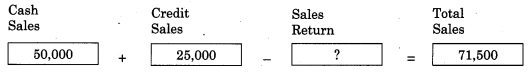
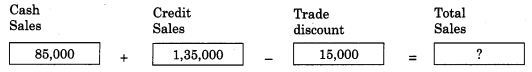
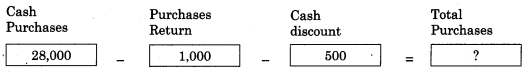
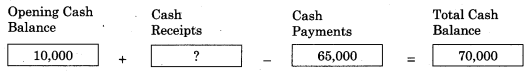
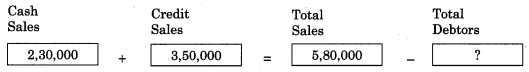
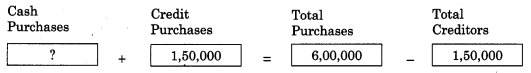
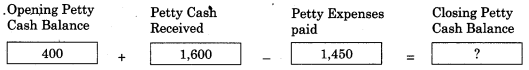
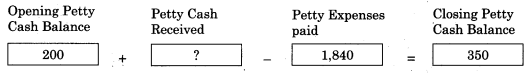
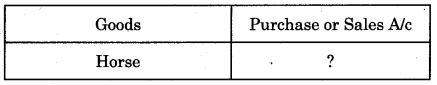
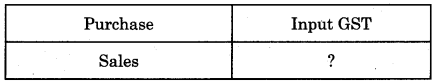
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 2 Systematics of Living Organisms Important Questions and Answers.
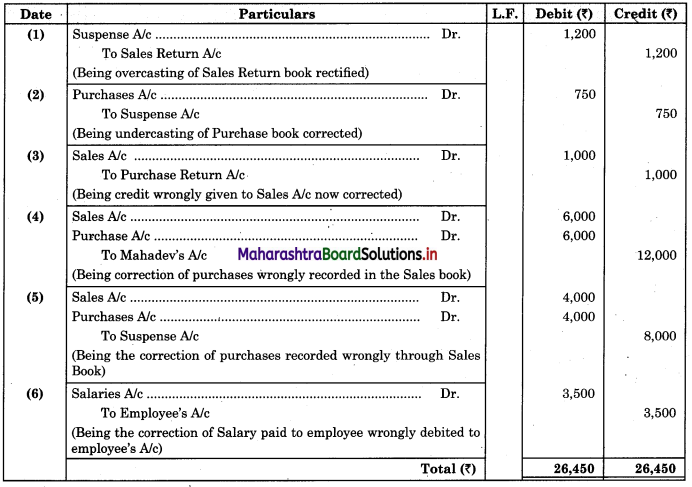
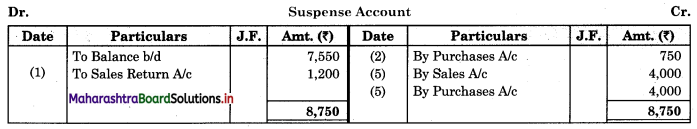
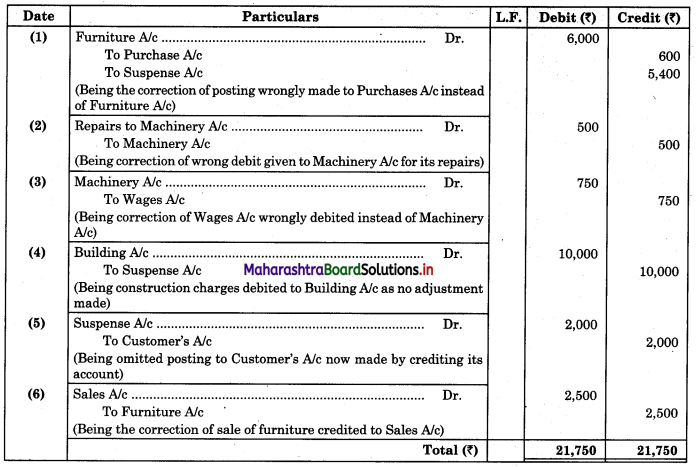
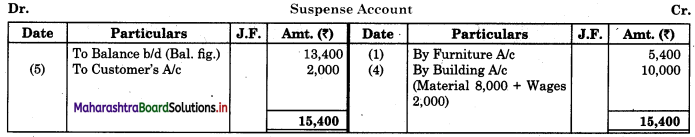
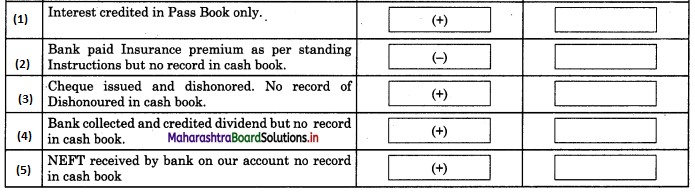
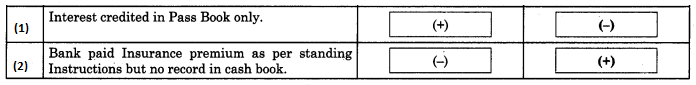
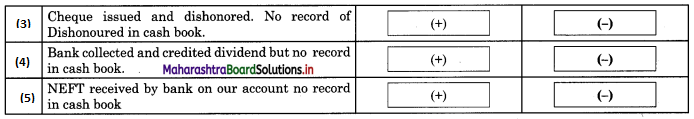
Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 2 Systematics of Living Organisms
Question 1.
Write the definition of systematics given by G. Simpson in 1961.
Answer:
Systematics is the study of the kinds and diversity of organisms and their comparative and evolutionary relationship.

Question 2.
Explain the term taxonomy.
Answer:
- Taxonomy means classification following certain rules or principles.
- The word taxonomy comes from two Greek words, taxis meaning arrangement, and nomos meaning law or rule.
- The term taxonomy was coined by A.P. de Candolle (Swiss Botanist) [1778-1841].
Question 3.
Who coined the term taxonomy?
Answer:
The term taxonomy was coined by A.P. de Candolle (Swiss Botanist) [1778-1841].
Question 4.
Define the term classification. What is the basis of classification?
Answer:
1. Classification is the arrangement of organisms or groups of organisms in distinct categories in accordance with a particular and well-established plan.
2. It is based on the similarities and differences among the organisms.

Question 5.
What are the three types of classification systems?
Answer:
The three types of classification systems are:
(i) Artificial system:
(a) It is based on few visible, easily observable characters, which are non-evolutionary such as habit, colour, form, etc.
(b) It does not consider the affinities (relationships) among different organisms.
E.g. Linnaeus system of classification.
(ii) Natural system:
It is based on objectively significant characters with respect to their affinities with other organisms.
E.g. Bentham and Hooker’s system of classification.
(iii) Phylogenetic system:
It is based on the phylogenetic relationship between different organisms with respect to common evolutionary descent (ancestor).
E.g. Engler and Prantl’s classification.
Question 6.
What is domain? Name the three domains of life.
Answer:
1. Domain is a unit larger than Kingdom in the system of classification.
2. Three domains of life are Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya.

Question 7.
Who proposed the three-domain system?
Answer:
Carl Woese proposed the three-domain system.
Question 8.
State one similarity and difference between archaea and bacteria?
Answer:
Both archaea and bacteria are prokaryotic. They differ in their cell wall structures.
Question 9.
Which domain has eukaryotic cells?
Answer:
Domain Eukarya has eukaryotic cells.
Question 10.
what is chemotaxonomy? Explain with example.
Answer:
- It is method of biological classification based on the similarities and differences in structure of certain chemical compounds present among the organisms being classified.
- Thus, it is a classification based on chemical constituents of organisms.
- For e.g. Cell wall with peptidoglycan is present in Bacteria while it is absent in Archaea. Among Eukarya, fungi have chitinous cell wall, while plants have cellulosic cell wall.
Question 11.
Write a short note on numerical taxonomy.
Answer:
Numerical taxonomy:
- It is based on quantification of characters and develops an algorithm for classification.
- The aim of this was to create a taxonomy using numeric algorithms like cluster analysis rather than using subjective evaluation of their properties.
- It was proposed by Sokel and Sneath in 1963.

