Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 3.2 Algebra 10th Class Maths Part 1 Answers Solutions Chapter 3 Arithmetic Progression.
Practice Set 3.2 Algebra 10th Std Maths Part 1 Answers Chapter 3 Arithmetic Progression
Question 1.
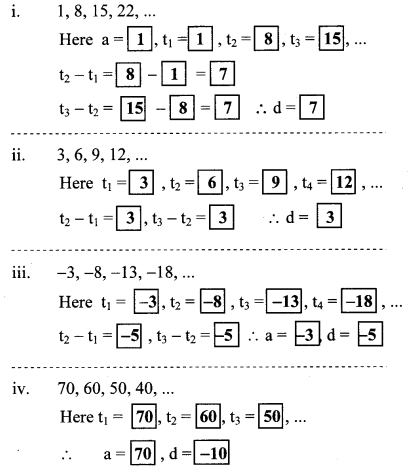
Write the correct number in the given boxes from the following A.P.
Solution:
Question 2.
Decide whether following sequence is an A.P., if so find the 20th term of the progression.
-12, -5, 2, 9,16, 23,30,…
Solution:
i. The given sequence is
-12, -5,2, 9, 16, 23,30,…
Here, t1 = -12, t2 = -5, t3 = 2, t4 = 9
∴ t2 – t1 – 5 – (-12) – 5 + 12 = 7
t3 – t2 = 2 – (-5) = 2 + 5 = 7
∴ t4 – t3 – 9 – 2 = 7
∴ t2 – t1 = t3 – t2 = … = 7 = d = constant
The difference between two consecutive terms is constant.
∴ The given sequence is an A.P.
ii. tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t20 = -12 + (20 – 1)7 …[∵a = -12, d = 7]
= -12 + 19 × 7
= -12 + 133
∴ t20 = 121
∴ 20th term of the given A.P. is 121.
Question 3.
Given Arithmetic Progression is 12, 16, 20, 24, … Find the 24th term of this progression.
Solution:
The given A.P. is 12, 16, 20, 24,…
Here, a = 12, d = 16 – 12 = 4 Since,
tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t24 = 12 + (24 – 1)4
= 12 + 23 × 4
= 12 + 92
∴ t24 = 104
∴ 24th term of the given A.P. is 104.
Question 4.
Find the 19th term of the following A.P. 7,13,19,25…..
Solution:
The given A.P. is 7, 13, 19, 25,…
Here, a = 7, d = 13 – 7 = 6
Since, tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t19 = 7 + (19 – 1)6
= 7 + 18 × 6
= 7 + 108
∴ t19 = 115
∴ 19th term of the given A.P. is 115.
Question 5.
Find the 27th term of the following A.P. 9,4,-1,-6,-11,…
Solution:
The given A.P. is 9, 4, -1, -6, -11,…
Here, a = 9, d = 4- 9 = -5
Since, tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t27 = 9 + (27 – 1)(-5)
= 9 + 26 × (-5)
= 9 – 130
∴ t27 = -121
∴ 27th term of the given A.P. is -121.
Question 6.
Find how many three digit natural numbers are divisible by 5.
Solution:
The three digit natural numbers divisible by
5 are 100, 105, 110, …,995
The above sequence is an A.P.
∴ a = 100, d = 105 – 100 = 5
Let the number of terms in the A.P. be n.
Then, tn = 995
Since, tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ 995 = 100 +(n – 1)5
∴ 995 – 100 = (n – 1)5
∴ 895 = (n – 1)5
∴ n – 1 = \(\frac { 895 }{ 5 } \)
∴ n – 1 = 179
∴ n = 179 + 1 = 180
∴ There are 180 three digit natural numbers which are divisible by 5.
Question 7.
The 11th term and the 21st term of an A.P. are 16 and 29 respectively, then find the 41st term of that A.P.
Solution:
Bor an A.P., let a be the first term and d be the common difference,
t11 = 16, t21 = 29 …[Given]
tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t11, = a + (11 – 1)d
∴ 16 = a + 10d
i.e. a + 10d = 16 …(i)
Also, t21 = a + (21 – 1)d
∴ 29 = a + 20d
i.e. a + 20d = 29 …(ii)
Subtracting equation (i) from (ii), we get a

Question 8.
8. 11, 8, 5, 2, … In this A.P. which term is number-151?
