Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Textbook Solutions Chapter 15 Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Solutions Chapter 15 Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues
1. Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
Observe the graph and select the correct option.
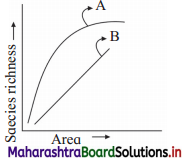
(a) Line A represents, S = CA²
(b) Line B represents, log C = log A + Z log S
(c) Line A represents, S = CAZ
(d) Line B represents, log S = log Z + C log A
Answer:
(c) Line A represents, S = CAZ
![]()
Question 2.
Select odd one out on the basis of Ex situ conservation.
(a) Zoological park
(b) Tissue culture
(c) Sacred groves
(d) Cryopreservation
Answer:
(a) Zoological park
Question 3.
Which of the following factors will favour species diversity?
(a) Invasive species
(b) Glaciation
(c) Forest canopy
(d) Co-extinction
Answer:
(a) Invasive species
Question 4.
The term “terror of Bengal’ is used for
(a) algal bloom
(b) water hyacinth
(c) increased BOD
(d) eutrophication
Answer:
(b) water hyacinth
Question 5.
CFC are air polluting agents which are produced by
(a) Diesel trucks
(b) Jet planes
(c) Rice fields
(d) Industries
Answer:
(b) Jet planes
2. Very short answer type questions.
Question 1.
Give two examples of biodegradable materials released from sugar industry.
Answer:
- Molasses
- Bagasse.
Question 2.
Name any two modern techniques of protection of endangered species.
OR
Two modern methods of ex-situ conservation of species
Answer:
- Tissue culture
- In vitro fertilization of eggs
- Cryopreservation.
Question 3.
Where was ozone hole discovered?
Answer:
Ozone hole was discovered in Antarctica.
Question 4.
Give one example of natural pollutant.
Answer:
Volcanic ash is a natural pollutant.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you understand by EW category of living being?
Answer:
A species which becomes extinct in the wild (EW) is called EW category, their members are seen only in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due to massive habitat loss.
3. Short answer type questions.
Question 1.
Dandiya raas is not allowed after 10.00 pm. Why?
Answer:
Dandiya rass involves blaring loudspeakers which cause noise pollution. It is undesired loud sound which could be hazardous for ears and general health. In India, the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act 1981, Amendment 1987, includes noise as an air pollutant. As per law noise after 10 pm is not allowed as many people may be resting. Therefore, Dandiya Raas is not allowed after 10 pm.
Question 2.
Tropical regions exhibit species richness as compared to polar regions. Justify.
Answer:
- Tropical regions are bestowed by thicker vegetation and ample food due to available sunlight and humidity.
- Polar regions are covered over with snow, with almost no vegetation.
- Only handful species of animals can survive here due to their adaptations.
- Species richness always shows latitudinal gradient for many plants and animal species. It is high at lower latitudes and there is a steady decline towards the poles. Therefore, tropical regions show more species richness.
Question 3.
How does genetic diversity affect sustenance of a species?
Answer:
- Genetic diversity develops the capability of the species to adapt to the varying changes in the environment.
- The large variation of the different gene sets allows an individual or the whole population to have the capacity to endure environmental stress in any form.
- Some individuals have, a better capacity to endure the increasing pollution in the environment whereas some do not have it.
- Those that do not have show infertility or even death from the same conditions.
- Those who are able to endure and adapt to this change survive and live in a better way.
- This is called natural selection which leads to a loss of genetic diversity in particular habitats.
- Thus, due to genetic diversity can affect sustenance of some species.
Question 4.
Greenhouse effect is boon or bane? Give your opinion.
Answer:
(1) The natural greenhouse effect is good, it is a boon but human enhanced greenhouse effect is a bane.
(2) In the absence of an atmosphere, Earth’s surface temperature would be about -18 °C, or 0 °F, which is too cold for sustaining life.
(3) Earth is habitable because of the natural greenhouse effect. Heating of Earth’s atmosphere due to the presence of greenhouse gases such as water vapour, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and oxides of nitrogen (NO2).
(4) Greenhouse gases have just the right molecular structure to absorb infrared radiation that the Earth emits. It re-emits most of that infrared energy in all directions, warming the atmosphere to its comfortable average temperature of 15 °C (60 °F). So, the greenhouse effect was a boon in olden days before industrialization and invention of automobiles.