Question 12.
What is cladogram? Give a diagrammatic representation of three domains of life with the help of cladogram.
Answer:
1. It is a representation of hypothetical relationship denoting a comparison of organisms and their common ancestors.
2. It has a typical branching pattern.
Question 13.
Write in detail about the Phylogeny.
Answer:
Phylogeny:
- It is the evolutionary relationship of organism.
- It is an important tool in classification as it considers not merely the morphological status but also the relationship of one group of organisms with other groups of life.
- The system helps to understand the evolution and also focuses on the similarities of their metabolic functioning.
- Woese’s three domain concept as well as Whittaker’s five kingdom system are examples of phylogenetic relationship.
Question 14.
What is the use of DNA barcoding?
Answer:
DNA barcoding helps to study newly identified species as well as understanding ecological and evolutionary relationships between living organisms.
Question 15.
What are the steps involved in the process of DNA barcoding?
Answer:
The process of DNA barcoding includes two basic steps:
1. Collecting DNA barcode data of known species.
2. Matching the barcode sequence of the unknown sample against the barcode library for identification.
Question 16.
What are the applications of DNA barcoding?
Answer:
The applications of DNA barcoding are as follows:
- It helps to protect endangered species.
- It plays an important role in preservation of natural resources.
- It is also used for pest control in agriculture.
- It is used for identification of disease vectors.
- It is used for authentication of natural health products.
- It is also used for identification of medicinal plants.

Question 17.
What is taxonomic category?
Answer:
- Category is a rank or level in the hierarchial classification of organisms.
- Each category is referred to as a unit of classification.
- Category is a part of taxonomic arrangements hence, called taxonomic category.
- All categories together constitute the taxonomic hierarchy.
Question 18.
What are the compulsory taxonomic categories?
Answer:
Kingdom, division, class, order, family, genus, species are the compulsory categories.
Question 19.
What are the facultative taxonomic categories?
Answer:
Sub-order, sub-family, etc. are the facultative categories which are used when required.
Question 20.
Define taxonomic hierarchy.
Answer:
The manner of scientific grouping of different taxonomic categories in a descending order on the basis of their ranks or positions in classification is called taxonomic hierarchy.
Question 21.
Define the term Taxon. Give some examples of taxa at different hierarchical levels.
Answer:
1. Taxon is a group of living organisms of any rank in the system of classification.
2. In plant kingdom, each taxonomic group such as angiospermae, dicotyledonae, polypetalae, malvaceae represents a taxon.
Question 22.
Write the classification of:
Answer:
1. China Rose
2. Cobra

Question 23.
Explain the following terms:
- Species
- Genus
- Family
- Order
- Class
- Division/Phylum
- Sub kingdom
- Kingdom
Answer:
(i) Species:
(a) Species is the principal natural taxonomic unit, ranking below a genus.
(b) It is a group of organisms that can interbreed under natural condition to produce fertile offspring.
(c) It was thought to be an indivisible, stable and static unit.
(d) However, in the modem taxonomy, subdivision of species such as sub-species, varities and populations are seen and given more importance.
(ii) Genus:
(a) Genus is a taxonomic rank or category larger than species used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms.
(b) Genus is a group of species bearing close resemblance to one another in their morphological characters but they do not interbreed.
(c) For e.g. Tiger, Leopard, Lion all three belong to same genus Panthera. They have common characters yet are different from each other because their genus is same but species is different.
(d) Another example is genus Solarium. Brinjal and potato both belong to this genus.
(iii) Family:
(a) It is one of the major hierarchial taxonomic rank.
(b) A family represents a group of closely related genera.
(c) For e.g. genera like Hibiscus, Gossypium, Sida, Bombax are included in same family Malvaceae.
(d) Although, there are many similarities between cat and dog, cat belongs to the family of leopards, tigers and lions, i.e. family Felidae and dog belongs to different family i.e. Canidae.
(iv) Cohort/Order:
(a) It is taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognised by nomenclature codes.
(b) An order is a group of closely related families showing definite affinities.
(c) Members belonging to same order but different families may show very few dissimilarities.
(d) For e.g. family Papaveraceae, Brassicaceae, Capparidaceae, etc with parietal placentation are grouped in order Parietales.
(e) Families of dogs and cats though are different, they belong to same order Carnivora.
(v) Class:
(a) The class is the distinct taxonomic rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name.
(b) Class is the assemblage of closely allied orders.
(c) For e.g. Orders Carnivora and order Primates belong to class Mammalia. Thus monkeys, gorillas, gibbons (Primates) and dogs, cats, tigers (Carnivora) belong to same class.
(vi) Division/ Phylum:
(a) The division is a category composed of related classes.
(b) For e.g. division Angiospermae includes two classes Dicotyledonae and Monocotyledonae.
(c) In animal classification, instead of division, the category Phylum is used.
(vii) Sub-kingdom:
(a) Different divisions having some similarities form sub-kingdom.
(b) The divisions Angiospermae and Gymnospermae forms the sub-kingdom Phanerogams or Spermatophyta (all seed producing plants).
(viii) Kingdom:
(a) It is the highest taxonomic category composed of different sub-kingdoms.
(b) For e.g. sub-kingdom Phanerogams and Cryptogams form the Plant kingdom or Plantae which includes all the plants, while all animals are included in kingdom Animalia.

Question 24.
Define nomenclature.
Answer:
The art of giving name to the organism is called nomenclature.
Question 25.
What is meant by vernacular name?
Answer:
Vernacular names are the names which are given to organisms in a particular region and language by local people.
Question 26.
What are the disadvantages of vernacular names of organisms?
Answer:
Disadvantages of vernacular names/ local names/ common names:
- Vernacular names do not indicate the necessary information about the organism.
- It does not indicate proper relationship of the organisms.
- Vernacular names are not universal, e.g. Pansy (Viola tricolor L.) grown in most European and American gardens has about 50 common english names. In Ayurveda, mango (Mangifera indica L.) is known by over 50 different names which are in Sanskrit language.
- Vernacular names have limited usage.
- Local names are different and confusing.
Question 27.
Who proposed binomial system of nomenclature?
Answer:
Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus proposed binomial system of nomenclature.

Question 28.
What is binomial nomenclature? Give the rules for binomial nomenclature.
Answer:
1. A system of nomenclature of plants and animals in which the scientific name consists of two words or parts or epithets is called binomial nomenclature.
2. This system of nomenclature was developed by Carl Linnaeus. He gave certain principles for this nomenclature in his book ‘Species Plantarum’.
Rules of binomial nomenclature:
- The name of the organism is composed of two Latin or Greek words.
- Generic epithet is a simple noun which should come first and always begin with a capital letter.
- Specific epithet is the descriptive adjective which should come later and begin with a small letter.
- The generic and specific epithet must be underlined separately if hand written or in italics when printed.
- The generic as well as specific epithet should not have less than three letters and more than thirteen letters.
- Usually the name of the author who names a plant or animal is also written in full or abbreviated form after scientific name. e.g. Mangifera indica L. Where L stands for Linnaeus.
Question 29.
In Mangifera indica L., what does letter ‘L’ indicate?
Answer:
In Mangifera indica L., letter L indicates author’s name i.e. Linnaeus.
Question 30.
Which kingdoms were included in two kingdom system of classification? Who introduced it?
Answer:
The two-kingdom system of classification included Kingdom plantae and Kingdom animalia. This system was introduced by Carl Linnaeus.
Question 31.
What was the drawback of two kingdom system of classification?
Answer:
Two kingdom system was found inadequate for classification of some organisms like bacteria, fungi, Euglena, etc.
Question 32.
Who suggested five kingdom system of classification?
Answer:
R.H. Whittaker suggested five kingdom system of classification.
Question 33.
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Vibrio | a. Rod-shaped |
| 2. Bacillus | b. Spherical |
| 3. Spirillum | c. Spiral shaped |
| d. Comma or kidney-shaped |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Vibrio | d. Comma or kidney-shaped |
| 2. Bacillus | a. Rod-shaped |
| 3. Spirillum | c. Spiral shaped |

