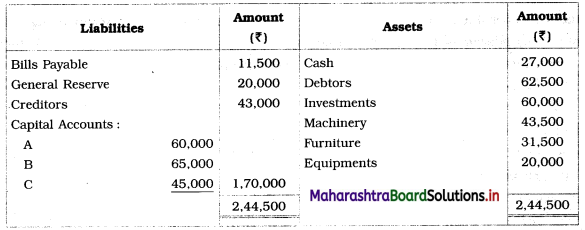
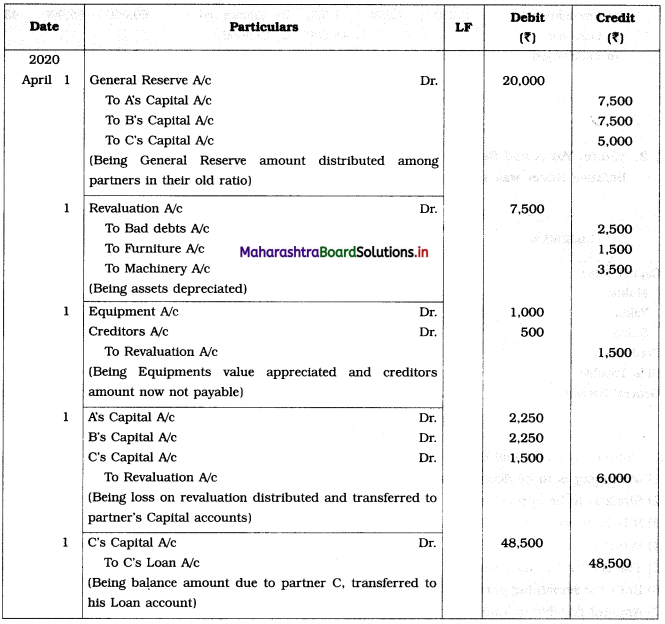
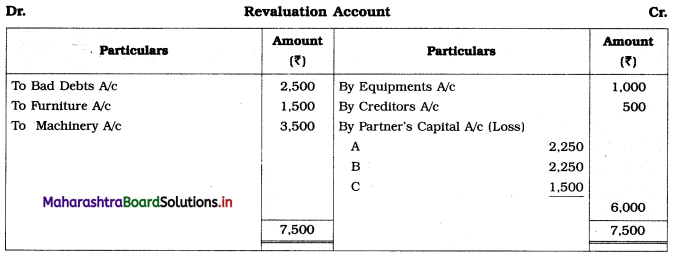
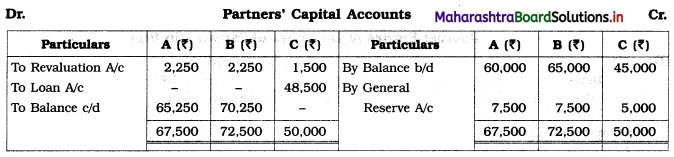
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 1 Solid State Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 1 Solid State
Question 1.
What are the physical states of matter? How can they be changed into one another?
Answer:
- There are three physical states of matter namely solid, liquid and gas.
- They differ in intermolecular or interatomic or interionic forces which are strongest in the solid-state.
- By raising the temperature of solids to their melting point, solids are converted into liquids while heating liquids to their boiling points, they can be converted into vapour or gaseous state.
- On the contrary, by cooling the gases to very low temperature and subjecting to high pressure they can be transformed into liquid which on further cooling can be transformed into solid-state.
The equilibrium existing between three states of matter may be represented as,
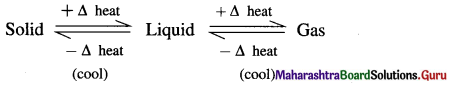
Question 2.
What are the constituents of solids?
Answer:
The smallest constituent particles of various solids are atoms, ions or molecules. All such small constituents are referred to as ‘particles’.
Question 3.
What are the characteristic properties of solids?
Answer:
- The solid state of matter is characterised by strong interparticle forces of attraction.
- There is regularity and periodicity in the arrangement of constituent particles of solid.
- Generally solids are hard, incompressible and rigid except some solids like Na, K, P which are soft.
- The constituent particles of solids like molecules, atoms or ions have fixed stationary positions in solid and can only oscillate about their equilibrium or mean positions. Hence, they have fixed shape and cannot be poured like liquids.
- Crystalline solids have sharp melting points and they melt at a definite temperature. Amorphous solids do not have sharp melting points.
- They are anisotropic or isotropic.
Question 4.
Give classification of solids.
Answer:
Depending on orderly arrangement of the constituent particles, the solids are classified into two types :
- Crystalline solids. For example, diamond, NaCl, K2SO4, etc.
- Amorphous solids or non-crystalline solids. For example, tar, glass, plastics, rubber, butter, etc.
![]()
Question 5.
Define :
(1) Crystalline solid.
(2) Amorphous solid.
Answer:
(1) Crystalline solid : A homogeneous solid in which the constituent particles like atoms, ions or molecules are arranged in a definite repeating pattern throughout the solid is called crystalline solid. For example, NaCl, KNO3, etc.
(2) Amorphous solid : A substance which appears like solid but does not have perfectly ordered crystalline structure and no regular arrangement of constituent particles in structure is called amorphous solid. For example, glass, rubber, plastics, etc.
Question 6.
Define the term anisotropy.
OR
Define and explain the term anisotropy.
Answer:
Anisotropy : The ability of crystalline solids to change their physical properties when measured in different directions is called anisotropy.
Explanation : This property is due to different arrangement of constituents in different directions. Different types of particles fall on the way of measurements in different directions. Hence the composition of crystalline solid changes with directions changing their physical properties.
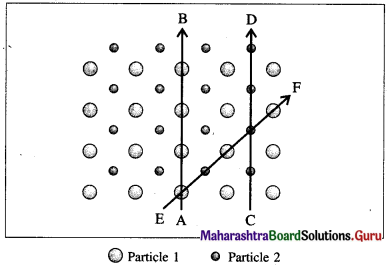
Fig. 1.1 : Anisotropy in crystals : Different arrangements of constituent particles about different directions, AB, CD and EF.
Question 7.
Define and explain isotropy.
Answer:
Isotropy : The ability of amorphous solids to exhibit identical physical properties even though measured in different directions is called isotropy.
Explanation : This property arises because there is no long range order of regular pattern of arrangement in them and hence the arrangement is irregular along all the directions. Therefore the magnitude of any physical property would be identical along all directions.
Question 8.
Why does crystalline solid show different refractive indices in different directions ?
Answer:
- Crystalline solid has long range order of regular pattern of arrangement which repeats periodically over entire crystal.
- Within the given pattern, the arrangements of different atoms or ions or molecules is different in different directions. Hence the properties like refractive indices in the different directions are different.
This shows that the crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature.
Question 9.
Explain the properties of amorphous solids.
Answer:
- The constituent particles in amorphous solids are arranged randomly.
- They have short range ordered structure.
- Amorphous solids are called supercooled liquids having very high viscosity.
- They do not have sharp melting points and they melt gradually over a temperature interval.
- Amorphous substances appear like solids but they do not have perfectly ordered crystalline structure, hence they are not real solids. Therefore they are pseudo solids.
- They are isotropic and exhibit the same magnitude of any property in every direction.
![]()
Question 10.
What is isomorphism ?
Answer:
Isomorphism : A phenomenon in which two or more crystalline substances show same crystalline structure is called isomorphism and the crystals are said to be isomorphous. For example, NaNO3 and CaCO3. They have atomic ratios 1 : 1 : 3.
Question 11.
What is isomorphous?
Answer:
Isomorphous : When two or more crystalline substances have the same crystalline structure, they are said to be isomorphous. For example, NaF and MgO, NaNO3 and CaCO3.
Question 12.
What is polymorphism ?
Answer:
Polymorphism : A phenomenon in which when a single substance crystallises in two or more forms under different conditions of solidification is called polymorphism and the substance is called polymorphous. For example, calcite and oragonite are two forms of CaCO3.
Question 13.
What is polymorphous ?
Answer:
Polymorphous: A single substance which crystallises in two or more forms under different conditions of solidification is called polymorphous. Polymorphic forms of an element are called allotropic forms or allotropes. For example, carbon exists as diamond and graphite, or sulphur exists in rhombic and monoclinic allotropic forms.
Question 14.
Identify isomorphous and polymorphous substances in the following :
K2SO4, graphite, β-quartz, Na2SeO4, CaCO3, diamond, cristobalite, CsNO3.
Answer:
| Isomorphous | Polymorphous |
| K2SO4, Na2SeO4 CaCO3, CsNO3 | Graphite, diamond Β-quartz, cristobalite |
Question 15.
Why does a crystalline solid has a sharp melting point ?
Answer:
- Crystalline solid is a homogeneous solid and it has long range order of regular pattern of arrangement which repeats periodically over entire crystal.
- The interatomic or intermolecular forces are identical, hence the thermal energy required to break the regular structure by overcoming the intermolecular forces is uniform throughout.
- Hence the heat and temperature needed to melt the solid are same, and therefore solids have sharp melting points.
Question 16.
Amorphous solids do not have sharp melting points. Explain.
Answer:
- Amorphous solids do not have perfectly ordered crystalline structure.
- They have short range order of regular pattern hence periodically repeating regular pattern is over a short distance.
- The thermal energy required to break the structure and separate constituent particles is not uniform.
- Hence the temperature needed to melt the solid is not same, therefore amorphous solids do not have sharp melting points but melt over a range of temperature.
![]()
Question 17.
Give examples of (1) crystalline solids and (2) amorphous solids.
Answer:
(1) Crystalline solids : Metallic solids (Cu, Fe, etc.) crystalline salts (NaCl, K2SO4, etc.)
(2) Amorphous solids : Glass, plastics, rubber, etc.
Question 18.
Distinguish between crystalline solids and amorphous solids.
Answer:
Crystalline solids:
- They have definite characteristic geometrical shape.
- They have long range order of regular pattern of arrangement of constituent particles.
- They are true solids.
- They have sharp melting points.
- They are anisotropic in nature.
- They have definite heat of fusion.
Amorphous solids:
- They have irregular shape.
- They have short range order of regular pattern of arrangement of constituent particles.
- They are pseudo solids or supercooled liquids.
- They do not have sharp melting points.
- They are isotropic in nature.
- They do not have definite heat of fusion.
Question 19.
How are crystalline solids classified ?
Answer:
Crystalline solids are classified as follows :
- Ionic crystals
- Covalent network crystals
- Molecular crystals
- Metallic crystals
Question 20.
What are crystalline solids?
Answer:
The solids in which the constituent particles are charged ions namely cations and anions held together by electrostatic force of attraction are called crystalline solids.
Question 21.
What are the characteristics of ionic crystals ?
Answer:
The characteristics of ionic crystals are as follows :
- The constituents of ionic crystals are charged ions namely cations and anions. They differ in ionic size.
