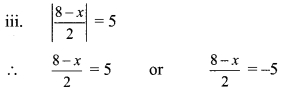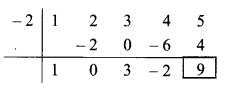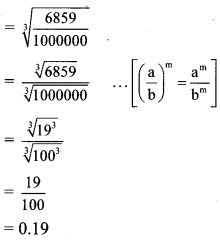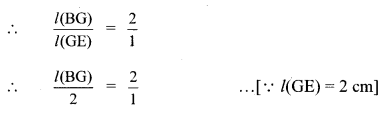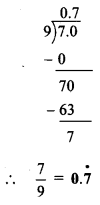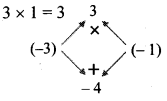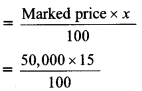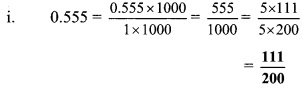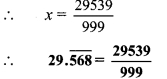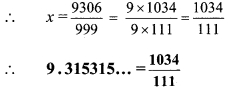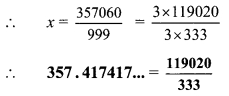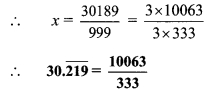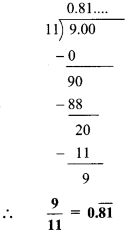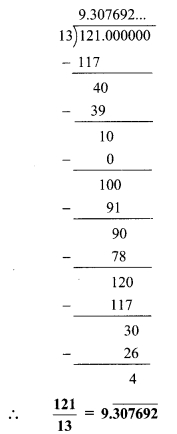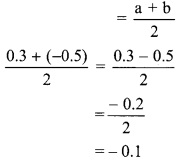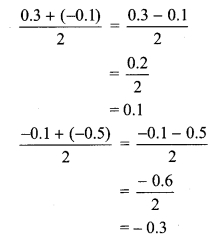Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Maths Solutions covers the Miscellaneous Exercise 1 8th Std Maths Answers Solutions.
Miscellaneous Exercise 1 8th Std Maths Answers
Question 1.
Choose the correct alternative answer for each of the following questions.
i. In ₹PQRS, m∠P = m∠R = 108°, m∠Q = m∠S = 72°. State which pair of sides of those given below is parallel. [Chapter 8]
(A) side PQ and side QR
(B) side PQ and side SR
(C) side SR and side SP
(D) side PS and side PQ
Solution:
(B) side PQ and side SR
Hint:
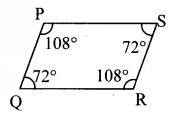
In ₹PQRS,
m∠P + m∠S = 108°+ 72
= 180°
Since, interior angles are supplementary.
∴ side PQ || side SR
ii. Read the following statements and choose the correct alternative from those given below them. [Chapter 8]
a. Diagonals of a rectangle are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
b. Diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
c. Diagonals of a parallelogram are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
d. Diagonals of a kite bisect each other.
(A) Statements (b) and (c) are true
(B) Only statement (b) is true
(C) Statements (b) and (d) are true
(D) Statements (a), (c) and (d) are true.
Solution:
(B) Only statement (b) is true
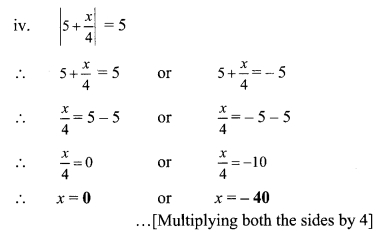
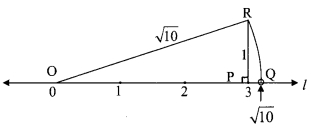
iii. If 19³ = 6859, find \(\sqrt[3]{0.006859}\). [Chapter 3]
(A) 1.9
(B) 19
(C) 0.019
(D) 0.19
Solution:
(D) 0.19
Hint:
\(\sqrt[3]{0.006859}\)
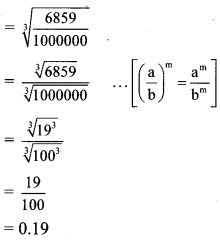
Question 2.