Question 34.
Identify the different shapes of bacterial cells shown in the given figures:
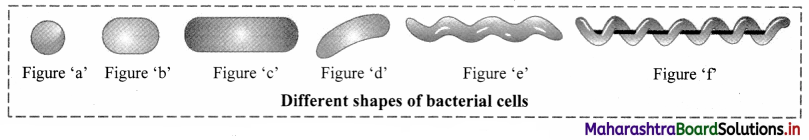
Answer:
Figure a: Coccus;
Figure b: Coccobacillus;
Figure c: Vibrio
Figure d: Bacillus;
Figure e: Spirillum; Figure f: Spirochete
Question 35.
What are Archaebacteria?
Answer:
- These are the most primitive type of bacteria.
- They are differentiated from other bacteria on the basis of their different cellular features.
- These bacteria are mostly found in the extreme environmental conditions, hence called extremophiles.
- Bacteria that can withstand high salinities are called halophiles, while those that withstand extreme temperature are known as thermophiles.
- Methanogenic bacteria found in gut of ruminants (cows and buffaloes) help in production of methane in biogas plants.
Question 36.
Why are archaebacteria called extremophiles?
Answer:
- These bacteria are mostly found in the extreme environments, hence called extremophiles.
- They have capacity to survive in very severe conditions.
- They are found in a variety of places from volcanic craters to salty lakes and hot springs.
Question 37.
Write in detail about Eubacteria.
Answer:
Eubaceria:
- These are commonly referred as true bacteria.
- They have cell wall made up of peptidoglycan.
- Eubacteria are mostly heterotrophic, few are autotrophic.
- The autotrophs can be photosynthetic like Chlorobium (Green sulphur bacteria) and Chromatium or chemosynthetic like sulphur bacteria.
- These are mostly multicellular filamentous forms living in fresh water.
- Filaments show heterocyst which helps in nitrogen fixation.
- The body is covered by mucilaginous sheath.
- The genetic material is typical prokaryotic.
- The photosynthetic pigments include Chl-a, Chl-b, carotenes and xanthophylls.
- Most of them are decomposers that help in breaking down large molecules in simple molecules or minerals.
Question 38.
Write a short note on useful and harmful bacteria.
Answer:
(i) Useful bacteria:
Most of the bacteria act as a decomposer. They breakdown large molecules in simple molecules or minerals. Examples of some useful bacteria:
Lactobacillus’. It helps in curdling of milk.
Azotobacter. It helps to fix nitrogen for plants.
Streptomyces: It is used in antibiotic production such as streptomycin.
Methanogens: These are used for production of methane (biogas) gas from dung.
Pseudomonas spp. and Alcanovorax borkumensis: These bacteria have the ability to destroy the pyridines and other chemicals. Hence, used to clear the oil spills.
(ii)Harmful bacteria:
This includes disease causing bacteria. They cause various diseases like typhoid, cholera, tuberculosis, tetanus, etc. Examples of some harmful bacteria:
Salmonella typhi: It is a causative organism of typhoid.
Vibrio cholerae: It causes cholera.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis’. It causes tuberculosis.
Clostridium tetani: It causes tetanus.
Clostridium spp.: It causes food poisoning.
Many forms of mycoplasma are pathogenic.
Agrobacterium , Erwinia, etc are the pathogenic bacteria causing plant diseases.
Animals and pets also suffer from bacterial infections caused by Brucella, Pastrurella, etc.

Question 39.
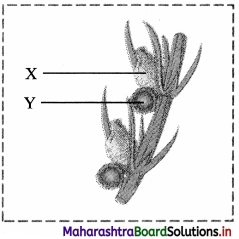
Identify label X and Y in the given figure of Cyanobacteria (Nostoc).
Answer:
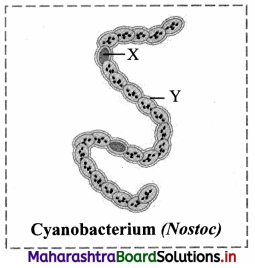
Question 40.
what is Mycoplasma?
Answer:
- These are the smallest living cells known.
- They lack cell wall.
- Many forms are pathogenic.
- They are resistant to common antibiotics because they lack cell wall.
Question 41.
Identify the following diagram, label it and write detail information in your words.
Answer:
The given figure represents Paramoecium.
Characteristics:
- It belongs to kingdom Protista. It is further classified as animal like protist.
- It lacks cell wall.
- It shows heterotrophic and holozoic nutrition.
- It is a ciliated protozoan where locomotion is due to cilia.
- It has gullet (a cavity) which opens on the cell surface.
Question 42.
Which kingdom shows link with all eukaryotic members?
Answer:
Kingdom Protista shows link with all eukaryotic kingdoms such as kingdom plantae, fungi and animalia.
Question 43.
Unicellular eukaryotic organisms are included in which kingdom?
Answer:
Unicellular eukaryotic organisms are included in kingdom Protista.

Question 44.
Give different types of Protists with examples.
Answer:
Protists are of different types:
(i) Plant like protists (Photosynthetic protists):
(a) They are termed as phytoplanktons, also known as Chrysophytes.
(b) They are autotrophic (photosynthetic) in nature and form major producers of ocean ecosystem.
(c)Most of them are referred as Diatoms because they have body wall made up of two soap-box like fitting silica covers. E.g. Diatoms.
1. Dinoflagellates:
(i) They are aquatic (mostly marine) and autotrophic (photosynthetic).
(ii) They have wide range of photosynthetic pigments which can be yellow, green, brown, blue and red.
(iii) The cell wall is made up of cellulosic stiff plates.
(iv) A pair of flagella is present, hence they are motile.
(v) They are responsible for famous ‘red tide’. E.g. Gonyaulax. It makes sea appear red.
2. Euglenoids:
(i) They lack cell wall but have a tough covering of proteinaceous pellicle.
(ii) Pellicle covering provides flexibility and contractibility to Euglena.
(iii) They possess two flagella, one short and other long.
(iv) They behave as heterotrophs in absence of light but possess pigments, similar to that of higher plants, for photosynthesis.
(ii) Animal like protists (Consumer protists):
(a) They are the primitive animal forms.
(b) They are also termed as protozoans.
(c) These are heterotrophic and lack cell wall.
(d) Amoeboid protozoans have pseudopodia as locomotory organs. E.g. Amoeba, Entamoeba.
Amoeba is free living form, but Entamoeba is endoparasite and causes amoebic dysentery.
(e) Flagellated protozoans have flagella as locomotory organ. E.g. Trypanosoma.
(f) Cilliated protozoans have cilia for locomotion. E.g. Paramoecium.
(g) Plasmodium is a Sporozoan protozoa. It causes malaria. It forms spores in one of its life stages.
(iii) Fungi like protists (Consumer decomposer protists):
(a) They form a group called Myxomycetes.
(b) They are saprophytic in nature, found on decaying leaves.
(c) Their cells aggregate to form a large cell mass called plasmodium.
(d) The spores of plasmodium are very tough and survive extreme conditions, e.g. Slime molds.
Question 45.
Why diatoms are used in filtration and polishing?
Answer:
Diatoms forms a substance called Diatomaceous earth. These are the shells of diatoms containing silica that left behind for many years. Diatomaceous earth is granular; hence it is used in polishing and filtration.

Question 46.
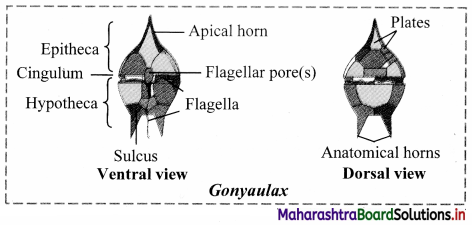
Label the given figures representing ventral and dorsal view of Gonyaulax.
Answer:
Question 47.
Identify the following diagram, label it and write detail information in your words.
Answer:
The given figure represents Euglena.
Characteristics:
(i) It belongs to kingdom Protista. It is further classified into euglenoids.
1. Dinoflagellates:
- They are aquatic (mostly marine) and autotrophic (photosynthetic).
- They have wide range of photosynthetic pigments which can be yellow, green, brown, blue and red.
- The cell wall is made up of cellulosic stiff plates.
- A pair of flagella is present, hence they are motile.
- They are responsible for famous ‘red tide’. E.g. Gonyaulax. It makes sea appear red.
2. Euglenoids:
- They lack cell wall but have a tough covering of proteinaceous pellicle.
- Pellicle covering provides flexibility and contractibility to Euglena.
- They possess two flagella, one short and other long.
- They behave as heterotrophs in absence of light but possess pigments, similar to that of higher plants, for photosynthesis.