- The ions in these crystals are held by strong electrostatic force of attraction.
- Ionic crystals have high melting points and they are hard and brittle.
- In solid state they are nonconductors of electricity but they are good conductors when melted or dissolved in water.
- In aqueous solution they dissociate forming ions.
- Example : NaCl, KCl. CaF2, K2SO4, etc.
Question 22.
Explain why ionic solids are hard and brittle.
Answer:
- In ionic crystalline solids, constituent particles are positively charged cations and negatively charged anions placed at alternate lattice points.
- The ions are held by strong coulombic electrostatic forces of attraction compensating opposite forces. Hence they are hard.
- Since there are no free electrons, they are not malleable and on applying a shearing force, ionic crystals break into small units. Hence they are brittle.
![]()
Question 23.
What are covalent network crystals ?
Answer:
The crystals in which the constituent particles are atoms linked by covalent bonds forming a continuous network are called covalent network crystals. For example, diamond, quartz.
Question 24.
What are the characteristics of covalent network crystals ?
Answer:
The characteristics of covalent network crystals are as follows :
- The constituent particles in these solids are atoms.
- The atoms in these crystals are held by covalent bonds forming a rigid three dimensional network which gives a giant molecule. Hence, the entire crystal is a single molecule.
- These crystals are very hard (or hardest) and most incompressible.
- They have high melting points and boiling points.
- Since the electrons are localised they are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- Example : Quartz (SiO2), diamond.
Question 25.
Give the examples of network solids.
Answer:
The examples of covalent network solids are as follows :
Quartz (SiO2), diamond, boron nitride carborundum.
Question 26.
What are allotropes ?
Answer:
Allotropes : When a substance exists in two or more forms then they are called allotropes. They are polymorphous. For example, carbon has allotropes diamond and graphite.
Question 27.
What are molecular crystals ?
Answer:
The crystals in which the constituent particles are molecules (or unbonded single atoms) of the same substance held together by intermolecular forces of attraction. For example solidified Cl2, CO2, etc.
Question 28.
What are the characteristics of molecular crystals ?
Answer:
The characteristics of molecular crystals are as follows :
- The constituent particles of these solids are molecules (or unbonded single atoms) of the same substance.
- The atoms within the molecules are bonded by covalent bonds.
- The molecules are held together by intermolecular forces of attraction.
![]()
Question 29.
What are intermolecular forces of attraction involved in molecular crystals ?
Answer:
The intermolecular forces involved in molecular crystals are as follows :
(1) Weak dipole-dipole interactions :
The solids constituting polar molecules like HCl, H2O, SO2, etc. which possess permanent dipole moment involve weak dipole-dipole interactions.
(2) Very weak dispersion or London forces :
The solids consisting of nonpolar molecules like CH4, H2, etc. involve weak dispersion forces. They are also involved in monoatomic solids like Ar, Ne.
(3) Intermolecular Hydrogen bonds :
- In this crystalline solids, the constituent particles are the molecules which contain hydrogen atom linked to highly electronegative atom like F, O or N.
- In these, molecules are held by hydrogen bonds in which H atom of one molecule is bonded to electronegative atom (like F, N or O) of another molecule.
- Since hydrogen bonding is weak, these solids have very low melting points and generally at room temperature they exist in the liquid or gaseous state.
- They are non-conductors of electricity.
Question 30.
What are metallic crystals ?
Answer:
These are crystalline solids formed by atoms of the same metallic element held together by metallic bonds.
Question 31.
What are the characteristics of metallic crystals ?
Answer:
- Metallic crystals are solids formed by atoms of the same metallic element held together by metallic bonds.
- Metallic crystals have high melting point and boiling point.
- Metals are malleable and can be hammered into thin sheets.
- Metals are ductile and can be drawn into thin wires.
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Examples are Cu, Ag, Au, Ni, etc.
Question 32.
Classify the following solids into different types :
(i) Plastic (ii) P4 molecule (iii) S8 molecule (iv) Iodine molecule (v) Tetra phosphorus decoxide (vi) Ammonium phosphate (vii) Brass (viii) Rubidium (ix) Graphite (x) Diamond (xi) NaCl (xii) Silicon.
Answer:
| Solid | Type |
| (i) Plastic | Covalent network crystal |
| (ii) P4 molecule | Covalent network crystal |
| (iii) S8 molecule | Covalent network crystal |
| (iv) Iodine molecule | Covalent network crystal |
| (v) Tetra phosphorus decoxide | Covalent network crystal |
| (vi) Ammonium phosphate | Ionic crystal |
| (vii) Brass | Metalic crystal |
| (viii) Rubidium | Metalic crystal |
| (ix) Graphite | Covalent crystal |
| (x) Diamond | Covalent crystal |
| (xi) NaCl | Ionic crystal |
| (xii) Silicon | Covalent crystal |
Question 33.
Mention the types of the following solids :
(i) CaF2 (ii) SiC (iii) Ice (iv) SO2 (v) CaCO3 (vi) ZnS (vii) HCl (viii) CO2
Answer:
| Solid | Type |
| (i) CaF2 | Ionic crystal |
| (ii) SiC | Covalent crystal |
| (iii) Ice | Hydrogen bonded molecular crystal |
| (iv) SO2 | Molecular crystal |
| (v) CaCO3 | Ionic crystal |
| (vi) ZnS | Ionic crystal |
| (vii) HCl | Polar molecular crystal |
| (viii) CO2 | Non-polar molecular crystal |
![]()
Question 34.
What is a giant solid ?
Answer:
Covalent solid formed by covalent bonds between neighbouring constituent atoms of non-metallic solid is called a giant solid. For example, graphite.
Question 35.
What is lattice ?
Answer:
Lattice is a geometrical arrangement of points in a three dimensional periodic array.
Question 36.
What is crystal lattice (space lattice) ?
Answer:
Crystal lattice (space lattice) : A regular arrangement of the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) of a crystalline solid having similar environment in three dimensional space is called crystal lattice or space lattice.
Question 37.
What is a lattice point?
Answer:
Lattice point : A position occupied by a crystal constituent particle like an atom, ion or a molecule in the crystal lattice is called lattice point or lattice site.
OR
Any point at the intersection of the lines in the unit cell occupied by a constituent particle like an atom, an ion or a molecule in the crystalline solid is called a lattice point.
![]()
Question 38.
What are the parameters of a unit cell ?
Answer:
A unit cell is characterised by following parameters :
(1) Edges or edge lengths : The intersection of two faces of crystal lattice is called as edge. The three edges denoted by a, b and c represent the dimensions (lengths) of the unit cell along three axes. These edges may or may not be mutually perpendicular.
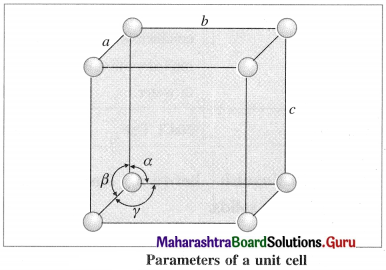
(2) Angles between the edges (or planes) : There are three angles between the edges of the unit cell represented as α, β and γ.
- The angle α is between edges b and c.
- The angle β is between edges a and c.
- The angle γ is between edges a and b.
The crystal is defined with the help of these parameters of its unit cell.
Question 39.
Represent space lattice and unit cell diagrammatically.
Answer:
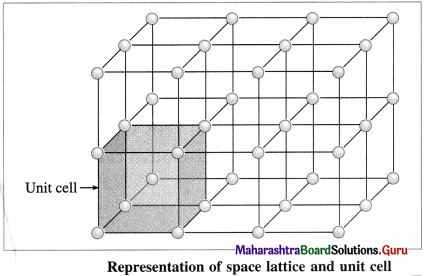
Question 40.
What do you understand by the basis of crystal lattice ?
Answer:
- A crystal structure is formed by attaching a constituent particle to lattice points.
- The constituent particles attached to the lattice points form the basis of the crystal lattice.
- The crystal structure is obtained by attaching a basis to each of the lattice points.
This is represented by the following schematic equation :
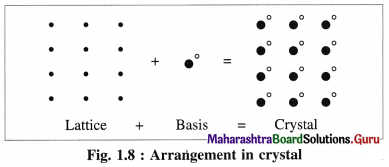
Question 41.
What are the types of unit cells?
Answer:
Basically unit cells are of two types as follows :
- Primitive unit cells : The unit cells in which the constituent particles like atoms, ions or molecules are present only at the corners of the unit cell are called primitive unit cells or simple unit cells.
- Body-centred unit cell : A unit cell in which the constituent particles are present at the corners as well as at its body-centre is called body-centred unit cell.
- Face-centred unit cell : A unit cell in which the constituent particles are present at the corners as well as at the centre of each face is called face-centred unit cell or cubic close packed (CCP) unit cell.
- Base-centred unit cell : A unit cell in which the constituent particles are present at the corners as well as at the centres of two opposite faces is called end-centred unit cell.
Question 42.
Explain briefly crystal systems.
Answer:
(1) The constituent particles like atoms, ions or molecules of the crystal can be arranged in seven different ways changing edges (a, b, c) and angles (α, β, γ) and accordingly they form seven systems or types of the crystal.
(2) These seven crystal system are named as :
(a) Cubic system, (b) Tetragonal system (c) Orthorhombic system (d) Rhombohedral system (e) Monoclinic system (f) Triclinic system (g) Hexagonal system.
![]()
Question 43.
What are Bravais lattices ?
Answer:
- There are seven crystal systems according to the edges (a. b, c) and angles (α, β, γ).
- The constituents of the crystal may be present at corners, face centres, body centres, edge centres and voids.
- By mathematical analysis, it has been proved that only fourteen different kinds of space lattices are possible.
- Hence there are fourteen different ways of arrangement of the lattice basis.
- These fourteen lattices of seven crystal systems are called Bravais lattices.
Question 44.
Explain Bravais lattices of a cubic system.
OR
Explain unit cells of a cubic system.
Answer:
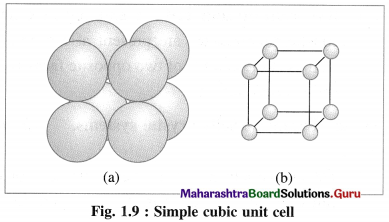
Cubic lattice : For this, edges are a = b = c and angles are α = β = γ = 90°. In this cubic system, there are three Bravais lattices.
(1) Simple (or primitive) cubic unit cell (SCC) : In this unit cell, atoms are present only at 8 corners of the cube.
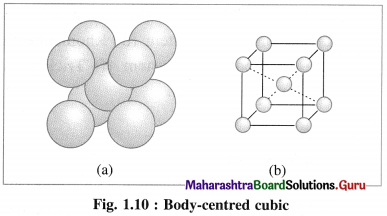
(2) Body-centred cubic unit cell (BCC) : In this, atoms are present at 8 corners along with one additional atom at the body-centre of the cube.