Find the cube roots of the following numbers. [Chapter 3]
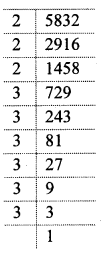
i. 5832
ii. 4096
Solution:
i. 5832 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= (2 × 3 × 3) × (2 × 3 × 3) × (2 × 3 × 3)
= (2 × 3 × 3)³
= (18)³
\(\sqrt[3]{5832}=18\)
ii. 4096 = (4 × 4) × (4 × 4) × (4 × 4)
= (4 × 4)
= 16³
\( \sqrt[3]{4096}=16\)

Question 3.
m∝n,n = 15 when m = 25. Hence
i. Find m when n = 87,
ii. Find n when m = 155. [Chapter 7]
Solution:
Given that, m ∝ n
∴ m = kn …(i)
where, k is the constant of variation.
When m = 25, n = 15
∴ Substituting, m = 25 and n = 15 in (i), we get
m = kn
∴ 25 = k × 15
∴ k = \(\frac { 25 }{ 15 }\)
∴ k = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }\)
Substituting k = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }\) in (i), we get
m = kn
∴ m = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }n\) …(ii)
i. When n = 87, m = ?
Substituting n = 87 in (ii), we get
m = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }n\)
m = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }\) × 87
m = 5 × 29
m = 145
ii. When m = 155, n = ?
∴ Substituting m = 155 in (ii), we get
m = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }n\)
∴ 155 = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }n\)
∴ \(\frac{155 \times 3}{5}=n\)
∴ n = 31 × 3
∴ n = 93
Question 4.
y varies inversely with x. If y = 30 when x = 12, find [Chapter 7]
i. y when x = 15,
ii. x when y = 18.
Solution:
Given that,
\(y \propto \frac{1}{x}\)
∴ \(y=k \times \frac{1}{x}\)
where, k is the constant of variation.
∴ y × x = k …(i)
When x = 12, y = 30
∴ Substituting, x = 12 and y = 30 in (i), we get
y × x = k
∴ 30 × 12 = k
∴ k = 360
Substituting, k = 360 in (i), we get
y × x = k
∴ y × x = 360 ….(ii)
i. When x = 15,y = ?
∴ Substituting x = 15 in (ii), we get
y × x = 360
∴ y × 15 = 360
∴ y = \(\frac { 360 }{ 15 }\)
∴ y = 24
ii. When y = 18, x = ?
∴ Substituting y = 18 in (ii), we get
y × x = 360
∴18 × x = 360
∴ x = \(\frac { 360 }{ 18 }\)
∴ x = 20
Question 5.
Draw a line l. Draw a line parallel to line l at a distance of 3.5 cm. [Chapter 2]
Solution:
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line l and take any two points M and N on the line.
- Draw perpendiculars to line l at points M and N.
- On the perpendicular lines take points S and T at a distance 3.5 cm from points M and N respectively.
- Draw a line through points S and T. Name the line as n.
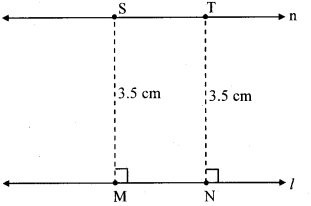
Line n is parallel to line l at a distance of 3.5 cm from it.
Question 6.
Fill in the blanks in the following statement.
The number \((256)^{\frac{5}{7}}\) is __ of __ power of __. [Chapter 3]
Solution:
The number \((256)^{\frac{5}{7}}\) is 7th root of 5th power of 256.
Question 7.
Expand.
i. (5x – 7) (5x – 9)
ii. (2x – 3y)³
iii. \(\left(a+\frac{1}{2}\right)^{3}\) [Chapter 5]
Solution:
i. (5x – 7) (5x – 9)
= (5x)² + (-7 -9) 5x + (-7) × (-9).
…[∵ (x + a) (x + b) = x² + (a + b)x + ab]
= 25x² + (-16) × 5x + 63
= 25x² – 80x + 63
ii. Here, a = 2x and b = 3y
(2x – 3y)³
= (2x)³ – 3 (2x)² (3y) + 3 (2x) (3y)² – (3y)³
…[∵ (a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³]
= 8x³ – 3 (4x²) (3y) + 3 (2x) (9y²) – 27y³
= 8x³ – 36x²y + 54xy² – 27p³
iii. Here, A= a and B = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
\(\left(a+\frac{1}{2}\right)^{3}=(a)^{3}+3(a)^{2}\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)+3(a)\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{3}\)
…[(A + B)³ = A³ + 3A²B + 3AB² + B³]
\(=\mathbf{a}^{3}+\frac{3 \mathbf{a}^{2}}{2}+\frac{3 \mathbf{a}}{4}+\frac{1}{8}\)
Question 8.