Question 48.
Write the characteristics of Kingdom plantae.
Answer:
Characteristics of Kingdom plantae:
- Kingdom plantae is dominated by autotrophs.
- Some members are insectivorous plants. E.g. Venus fly trap, pitcher plant, bladderwort, while some are heterotrophic parasitic members like Cuscuta.
- Members of this kingdom are eukaryotic, multicellular, having eukaryotic cells containing chlorophyll.
- Their cell wall is mostly made up of cellulose.
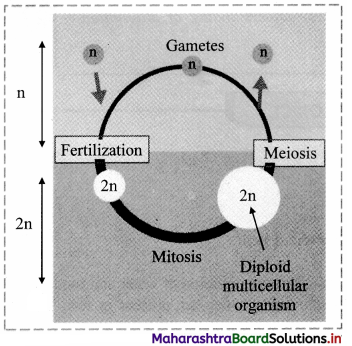
- They exhibit alternation of generation i.e. life cycle has two distinct phases.
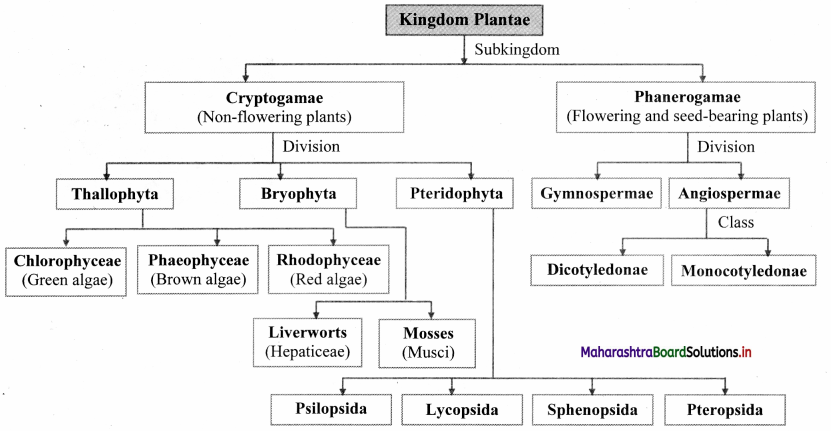
- It is divided into two major groups Cryptogams and Phanerogams.
Question 49.
Give the general characters of Kingdom Fungi with examples.
Answer:
General characters of Kingdom Fungi:
1. Type of organisms: It is a unique kingdom of eukaryotic heterotrophic organisms, showing extracellular digestion. They may be unicellular or multicellular and filamentous. These are commonly found in warm and humid places.
2. Nucleus: The cells may be multinucleate or uninucleate.
3. Body: Multicellular organisms consist of a body called mycelium in which a number of thread or fibre-like structures called hyphae are present. The hyphae may be with septa (septate) or without septa (aseptate). The non-septate multinucleated hyphae are called coenocytic hyphae.
4. Cell wall: The cell wall in fungi is composed of chitin or fungal cellulose.
5. Cell organelles: The fungi contain well organized membrane bound cell organelles except the chloroplasts.
6. Nutrition: The fungi exhibit heterotrophic mode of nutrition and most of the members are saprophytes and absorb food which is decomposed (digested) outside. Some are parasitic or predators.
7. Reproduction: They reproduce both sexually as well as asexually. Asexual reproduction takes place by fragmentation, fission and budding.
8. Some fungi are symbiotic. These fungi either live with algae as lichens or as mycorrhiza in association with roots of higher plants.
Question 50.
Identify the following diagram, label it and write detail information in your words.
Answer:
The given figure represents Mucor.
Characteristics:
- It belongs to class phycomycetes of kingdom fungi.
- Mycelium is made up of aseptate coenocytic hyphae.
- It commonly grows on decaying fruits,vegetables, in soil, on various food- stuff-like bread, jellies, jams, etc.
- In favourable conditions mucor reproduces asexually by formation of spores within sporangia. It can also reproduce by sexual means.
Question 51.
Identify the following diagram, label it and write detail information in your words.
Answer:
The given figure represents Aspergillus.
Characteristics:
- It belongs to class ascomycetes of kingdom Fungi.
- It is multicellular.
- The hyphae are branched and septate.
- Aspergillus grows well in soil, decaying vegetation, hay, dung, on
- plants, etc.
- Asexual reproduction takes place by spores called conidia which are produced at the tip of hyphae called conidiophores.

Question 52.
Identify the following diagram, label it and write detail information in your words.
Answer:
The given figure represents Agaricus (Mushroom).
Characteristics:
- It belongs to class basidiomycetes of kingdom Fungi.
- It has branched septate hyphae.
- It grows in soil, on rotten wood, etc.
- It is edible and rich in proteins.
- Vegetative reproduction takes place by fragmentation.
Question 53.
Explain how fungi exhibit heteromorphic mode of nutrition?
Answer:
- Most of the members of kingdom fungi are saprophytes.
- They absorb food which is decomposed (digested) outside.
- Some are parasites or predators and some are symbiotic.
- In fungi, chloroplast is absent, thus they cannot synthesize their own food by photosynthesis. Due to this, fungi exhibit heteromorphic mode of nutrition.
Quesiton 54.
Identify the given picture and explain in detail.
Answer:
The given picture represents Lichens.
- Lichen is an association of an alga and fungus.
- It is the best example of symbiosis or mutualism.
- They are found in extreme environments like snow clad poles.
- The algal component of lichen is phycobiont, mostly belongs to cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) or green algae and fungal component is mycobiont.
- Algae prepares the food and supplies it to the fungal component, while fungal component provides shelter to algae and also absorbs water and minerals for algae.
- The association is intense and it is difficult to identify them as separate living beings.
- They are very sensitive to pollutions, hence not found in polluted areas.
- They are used as pollution indicators.
- They play an important role in soil formation by using specific acid productions.
[Note: Lichens cannot be categorized as acellular organisms]
Question 55.
Write the general characters of Kingdom Animalia with examples.
Answer:
General characters of Kingdom Animalia:
- Types of organisms: The organisms are multicellular and eukaryotic.
- Habitat: The organisms may be aquatic, terrestrial, amphibious or aerial in habitat.
- Cell organelles: The organisms do not possess cell wall, plastids and central vacuole.
- Locomotion: Majority of the animals are motile. However, few like sponges are sedentary.
- Sense orgAnswer: They possess sense organs, nervous system and respond to stimuli by exhibiting certain behaviour.
- Reproduction: They mostly reproduce sexually by producing gametes, while some can reproduce asexually.
- Nutrition: They are heterotrophic, mostly holozoic, sometimes parasitic.
- Growth: It is determinate, (follow definite pattern)

Question 56.
Observe and discuss:
Complete the following table on the basis of previous knowledge.
| Characters | Monera | Protista | Fungi | Plantae | Animalia |
| Cell type | Prokaryotic | Eukaryotic | Eukaryotic | Eukaryotic | Eukaryotic |
| Cell wall | | Present in some organisms | | Present (cellulose) | |
| Nuclear membrane | Absent | Present | Present | | Present |
| Body organization | Unicellular | | Multicellular/ loose tissue | Tissue /organ | Tissue /organ system |
| Mode of nutrition | | Autotrophic Photosynthetic, Heterotrophic | | Autotrophic (Photosynthetic) | |
| Ecological role | Decomposers | | Decomposers | | Consumers |
Answer:
| Characters | Monera | Protista | Fungi | Plantae | Animalia |
| Cell type | Prokaryotic | Eukaryotic | Eukaryotic | Eukaryotic | Eukaryotic |
| Cell wall | Present (Peptidoglycan) | Present in some organisms | Present (chitin) | Present (cellulose) | Absent |
| Nuclear membrane | Absent | Present | Present | Present | Present |
| Body organization | Unicellular | Unicellular | Multicellular/ loose tissue | Tissue /organ | Tissue /organ system |
| Mode of nutrition | Heterotrophic (saprophytic/ parasitic) Autotrophic (Photoautotrophic/ Chemoautotrophic) | Autotrophic Photosynthetic, Heterotrophic | Heterotrophic (saprophytic/ parasitic) | Autotrophic (Photosynthetic) | Heterotrophic (holozoic) |
| Ecological role | Decomposers | Producers and consumers | Decomposers | Producers | Consumers |
Question 57.
Who referred virus as ‘contagium vivum fluidum’?
Answer:
M. W. Beijerinck referred virus as ‘contagium vivum fluidum (infectious living fluid).’
Question 58.
Who demonstrated that viruses are inert outside the host cell and can be crystallised?
Answer:
Stanley demonstrated that viruses are inert and can be crystallised.
[Note: Students can scan the adjacent QR code for detail classification of given tree diagram.]

