency or profitability of the business.
Answer:
Return On Investment (ROI)
C. Answer in one sentence only.
Question 1.
Define financial statements.
Answer:
The statements which are prepared by the business to find out profitability, efficiency, solvency, growth of the business to judge the financial strength and status are called financial statements.
Question 2.
Who prepares financial statements?
Answer:
The financial statements are prepared by the Profit-making organisations as well as Non-profit concerns or organisations.
Question 3.
State the main tools or techniques of financial analysis.
Answer:
The main tools or techniques of financial analysis are as follows:
- Comparative financial statement
- Common size statement
- Cash flow analysis.
Question 4.
State the primary objective of the cash flow statement.
Answer:
The primary objective of the cash flow statement is to help management in taking decisions and making a plan by providing current information on cash inflow and outflow of any particular period.
![]()
Question 5.
What is Financial Ratio?
Answer:
A financial ratio is a mathematical number that measures the relationship between two accounting figures.
Question 6.
Write the names of the Balance Sheet ratio.
Answer:
Balance Sheet ratios are
- Current ratio
- Liquid ratio.
Question 7.
Write the names of the Income Statement ratio.
Answer:
Income Statement ratios are-
- Gross Profit ratio
- Net Profit ratio
- Operating Expense ratio.
Question 8.
Give three examples of current liability.
Answer:
Examples of current liability are Sundry creditors, Bills payable, Bank overdraft, Short-term loans, etc.
Question 9.
Write the names of combined/mixed ratios.
Answer:
Names of combined/mixed ratios are-
- Return On Capital Employed (ROCE)
- Return On Investment (ROI)
![]()
Solved Problems
Question 1.
Calculate Current Ratio:
Debtors = ₹ 90,000, Creditors = ₹ 30,000, Bills receivables = ₹ 10,000, Bills payable = ₹ 12,000, Stock of goods = ₹ 40,000, Short-term loan = ₹ 40,000, Outstanding expenses = ₹ 14,000, Cash balance = ₹ 70,000, Machinery = ₹ 1,00,000, Current investments = ₹ 25,000, Non-current investments = ₹ 25,000, Loose tools = ₹ 15,000, Bank overdraft = ₹ 29,000.
Solution:
Current assets = Debtors + Bills receivable + Stock of goods + Cash balance + Current investments + Loose tools
= 90,000 + 10,000 + 40,000 + 70,000 + 25,000 + 15,000
= ₹ 2,50,000
Current liabilities = Creditors + Bills payable + Short-term loan + Outstanding expenses + Bank overdraft
= 30,000 + 12,000 + 40,000 + 14,000 + 29,000
= ₹ 1,25,000
Current ratio = \(\frac{\text { Current assets }}{\text { Current liabilities }}\)
= \(\frac{2,50,000}{1,25,000}\)
= 2 : 1
Note: Machinery and Non-current investment are to be committed as it is not to be included in current assets.
Question 2.
Calculate Quick Ratio:
Working capital = ₹ 1,70,000, Prepaid expenses = ₹ 10,000, Inventory/Stock = ₹ 15,000, Prepaid expenses = ₹ 10,000, Current liabilities = ₹ 1,25,000, Bank overdraft = ₹ 35,000
Solution:
Current assets = Current liabilities + Working capital
= 1,25,000+ 1,70,000
= ₹ 2,95,000
Quick assets = Current assets – Inventory – Prepaid expense
= 2,95,000 – 15,000 – 10,000
= ₹ 2,70,000
Quick liabilities = Current liabilities – Bank overdraft
= 1,25,000 – 35,000
= ₹ 90,000
Quick ratio = \(\frac{\text { Quick assets }}{\text { Quick liabilities }}\)
= \(\frac{2,70,000}{90,000}\)
= 3 : 1
![]()
3. Calculate Gross Profit Ratio:
Opening stock = ₹ 20,000, Closing stock = ₹ 25,000, Purchases = ₹ 1,00,000, Purchase return = ₹ 10,000, Sales = ₹ 2,25,000, Sales return = ₹ 15,000, Direct expenses = ₹ 20,000.
Solution:
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Purchases – Purchase return + Direct expenses – Closing stock
= 20,000 + 1,00,000 – 10,000 + 20,000 – 25,000
= 1,30,000 – 25,000
= ₹ 1,05,000
Net sales = Sales – Sales return
= 2,25,000 – 15,000
= ₹ 2,10,000
Gross profit = Net sales – Cost of goods sold
= 2,10,000 – 1,05,000
= ₹ 1,05,000
Gross Profit ratio = \(\frac{\text { Gross profit }}{\text { Net sales }} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{1,05,000}{2,10,000} \times 100\)
= 50%
Question 4.
Calculate Gross Profit Ratio :
Sales ₹ 9,00,000, Gross profit ratio 20% on cost.
Solution:
Gross profit is 20% on cost.
Goods costing ₹ 100 must have been sold for ₹ 120.
Hence, if sales is ₹ 120, gross profit is ₹ 20.
If sales is ₹ 9,00,000 then Gross profit =?
Gross profit = 9,00,000 × \(\frac{20}{100}\) = ₹ 1,50,000
Gross profit ratio = \(\frac{\text { Gross profit }}{\text { Net sales }} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{1,50,000}{9,00,000} \times 100\)
= 16.67%
![]()
Question 5.
Calculate Net Profit Ratio:
Sales = ₹ 10,00,000, Cost of goods sold = ₹ 4,20,000, Indirect expenses = ₹ 30,000, Administrative expenses = ₹ 1,00,000, Selling and Distribution expenses = ₹ 80,000, Interest on debentures shares = ₹ 40,000.
Solution:
Gross profit = Sales – Cost of goods sold
= 10,00,000 – 4,20,000
= ₹ 5,80,000
Net profit = Gross profit – Administrative expenses – Selling and Distribution expenses – Indirect expenses – Interest on debentures
= 5,80,000 – 1,00,000 – 80,000 – 30,000 – 40,000
= ₹ 3,30,000
Net profit ratio = \(\frac{\text { Net profit }}{\text { Sales }} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{3,30,000}{10,00,000} \times 100\)
= 33%
Question 6.
Calculate Operating Ratio:
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c of Kalpana for the year ending 31st March 2019.
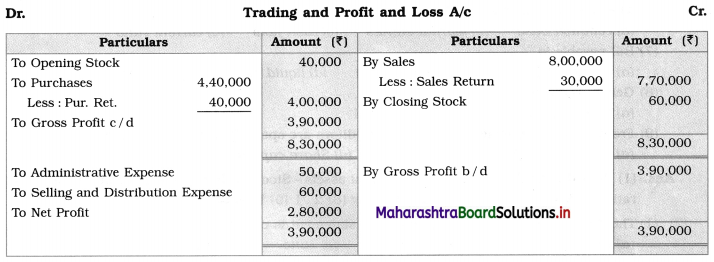
Solution:
Cost of goods sold = Net sales – Gross profit
= 7,70,000 – 3,90,000
= ₹ 3,80,000
Operating expenses = Adm. exp. + Selling and Distribution expenses
= 50,000 + 60,000
= ₹ 1,10,000
Operating ratio = \(\frac{\text { Cost of goods sold }+\text { Operating expense }}{\text { Net sales }} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{3,80,000+1,10,000}{7,70,000} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{4,90,000}{7,70,000} \times 100\)
= 63.64%