Draw an obtuse angled triangle. Draw all of its medians and show their point of concurrence. [Chapter 4]
Solution:
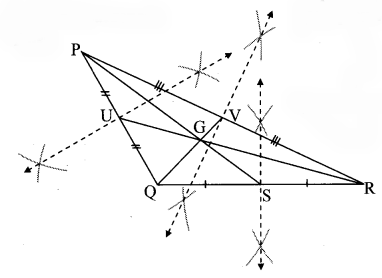
The point of concurrence of the medians PS, RU and QV is G.
Question 9.
Draw ∆ABC such that l(BC) = 5.5 cm, m∠ABC = 90°, l(AB) = 4 cm. Show the orthocentre of the triangle. [Chapter 4]
Solution:
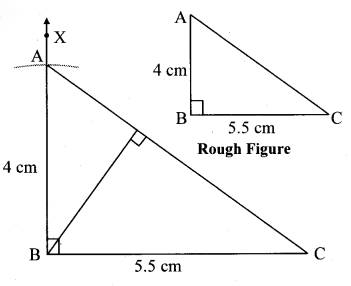
Here, point B is the orthocentre of ∆ABC.
Question 10.
Identify the variation and solve.
It takes 5 hours to travel from one town to the other if speed of the bus is 48 km/hr. If the speed of the bus is reduced by 8 km/hr, how much time will it take for the same travel? [Chapter 7]
Solution:
Let, v represent the speed of the bus and t represent the time required to travel from one town to the other.
The speed of the bus varies inversely with the time required to travel from one town to the other.
∴ \(\mathbf{v} \propto \frac{1}{\mathbf{t}}\)
∴ \(\mathbf{v}=\mathbf{k} \times \frac{1}{\mathbf{t}}\)
where, k is the constant of variation.
∴ v × t = k …(i)
It takes 5 hours to travel from one town to the other if speed of the bus is 48 km/hr.
i.e., when v = 48, t = 5
∴ Substituting v = 48 and t = 5 in (i), we get
v × t = k
∴ 48 × 5 = k
∴ k = 240
Substituting k = 240 in (i), we get
v × t = k
∴ v × t = 240 …(ii)
Since, the speed of the bus is reduced by 8 km/hr,
∴ Speed of the bus in second case (v)
= 48 – 8 = 40 km/hr
∴ When v = 40, t = ?
∴ Substituting v = 40 in (ii), we get
v × t = 240
∴ 40 × t = 240
∴ \(t=\frac { 240 }{ 40 }\)
∴ t = 6
∴ The problem is of inverse variation and the bus would take 6 hours to travel the distance if its speed is reduced by 8 km/hr.
Question 11.
Seg AD and seg BE are medians of ∆ABC and point G is the centroid. If l(AG) = 5 cm, find l(GD). If l(GE) = 2 cm, find l(BE). [Chapter 4]
Solution:
The centroid of a triangle divides each median in the ratio 2:1.
i. Point G is the centroid and seg AD is the median.
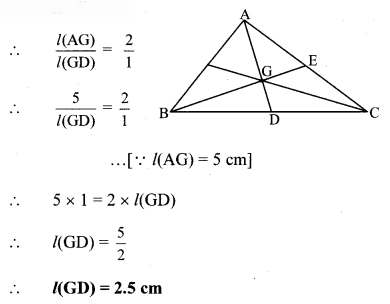
ii. Point G is the centroid and seg BE is the median.
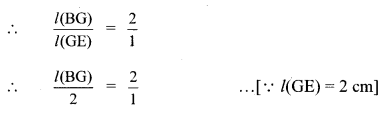
∴ l(BG) × 1 = 2 × 2
∴ l(BG) = 4 cm
Now, l(BE) = l(BG) + l(GE)
∴ l(BE) = 4 + 2
∴ l(BE) = 6 cm
Question 12.