Question 59.
What is the structure of virus?
Answer:
- Viruses are acellular and ultramicroscopic.
- The genetic material in viruses is either single or double-stranded RNA or double-stranded DNA.
- Their genetic material is protected by a protein coat called capsid.
- Capsid is made up of smaller units called capsomeres.
- Capsomeres are arranged in polyhedral or helical forms thus, imparting that particular shape to the virus.
Question 60.
Give examples of:
1. Diseases caused by viruses in plants:
2. Diseases caused by viruses in animals:
Answer:
1. Diseases caused by viruses in plants: Leaf curling, yellowing, mosaic formation, etc.
2. Diseases caused by viruses in animals: Swine flu, Small pox, mumps, herpes, common cold, AIDS, etc.
Question 61.
Write a short note on viroids.
Answer:
Viroids:
- These are mainly plant pathogens.
- Viroids were discovered by Theodor Diener.
- The first viroid discovered was PSTV (Potato spindle tuber viroid) which causes a disease in potato.
- Viroids are very small, circular, single stranded RNA which are without any protein coat.
- Viroids are smaller in size than viruses.
Question 62.
Apply Your Knowledge:
Question 1.
In your laboratory you accidentally discover an old permanent slide without a label. You are curious to identify it, and you place the slide under the microscope. You observe the following features:
1. Well-organized nucleus
2. Unicellular
3. Biflagellate – one placed longitudinally and the other transversely.
Answer:
All unicellular eukaryotes form a connecting link between prokaryotic Kingdom Monera and complex eukaryotic Kingdoms Plantae, Fungi and Animalia. Since the specimen shows the presence of two flagella, one placed longitudinally and the other transversely, the given organism can be dinoflagellate and has to be placed under Kingdom Protista.

Question 2.
Name the following:
1. The kingdom which includes the smallest living forms.
2. The protists which behave as heterotroph in absence of light but performs photosynthesis in presence of light
3. These are infectious single stranded RNA, smaller than virus
Answer:
1. Kingdom Monera
2. Euglena
3. Viroids
Question 63.
Quick Review
Answer:
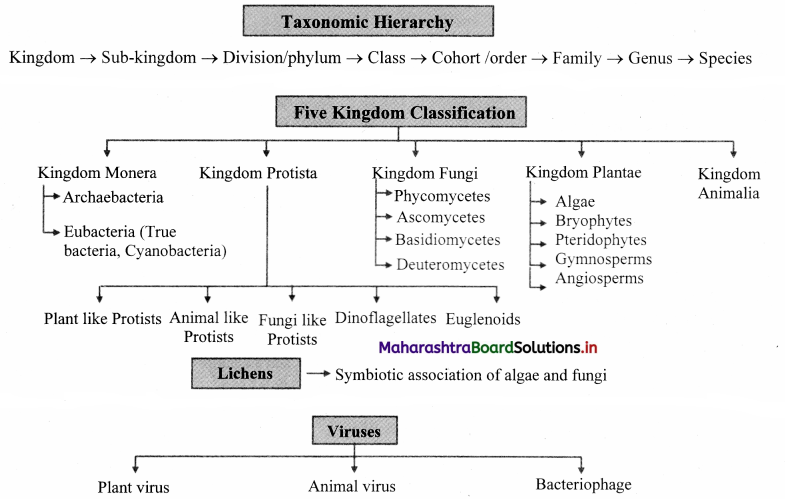
Taxonomic Hierarchy
Kingdom → Sub-kingdom → Division/phylum → Class → Cohort /order → Family → Genus → Species
Question 64.
Exercise
Question 1.
Define Systematics.
Answer:
Systematics is the study of kinds and diversity of organisms and their comparative and evolutionary relationship.
Question 2.
What is classification?
Answer:
Classification is the arrangement of organisms or groups of organisms in distinct categories in accordance with a particular and well-established plan.

Question 3.
Explain different methods of classification.
Answer:
The three types of classification systems are:
(i) Artificial system:
(a) It is based on few visible, easily observable characters, which are non-evolutionary such as habit, colour, form, etc.
(b) It does not consider the affinities (relationships) among different organisms.
E.g. Linnaeus system of classification.
(ii) Natural system:
It is based on objectively significant characters with respect to their affinities with other organisms.
E.g. Bentham and Hooker’s system of classification.
(iii) Phylogenetic system:
It is based on the phylogenetic relationship between different organisms with respect to common evolutionary descent (ancestor).
E.g. Engler and Prantl’s classification.
Question 4.
Domain eukarya has which cells?
Answer:
Domain Eukarya has eukaryotic cells.
Question 5.
Name three domains of life.
Answer:
Three domains of life are Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya.

Question 6.
Write a short note on chemotaxonomy.
Answer:
1. It is method of biological classification based on the similarities and differences in structure of certain chemical compounds present among the organisms being classified.
2. Thus, it is a classification based on chemical constituents of organisms.
3. For e.g. Cell wall with peptidoglycan is present in Bacteria while it is absent in Archaea.
Among Eukarya, fungi have chitinous cell wall, while plants have cellulosic cell wall.
Question 7.
What is numerical taxonomy? Who proposed it?
Answer:
Numerical taxonomy:
- It is based on quantification of characters and develops an algorithm for classification.
- The aim of this was to create a taxonomy using numeric algorithms like cluster analysis rather than using subjective evaluation of their properties.
- It was proposed by Sokel and Sneath in 1963.
Question 8.
Write a note on cladogram?
Answer:
1. It is a representation of hypothetical relationship denoting a comparison of organisms and their common ancestors.
2. It has a typical branching pattern.
Question 9.
Write a short note on phylogeny.
Answer:
Phylogeny:
- It is the evolutionary relationship of organism.
- It is an important tool in classification as it considers not merely the morphological status but also the relationship of one group of organisms with other groups of life.
- The system helps to understand the evolution and also focuses on the similarities of their metabolic functioning.
- Woese’s three domain concept, as well as Whittaker’s five-kingdom system, are examples of phylogenetic relationship.
Question 10.
Explain DNA barcoding.
Answer:
DNA barcoding is a new method for identification of any species based on its DNA sequence, which is obtained from a tiny tissue sample of the organism under study.
DNA barcoding helps to study newly identified species as well as understanding ecological and evolutionary relationships between living organisms.
The process of DNA barcoding includes two basic steps:
(i) Collecting DNA barcode data of known species.
(ii) Matching the barcode sequence of the unknown sample against the barcode library for identification.
The applications of DNA barcoding are as follows:
- It helps to protect endangered species.
- It plays an important role in preservation of natural resources.
- It is also used for pest control in agriculture.
- It is used for identification of disease vectors.
- It is used for authentication of natural health products.
- It is also used for identification of medicinal plants.

Question 11.
Explain the term taxonomic category.
Answer:
- Category is a rank or level in the hierarchial classification of organisms.
- Each category is referred to as a unit of classification.
- Category is a part of taxonomic arrangements hence, called taxonomic category.
- All categories together constitute the taxonomic hierarchy.
Question 12.
Give the classification of cobra.
Answer:
Cobra
Question 13.
Give the classification of china-rose.
Answer:
China Rose
Question 14.
What is taxon? Give any one example of it.
Answer:
1. Taxon is a group of living organisms of any rank in the system of classification.
2. In plant kingdom, each taxonomic group such as angiospermae, dicotyledonae, polypetalae, malvaceae represents a taxon.

