Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 3 Basic Analytical Techniques Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 3 Basic Analytical Techniques
Question 1.
Give reason: Purification of a chemical substance is important before investigating its composition and properties.
Answer:
- Chemical substances occur in nature in the impure stage.
- Also, chemical substances synthesized in the laboratory are obtained in crude and impure form.
- Impurities present in the chemical substances may interfere with the properties to be determined (e.g. melting point or boiling point).
- Therefore, before investigating the composition and properties of a given chemical substance, it is important to obtain it in pure form.
Question 2.
What are the different types of impurities that a solid may contain?
Answer:
A solid substance may contain two types of impurities:
- Impurities that are soluble in the same solvent as the main substance.
- Impurities that are not soluble in the same solvent as the main substance.
Question 3.
For which of the following cases, is the process of filtration feasible? Why?
Case 1: A solid substance containing impurities that are soluble in the same solvent as the main substance.
Case 2: A solid substance containing impurities that are not soluble in the same solvent as the main substance.
Answer:
Impurities which are not soluble in the same solvent as the main compound can be separated by a simple process called filtration. Hence, for ‘Case 2’, filtration is more feasible.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the process of filtration with a neat and labelled diagram.
Answer:
i. Impurities which are not soluble in the same solvent as the main compound can be separated by a simple process called filtration.
ii. Procedure:
a. A circular piece of filter paper is folded to form a cone and fitted in the funnel.
b. The funnel is fixed on a stand and a beaker is kept below.
c. The mixture which has to be purified is added to a suitable solvent in which the main compound dissolves.
d. The paper is made moist, and the solution to be filtered is poured on the filter paper.
e. Diagram:
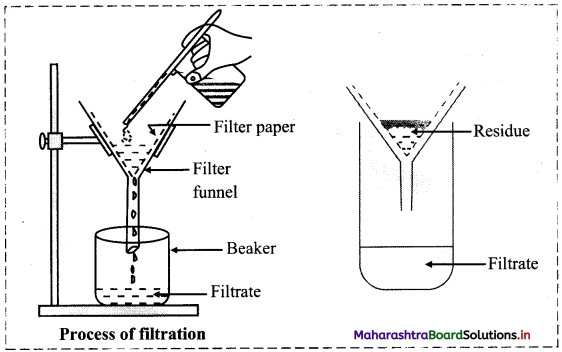
iii. The insoluble part remaining on the filter paper is called residue and the liquid which pass through the filter paper and collected in the beaker is called filtrate.
iv. This process is similar to separating tea leaves from decoction of tea or sand from mixture of sand and water.
Question 5.
Why is safety bottle used when filtration is carried out under suction?
Answer:
The safety bottle is used to prevent sucking of the filtrate into suction pump.
Question 6.
Name the steps involved in the process of crystallization.
Answer:
Steps involved in the process of crystallization:
- Preparation of a saturated solution
- Hot filtration
- Cooling of the filtrate
- Filtration
Question 7.
How is saturated solution of the crude solid prepared?
Answer:
- A saturated solution of the crude solid is prepared by boiling it in a small but sufficient quantity of a suitable solvent.
- The main solute from the sample of the crude solid dissolves to form a saturated solution on boiling.
[Note: The solution is not saturated with respect to the soluble impurities, as they are in small proportion.]
Question 8.
Explain the following steps with respect to the process of crystallization.
i. Preparation of a saturated solution
ii. Hot filtration
iii. Cooling of the filtrate
iv. Filtration
Answer:
i. Preparation of a saturated solution:
- A saturated solution of the crude solid is prepared by boiling it in a small but sufficient quantity of a suitable solvent.
- On doing so the main solute forms an almost saturated solution, but the solution is not saturated with respect to the soluble impurities, as they are in small proportion.
ii. Hot filtration: The hot saturated solution is quickly filtered to remove undissolved impurities as residue. Filtration under suction can be employed for rapid filtration.
iii. Cooling of the filtrate:
- The hot filtrate is allowed to cool.
- On cooling, the filtrate becomes supersaturated with respect to the main dissolved solute because solubility of a substance decreases with lowering of temperature.
- The excess quantity of the dissolved solute comes out of the solution in the form of crystals.