(5) However, due to human impact, the proportion of greenhouse gases has increased tremendously causing global warming. Thus, now greenhouse effect has become a bane.
![]()
Question 5.
State the effects of CO in human body.
OR
How does CO cause giddiness and exhaustion?
Answer:
Effects of Carbon monoxide:
- Carbon monoxide is tasteless, colourless and odourless gas, therefore its presence goes unnoticed.
- It can inhibit the blood’s ability to carry oxygen to body tissues.
- Supply of oxygen to vital organs such as.the heart and brain is affected due to presence of CO.
- When CO is inhaled, it combines with the oxygen carrying haemoglobin of the blood to form carboxyhaemoglobin. Once combined with the haemoglobin, that haemoglobin is no longer available for transporting oxygen.
- The symptoms of CO poisoning are headache, nausea, giddiness, etc.
Question 6.
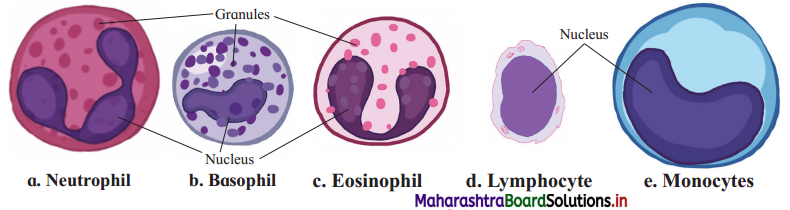
Name two types of particulate pollutants found in air. Add a note on ill effects of the same on human health.
OR
Describe any 2 particulate and gaseous pollutants.
Answer:
I. Types of gaseous pollutants include CO2, CO, SO2, NO, NO2, etc.
(1) Carbon dioxide : It is a greenhouse gas. It is produced in excess due to human activities such as burning of fossil fuels. It is also rising due to increasing deforestation. The natural cycle of Carbon dioxide is disturbed due to human interference. Otherwise, the process of photosynthesis can balance CO2 : O2 ratio of the air. Aeroplane traffic such as a jet plane also emits lots of CO2.
(2) Carbon monoxide (CO) : CO is produced due to incomplete combustion of fuels. It is a toxic gas. Vehicular exhausts produce lot of CO.
II. Types of particulate pollutants are mist, dust, fume and smoke particles, smog, pesticides, heavy metals and radioactive elements, etc.
(1) Dust are fine particles which enter the respiratory passage and can cause damage to delicate tissues in the lungs. Various processes such as construction work, demolition of buildings and traffic can cause dust pollution. There are natural causes of release of dust too, through wind or volcanic eruption.
(2) Smoke and smog are worst type of particulate air pollutants which can cause many respiratory problems like emphysema or asthma.
4. Long answer type questions.
Question 1.
Montreal Protocol is an essential step. Why is it so?
Answer:
- Montreal Protocol was an international treaty signed at Montreal in Canada in 1987.
- Later many more efforts have been made and protocols have laid down definite roadmaps separately for developing and developed countries.
- All these efforts were for reducing emission of CFCs and other ozone depleting chemicals.
- All nations realized that ozone depletion can cause penetration of harmful UV radiations to the earth’s surface. This is very hazardous, for flora, fauna and for mainly human beings. Therefore, urgent action was needed to combat this effect.
- Montreal Protocol was a very positive move because after 1987, there have been much better condition of ozone layer.
![]()
Question 2.
Name any 2 personalities who have contributed to control deforestation in our country. Elaborate on importance of their work.
Answer:
Two personalities who have contributed to control deforestation in our country are:
Saalumara Thimmakka from Karnataka and Moirangthem Loiya from Manipur.
1. Saalumara Thimmakka :
- Saalumara Thimmakka is the best example of peoples’ participation in reforestation.
- She is an Indian environmentalist from Karnataka. She has taken up work of planting and tending to 385 banyan trees along a 4 km stretch of highway between Hulikal and Kudur. Other 800 trees are also planted by her.
- She is honoured with the National Citizens Award of India and Padma Shri in 2019.
2. Moirangthem Loiya :
- Moirangthem Loiya is from Manipur who has restored Punshilok forest. For last 17 years he is planting trees after leaving his job.