Question 15.
Which are the units of classification?
Answer:
(i) Species:
(a) Species is the principal natural taxonomic unit, ranking below a genus.
(b) It is a group of organisms that can interbreed under natural condition to produce fertile offspring.
(c) It was thought to be an indivisible, stable and static unit.
(d) However, in the modem taxonomy, subdivision of species such as sub-species, varities and populations are seen and given more importance.
(ii) Genus:
(a) Genus is a taxonomic rank or category larger than species used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms.
(b) Genus is a group of species bearing close resemblance to one another in their morphological characters but they do not interbreed.
(c) For e.g. Tiger, Leopard, Lion all three belong to same genus Panthera. They have common characters yet are different from each other because their genus is same but species is different.
(d) Another example is genus Solarium. Brinjal and potato both belong to this genus.
(iii) Family:
(a) It is one of the major hierarchial taxonomic rank.
(b) A family represents a group of closely related genera.
(c) For e.g. genera like Hibiscus, Gossypium, Sida, Bombax are included in same family Malvaceae.
(d) Although, there are many similarities between cat and dog, cat belongs to the family of leopards, tigers and lions, i.e. family Felidae and dog belongs to different family i.e. Canidae.
(iv) Cohort/Order:
(a) It is taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognised by nomenclature codes.
(b) An order is a group of closely related families showing definite affinities.
(c) Members belonging to same order but different families may show very few dissimilarities.
(d) For e.g. family Papaveraceae, Brassicaceae, Capparidaceae, etc with parietal placentation are grouped in order Parietales.
(e) Families of dogs and cats though are different, they belong to same order Carnivora.
(v) Class:
(a) The class is the distinct taxonomic rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name.
(b) Class is the assemblage of closely allied orders.
(c) For e.g. Orders Carnivora and order Primates belong to class Mammalia. Thus monkeys, gorillas, gibbons (Primates) and dogs, cats, tigers (Carnivora) belong to same class.
(vi) Division/ Phylum:
(a) The division is a category composed of related classes.
(b) For e.g. division Angiospermae includes two classes Dicotyledonae and Monocotyledonae.
(c) In animal classification, instead of division, the category Phylum is used.
(vii) Sub-kingdom:
(a) Different divisions having some similarities form sub-kingdom.
(b) The divisions Angiospermae and Gymnospermae forms the sub-kingdom Phanerogams or Spermatophyta (all seed producing plants).
(viii) Kingdom:
(a) It is the highest taxonomic category composed of different sub-kingdoms.
(b) For e.g. sub-kingdom Phanerogams and Cryptogams form the Plant kingdom or Plantae which includes all the plants, while all animals are included in kingdom Animalia.

Question 16.
Explain the following terms by giving one example of each:
1. Sub-kingdom
2. Genus
3. Order
Answer:
1. Sub-kingdom:
(a) Different divisions having some similarities form sub-kingdom.
(b) The divisions Angiospermae and Gymnospermae forms the sub-kingdom Phanerogams or Spermatophyta (all seed producing plants).
2. Genus:
(a) Genus is a taxonomic rank or category larger than species used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms.
(b) Genus is a group of species bearing close resemblance to one another in their morphological characters but they do not interbreed.
(c) For e.g. Tiger, Leopard, Lion all three belong to same genus Panthera. They have common characters yet are different from each other because their genus is same but species is different.
(d) Another example is genus Solarium. Brinjal and potato both belong to this genus.
3. Cohort/Order:
(a) It is taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognised by nomenclature codes.
(b) An order is a group of closely related families showing definite affinities.
(c) Members belonging to same order but different families may show very few dissimilarities.
(d) For e.g. family Papaveraceae, Brassicaceae, Capparidaceae, etc with parietal placentation are grouped in order Parietales.
(e) Families of dogs and cats though are different, they belong to same order Carnivora.
Question 17.
‘A family represents a group of closely related genera’. Give one example to justify the statement.
Answer:
(c) For e.g. genera like Hibiscus, Gossypium, Sida, Bombax are included in same family Malvaceae.

Question 18.
What does letter ‘L’ indicates in Man gif era indica L., ?
Answer:
In Mangifera indica L., letter L indicates author’s name i.e. Linnaeus.
Question 19.
1. Define binomial nomenclature system.
2. Who proposed it?
3. Why a unique name for a particular individual is essential in a multilingual country like India?
Answer:
1. The name of the organism is composed of two Latin or Greek words.
2. Generic epithet is a simple noun which should come first and always begin with a capital letter.
3. The generic and specific epithet must be underlined separately if hand written or in italics when printed.
Question 20.
Why is binomial nomenclature useful for classification of organisms?
Answer:
Binomial nomenclature is important because:
- The binomials are simple, meaningful and precise.
- They are standard since they do not change from place to place.
- These names avoid confusion and uncertainty created by local or vernacular names. The organisms are known by the same name throughout the world.
- The binomials are easy to understand and remember.
- It indicates phylogeny (evolutionary history) of organisms.
- It helps to understand inter-relationship between organisms.
Question 21.
Which are the two kingdoms of organisms given by Carl Linnaeus? What was the drawback of this system?
Answer:
The two-kingdom system of classification included Kingdom plantae and Kingdom animalia. This system was introduced by Carl Linnaeus. Two kingdom system was found inadequate for classification of some organisms like bacteria, fungi, Euglena, etc.

Question 22.
Name the five kingdoms given by Whittaker?
Answer:
Five kingdom system of classification was proposed by R.H. Whittaker in 1969. This system shows the phylogenetic relationship between the organisms.
The five kingdoms are:
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Fungi
- Kingdom Animalia
Question 23.
Unicellular prokaryotic organisms are included in which kingdom?
Answer:
(i) Size: The organisms included in this kingdom are microscopic, unicellular and prokaryotic.
Question 24.
Explain kingdom Monera with the help of given points:
i. Nucleus
ii. Reproduction
iii. Nutrition
Answer:
(i) Nucleus: These organisms do not have well defined nucleus. DNA exists as a simple double stranded circular single chromosome called as nucleoid. Apart from the nucleoid they often show presence of extrachromosomal DNA which is small circular called plasmids.
(ii) Reproduction: The mode of reproduction is asexual or with the help of binary fission or budding. Very rarely, sexual reproduction occurs by conjugation method.
(iii) Nutrition: Majority are heterotrophic, parasitic or saprophytic in nutrition. Few are autotrophic that can be either photoautotrophs or chemoautotrophs.
Question 25.
Give examples of archaebacteria and eubacteria.
Answer:
Examples:
Archaebacteria: e.g. Methanobacillus, Thiobacillus, etc.
Eubacteria: e.g. Chlorobium, Chromatium, and Cyanobacteria e.g. Nostoc, Azotobacter, etc.
Question 26.
What is mycoplasma?
Answer:
1. These are the smallest living cells known.
2. They lack cell wall.
3. Many forms are pathogenic.
4. They are resistant to common antibiotics because they lack cell wall.