- The dissolved impurities, however, do not supersaturate the solution, as their quantity is small.
- These continue to stay in the solution in dissolved state even on cooling. Therefore, the separated crystals are free from soluble impurities.
iv. Filtration:
- The crystals obtained on cooling are further purified by filtration to remove insoluble impurities.
- The filtrate obtained is called as mother liquor.
- The crystals obtained after filtration are free from soluble as well as insoluble impurities.
![]()
Question 9.
Name the common solvents used in the process of crystallization.
Answer:
The commonly used solvents are water, ethyl alcohol, methyl alcohol, acetone, ether or their combinations.
Question 10.
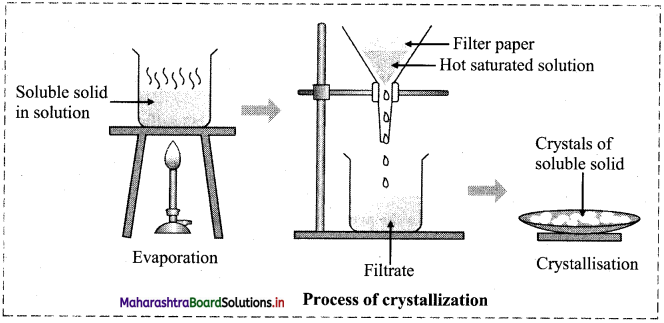
Describe the process of crystallization of common salt from impure sample with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
- Impure sample of a common salt is added to the required quantity of water and stirred with a glass rod.
- More amount of salt is added and the solution is heated till no more salt dissolves.
- The hot saturated solution is filtered off to remove insoluble impurities while the filtrate is collected in an evaporating dish.
- The filtrate is allowed to cool which results in the formation crystals of pure salt (NaCl) leaving behind the soluble impurities.
- The crystals are filtered and dried.
The diagram is as follows:
Question 11.
Which solvent is used for the purification of copper sulphate and benzoic acid?
Answer:
The solvent used for the purification of copper sulphate and benzoic acid is water.
Question 12.
Define: Fractional crystallization
Answer:
Fractional crystallization is a process wherein two or more soluble substances having widely different solubilities in the same solvent at same temperature are separated by crystallization.
Question 13.
Give a brief description of the principle of fractional crystallization.
Answer:
Fractional crystallization is based on the differences in solubilities of two or more compounds in the same solvent at the same temperature. That is, the substance which is least soluble crystallizes out first and the most soluble substance crystallizes out last.
e.g. Mixture of two solutes A and B can be purified by fractional crystallization as follows:
- Preparation of a saturated solution: Mixture of two solutes A and B are dissolved in a suitable hot solvent to prepare a saturated solution.
- Hot filtration: The hot saturated solution is filtered to remove insoluble impurities.
- Cooling of the filtrate: Hot filtrate is allowed to cool. On cooling, the solute which is least soluble crystallizes out first leaving behind the most soluble substance in the mother liquor.
- Filtration: The crystals formed are filtered, washed with solvent and dried. Crystals obtained will be of a solute which is least soluble in a given solvent.
- Concentration of a mother liquor: The mother liquor is concentrated by evaporating the solvent. These crystals are filtered and dried to obtain the second purified component (which was more soluble in given solvent).
![]()
Question 14.
Which type of impure liquids can be purified by the process of distillation?
Answer:
Distillation technique can be employed for the purification of
- volatile liquids from non-volatile impurities.
- liquids having sufficient difference in their boiling point.
Question 15.
Explain the construction of simple distillation unit using neat labelled diagram.
Answer:
i. The apparatus used for simple distillation is shown in the figure below:
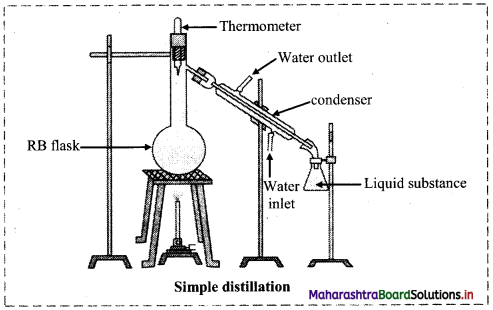
ii. It consists of round bottom flask fitted with a cork having a thermometer.
iii. The flask has a sidearm through which it is connected to a condenser.
iv. The condenser has a jacket with two outlets through which water is circulated.
v. The liquid to be distilled is taken in the round bottom flask fixed by clamp.
vi. The flask is placed in a water bath or oil bath or sometimes wire gauze is kept on a stand as shown in the figure.