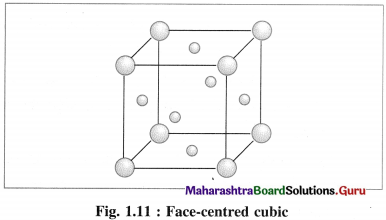
(3) Face-centred cubic unit cell (FCC) : In this unit cell, atoms are present at 8 comers and at 6 face centres.
Question 45.
Give the number of lattice points in one unit cell of the following crystal structures :
(1) Simple cubic
(2) Face-centred cubic
(3) Body-centred cubic.
Answer:
Lattice points in one unit cell represent the positions of atoms, ions or molecules in the unit cell.
(1) Simple cubic unit cell : In this primitive unit cell, the lattice points are at 8 corners of the unit cell. Hence there are 8 lattice points.
(2) Face-centred cubic unit cell : In this unit cell, the lattice points are at 8 comers and 6 face centres.
(In cubic close packing unit cell, the lattice points are also at edge centres and body centre.)
(3) Body-centred cubic unit cell : In this, the lattice points are at 8 comers and one at body centre.
Question 46.
Find the number of atoms per unit cell in the following crystal structures.
(1) Simple cubic unit cell
(2) Body-centred cubic unit cell
(3) Face-centred cubic cell.
Answer:
(1) Number of atoms in primitive simple cubic (scc) unit cell :
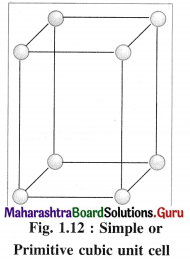
In simple or primitive cubic unit cell, there are 8 atoms at 8 corners. Each corner contributes 1/8th atom to the unit cell.
∴ Number of atoms present in the unit cell = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 = 1
Hence the volume of the unit cell is equal to the volume of one atom.
(2) Number of atoms in body-centred cubic (bcc) unit cell:
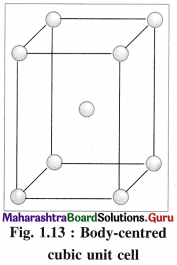
In this unit cell, there are 8 atoms at 8 corners and one additional atom at the body centre. Each corner contributes 1/8th atom, to the unit cell, hence due to 8 corners.
Number of atoms = 8 × \(\frac {1}{8}\)
= 1 atom.
An atom at the body centre wholly belongs to the unit cell.
∴ Total number of atoms present in bcc unit cell = 1 + 1 = 2.
Hence the volume of unit cell is equal to the volume of two atoms.
(3) Number of atoms in face-centred cubic (fcc) unit cell :
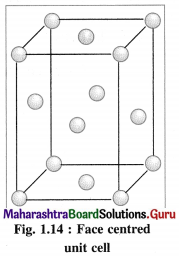
In this unit cell, there are 8 atoms at 8 comers and 6 atoms at 6 face centres. Each corner contributes 1/8th atom to the unit cell, hence due to 8 corners,
Number of atoms = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 = 1.
Each face centre contributes half of the atom to the unit cell, hence due to 6 face centres,
Number of atoms = \(\frac {1}{2}\) × 6 = 3.
∴ Total number of atoms present in fee unit cell = 1 + 3 = 4.
Hence the volume of the unit cell is equal to the volume of four atoms.
![]()
Question 47.
Obtain a relation for the density of the unit cell and radius of atom or sphere for the following :
(1) Simple cubic (scc) crystal
(2) Body centred cubic (bcc) crystal
(3) Face centred cubic (fcc) crystal.
Answer:
(1) Consider a unit cell of a simple cubic crystal. It has 8 atoms at 8 corners of the unit cell.
∴ Total number of atoms in unit cell = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 = 1
If a is the length of edge of cubic unit cell and r is the radius of the atom, then r = a/2 or a = 2r.
Volume of the unit cell = a3 = (2r)3 = 8r3
If M is atomic mass of the element, then mass of one atom is M/NA where NA is Avogadro number. If there are V atoms in one unit cell then,
Mass of unit cell = n × Mass of one atom = n × \(\frac{M}{N_{\mathrm{A}}}\)
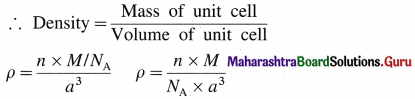
Since there is one atom present in one unit cell,
ρ = \(\frac{M}{N_{\mathrm{A}} \times a^{3}}\)
(2) Consider a unit cell of body centred cubic (bcc) crystal. It has 8 atoms at 8 comers and one additional atom at the centre of body of unit cell.
Number of atoms due to 8 corners = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 = 1
Body centred atom, wholly belong to the unit cell. Hence total number of atoms in the unit cell is two. If M is atomic mass of an element then M/NA is mass of one atom where NA is Avogadro number.
Mass of unit cell = Mass of 2 atoms in unit cell = 2 M/NA
If a is the edge length or lattice parameter then,
Volume of cubic unit cell = a3
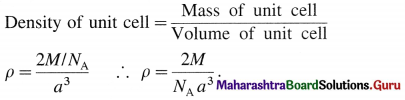
(3) Consider a unit cell of face centred cubic (fcc) crystal.
It has 8 atoms at 8 comers and 6 atoms at 6 face centres.
∴ Total number of atoms in unit cell = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 + \(\frac {1}{2}\) × 6 = 1 + 3= 4
If M is the atomic mass of an element, then mass of one atom is M/NA, where NA is Avogadro number. Mass of unit cell = Mass of 4 atoms
= \(4 \times \frac{M}{N_{\mathrm{A}}}\)
If a is the edge length of this cubic unit cell then,
volume of unit cell = a3

Question 48.
What is coordination number? What is its significance?
Answer:
(1) Coordination number : The number of the closest neighbouring constituent particles like atoms, ions or molecules which are in contact with a particular particle or an atom in the crystal lattice is called coordination number of that particle.
(In the crystal lattice, all atoms may have same or different coordination numbers.)
(2) The magnitude of the coordination number is a measure of compactness of spheres in close-packed structures.
(3) The higher the coordination number, the closer are the spheres to each other.
Question 49.
Explain linear packing in one direction.
OR
Explain close packing in one dimension.
Answer:
Linear packing in one direction or close packing in one dimension :
The constituent particles of the crystal may be of varying shapes but for better understanding we consider particles as hard spheres of equal size.
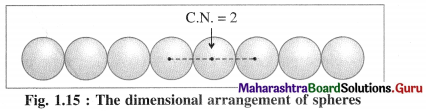
There is only one way of arranging or packing spheres placed in a horizontal row touching one another. Since one sphere is in contact with two neighbouring spheres except the end atoms, the coordination number in this arrangement is two. This packing may be in any one direction x, y or z.
Question 50.
Explain the following :
Planar packing arrangement of spheres.
OR
Close packing in two dimensions.
OR
AAAA type and ABAB type of two dimensional arrangement.
OR
(i) Square close packing
(ii) Hexagonal close packing.
Answer:
Two dimensional close packing crystal structure can be generated by placing one dimensional linear crystal structure over another to form multiple layers. This staking of linear rows may be taking place in two different ways giving two different two dimensional structures as follows :
(i) AAAA type two dimensional close packing or square close packing :
In this arrangement, various one dimensional rows are placed on one over other so that each sphere in one row is over the another sphere of another row forming planar structure. In this, spheres have horizontal as well as vertical alignment. All the rows of spheres are identical in planar structure. All crests as well as all the depressions or troughs formed by the arrangement are also aligned.
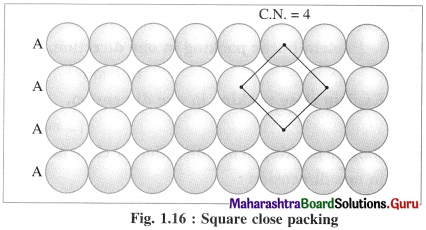
If the first row is labelled as A type, then second and all subsequent rows are also identical, hence are of A type. Therefore this planar two dimensional close packing is called AAAA type packing.
In this arrangement, each sphere is in contact with (or touching) four other spheres around it, hence the coordination number of each sphere is four and the packing is called two dimensional or planar square close packing. In this, packing efficiency is 52.4%.
(ii) ABAB type two dimensional packing or hexag-onal close packing :
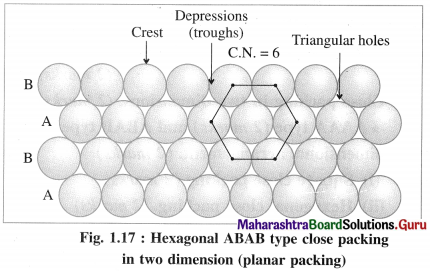
In this arrangement, crests of the spheres of one row are placed into the depressions or troughs formed between adjacent spheres of next row. This arrangement is repeated consecutively throughout.
In this arrangement, crests of the spheres of one row are in contact with depressions or troughs of next row.
If one row of spheres is labelled as A then the next row will be B, third row will again be A, fourth row B and so on. Hence this planar or two dimensional close packing is called ABAB… type packing.
In this arrangement, each sphere is in contact with six other spheres around it hence the coordination number of each sphere is six and the packing is called two dimensional or planar hexagonal close packing. In this, the packing efficiency is 60.4% which is more than linear close packing.
Question 51.
Explain close packing in three dimensions.
Answer:
Close packing in three dimensions :
Three dimensional crystal structures are obtained by stacking of two dimensional layers. Simple cubic lattice is obtained by stacking of two dimensional square layers.
The stacking of two dimensional hexagonal close packed layers gives two structures namely hexagonal close packed (hcp) structure and face centred (fcc) structure.
(i) Stacking of square close packed layers :
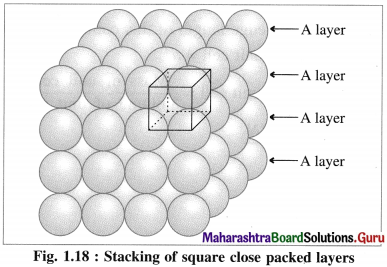
In this arrangement, the two dimensional AAAA type square closed packed layers are placed one over the other in such a way that the crests of all spheres are in contact with successive layers in all directions. All spheres of different layers are perfectly aligned horizontally and vertically forming unit cells having primitive or simple cubic structure. Since all the layers are identical and if each layer is labelled as layer A, then whole three dimensional crystal lattice will be of AAAA… type.
Each sphere is in contact with six surrounded spheres, hence the co-ordination number of each sphere is six.
(ii) Stacking of two hexagonal close packed layers :
A close packed three dimensional structure can be generated by arranging hexagonal close packed layers in a particular manner.
In this the spheres of second layer are placed in the depression of the first layer.
In this if first layer is labelled as A then second layer is labelled as B since they are aligned differently.
In this, all triangular voids of the first layers are not covered by the spheres of the second layer. The triangular voids which are covered by second layer spheres generate tetrahedral void which is surrounded by four spheres. The triangular voids in one layer have above them triangular voids of successive layers.