Solution:
The given A.P. is 11, 8, 5, 2,…
Here, a = 11, d = 8 – 11 = -3
Let the nth term of the given A.P. be -151.
Then, tn = – 151
Since, tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ -151= 11 + (n – 1)(-3)
∴ -151 – 11 =(n – 1)(-3)
∴ -162 = (n – 1)(-3)
∴ n – 1 = \(\frac { -162 }{ -3 } \)
∴ n – 1 = 54
∴ n = 54 + 1 = 55
∴ 55th term of the given A.P. is -151.
Question 9.
In the natural numbers from 10 to 250, how many are divisible by 4?
Solution:
The natural numbers from 10 to 250 divisible
by 4 are 12, 16, 20, …,248
The above sequence is an A.P.
∴ a = 12, d = 16 – 12 = 4
Let the number of terms in the A.P. be n.
Then, tn = 248
Since, tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ 248 = 12 + (n – 1)4
∴ 248 – 12 = (n – 1)4
∴ 236 = (n – 1)4
∴ n – 1 = \(\frac { 236 }{ 4 } \)
∴ n – 1 = 59
∴ n = 59 + 1 = 60
∴ There are 60 natural numbers from 10 to 250 which are divisible by 4.
Question 10.
In an A.P. 17th term is 7 more than its 10th term. Find the common difference.
Solution:
For an A.P., let a be the first term and d be the common difference.
According to the given condition,
t17 = t10 + 7
∴ a + (17 – 1)d = a + (10 – 1)d + 7 …[∵ tn = a + (n – 1)d]
∴ a + 16d = a + 9d + 7
∴ a + 16d – a – 9d = 7
∴ 7d = 7
∴ d = \(\frac { 7 }{ 7 } \) = 1
∴ The common difference is 1.
Question 1.
Kabir’s mother keeps a record of his height on each birthday. When he was one year old, his height was 70 cm, at 2 years he was 80 cm tall and 3 years he was 90 cm tall. His aunt Meera was studying in the 10th class. She said, “it seems like Kabir’s height grows in Arithmetic Progression”. Assuming this, she calculated how tall Kabir will be at the age of 15 years when he is in 10th! She was shocked to find it. You too assume that Kabir grows in A.P. and find out his height at the age of 15 years. (Textbook pg. no. 63)
Solution:
Height of Kabir when he was 1 year old = 70 cm Height of Kabir when he was 2 years old = 80 cm
Height of Kabir when he was 3 years old = 90 cm The heights of Kabir form an A.P.
Here, a = 70, d = 80 – 70 = 10
We have to find height of Kabir at the age of 15years i.e. t15.
Now, tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t15 = 70 + (15 – 1)10
= 70 + 14 × 10 = 70 + 140
∴ t15 = 210
∴ The height of Kabir at the age of 15 years will be 210 cm.
Question 2.
Is 5, 8, 11, 14, …. an A.P.? If so then what will be the 100th term? Check whether 92 is in this A.P.? Is number 61 in this A.P.? (Textbook pg. no, 62)
Solution:
i. The given sequence is
5, 8,11,14,…
Here, t1 = 5, t2 = 8, t3 = 11, t4 = 14
∴ t2 – t1 = 8 – 5 = 3
t3 – t2 = 11 – 8 = 3
t4 – t3 = 14 – 11 = 3
∴ t2 – t1 = t3 – t2 = t4 – t3 = 3 = d = constant
The difference between two consecutive terms is constant
∴ The given sequence is an A.P.
ii. tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t100 = 5 + (100 – 1)3 …[∵ a = 5, d = 3]
= 5 + 99 × 3
= 5 + 297
∴ t100 = 302
∴ 100th term of the given A.P. is 302.
iii. To check whether 92 is in given A.P., let tn = 92
∴ tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ 92 = 5 + (n – 1)3
∴ 92 = 5 + 3n – 3
∴ 92 = 2 + 3n
∴ 90 = 3n
∴ n = \(\frac { 90 }{ 3 } \) = 30
∴ 92 is the 30th term of given A.P.
iv. To check whether 61 is in given A.P., let tn = 61
61 = 5 + (n – 1)3
∴ 61 = 5 + 3n – 3
∴ 61 = 2 + 3n
∴ 61 – 2 = 3n
∴ 59 = 3n
∴ n = \(\frac { 59 }{ 3 } \)
But, n is natural number 59
∴ n ≠ \(\frac { 59 }{ 3 } \)
∴ 61 is not in given A.P.