Question 16.
State the principle involved and describe the process to separate acetone and water from their mixture.
Answer:
i. Acetone and water can be separated from their mixture by simple distillation.
ii. Principle: Acetone and water are two miscible liquids having an appreciable difference (more than 30 K) in their boiling points. Acetone boils at 56 °C while boiling point of water is 100 °C. When the mixture of acetone and water is heated and temperature of the mixture reaches 56 °C acetone will distil out first. Once all acetone distils out, and when the temperature rises to 100 °C water will distil out.
iii. Process to separate acetone and water from their mixture:
- Take the mixture of water and acetone in the distillation flask.
- Heat the flask on a water bath carefully. At 56 °C acetone will distil out, collect it in receiver.
- After all acetone distilled, change the receiver. Discard a few mL of the liquid. As the temperature reaches 100 °C water will begin to distil. Collect this in another receiver.
Question 17.
What is the advantage of fractional distillation over simple distillation?
Answer:
If in a mixture, the difference in boiling points of two liquids is not appreciable/large, they cannot be separated using simple distillation. To separate such liquids, fractional distillation is used.
![]()
Question 18.
Label the following diagram and explain the process by giving example.
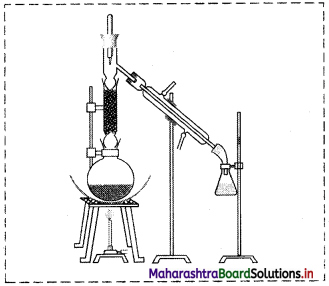
Answer:
The labelled diagram is as follows:
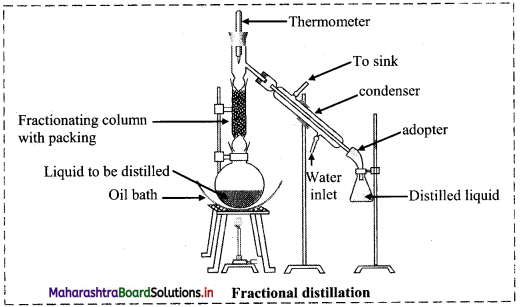
i. In fractional distillation, vapours first pass through the fractionating column.
ii. Vapours of more volatile liquid with lower boiling point rise up more than the vapours of liquid having higher boiling point.
e.g.
- Suppose we have a mixture of two liquid ‘A’ and ‘B’ having boiling points 363 K and 373 K respectively.
- ‘A’ is more volatile and ‘B’ is less volatile. As the mixture is heated, vapours of ‘A’ along with a little vapours of ‘B’ rise up and come in contact with the large surface of the fractionating column.
- Vapours of ‘B’ condense rapidly into the distillation flask. While passing through the fractionating column, there is an exchange between the ascending vapours and descending liquid. The vapours of ‘B’ are scrubbed off by the descending liquid, this makes the vapours richer in ‘A’.
- This process is repeated each time the vapours and liquid come in contact with the surface in the fractionating column.
- Rising vapours become richer in ‘A’ and escape through the fractionating column and reach the condenser while the liquid in the distillation flask is richer in ‘B.
- The separated components are further purified by repeating the process.
Question 19.
Give two examples of a mixture that can be separated by fractional distillation.
Answer:
- Mixture of acetone (b.p. 329 K) and methyl alcohol (b.p. 337.7 K)
- Mixture of acetone (b.p. 329 K) and benzene (b.p. 353 K)
Question 20.
Give one industrial application of fractional distillation.
Answer:
Fractional distillation is used in petroleum industry to separate different fractions of crude oil.
Question 21.
Write a short note on distillation under reduced pressure.
Answer:
- Liquids having very high boiling points or which decompose on heating are purified by the method of distillation under reduced pressure.
- In this method, the liquid is made to boil at a temperature lower than its normal boiling point by reducing the pressure on its surface.
- The external pressure is reduced using a water pump or vacuum pump, e.g. Glycerol can be separated from soap by using this method.