The overlapping triangular voids from two layers together form an octahedral void which is surrounded by six spheres.
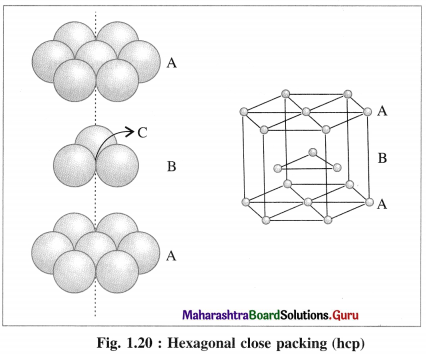
(iii) Placing third hexagonal close packed layer :
(a) Hexagonal close packing (hcp) : If the crests of spheres of third layer are placed on the triangular shaped tetrahedral voids C of the second layer, then three dimensional closest packing structure is obtained in which the spheres of third layer lie directly above the spheres of first layer, i.e., first and third layers are identical. Following same placing of layers, fourth layer will be identical to second layer.
If the first layer is labelled A and second layer B, then the arrangement of packing will be of ABAB type. This is also called hexagonal close packing (hcp) as shown in the figure. In this, packing efficiency is 74%. The coordination number of each sphere is 12. The metals Be. Mg, Zn, Cd crystallise in HCP crystalline structure.
(b) Cubic close packing (ccp) : If the crests of spheres of third layer are placed in the positions of tetrahedral void ‘a’ having apex upward of first layers, then the third layer will not be identical to the first, and may be labelled as C, which is different from A and B layers. Fourth layer may be arranged above third layer such that the spheres are aligned, so that the first layer and fourth layer are identical, second and fifth layers are identical and so on.
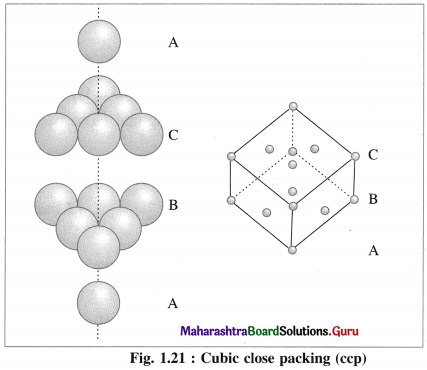
If first, second and third layers are labelled as A, B and C respectively then the arrangement of packing will be ABCABC type. This is also called cubic close packing (ccp) as shown in the figure. This is similar to face centred cubic (fcc) packing.
In this, arrangement packing efficiency is 74% and the coordination number of each sphere is 12.
![]()
Question 52.
Explain tetrahedral void.
Answer:
(1) Tetrahedral void : The vacant space or void among four constituent particles having tetrahedral arrangement in the crystal lattice is called tetrahedral void.
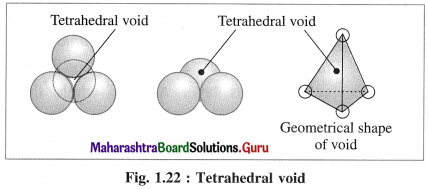
The arrangement of four spheres around the void is tetrahedral. A tetrahedral void is formed when a triangular void made by three coplanar spheres is in contact with fourth sphere above or below it.
(2) Characteristics of tetrahedral void :
- The volume of the void is much smaller than that of atom or sphere.
- Larger the size of sphere, more is the size of void.
- If R is the radius of the constituent atom, then the radius of the tetrahedral void is 0.225 R.
- Coordination number of tetrahedral void is four.
- There are two tetrahedral voids per sphere, in the crystal lattice. If the number of closed packed spheres is N then the number of tetrahedral voids is 2N.
Question 53.
Explain octahedral void.
Answer:
(1) Octahedral void : The vacant space or void at the centre of six spheres (or atoms) which are placed octahedrally is called octahedral void.
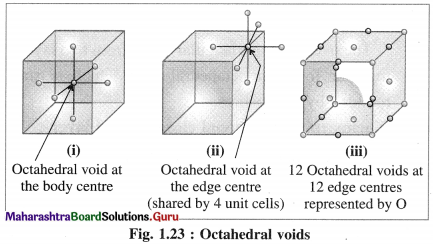
(2) Characteristics of octahedral void :
- The volume of the void is small.
- There is one octahedral void at the body centre and twelve octahedral void positions at twelve edge centres.
- If R is the radius of constituent atom, then the radius of the octahedral void is 0.414 R.
- The coordination number of octahedral void is six.
- There is one octahedral void per sphere in the crystal lattice. If the number of closed packed spheres is N then the number of octahedral voids is N.
Question 54.
What are number of voids per atom in hep and ccp ?
Answer:
The tetrahedral and octahedral voids occur in hep and ccp/fcc structures. There are two tetrahedral voids associated with each atom. The number of octahedral voids is half that of tetrahedral voids. Thus, there is one octahedral void per atom.
Question 55.
What is packing efficiency?
Answer:
(1) Packing efficiency : It is the fraction of a percentage of the total space (of the unit cell) occupied by the particles (spheres).

( 2) The magnitude of packing efficiency gives a measure of how tightly particles are packed together.
Question 56.
Calculate packing efficiency in body-centred cubic lattice.
Answer:
Step 1 : Radius of sphere :
In the unit cell of body-centred cubic lattice, there are 8 atoms at 8 corners and one atom at the centre of the cube.
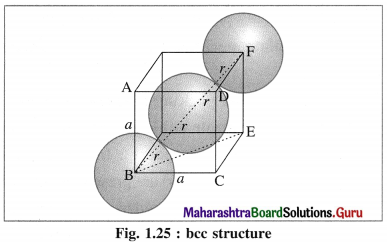
The atoms are in contact along the body diagonal BF. Let a be the edge length and r the radius of an atom.
Consider a triangle BCE.
BE2 = BC2 + CE2 = a2 + a2 = 2a2
Consider triangle BEF,
BF2 = BE2 + EF2 = 2a2 + a2 = 3a2
BF = \(\sqrt{3}\)a.
From figure, BF = 4r
∴ 4r = \(\sqrt{3}\)a
∴ r = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a\)
Step 2 : Volume of sphere :
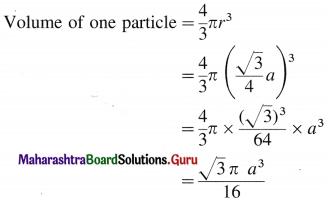
Step 3 : Total volume of particles :
The unit cell of bcc structure contains 2 particles.

Step 4 : Packing efficiency
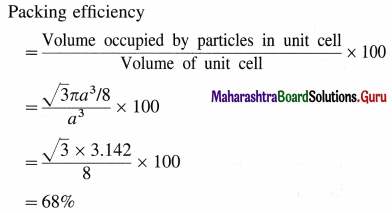
∴ Packing efficiency = 68%
∴ Percentage of void space = 100 – 68
= 32%
![]()
Question 57.
Calculate packing efficiency in face-centred cubic lattice.
Answer:
Step 1 : Radius of sphere :
In the unit cell of face-centred cubic lattice, there 8 atoms at 8 corners and 6 atoms at 6 face centres. Consider the face ABCD.
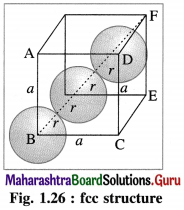
The atoms are in contact along the face diagonal BD.
Let a be the edge length and r, the radius of an atom.
Consider a triangle BCD.
BD2 = BC2 + CD2
= a2 + a2 = 2a
∴ BD = \(\sqrt{2} a\)
From figure, BD = 4r

Step 3 : Total volume of particles :
The unit cell of fee crystal lattice contains 4 particles.
∴ Volume occupied by 4 particles = \(4 \times \frac{\pi a^{3}}{12 \sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\frac{\pi a^{3}}{3 \sqrt{2}}\)
Step 4 : Packing efficiency :

∴ Packing efficiency = 74%
∴ Percentage of void space = 100 – 74
= 26%
Edge length and particle parameters in cubic system
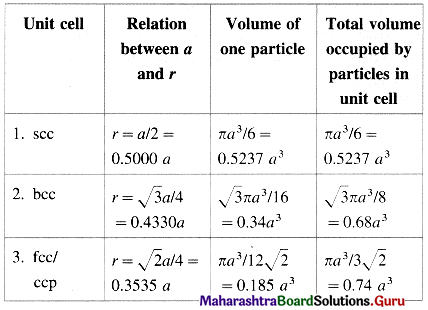
Coordination number and packing efficiency in systems
| Lattice | Coordination number of atoms | Packing efficiency |
| 1. scc | 6 : four in the same layer, one directly above and one directly below | 52.4% |
| 2. bcc | 8 : four in the layer below and four in the layer above | 68% |
| 3. fcc/ccp/hcp | 12 : six in its own layer, three above and three below | 74% |
Question 58.
Calculate the number of particles and unit cells in ‘x’ g of metallic crystal.
Answer:
Consider ‘x’ gram of a metallic crystal of molar mass M and density ρ. If the unit cell of the crystal has edge length ‘a’ then, volume of unit cell = a3.
Mass of one metal atom = \(\frac{M}{N_{\mathrm{A}}}\). If ‘n’ number of atoms are present in one unit cell then
Mass of unit cell = \(\frac{n \times M}{N_{\mathrm{A}}}\)
If ‘a’ is the edge length of the unit cell then, Volume of unit cell = a3
Density of unit cell = ρ = \(\frac{n \times M}{N_{\mathrm{A}}} \times \frac{1}{a^{3}}\)
∴ M = \(\frac{\rho \times N_{\mathrm{A}} \times a^{3}}{n}\)
∵ Molar mass M gram contains NA particles
∴ x gram contains \(\frac{x \times N_{\mathrm{A}}}{M}\) particles.
Substituting the value M,
(i) Number of particles in x g crystal
= \(\frac{x \times N_{\mathrm{A}}}{\rho \times N_{\mathrm{A}} \times a^{3} / n}\)
= \(\frac{x \times n}{\rho \times a^{3}}\) particles
(ii) Number of unit cells in x g crystal :
∵ n particles are present in 1 unit cell
∴ \(\frac{x \times n}{\rho \times a^{3}}\) are present in, \(\frac{x \times n}{\rho \times a^{3}} \times \frac{1}{n}\)
= \(\frac{x}{\rho \times a^{3}}\) unit cells
(iii) Number of unit cells in V volume of crystal = \(\frac{V}{a^{3}}\)
Alternative method :
Consider ‘x’ g metal of atomic mass M g mol-1.
Number of moles of metal = \(\frac{x}{M}\)
(a) Number of atoms (particles) of metal = \(\frac{x}{M} \times N_{\mathrm{A}}\)
(b) If unit cell contains ‘n’ atoms,
Number of unit cells = \(\frac{x}{M} \times \frac{N_{\mathrm{A}}}{n}\)
(c) If ‘a’ is the edge length then,
Volume of unit cells = a3
∴ Number of unit cells in V volume of crystal = \(\frac{V}{a^{3}}\).