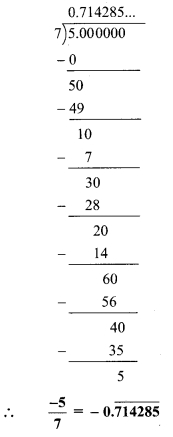
Convert the following rational numbers into decimal form. [Chapter 1]
i. \(\frac { 8 }{ 13 }\)
ii. \(\frac { 11 }{ 7 }\)
iii. \(\frac { 5 }{ 16 }\)
iv. \(\frac { 7 }{ 9 }\)
Solution:
i. \(\frac { 8 }{ 13 }\)
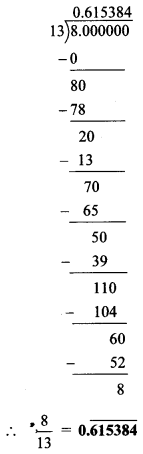
ii. \(\frac { 11 }{ 7 }\)

iii. \(\frac { 5 }{ 16 }\)

iv. \(\frac { 7 }{ 9 }\)
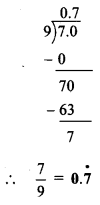
Question 13.
Factorize.
i. 2y² – 11y + 5
ii. x² – 2x – 80
iii. 3x² – 4x + 1
Solution:
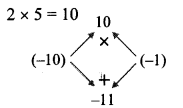
i. 2y² – 11y + 5
= 2y² – 10y – y + 5
= 2y(y – 5) – 1(y – 5)
= (y – 5)(2y – 1)
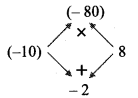
ii. x² – 2x – 80
= x² – 10x + 8x – 80
= x (x – 10) + 8 (x – 10)
= (x – 10)(x + 8)
iii. 3x² – 4x + 1
= 3x² – 3x – x + 1
= 3x(x – 1) – 1(x – 1)
= (x – 1) (3x – 1)
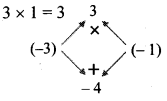
Question 14.
The marked price of a T.V. set is Rs 50,000. The shopkeeper sold it at 15% discount. Find the price of it for the customer. [Chapter 9]
Solution:
Here, marked price = Rs 50,000,
discount = 15%
Let the discount percent be x
∴x = 15%
i. Discount
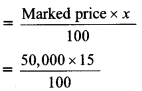
= 500 × 15
= Rs 7,500
ii. Selling price = Marked price – Discount
= 50,000 – 7,500
= Rs 42,500
∴The price of the T.V. set for the customer is Rs 42,500.
Question 15.
Rajabhau sold his flat to Vasantrao for Rs 88,00,000 through an agent. The agent charged 2 % commission for both of them. Find how much commission the agent got. [Chapter 9]
Solution:
Here, selling price of the flat = Rs 88,00,000
Rate of commission = 2%
Commission = 2% of selling price
= \(\frac { 2 }{ 100 }\) × 88,00,000
= 2 × 88,000
= Rs 1,76,000
∴ Total commission = Commission from Rajabhau + Commission from Vasantrao
= Rs 1,76,000 + Rs 1,76,000
= Rs 3,52,000
∴ The agent got a commission of Rs 3,52,000.
Question 16.
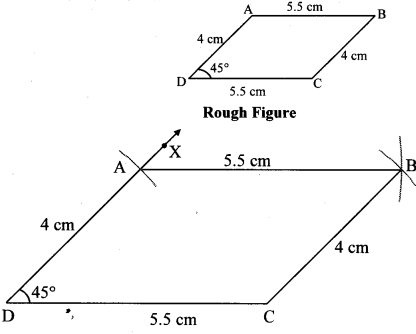
Draw a parallelogram ABCD such that l(DC) = 5.5 cm, m∠D = 45°, l(AD) = 4 cm. [Chapter 8]
Solution:
Opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent.
∴ l(AD) = l(BC) = 4 cm and
l(DC) = l(AB) = 5.5 cm
Question 17.
In the figure, line l || line m and line p || line q. Find the measures of ∠a, ∠b, ∠c and ∠d. [Chapter 2]
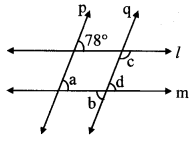
Solution:
i. line l|| line m and line p is a transversal.
∴m∠a = 78° …(i) [Corresponding angles]
ii. line p || line q and line m is a transversal.
∴m∠d = m∠a …[Corresponding angles]
∴m∠d = 78° …(ii)[From (i)]
iii. m∠b = m∠d …[Vertically opposite angles]
∴m∠b = 78° …[From (ii)]
iv. line l|| line m and line q is a transversal.
∴m∠c + m∠d = 180° …[Interior angles]
∴m∠c + 78° = 180° … [From (ii)]
∴m∠c =180° – 78°
∴m∠c = 102°
∴m∠a = 78°, m∠b = 78°, m∠c = 102°, m∠d = 78°