![]()
Question 22.
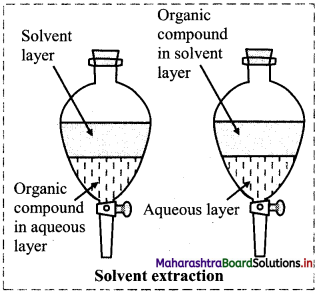
Write the principle of solvent extraction and explain the process with labelled diagram.
Answer:
Principle: Extraction of compound takes place based on the difference in solubility of compound in two liquids.
- In this process, the solute distributes itself between two immiscible liquids. From the aqueous phase the solute gets extracted in the organic phase.
- On shaking for a few times with small volumes of organic phase, most of the solute gets extracted into the organic phase.
- Then solute is then recovered from organic solvent either by evaporation of organic solvent or distillation.
Diagram:
Question 23.
Write a short note on continuous extraction method.
Answer:
- During solvent extraction, if the solute is found to be less soluble in organic phase, then continuous extraction method is employed.
- In this method, the same amount of organic solvent is used repeatedly for extraction.
- This ensures that the most of the solute gets extracted in the organic phase.
- This technique involves continuous distillation of the solvent within the same assembly. Hence, the use of large quantity of organic solvent is avoided.
Question 24.
Match the following:
| Process | Used in the purification/separation of | ||
| i. | Crystallization | a. | Acetone and benzene |
| ii. | Simple distillation | b. | Benzoic acid and water |
| iii. | Fractional distillation | c. | Impure copper sulphate |
| iv. | Solvent extraction | d. | Acetone and water |
Answer:
i – c,
ii – d,
iii – a,
iv – b
Question 25.
What is chromatography? Explain the principle behind it.
Answer:
Chromatography is a technique used to separate components of a mixture, and also purify compounds.
Principle: The principle of separation of substances in chromatography is based on the distribution of the solutes in two phases, i.e., stationary phase and mobile phase.
- Chromatography uses two phases for separation.
- This technique is based on the difference in rates at which components in the mixture move through the stationary phase under the influence of the mobile phase.
- In this technique, first the mixture of components is loaded at one end of the stationary phase and then the mobile phase is allowed to move over the stationary phase. The mobile phase can be a pure solvent or a mixture of solvents.
- Depending on the relative affinity of the components toward the stationary phase and mobile phase, they remain on the surface of the stationary phase or move along with the mobile phase, and gradually get separated.
![]()
Question 26.
Give a brief description of column chromatography with an illustration.
Answer:
Column chromatography involves the separation of components over a column of stationary phase. The stationary phase material can be alumina, silica gel.
Procedure:
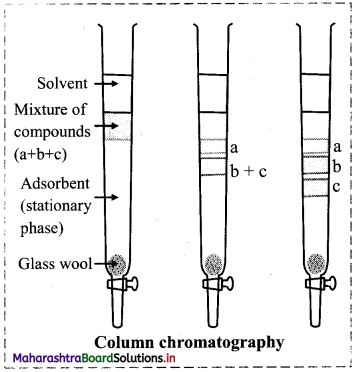
- A slurry of the stationary phase material is filled in a long glass tube provided with a stopcock at the bottom and a glass wool plug at the lower end.
- The mixture to be separated is dissolved in a suitable solvent and then it is loaded on top of adsorbent column.
- A suitable mobile phase which could be a single solvent or a mixture of solvents is then poured over the adsorbent column.
- The mixture along with the mobile phase slowly moves down the column.
- The solutes get adsorbed on the stationary phase and depending on the degree to which they are adsorbed, they get separated from each other.
- The component which is readily adsorbed are retained on the column and others move down the column to various distances forming distinct bands.
- The component which is less strongly adsorbed is desorbed first and leaves the column first, while the strongly adsorbed component is eluted later.
- The solutions of these components are collected separately.
- These different components can be recovered by evaporating the solvent.
Question 27.
How is TLC plate or chromplate prepared?
Answer:
TLC plate or chromplate is prepared by applying a thin layer (0.2 mm thick) of adsorbent silica gel or alumina spread over a glass plate.
Question 28.
Describe the process of thin layer chromatography (TLC) and separation of components in it.