- He brought the lost glory back for the 300 acres forest land. He planted a variety of trees like, bamboo, oak Ficus, teak, jackfruit and Magnolia.
- This forest now has over 250 varieties of plants including 25 varieties of bamboo along with many animals making the forest rich in biodiversity.
Question 3.
How BS emission standards changed over time? Why is it essential?
Answer:
- BS emission standards changed over the time due to changing city life and more vehicular traffic on the road, especially in the megacities.
- Since capital city of Delhi was declared as worst polluted city as far as its air quality is concerned, various measures were taken by the Government of India. There was new fuel policy declared, in which Bharat stage emission standards (BS) were set.
- These norms were set to reduce sulphur and aromatic content of petrol and diesel. Also the vehicular engines were upgraded.
- Bharat stage emission standards (BS) are standards which are equivalent to Euro norms and have evolved on similar lines as Bharat Stage II (BS II) to BS VI from 2001 to 2017.
- Since population of Delhi was to be saved, in 2001, Bharat stage II emission norms were set for CNG and LPG vehicles.
- This helped in reduced emission of sulphur which was controlled at 50 ppm in diesel and 150 ppm in petrol. Also aromatic hydrocarbons were reduced at 42% in concerned fuel according to norms.
- Because, in spite of all the efforts, Delhi was declared as worst air-polluted city in the world in 2016, therefore, Government of India directly adapted BS VI in the year 2018, skipping BS V These efforts decreased the levels of CO2 and SO2 in Delhi.
Question 4.
During large public gatherings like Pandharpur vari, mobile toilets are deployed by the government. Explain how this organic waste is disposed.
Answer:
- The toilets deployed at Pandharpur at the time of vari are of the Ecosan type.
- Ecosan toilet is a closed system without water and it is an alternative to leach pit toilets.
- When the pit of an Ecosan toilet fills up after some time, then it is closed and sealed for about 8-9 months.
- In this time the faeces get completely composted to organic manure. In this way the organic waste can be disposed.
- It is a practical, efficient and cost-effective solution for human waste disposal.
- Also, open-air defecation is prohibited which can cause health problems. Therefore, during large public gatherings like Pandharpur vari mobile toilets like Ecosan are deployed by the government.
Question 5.
How Indian culture and traditions helped in bio-diversity conservation? Give importance of conservation in terms of utilitarian reasons.
Answer:
In Indian culture and traditions in different religions, biodiversity is protected and conserved. Few examples of worship of animals and plants can be given here.
- Nagpanchami festival is towards the respect of snakes. They are worshipped on that day and the local people are aware of their role in ecosystem of control of rat population.
- Vatapournima festival is worshipping a banyan tree.
- Various other festivals teach the value of plants and animals surrounding us. Even the cattle are worshipped on a particular day as a tradition.
- Jain religion strongly advocates protection of all animals through vegetarianism.
![]()
Conservation in terms of utilitarian reasons:
The conservation of biodiversity can be done in utilitarian way or for ethical reasons. Utilitarian reasons are further classified into narrowly utilitarian and broadly utilitarian reasons:
I. Narrowly utilitarian reasons:
- Humans always reap material benefits from biodiversity in the form of resources for basic needs such as food, clothes, shelter.
- Industrial products like resins, tannins, perfume base, etc. are also obtained through biodiversity resources.
- For making ornaments or artefacts for aesthetic purpose, again biodiversity is sacrificed.
- Many medicines are also obtained through biodiversity resources which shares 25% of global medicine market.
- Around 25000 species are used for traditional medicines by tribal population worldwide.
- Bioprospecting which is a systematic search for development of new sources of chemical compounds, genes, microorganisms, macroorganisms, and other valuable products from nature which is of economically important species is also due to biodiversity.
II. Broadly utilitarian reasons:
- Production of oxygen done by all green plants helps human beings to thrive. Amazon forest alone gives 25% of the oxygen to the entire world.
- Insects carry out pollination and seed dispersal.
- If insects do not carry out pollination and seed dispersal, man would go hungry without crops and fruits.
- Biodiversity also is useful in recreation of human beings.
III. Taking all these aspects in consideration, conservation of biodiversity becomes essential. Therefore, to protect and conserve our rich biodiversity on the planet, we have to remember all the utilitarian reasons.