![]()
Solved Examples 1.5 – 4.7
Question 59.
Solve the following :
[1 m = 10 dm = 100 cm = 109 nm = 1012 pm, 1Å = 10-8 cm = 100 pm]
(1) A cubic unit cell of a crystal consists of atoms of A and B elements. Atoms of A occupy corners of the unit cell while one B atom is present at the body centre. Determine the formula of the crystalline compound.
Solution :
Given : Atoms of A are at the comers while atom B is at the body centre of the cubic unit cell.
Since \(\frac {1}{8}\)th atom is contributed at each comer and there are 8 comers in unit cell, number of atoms of A due to comers is \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 = 1.
In addition there is one atom of B at body centre. Hence this unit cell contains one atom of each, A and B, therefore the formula of the compound is AB.
Ans. The formula of the compound = AB.
(2) Atoms C and D form fee crystalline structure. Atom C is present at the corners of the cube and D is at the face centres of the cube. What is the formula of the compound ?
Solution :
Given : Crystal has fee structure.
Atoms C are at 8 comers while atoms D are at 6 face centres of the cubic unit cell.
At the comer, \(\frac {1}{8}\)th of each C atom is present while at each face centre, half of each D atom is present.
Number of C atoms = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 = 1.
Number of D atoms = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 6 = 3.
Thus unit cell contains one C atom and three D atoms.
Hence the formula of the compound is CD3.
Ans. Formula of the compound = CD3.
(3) A cubic unit cell contains atoms A at the corners, atoms B at face centres and atom C at the body centre. What is the formula of the crystalline compound?
Solution :
Given : Atoms A are at 8 comers, atoms B at the 6 face centres and one atom C at body centre.
Total number of atoms of A = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 = 1.
Total number of atoms of B = \(\frac {1}{2}\) × 6 = 3.
One atom of C at the body centre.
Therefore the unit cell contains one atom of A, three atoms of B and one atom of C.
Hence the formula of the compound is AB3C.
Ans. The formula of the crystalline compound is AB3C.
(4) An element A and B constitute bcc type crystalline structure. Element A occupies body centre position and B is at the corners of cube. What is the formula of the compound? What are the coordination numbers of A and B ?
Solution :
Given : Crystalline structure is bcc type.
Atoms A are at 8 comers and atom B is at body centre.
∴ Number of atoms of A in a unit cell
= \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 = 1.
Number of atom B in a unit cell = 1.
Since unit cell contains one atom each of A and B, the formula of the compound is AB.
The coordination number of an atom A at comer is 8.
The coordination number of an atom B at body centre is 8.
Answer. Formula of the compound = AB.
Coordination number of A = 8
Coordination number of B = 8.
(5) Mention the number of atoms in the following unit cells :
(a) scc (b) bcc (c) fcc (d) hcp.
Answer:
| Unit cell | Number of atoms |
| (a) scc | 1 |
| (b) bcc | 2 |
| (c) fcc | 4 |
| (d) hcp | 3 |
(6) 0.1 mole of Buckminster fullerene of molar mass 720 gmol-1 contains how many Kg of carbon ?
Solution :
Molar mass of fullerene, C60 = 720 gmol-1
∵ Mass of 1 mole of fullerene = 720 g = 0.72 kg
∴ Mass of 0.1 mole of fullerene = 0.72 × 0.1
= 0.072 kg
Ans. 0.072 kg.
![]()
(7) In a cubic crystalline structure of zinc blende (ZnS), sulphide ions are at corners and face centres while zinc ions occupy half of tetrahedral voids.
Find in the unit cell :
(i) Number of Zn2+ ions
(ii) Number of S2- ions
(iii) Number of ZnS molecules
(iv) Molecular formula of zinc blende.
Solution :
Given : S2- ions are at 8 comers and 6 face centres.
Zn2+ ions occupy half of tetrahedral voids.
Number of S2- ions in unit cell

= 1 + 3 = 4
Cubic unit cell has 8 tetrahedral voids. Since half of them are occupied by Zn2+ ions, there are 4Zn2+ ions in the unit cell.
Hence number of zinc sulphide (ZnS) molecules is 4.
Molecular formula of zinc blende is ZnS.
Ans. (i) Number of Zn2+ ions = 4
(ii) Number of S2- ions = 4
(iii) Number of ZnS molecules = 4
(iv) Molecular formula of zinc blende = ZnS.
(8) In a crystalline compound, atoms A occupy ccp lattices while atoms B occupy 2/3 rd tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound ?
Solution :
In ccp unit, lattice points are 8 comers and 6 face centres where atoms A are present.
∴ Number of A atoms
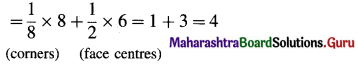
In cubic unit cell, there are 8 tetrahedral voids.
Hence,
Number of B atoms = \(\frac {2}{3}\) × 8 = \(\frac {16}{3}\).
Hence the formula should be A4B16/3 or A12B16 or A3B4.
Ans. The formula of the compound is A3B4.
(9) A compound forms hep structure. What is the number of (a) octahedral voids, (b) tetrahedral voids, (c) total voids formed in 0.2 mol of the compound?
Solution :
Number of atoms in 0.2 mol of the compound
= 0.2 × NA = 0.2 × 6.022 × 1023
= 1.2044 × 1023 atoms
(a) Number of octahedral voids
= Number of atoms
= 1.2044 × 1023
(b) Number of tetrahedral voids
= 2 × Number of atoms
= 2 × 1.2044 × 1023
= 2.4088 × 1023
(c) Total number of voids
= 1.2044 × 1023 + 2.4088 × 1023
= 3.6132 × 1023
Ans. (a) Number of octahedral voids
= 1.2044 × 1023
(b) Number of tetrahedral voids = 2.4088 × 1023
(c) Total number of voids = 3.6132 × 1023
(10) Copper crystallises into a fcc structure and the unit cell has length of edge 3.61 × 10-8 cm. Calculate the density of copper. Atomic mass of copper is 63.5 g mol-1.
Solution :
Given : Crystalline structure of Cu is fcc.
Edge length = a = 3.61 × 10-8 cm
Atomic mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1
Avogadro number = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1
Density = d = ?
In fcc structure, there are 8 Cu atoms at 8 comers and 6 Cu atoms at 6 face centres.
∴ Total number of Cu atoms
= \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 + \(\frac {1}{2}\) × 6 = 1 + 3
= 4
Mass of one Cu atom
= \(\frac{63.5}{6.022 \times 10^{23}}\) = 1.054 × 10-22 g
∴ Mass of 4 Cu atoms = 4 × 1.054 × 10-22
= 4.216 × 10-22 g
Mass of unit cell = Mass of 4 Cu atoms
= 4.216 × 10-22g
Volume of unit cell = a3 = (3.61 × 10-8)3
= 4.7 × 10-24 cm3
Density of unit cell = \(\frac{\text { Mass of unit cell }}{\text { Volume of unit cell }}\)
∴ ρ = \(\frac{4.216 \times 10^{-22}}{4.7 \times 10^{-23}}\) = 8.97 g cm-3
Ans. Density of Cu = 8.97 g cm-3.
![]()
(11) Niobium is found to crystallise with bcc structure and found to have density of 8.55 g cm-3 (OR 8.55 kg m-3). Determine the atomic radius of niobium if its atomic mass is 93.
Solution :
Given : Density of Niobium (Nb) crystal = 8.55 g cm-3
Crystalline stmeture is bcc.
Atomic mass of Nb = 93 g mol-1
Avogadro number = NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1
Atomic radius of Niobium = ?
In bcc unit cell, there are 8 atoms at 8 comers and 1 atom at the body centre.
∴ Number of Nb atoms = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2.
Mass of one Nb atom = \(\frac{93}{6.022 \times 10^{23}}\) = 1.544 × 10-22
∴ Mass of 2 Nb atoms = 2 × 1.544 × 10-22 = 3.088 × 10-22 g
Mass of unit cell
= Mass of 2Nb atoms = 3.088 × 10-22 g
If a is edge length of bcc unit cell, volume of unit cell = a3
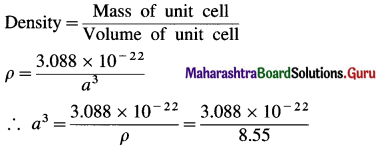
= 0.361 × 10-22 cm3 = 36.1 × 10-24 cm3
∴ a = (36.1 × 10-24)-1/3 = 3.3 × 10-8 cm
If r is the radius of 1 Nb atom, then in bcc structure
r = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\) × 3.3 × 10-8
= 1.43 × 10-8 cm
= 1.43 × 10-10 m
= 1.43 × 10-10 × 109 nm
= 0.143 nm
Ans. Atomic radius of niobium atom = 0.143 nm
(12) Gold occurs as face centred cube and has a density of 19.30 kg dm-3. Calculate atomic radius of gold. (Molar mass of Au = 197)
Solution :
Given : Density of Au = 19.3 kg dm-3
Molar mass = 197 g mol-1
Avogadro constant = NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1
Atomic radius of Au = ?
In fcc unit cell, there are 8 atoms of Au at 8 comers and 6 atoms at 6 face centres.
Number of Au atoms in the unit cell = \(\frac {1}{8}\) × 8 + \(\frac {1}{2}\) × 6
= 4 atoms
Mass of 1 Au atom = \(\frac{197}{6.022 \times 10^{23}}\) = 3.271 × 10-22 g
∴ Mass of 4 Au atoms = 4 × 3.271 × 10-22 g = 1.308 g × 10-21 g
∴ Mass of unit cell = 1.308 × 10-21 g
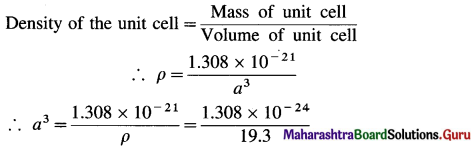
= 6.777 × 10-24 dm3
= 6.777 × 10-23 cm3
∴ a = (6.777 × 10-23)1/3 = (67.77 × 10-24)-1/3
= 4.077 × 10-8 cm
If r is the radius of Au atom, then for fcc unit cell,
r = \(\frac{a}{2 \sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\frac{4.077 \times 10^{-8}}{2 \sqrt{2}}\) = 1.442 x 10-8 cm = 144.2 pm
Ans. Radius of Au atom = 144.2 pm.
(13) A compound is formed by two elements X and Y. The atoms of Y form ccp structure. The atoms of A occupy \(\frac {1}{3}\) of tetrahedral voids. Find the formula of the compound.
Solution :
In ccp structure, Y atoms are present at 8 comers and 6 face-centres of the ccp structure.