Answer:
i. Process:
- A thin layer (about 0.2 mm thick) of an adsorbent like silica gel or alumina is spread over a thin glass plate (called chromplate or TLC plate). This plate acts as a stationary phase.
- With the help of a capillary tube, the solution of the mixture to be separated is spotted at above 2 cm (on base line) from one end of the TLC plate.
- The TLC plate is then placed in a closed jar containing a suitable solvent (mobile phase or eluant).
- As the mobile phase rises up the plate, the components of the mixture move up along with the mobile phase to different distances depending upon their degree of adsorption, thus resulting in complete separation.
ii. Separation of components:
- If the components are coloured, they appear as separated coloured spots on the plate.
- If the components are not coloured but have property of fluorescence, they can be visualised under UV light, or the plate can be kept in a chamber containing a few iodine crystals. The Iodine vapours are adsorbed by the components and the spots appear brown.
- Amino acids are visualised by spraying the plate with a solution of ninhydrin. This is known as spraying agent.
Question 29.
Name the physical state each of stationary phase and mobile phase in partition chromatography.
Answer:
In partition chromatography, both stationary and mobile phases are in liquid state.
![]()
Question 30.
State the principle of partition chromatography.
Answer:
Partition chromatography is based on continuous differential partitioning of components of a mixture between stationary and mobile phases.
Question 31.
Describe the process of paper chromatography.
Answer:
Process of paper chromatography:
- The mixture of the compound to be analysed is dissolved in a suitable solvent and spotted on the chromatography paper about 2 cm from one end of the paper using a glass capillary.
- The paper is then suspended in a chamber containing the mobile phase.
- The mobile phase rises up the paper and flows over the spot, due to capillary action.
- Different solutes are retained differently on the paper depending on their selective partitioning between the two phases. The paper strip so developed, is known as chromatogram.
Question 32.
Name the following:
i. A glass plate coated with a thin layer of silica gel.
ii. A spraying agent used for the visualization of amino acids.
Answer:
i. Chromplate/TLC plate
ii. Ninhydrin
Question 33.
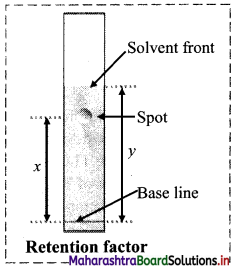
Write a short note on Rf value.
Answer:
i. In chromatography, migration of the solute relative to the solvent front gives an idea about the relative retention of the solutes (or components of t the mixture) on the stationary phase.
ii. The relative adsorption of solutes is expressed in terms of its Rf value.
The symbol Rf stands for Retardation Factor.
![]()
Question 34.
In a chemical laboratory, Priyal was asked to isolate an organic compound from its aqueous solution. She added ethyl acetate to the given sample, separated the organic layer and kept it for evaporation. At the end of her practical, Priyal found few crystals in the beaker which she kept for evaporation. Answer the following questions:
i. In the above passage, which method was used by Priyal for separation? State its principle.
ii. Why do you think the organic compound dissolved in ethyl acetate?
iii. Illustrate the method of separation used in the passage with an example.
Answer:
i. Method used: Solvent extraction method.
Principle: Extraction of compound takes place based on the difference in solubility of compound in two liquids,
- In this process, the solute distributes itself between two immiscible liquids. From the aqueous phase the solute gets extracted in the organic phase.
- On shaking for a few times with small volumes of organic phase, most of the solute gets extracted into the organic phase.
- Then solute is then recovered from organic solvent either by evaporation of organic solvent or distillation.
ii. An organic compound (non-polar) dissolves in organic solvents (non-polar) because of the dipole-dipole interactions in between them (like dissolves like). Water is a polar solvent and it is unlikely that the covalent constituents of the organic substance is strong enough to break the ionic bonds. Any substance dissolves in other because it is able to break the bonds between the solvent molecules and form weak bonds with the solvent molecules. Hence, the organic compound will be more soluble in ethyl acetate as compared to water and this helps in its isolation from aqueous solution.
iii. An example for the separation of organic compound using solvents extraction method is: Benzoic acid in water can be extracted from its aqueous solution by using benzene.
![]()
Question 35.