Question 27.
Enlist different types of protozoa.
Answer:
(ii) Animal like protists (Consumer protists):
(a) They are the primitive animal forms.
(b) They are also termed as protozoans.
(c) These are heterotrophic and lack cell wall.
(d) Amoeboid protozoans have pseudopodia as locomotory organs. E.g. Amoeba, Entamoeba.
Amoeba is free living form, but Entamoeba is endoparasite and causes amoebic dysentery.
(e) Flagellated protozoans have flagella as locomotory organ. E.g. Trypanosoma.
(f) Cilliated protozoans have cilia for locomotion. E.g. Paramoecium.
(g) Plasmodium is a Sporozoan protozoa. It causes malaria. It forms spores in one of its life stages.
Question 28.
Which are the different types of protists?
Answer:
Protists are of different types:
(i) Plant like protists (Photosynthetic protists):
(a) They are termed as phytoplanktons, also known as Chrysophytes.
(b) They are autotrophic (photosynthetic) in nature and form major producers of ocean ecosystem.
(c)Most of them are referred as Diatoms because they have body wall made up of two soap-box like fitting silica covers. E.g. Diatoms.
1. Dinoflagellates:
(i) They are aquatic (mostly marine) and autotrophic (photosynthetic).
(ii) They have wide range of photosynthetic pigments which can be yellow, green, brown, blue and red.
(iii) The cell wall is made up of cellulosic stiff plates.
(iv) A pair of flagella is present, hence they are motile.
(v) They are responsible for famous ‘red tide’. E.g. Gonyaulax. It makes sea appear red.
2. Euglenoids:
(i) They lack cell wall but have a tough covering of proteinaceous pellicle.
(ii) Pellicle covering provides flexibility and contractibility to Euglena.
(iii) They possess two flagella, one short and other long.
(iv) They behave as heterotrophs in absence of light but possess pigments, similar to that of higher plants, for photosynthesis.
(ii) Animal like protists (Consumer protists):
(a) They are the primitive animal forms.
(b) They are also termed as protozoans.
(c) These are heterotrophic and lack cell wall.
(d) Amoeboid protozoans have pseudopodia as locomotory organs. E.g. Amoeba, Entamoeba.
Amoeba is free living form, but Entamoeba is endoparasite and causes amoebic dysentery.
(e) Flagellated protozoans have flagella as locomotory organ. E.g. Trypanosoma.
(f) Cilliated protozoans have cilia for locomotion. E.g. Paramoecium.
(g) Plasmodium is a Sporozoan protozoa. It causes malaria. It forms spores in one of its life stages.
(iii) Fungi like protists (Consumer decomposer protists):
(a) They form a group called Myxomycetes.
(b) They are saprophytic in nature, found on decaying leaves.
(c) Their cells aggregate to form a large cell mass called plasmodium.
(d) The spores of plasmodium are very tough and survive extreme conditions, e.g. Slime molds.
Question 29.
What are dinoflagellates?
Answer:
Protists are of different types:
(i) Plant like protists (Photosynthetic protists):
(a) They are termed as phytoplanktons, also known as Chrysophytes.
(b) They are autotrophic (photosynthetic) in nature and form major producers of ocean ecosystem.
(c)Most of them are referred as Diatoms because they have body wall made up of two soap-box like fitting silica covers. E.g. Diatoms.
1. Dinoflagellates:
(i) They are aquatic (mostly marine) and autotrophic (photosynthetic).
(ii) They have wide range of photosynthetic pigments which can be yellow, green, brown, blue and red.
(iii) The cell wall is made up of cellulosic stiff plates.
(iv) A pair of flagella is present, hence they are motile.
(v) They are responsible for famous ‘red tide’. E.g. Gonyaulax. It makes sea appear red.
Question 30.
Explain animal like protists.
Answer:
(ii) Animal like protists (Consumer protists):
(a) They are the primitive animal forms.
(b) They are also termed as protozoans.
(c) These are heterotrophic and lack cell wall.
(d) Amoeboid protozoans have pseudopodia as locomotory organs. E.g. Amoeba, Entamoeba.
Amoeba is free living form, but Entamoeba is endoparasite and causes amoebic dysentery.
(e) Flagellated protozoans have flagella as locomotory organ. E.g. Trypanosoma.
(f) Cilliated protozoans have cilia for locomotion. E.g. Paramoecium.
(g) Plasmodium is a Sporozoan protozoa. It causes malaria. It forms spores in one of its life stages.
Question 31.
Give examples of insectivorous plants.
Answer:
(ii) Some members are insectivorous plants. E.g. Venus fly trap, pitcher plant, bladderwort, while some are heterotrophic parasitic members like Cuscuta.
Question 32.
What are the two major group in which kingdom plantae is divided?
Answer:
(vi) It is divided into two major groups Cryptogams and Phanerogams.

Question 33.
Explain fungi like protist.
Answer:
(iii) Fungi like protists (Consumer decomposer protists):
(a) They form a group called Myxomycetes.
(b) They are saprophytic in nature, found on decaying leaves.
(c) Their cells aggregate to form a large cell mass called plasmodium.
(d) The spores of plasmodium are very tough and survive extreme conditions, e.g. Slime molds.
Question 34.
What are the characteristics of euglenoids?
Answer:
Euglenoids:
- They lack cell wall but have a tough covering of proteinaceous pellicle.
- Pellicle covering provides flexibility and contractibility to Euglena.
- They possess two flagella, one short and other long.
- They behave as heterotrophs in absence of light but possess pigments, similar to that of higher plants, for photosynthesis.
Question 35.
Explain in detail general characters of Kingdom Fungi.
Answer:
Euglenoids:
- They lack cell wall but have a tough covering of proteinaceous pellicle.
- Pellicle covering provides flexibility and contractibility to Euglena.
- They possess two flagella, one short and other long.
- They behave as heterotrophs in absence of light but possess pigments, similar to that of higher plants, for photosynthesis.
Question 36.
Why do fungi exhibit heterotrophic mode of nutrition?
Answer:
Nutrition: The fungi exhibit heterotrophic mode of nutrition and most of the members are saprophytes and absorb food which is decomposed (digested) outside. Some are parasitic or predators.
Question 37.
Name the four classes of kingdom fungi.
Answer:
Fungi are classified into four types on the basis of their structure, mode of spore formation and fruiting bodies as follows:
1. Phycomycetes:
Members of this class are commonly called as algal fungi.
These are consisting of aseptate coenocytic hyphae.
They grow well in moist and damp places on decaying organic matter as well as in aquatic habitats or as parasites on plants.
e.g. Mucor, Rhizopus (bread mold), Albugo (parasitic fungus on mustard).
2. Ascomycetes:
These are commonly called as sac fungi.
These are multicellular. Rarely they are unicellular (e.g. Yeast).
Hyphae are branched and septate.
They can be decomposers, parasites or coprophilous (grow on dung).
Some varieties of this class are consumed as delicacies such as morels and truffles.
Neurospora is useful in genetic and biochemical assays.
e.g. Aspergillus, Penicillium, Neurospora, Claviceps, Saccharomyces (unicellular ascomycetes).
3. Basidiomycetes:
These are commonly called as club fungi.
They have branched septate hyphae.
e.g. Agaricus (mushrooms), Ganoderma (bracket fungi), Ustilago (smuts), Puccinia (rusts), etc.
4. Deuteromycetes:
It is a group of fungi which are known to reproduce only asexually.
They are commonly called imperfect fungi.
They are mainly decomposers, while few are parasitic, e.g. Alternaria.

Question 38.
Explain in detail the class of kingdom fungi which includes yeast.
Answer:
Ascomycetes:
- These are commonly called as sac fungi.
- These are multicellular. Rarely they are unicellular (e.g. Yeast).
- Hyphae are branched and septate.
- They can be decomposers, parasites or coprophilous (grow on dung).
- Some varieties of this class are consumed as delicacies such as morels and truffles.
- Neurospora is useful in genetic and biochemical assays.
e.g. Aspergillus, Penicillium, Neurospora, Claviceps, Saccharomyces (unicellular ascomycetes).
Question 39.
Why deuteromycetes are called imperfect fungi?
Answer:
Deuteromycetes:
- It is a group of fungi which are known to reproduce only asexually.
- They are commonly called imperfect fungi.
- They are mainly decomposers, while few are parasitic, e.g. Alternaria.
Question 40.
What are lichens?
Answer:
The given picture represents Lichens.
- Lichen is an association of an alga and fungus.
- It is the best example of symbiosis or mutualism.
- They are found in extreme environments like snow clad poles.
- The algal component of lichen is phycobiont, mostly belongs to cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) or green algae and fungal component is mycobiont.
- Algae prepares the food and supplies it to the fungal component, while fungal component provides shelter to algae and also absorbs water and minerals for algae.
- The association is intense and it is difficult to identify them as separate living beings.
- They are very sensitive to pollutions, hence not found in polluted areas.
- They are used as pollution indicators.
- They play an important role in soil formation by using specific acid productions.
[Note: Lichens cannot be categorized as acellular organisms]

Question 41.
What is the fungal partner in lichen called?
Answer:
The algal component of lichen is phycobiont, mostly belongs to cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) or green algae and fungal component is mycobiont.
Question 42.
What is the algal partner in lichen called?
Answer:
The algal component of lichen is phycobiont, mostly belongs to cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) or green algae and fungal component is mycobiont.
Question 43.
Why lichens are considered as pollution indicators?
Answer:
They are very sensitive to pollutions, hence not found in polluted areas.
Question 44.
Holozoic mode of nutrition is observed in which kingdom?
Answer:
Nutrition: They are heterotrophic, mostly holozoic, sometimes parasitic.
Question 45.
Who coined the name contagium vivum fluidum?
Answer:
M. W. Beijerinck referred virus as ‘contagium vivum fluidum (infectious living fluid).’
Question 46.
What is the genetic material in viruses?
Answer:
Viruses possess their own genetic material in the form of either DNA or RNA, but never both. The genetic material in viruses is covered by a protein coat (capsid), hence called nucleoprotein.
Question 47.
What are bacteriophages?
Answer:
Bacteriophage:
(a) They have tadpole-like shape.
(b) They infect bacteria and hence are called as bacteriophage.
(c) Bacteriophages were discovered by Twort.
(d) Bacteriophages have double stranded DNA as the genetic material.
(e) Its body consists of head, collar and tail.
Question 48.
Give example of viral disease caused in humans.
Answer:
Diseases caused by viruses in animals: Swine flu, Small pox, mumps, herpes, common cold, AIDS, etc.
Question 49.
Who discovered viroids?
Answer:
Viroids were discovered by Theodor Diener.
Question 50.
What is the genetic material in viroids?
Answer:
Viroids are very small, circular, single stranded RNA which are without any protein coat.