There are 8 tetrahedral voids of which \(\frac {1}{3}\)rd are occupied by atoms X. Hence unit cell has \(\frac {8}{3}\) atoms of X and 4 atoms of Y. The formula will be,
X8/3 Y4 or X8Y12 or X2Y3
Ans. Formula of the compound = X2Y3.
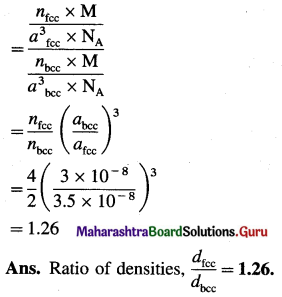
(14) A metal crystallises into two cubic faces namely face centered (FCC) and body centered (BCC), whose unit cell edge lengths are 3.5 Å and 3.0 Å respectively. Find the ratio of the densities of FCC and BCC.
Solution :
Given : Edge length of unit cell of fcc metal = 3.5 Å
= 3.5 × 10-8 cm
Edge length of unit cell of bcc metal = 3 Å = 3 × 10-8 cm
Density d = \(\frac{n \times \mathbf{M}}{a^{3} \times \mathbf{N}_{\mathrm{A}}}\)
where, n = Number of Fe atoms in the unit cell
M = Atomic mass of metal
a = Edge length of unit cell
NA = Avogadro number
∴ For fcc unit cell = n = 4
For bcc unit cell = n = 2
∴ \(\frac{\text { Density of fcc unit cell }}{\text { Density of bcc unit cell }}=\frac{d_{\mathrm{fcc}}}{d_{\mathrm{bcc}}}\)
(15) The density of silver having atomic mass 107.8 gram mol-1 is 10.8 gram cm-3. If the edge length of cubic unit cell is 4.05 × 10-8 cm, find the number of silver atoms in the unit cell. (NA = 6.022 × 1023, 1Å = 10-8 cm)
Solution :
Given : d = 10.8 g cm-3
M= 107.8 g mol-1
a = 4.05 × 10-8 cm
Number of Ag atoms in unit cell = n = ?
Mass of one Ag atom = \(\frac{107.8}{6.022 \times 10^{23}}\)
= 1.79 × 10-22 g
If there are n atoms, then
Mass of unit cell = n × 1.79 × 10-22 g
Volume of unit cell = a3 = (4.05 × 10-8)3
= 6.643 × 10-23 cm3
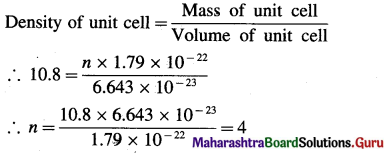
Ans. Number of silver atoms (Ag) atoms in unit cell = 4.
(16) Aluminium having atomic mass 27 g mol-1 crystallises in face centred packed cubic crystal. Find the number of Al atoms in 10 g aluminium. How many unit cells will be present in it?
Solution :
Given : Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol-1
Mass of Al = 10 g
Avogadro number = NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1
Number of Al atoms = ?
Number of unit cells = ?
1 gram atom of Al = 27 g Al contains 6.022 × 1023
Al atoms
∴ Number of Al atoms in 10 g
= \(\frac{10 \times 6.022 \times 10^{23}}{27}\)
= 2.23 × 1023
In fcc structure, each unit cell contains 4Al atoms.
∴ Number of unit cells = \(\frac{2.23 \times 10^{23}}{4}\)
= 5.575 × 1022
Ans. Number of Al atoms = 2.23 × 1023
Number of unit cells = 5.575 × 1022.
![]()
(17) The density of iron crystal is 8.54 gram cm-3. If the edge length of unit cell is 2.8 Å and atomic mass is 56 gram mol-1, find the number of atoms in the unit cell. What is the type of crystal ?
Solution :
Given :
Density of Fe crystal = d = 8.54 g cm-3
a = 2.8 Å = 2.8 × 10-8 cm
Atomic mass = M = 56 g mol-1
Number of atoms in unit cell, n = ?
Mass of one atom = \(\frac{56}{6.022 \times 10^{23}}\) = 9.3 × 10-23 g
Volume of unit cell = a3 = (2.8 × 10-8)3
= 2.195 × 10-23 cm3
If there are n atoms in the unit cell, then
Mass of unit cell = n × 9.3 × 10-23 g
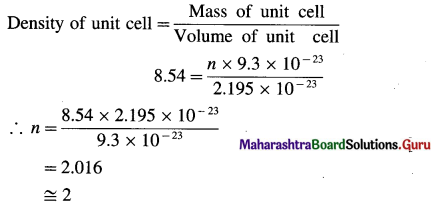
Since unit cell contains 2 atoms, the crystal has bcc structure.
Ans. Number of atoms in unit cell = 2
Type of crystal = bcc
Question 60.
What is meant by crystal defects or imperfections?
Answer:
- Defect in crystalline structure : Any deviation from orderly and stoichiometrically perfect arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in the crystal lattice is called a defect in the crystalline structure.
- Defects are created during the crystallisation process. If the process occurs at faster rate, the defects are more.
- The properties of solids are affected due to imperfactions.
Question 61.
Mention the types of defects in the solids or crystal structures.
Answer:
The defects in crystalline solids are of two types viz., (1) Point defect and (2) Line defect.
(1) Point defects are further classified as :
(a) Vacancy defect or Schottky defect
(b) Interstitial defect or Frenkel defect
(c) Impurity defect :
This is further classified as
- Substitution impurity defect
- Interstitial impurity defect.
(2) Line defects are further classified as
- Edge dislocation
- Screw dislocation.
Question 62.
What are point defects?
Answer:
Point defects : These defects arise due to irregularities produced in the arrangement of basis of lattice points in crystalline solids.
Question 63.
What are major classes of point defects ?
Answer:
There are three major classes of point defects : stoichiometric point defects, impurity defects and nonstoichiometric point defects.
There are four types of stoichiometric point defects as vacancy defect, self interstitial defect, Schottky defect and Frenkel defect.
![]()
Question 64.
Explain vacancy defect.
Answer:
Vacancy defect :
(1) During crystallisation, some of regular sites in solid remain unoccupied and the missing particle creates a vacancy defect.
(2) The defect can be developed by heating the substance.
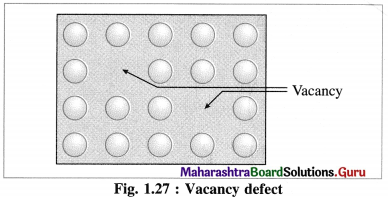
(3) The mass of solid decreases due to absence of particles in regular sites.
(4) Since the volume remains the same the density of the substance decreases.
Question 65.
Explain self interstitial defect in elemental solid.
Answer:
Self Interstitial defect in elemental solid : The empty spaces or voids in between the particles at lattice points represent interstitial defective sites or self interstitial defects.
This defect arises in the following two ways :
(1) An extra particle occupies the empty interstitial space. This extra particle is similar to those already present in the crystal.
(2) (i) A particle gets shifted from its original regular site to an empty interstitial space in the crystal.
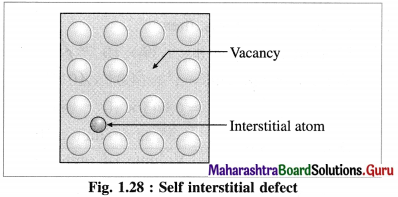
(ii) This displacement of a particle produces a vacancy defect at its regular site.
(iii) This defect is referred to as a combination of vacancy defect and self interstitial defect.
(iv) Since there is neither loss or gain in mass of the substance, the density of it remains unchanged.
Question 66.
How does Schottky defect arise?
Answer:
(1) Schottky defect arises in ionic solids due to missing of equal number of cations and anions from their regular positions in the crystal lattice creating vacancies.
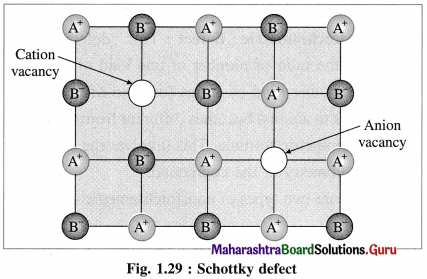
(2) There arises formation of two holes per loss of ion pair.
(3) Conditions for formation of Schottky defect :
Characteristics of ionic solids showing Schottky defect :
- High degree of ionic character
- High coordination number of anion
- Small difference between ionic size or radii of cation and anion. The ionic ratio \(\frac{r_{\text {cation }}}{r_{\text {anion }}}\) is not below unity.
Question 67.
How does Frenkel defect arise?
Answer:
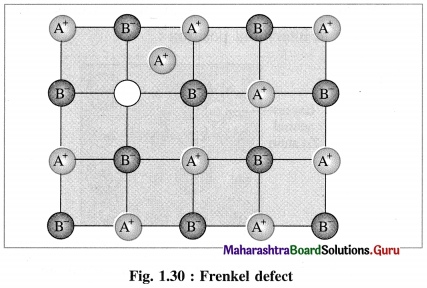
- Frenkel defect : This defect arises when an ion of an ionic compound is missing from its regular site and occupies interstitial vacant position between lattice points.
- Cations have smaller size than anions, hence generally cations occupy the interstitial sites.
- This creates a vacancy defect at its original position and interstitial defect at new position.
- Frenkel defect is regarded as the combination of interstitial defect and vacancy defect.
Conditions for the formation of Frenkel defect :
- This defect arises in ionic compounds with a large difference between the sizes of cation and anion.
- The ionic compounds must have ions with low coordination number.
Question 68.
What are the consequences of Frenkel defect ?
Answer:
Consequences of Frenkel defect :
- Since there is no loss of ions from the crystal lattice, the density of the solid remains unchanged.
- The crystal remains electrically neutral.
- This defect is observed in ZnS, AgCl, AgBr, AgI, CaF2, etc.
![]()
Question 69.
Explain nonstoichiometric defect.
Answer:
Nonstoichiometric defect : This defect arises when the ratio of number of one kind of atoms to that of other kind of atoms (or ratio of number of cations to anions) becomes different from the actual stoichiometric formula. This involves the change in stoichiometry of the compound.
There are two types of nonstoichiometric defects as follows :
(1) Metal deficiency defect : This defect arises in compounds of metal which show variable oxidation states. In some metal crystals, positive metal ions are missing from their regular lattice sites. The extra negative charge is balanced by cations of the same metal with higher oxidation state than that of missing cation at site.
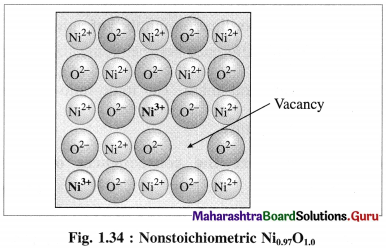
Consider a crystal of NiO. When one Ni2+ is missed from its lattice point, it creates a vacant site.
The deficiency of two positive charges is compensated by two Ni3+ ions at other lattice points of Ni2+ ions and the composition of NiO crystal becomes Ni0.97O1.0.