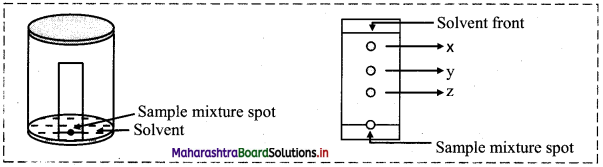
Based on the above diagram, answer the following questions:
i. Name the chromatographic technique involved.
ii. From the developed chromatogram, state which has the highest and which has the lowest Rf value?
iii. Based on the TLC, which component would elute out at the end of a column chromatography?
iv. Mention two applications of TLC method.
Answer:
i. Thin layer chromatography
ii. Based on the developed chromatogram, spot ‘x’ has the highest Rf value while spot ‘z’ the lowest Rf value.
iii. Based on the TLC, spot ‘z’ being strongly adsorbed will elute at the end of a column chromatography.
iv. Applications of TLC are:
- Separation of plant pigments from its mixture.
- Separation of impurities from a given organic compound.
- Separation of different amino acid.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. If a crude solid is made of mainly one substance and has some impurities then it is purified by ……………..
(A) crystallization
(B) distillation
(C) extraction
(D) sublimation
Answer:
(A) crystallization
2. Impure common salt can be purified by ……………
(A) crystallization
(B) distillation
(C) extraction
(D) sublimation
Answer:
(A) crystallization
3. Which of the following solvents is most commonly used for the crystallization of copper sulphate?
(A) Water
(B) Acetone
(C) Ether
(D) Methanol
Answer:
(A) Water
![]()
4. In distillation of liquid, water condenser is used ……………
(A) to boil the liquid
(B) to collect the liquid
(C) to condense hot vapours of the liquid
(D) to adsorb the liquid
Answer:
(C) to condense hot vapours of the liquid
5. Separation of binary mixture of acetone and methyl alcohol is done by ……………
(A) simple distillation
(B) fractional distillation
(C) fractional crystallization
(D) re-crystallization
Answer:
(B) fractional distillation
6. Which of the following method is used to separate different fractions of crude oil?
(A) Solvent extraction
(B) Simple distillation
(C) Fractional distillation
(D) TLC
Answer:
(C) Fractional distillation
7. The method used to separate a given organic compound present in aqueous solution by shaking with a suitable solvent in which the compound is more soluble than water is called ……………….
(A) simple distillation
(B) fractional distillation
(C) solvent extraction
(D) crystallization
Answer:
(C) solvent extraction
8. Adsorption chromatography is a chromatographic technique based on the principle of ……………
(A) differential adsorption
(B) differential solubility
(C) differential extraction
(D) all of these
Answer:
(A) differential adsorption
![]()
9. The stationary phase and mobile phase in TLC are ……………. respectively.
(A) solid and liquid
(B) solid and gas
(C) liquid and solid
(D) liquid and liquid
Answer:
(A) solid and liquid
10. Which of.the following is most commonly used for the visualization of amino acids in chromatography?
(A) Ultraviolet light
(B) Spraying agent
(C) Sunlight
(D) X-rays
Answer:
(B) Spraying agent
11. The stationary phase and mobile phase in partition chromatography are ………….. respectively.
(A) solid and liquid
(B) solid and gas
(C) liquid and solid
(D) liquid and liquid
Answer:
(D) liquid and liquid
12. Paper chromatography is based on the principle of …………….
(A) adsorption
(B) partition
(C) solubility
(D) volatility
Answer:
(B) partition
13. In paper chromatography, the mobile phase rises up the chromatography paper due to ………………
(A) evaporation of volatile solvent
(B) capillary action
(C) gravitational force
(D) differential adsorption
Answer:
(B) capillary action
![]()
14. Which of the following is a type of partition chromatography?
(A) Column chromatography
(B) Thin layer chromatography
(C) Paper chromatography
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(C) Paper chromatography
15. The principle of differential adsorption is applicable for which of the following chromatographic technique?
(A) Column chromatography
(B) Thin layer chromatography
(C) Paper chromatography
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (B)
16. Which of the following method will give clean separation of a sample of chloroform (organic liquid) and water in a short time span?
(A) TLC
(B) Distillation under reduced pressure
(C) Solvent extraction
(D) Simple distillation
Answer:
(C) Solvent extraction