(2) Metal excess defect : There are two types of metal excess defect as follows :
(a) Presence of a neutral atom or an extra positive ion at interstitial position :
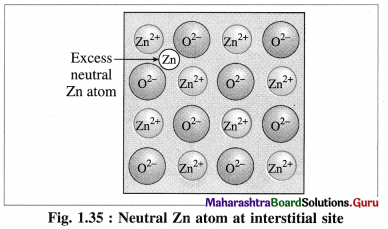
There are two types or ways of metal excess defects in ZnO. In the first case, Zn atom is present in the interstitial space as shown in figure.
(b) Metal ions and electrons at interstitial sites :
The second case arises when ZnO is heated, Zn2+ and electrons are obtained,
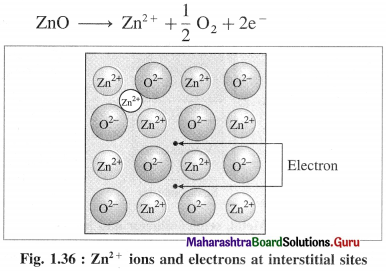
The excess Zn2+ ions are trapped in interstitial sites in the crystal lattice. Electrons occupy interstitial sites by diffusing into the interstitial sites.
In above both cases, the nonstoichiometric formula of ZnO is Zn1 + x O1.0
Question 70.
Explain defects due to anion vacancies.
OR
Explain colour of crystals or F centres.
Answer:
- The defect due to anion vacancies imparts colour to the colourless crystal.
- When a colourless crystal of NaCl is heated in the atmosphere of sodium vapour, the sodium atoms are deposited on the crystal surface.
- Due to diffusion of Cl– ions to the crystal surface vacancies are created at their regular sites.
- These diffused Cl– ions combine with Na atoms on the surface forming NaCl along with releasing electrons from sodium atoms. Na + Cl– → NaCl + e–
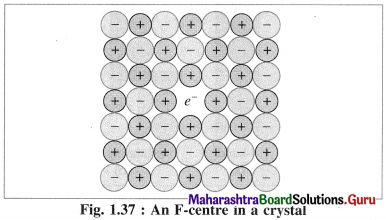
The released electrons diffuse into the crystal and occupy vacant sites of anions Cl– in the crystal.
The anion vacant sites occupied by electrons are called F-centres or colour centres. Due to colour centres NaCl shows yellow colour.
Now NaCl crystal has excess of Na atoms having nonstoichiometric formula Na1+x Cl1.0.
Question 71.
How are solids classified according to electrical conductivity?
Answer:
According to electrical conductivity, solids are classified as follows :
(1) Conductors :
- The solids having electrical conductivity in the range of 104 to 107 Ohm-1m-1 are called conductors.
- The examples of conductors are metals and electrolytes.
- Electrical conductivity in metals is due to free movement of electrons while electrolytes conduct electricity due to migration ions.
(2) Insulators :
- Solids having very low electrical conductivity in the range of 10-20 to 10-10 Ohm-1 m-1 are called insulators.
- The examples of insulators are nonmetals and molecular solids.
(3) Semiconductors :
- Solids having conductivity in the range of 10-6 to 104 Ohm-1m-1 are semiconductors.
- The conductivity range is intermediate between conductors and insulators.
- The examples of semiconductors are silicon and germanium.
Question 72.
Explain band theory.
OR
Explain the origin of electrical properties in solids.
Answer:
(1) Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. This is explained on the basis of band theory which involves the presence of free electrons.
(2) According to band theory, the atomic orbitals of metal atoms overlap to form molecular orbitals which are spread all over the crystal structure.
(3) The energy difference between adjacent molecular orbitals decreases as the number of molecular orbitals increases and when it becomes very less, the orbitals merge into one another forming continuous bands which extent over the entire crystal.
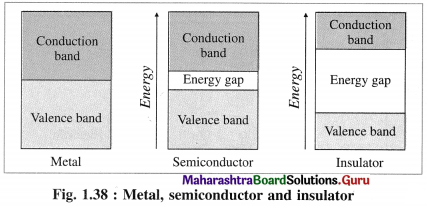
(4) There are two types of bands of molecular orbitals as follows :
- Valence band : The atomic orbitals with filled electrons from the inner shells form valence bands, where there are no free mobile electrons since they are involved in bonding.
- Conduction band : Atomic orbitals which are partially filled or empty on overlapping form closely placed molecular orbitals giving conduction bands where electrons are delocalised and can conduct, heat and electricity.
(5) Band gap :
- The energy difference between valence band and conduction band is called band gap.
- Band gap decides whether electrons from valence band can be promoted to vacant conduction band or not.
- The conductors like metals have very small or no band gap and electron can be promoted by thermal energy. The nonconductors have large band gap. The insulators have very large band gap.
![]()
Question 73.
Metals are good conductors of electricity. Explain.
Answer:
(1) Metals are good conductors of electricity since the outermost electrons of atoms in metallic crystal occupy conduction bands.
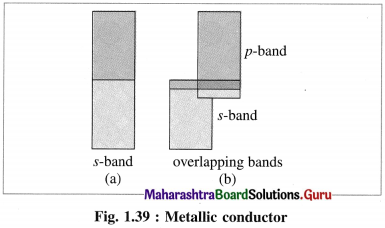
(2) The number of electrons in conduction bands is very large.
(3) The conduction bands in metals can be labelled as ‘s’ band, overlapping s and p bands etc. according to overlapping of orbitals.
(4) This results in delocalisation of outermost electrons forming metal ions. Hence, this is analogous to metal cations immersed in the sea of electrons.
Question 74.
Why does metallic conductivity decrease by increasing temperature?
Answer:
- In metals a large number of outermost electrons of atoms occupy conduction bands.
- Band formation in metals results in delocalisation of outermost electrons forming metal ions or cations.
- The metallic cations occupying crystal lattice sites vibrate about mean positions.
- As temperature increases the vibrational motion increases which interrupts flow of electrons decreasing electrical conductivity.
Question 75.
Explain insulators.
Answer:
(1) In insulators the valence band is completely filled by electronics while conduction band is empty.
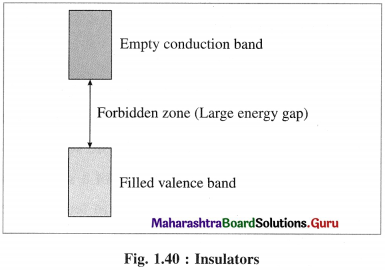
(2) The energy gap between valence band and conduction band in insulator is very large.
(3) Thermal energy is not sufficient to promote electrons from valence band to conduction band.
(4) Therefore, the conduction band in insulator remains vacant and does not allow the conduction of electricity.
Question 76.
What are semiconductors ? Mention the types of semiconductors.
Answer:
(1) Semiconductors : The substances like silicon, germanium which have poor electrical conductance at low temperature but the conductance increases with the increase in temperature are called semiconductors.
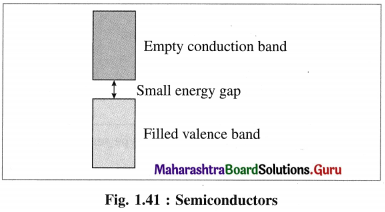
(2) Their conductivity lies between metallic conductors and insulators.
(3) The energy difference between valence band and conduction band is relatively small, hence the electrons from valence band can be excited to conduction band by heating.
(4) Types of semiconductors : There are two types of semiconductors :
(a) Intrinsic semiconductor
(b) Extrinsic semiconductor
(a) Intrinsic semiconductor :
- A pure semiconductor material like pure Si, Ge which have a very low but finite electrical conductivity is called intrinsic semiconductor.
- The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor increases with the increase in temperature.
(b) Extrinsic semiconductor :
- Semiconductor doped with different element is called extrinsic semiconductor.
- By doping with elements like Ga or P, the electrical conductivity is increased.
Question 77.
Explain extrinsic semiconductor and doping.
Answer:
(1) A semiconductor obtained by doping intrinsic semiconductor with elements of third group and fifth group is called extrinsic semiconductor.
(2) This extrinsic semiconductor has higher electrical conductivity than pure intrinsic semiconductor.
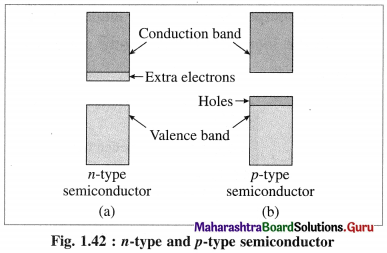
(3) There ate two types of extrinsic semiconductors:
(A) n-type semiconductors:
(i) n-type semiconductor contains increased number of electrons in the conduction band.
(ii) When Si semiconductor is doped with 15th group element phosphorus, P, the new atoms occupy some vacant sites in the lattice in place of Si atoms.
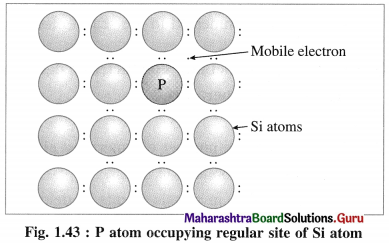
(iii) P has five valence electrons, out of which four are involved in covalent bonding with neigh-bouring Si atoms while one electrons remains free and delocalised.
(iv) These free electrons increase the electrical conductivity of the semiconductor.
(v) The semiconductors with extra non-bonding free electrons are called n-type semiconductors.
(B) p-type semiconductor :
(i) p-type semiconductor is obtained by doping a pure semiconductor by an element of 13th group like B.
(ii) 13th group element has less number of valence electrons. When pure Si is doped with B atoms, these atoms occupy Si lattice points.
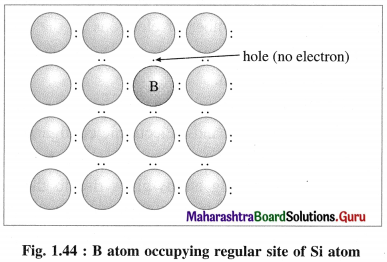
(iii) Boron (5B) has only 3 valence electrons which form covalent bonds with the neighbouring Si atoms, while one bond has shortage of one electron.
(iv) This creates a vacancy or a hole, hence the electron from neighbouring Si atom jumps into this hole creating a vacancy in itself. This process continues, i.e., positive holes move in one direction while electrons moves in opposite direction.
(v) Due to electron deficient positions, this semiconductor is called p-type semiconductor.
(vi) When p-type semiconductor is connected to the external source of electricity, electrons from neighbouring silicon atoms jump into the holes so that electrons move towards positive electrode and holes migrate towards negative electrode.
(vii) Hence electrical conduction in p-type semiconductor is due to electrons and holes.
![]()
Question 78.
What are the uses of semiconductors ?
Answer:
The uses of semiconductors are as follows :
- They are used in transistors, digital computers and cameras.
- They are used in solar cells and television sets.
- By combining n-type and p-type semiconductors, n-p junctions are formed which are effectively used in rectifiers or to convert light energy into electrical energy.
Question 79.
Classify the following semiconductors into n or p-type.
(i) B doped with Si
(ii) As doped with Si
(iii) P doped with Si
(vi) Ge doped with In.
Answer:
| Semiconductor | Type |
| (i) B doped with Si | p-type |
| (ii) As doped with Si | n-type |
| (iii) P doped with Si | n-type |
| (iv) Ge doped with In | p-type |
Question 80.
Explain the origin of magnetic properties in solids.
Answer:
(1) The magnetic properties of a substance arise due to the presence of electrons in their atoms or molecules.
(2) The electrons while revolving around the nucleus in various orbits, also spin around their own axes. Both these motions of electrons result in generating magnetic field and magnetic moments. Hence electron be haves as a tiny magnet.
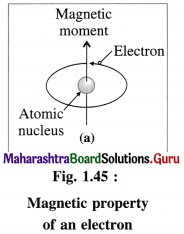
(3) An atomic orbital can accommodate maximum two electrons with opposite spins, clockwise and anticlockwise. The degenerate orbitals like p, d and f orbitals can accommodate electrons with same spins until they are half filled.
(4) When a substance contains one or more unpaired electrons spinning in same direction, then their magnetic moments and magnetic properties add and the substance is said to be paramagnetic.

If a substance contains all electrons paired then their spins are balanced and magnetic moments and magnetic properties are cancelled and the substance is said to be diamagnetic.
Question 81.
Explain diamagnetism.
Answer:
(1) The magnetic properties of a substance arise due to presence of the electrons.
(2) An electron while revolving around the nucleus, also spins around its own axis and generates a magnetic moment and a magnetic property.
(3) If an atom or a molecule of the substance contains all electrons paired, spinning clockwise and anticlockwise, their magnetic moments and magnetic properties get cancelled. Hence they oppose and repel the applied magnetic field. This phenomenon is called diamagnetism and the substance is said to be diamagnetic.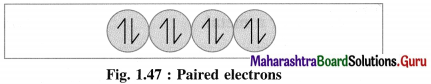
For example : Zn, Cd, H2O, NaCl, etc.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 82.
Select and write the most appropriate answer from the given alternatives for each subquestion :
1. A substance which on cutting will give irregular cleavage is
(a) glass
(b) KBr
(c) ZnS
(d) NaCl
Answer:
(a) glass
2. A solid which has definite heat of fusion is
(a) plastic
(b) CaCl2
(c) glass
(d) soda lime glass
Answer:
(b) CaCl2
![]()
3. In solids the constituent particles may be
(a) atoms
(b) ions
(c) molecules
(d) any one of the above three
Answer:
(d) any one of the above three
4. A single substance that exists in two or more forms is called
(a) polymorphous
(b) amorphous
(c) isomorphous
(d) monomorphous
Answer:
(a) polymorphous
5. Graphite is a
(a) metallic crystal
(b) covalent crystal
(c) ionic crystal
(d) molecular crystal
Answer:
(b) covalent crystal
6. Anisotropy is observed in
(a) Pyrex glass
(b) plastic
(c) K2SO4
(d) fullerene
Answer:
(c) K2SO4
7. The number of crystal systems (or types) is
(a) 4
(b) 7
(c) 8
(d) 12
Answer:
(b) 7
8. The number of Bravais lattices are
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 12
(d) 14
Answer:
(d) 14
9. Face centred cubic crystal is
(a) Cubic lattice of Bravais system
(b) Bravais lattice of HCP
(c) Bravais lattice of cubic system
(d) Cubic lattice with 5 atoms
Answer:
(c) Bravais lattice of cubic system
![]()
10. The number of tetrahedral sites per sphere in ccp structure is,
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
11. The packing fraction for a body centred cubic structure is
(a) 0.42
(b) 0.53
(c) 0.68
(d) 0.82
Answer:
(c) 0.68
12. If r is the radius of an atom and a is an edge length of fcc unit cell, then
(a) r = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a\)
(b) r = \(\frac{a}{2 \sqrt{2}}\)
(c) r = \(\frac{a}{2}\)
(d) r = \(2 \sqrt{2} a\)
Answer:
(b) r = \(\frac{a}{2 \sqrt{2}}\)
13. The ratio of packing efficiency in see, bcc and fee crystalline structures is
(a) 1 : 1.2 : 1.3
(b) 1 : 1.12 : 1.23
(c) 1 : 1.3 : 1.4
(d) 1 : 1.25 : 1.38
Answer:
(c) 1 : 1.3 : 1.4
14. The correct sequence of the atomic layers in cubic close packing is
(a) ABABA
(b) ABACABAC
(c) ABCABC
(d) AABBAABB
Answer:
(c) ABCABC
15. The major binding force in diamond is
(a) Covalent bond
(b) Ionic bond
(c) Metallic bond
(d) Coordinate covalent bond
Answer:
(a) Covalent bond
16. The ratio of close packed atoms to octahedral holes in cubic packing is
(a) 1 : 1
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 1 : 3
Answer:
(a) 1 : 1
![]()
17. A defect present in AgCl is
(a) Frenkel defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) point defect
(d) interstitial impurity defect
Answer:
(a) Frenkel defect
18. An ionic solid crystallises in bcc structure. If the ionic radii of cation and anion are 0.84 Å and 1.07 Å, the length of the body diagonal is
(a) 1.91 Å
(b) 2.75 Å
(c) 3.82 Å
(d) 2.32 Å
Answer:
(c) 3.82 Å
19. The type of defect in NaCl crystal will be
(a) point defect
(b) interstitial defect
(c) vacancy defect
(d) impurity defect
Answer:
(c) vacancy defect
20. Schottky defects are observed in which solid among the following ?
(a) Brass
(b) Cesium chloride
(c) Zinc sulphide
(d) Stainless steel
Answer:
(b) Cesium chloride
21. An ionic compound crystallises in FCC type structure with ‘A’ ions at the centre of each face and ‘B’ ions occupying comers of the cube. The formula of compound is
(a) AB4
(b) A3B
(c) AB
(d) AB3
Answer:
(b) A3B
22. Total number of different primitive unit cells are
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 12
(d) 14.
Answer:
(d) 14
23. The volume of atoms present in body centred cubic unit cell of a metal of atomic radius r is,
(a) \(\frac{16}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
(b) \(\frac{8}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
(c) \(\frac{12}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
(d) \(\frac{24}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{8}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
24. The substances which can be permanently magnetised are
(a) diamagnetic
(b) paramagnetic
(c) ferromagnetic
(d) non-magnetic
Answer:
(c) ferromagnetic
25. CrO2 is
(a) diamagnetic
(b) paramagnetic
(c) metalic
(d) ferromagnetic
Answer:
(d) ferromagnetic
![]()
26. A metallic element crystallises in face centred cubic structure. If the radius of metal ion is 0.92 Å, the edge length of the unit cell of the crystal is
(a) 0.8464 Å
(b) 1.252 Å
(c) 5.187 Å
(d) 2.6 Å
Answer:
(d) 2.6 Å
27. The volume of unit cell of a metallic crystal of bcc type is 8.4 × 10-23 cm3. The volume occupied by 10 atoms in the crystalline structure is
(a) 4.2 × 10-22 cm3
(b) 3.12 × 10-23 cm3
(c) 1.74 × 10-23 cm3
(d) 2.856 × 10-22 cm3
Answer:
(d) 2.856 × 10-22 cm3
28. Copper crystallises in face centred cubic structure. If the unit cell length is 360 pm, the radius of copper atom is
(a) 180 pm
(b) 156 pm
(c) 127 pm
(d) 110 pm
Answer:
(c) 127 pm
29. If all the lattice points in ccp structure namely comers, face and edge centres and body centre are occupied by atoms then the total number of atoms in the unit cell will be
(a) 8
(b) 12
(c) 14
(d) 16
Answer:
(a) 8
30. Gold crystallises in face centred cubic structure. If atomic mass of gold is 197 g mol-1, the mass of the unit cell of gold will be
(a) 3.25 × 10-23 kg
(b) 6.5 × 10-23 kg
(c) 3.9 × 10-24 kg
(d) 1.3 × 10-24 kg
Answer:
(d) 1.3 × 10-24 kg
31. The mass of a unit cell of a body centred cubic crystal of a metal is 72.2 × 10-23 g. The atomic mass of the metal is
(a) 128.6 gmol-1
(b) 108.7 gmol-1
(c) 217.3 gmol-1
(d) 57.86 gmol-1
Answer:
(c) 217.3 gmol-1
32. An element crystallises in fee structure. If the atomic mass of the element is 72.7 U, the mass of one unit cell of it will be
(a) 2.9 × 10-24 g
(b) 4.83 × 10-25 kg
(c) 1.2 × 10-22 g
(d) 2.41 × 10-24 kg
Answer:
(b) 4.83 × 10-25 kg
![]()
33. Edge length of a cubic unit cell is 354 pm. The distance between two atoms diagonally opposite on the face is
(a) 500 pm
(b) 354 pm
(c) 708 pm
(d) 627 pm
Answer:
(a) 500 pm
34. The unit cell has an edge length 403 pm. The distance between two atoms placed opposite ends of body diagonal will be
(a) 806 pm
(b) 201.5 pm
(c) 698 pm
(d) 578 pm
Answer:
(c) 698 pm
35. An element having atomic mass 115 u, crystallises in bcc structure. The number of unit cells in 1 g of the element will be
(a) 2.6 × 1021
(b) 3.8 × 1023
(c) 8.7 × 10-3
(d) 6.17 × 1020
Answer:
(a) 2.6 × 1021
36. The edge length of a bcc unit cell of a metallic crystal is 2.9 Å. Hence the diameter of an atom is
(a) 1.025 Å
(b) 2.512 Å
(c) 1.45 Å
(d) 1.31 Å
Answer:
(b) 2.512 Å
37. An element crystallises in fee structure. If the atomic radius is 130 pm, the edge length of unit cell is
(a) 332.5 pm
(b) 410 pm
(c) 390 pm
(d) 367.6 pm
Answer:
(d) 367.6 pm
38. The arrangement of layers in hexagonal close packing is
(a) ABCABC
(b) ABAB
(c) ABBABBA
(d) ABBCABBC
Answer:
(b) ABAB
39. For square close packing, the planar arrangement is
(a) AAAA
(b) ABAB
(c) ABCABC
(d) AABBAA
Answer:
(a) AAAA
![]()
40. Semiconductors are manufactured by addition of impurities of
(a) p-block elements
(b) actinoids
(c) Lanthanoids
(d) s-block elements
Answer:
(a) p-block elements
41. p-type semiconductor is formed when trace amount of impurity is added to silicon. The number of valence electrons in the impurity atom must be
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 1
(d) 2
Answer:
(a) 3
42. n-type semiconductor is formed when trace amount of impurity is added to silicon. The number of valence electrons in the impurity atom must be
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 1
(d) 2
Answer:
(b) 5