Question 51.
Multiplechoice Questions:
Question 1.
The term ‘Taxonomy’ was coined by
(A) Carl Linnaeus
(B) A.P. de Candolle
(C) Carl Woese
(D) R.H Whittaker
Answer:
(B) A.P. de Candolle
Question 2.
Arrangement of organisms into distinct categories is called
(A) Taxonomy
(B) Taxon
(C) Nomenclature
(D) Classification
Answer:
(D) Classification
Question 3.
The domain known for its survival in very extreme condition like high temperature, salinity, etc. is
(A) Eukarya
(B) Archaea
(C) Bacteria
(D) Cyanobacteria
Answer:
(B) Archaea
Question 4.
Kingdom Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia are included under domain
(A) Eukarya
(B) Archaea
(C) Bacteria
(D) Cyanobacteria
Answer:
(A) Eukarya
Question 5.
Which system of classification was based upon easily observable characters?
(A) Natural
(B) Phylogenetic
(C) Artificial
(D) DNA barcoding
Answer:
(C) Artificial
Question 6.
System based upon chemical constituents of organisms is
(A) Cladogram
(B) Phylogeny
(C) DNA barcoding
(D) chemotaxonomy
Answer:
(D) chemotaxonomy

Question 7.
Woese’s three domain and Whittaker’s five kingdom concept is based upon
(A) Visible characters
(B) Phylogenetic relationship
(C) Numerical taxonomy
(D) DNA barcoding
Answer:
(B) Phylogenetic relationship
Question 8.
A taxonomic group of any rank is called
(A) grade
(B) category
(C) variety
(D) taxon
Question 9.
One of the following has correct descending sequence hierarchy
(A) class, division, order, family
(B) division, class, order, family
(C) order, family, class, division
(D) family, order, class, genus
Answer:
(B) division, class, order, family
Question 10.
Which among the following is an order?
(A) Malvales
(B) Polypetalae
(C) Angiospermae
(D) Hibiscus
Answer:
(A) Malvales
Question 11.
The basic unit of classification
(A) genus
(B) species
(C) kingdom
(D) family
Answer:
(B) species

Question 12.
As we go higher in taxonomical ladder i.e. from species to kingdom, the number of common characters
(A) remains constant
(B) goes on increasing
(C) goes on decreasing
(D) increases till class and then starts decreasing
Answer:
(C) goes on decreasing
Question 13.
Group of species which resemble closely in morphological characters but do not interbreed is called
(A) genus
(B) species
(C) family
(D) order
Answer:
(A) genus
Question 14.
Highest category of taxonomy is
(A) species
(B) class
(C) order
(D) kingdom
Answer:
(D) kingdom
Question 15.
Carl Linnaeus introduced binomial system of nomenclature in his book
(A) Species Plantarum
(B) ICBN
(C) Plantarum Linnaeus
(D) Species Linnaeus
Answer:
(A) Species Plantarum
Question 16.
Before 2011, scientific names were confirmed by
(A) ICBN
(B) IBC
(C) ICZN
(D) IBA
Answer:
(A) ICBN

Question 17.
Which code is also known as “Shenzhen code”?
(A) ICBN
(B) IBC
(C) ICZN
(D) IBA
Answer:
(B) IBC
Question 18.
In Helianthus annuus, ‘annuus ’ indicates
(A) genus
(B) species
(C) family
(D) class
Answer:
(B) species
Question 19.
In five kingdom classification, unicellular prokaryotes are included in kingdom
(A) Protista
(B) Fungi
(C) Monera
(D) Animalia
Answer:
(C) Monera
Question 20.
The bacteria that can withstand high salinities are called
(A) Saltophiles
(B) Thermophiles
(C) Halophiles
(D) Psychrophiles
Answer:
(C) Halophiles
Question 21.
The bacteria that can withstand extreme temperature are known as
(A) Saltophiles
(B) thermophiles
(C) Halophiles
(D) both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(B) thermophiles
Question 22.
Bacillus is
(A) comma shaped
(B) rod shaped
(C) kidney shaped
(D) spiral
Answer:
(B) rod shaped

Question 23.
Which organism belongs Monera?
(A) Cyanobacteria
(B) Mushroom
(C) Euglena
(D) Moss
Answer:
(A) Cyanobacteria
Question 24.
_________ is an example of plant like protists.
(A) Diatoms
(B) Ustilago
(C) Entamoeba
(D) Euglena
Answer:
(A) Diatoms
Question 25.
Fungi like protist are also called as ________.
(A) Myxomycetes
(B) Mycomycetes
(C) Mycoplasm
(D) Yeast
Answer:
(A) Myxomycetes
Quesiton 26.
The body of a fungus is made up of
(A) hyphae
(B) sporangium
(C) rhizoid
(D) fruiting body
Answer:
(A) hyphae
Question 27.
Agaricus belongs to class
(A) Deuteromycetes
(B) Phycomycetes
(C) Basidiomycetes
(D) Ascomycetes
Answer:
(C) Basidiomycetes

Question 28.
Which of the following is harmful fungus that causes diseases in plants?
(A) Puccinia
(B) Mushroom
(C) Yeast
(D) Streptomyces
Answer:
(A) Puccinia
Question 29.
Which of the following is NOT true about kingdom animalia?
(A) Members are heterotrophs.
(B) They lack chlorophyll as well as cell wall.
(C) Growth is indeterminate.
(D) Most of the members have capacity of locomotion.
Answer:
(C) Growth is indeterminate.
Question 30.
Which of the following are virus free varieties of banana produced by tissue culture technique?
(A) Shrimanti
(B) Basarai
(C) G-9
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 31.
The fungal component of lichen is called
(A) phycobiont
(B) photobiont
(C) mycobiont
(D) symbiont
Answer:
(C) mycobiont

Question 52.
Competitive Corner:
Question 1.
Which of the following is against the rules of ICBN?
(A) Generic and specific names should be written starting with small letters.
(B) Hand written scientific names should be underlined.
(C) Every species should have a generic name and a specific epithet.
(D) Scientific names are in Latin and should be italized.
Hint: The generic name should start with a capital letter while the species name should start with small letter.
Answer:
(A) Generic and specific names should be written starting with small letters.
Question 2.
Select the correctly written scientific name of Mango which was first described by Carolus Linnaeus: [NEET Odisha 2019]
(A) Mangifera indica
(B) Mangifera Indica
(C) Mangifera indica Car. Linn.
(D) Mangifera indica Linn
Hint: The author’s name appears after the specific epithet i.e. at the end of the biological name in this manner – Mangifera indica Linn.
Answer:
(D) Mangifera indica Linn
Question 3.
Match the organisms in Column I with habitats in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Halophiles | (a) Hot springs |
| 2. Thermoacidophiles | (b) Aquatic environment |
| 3. Methanogens | (c) Guts of ruminants |
| 4. Cyanobacteria | (d) Salty areas |
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) i – b, ii – d, iii – c, iv – a
(B) i – d, ii – a, iii – c, iv – b
(C) i – a, ii – b, iii – c, iv – d
(D) i – c, ii – d, iii – b, iv – a
Answer:
(B) i – d, ii – a, iii – c, iv – b

Question 4.
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
(A) Lichens are not good pollution indicators.
(B) Lichens do not grow in polluted areas.
(C) Algal component of lichens is called mycobiont.,
(D) Fungal component of lichens is called phycobiont.
Hint: Lichens bare good pollution indicators as they do not grow in polluted areas.
Answer:
(B) Lichens do not grow in polluted areas.
Question 5.
Match Column – I with Column – II. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| 1. Saprophyte | (a) Symbiotic association of fungi with plants roots |
| 2. Parasite | (b) Decomposition of dead |
| 3. Lichens | (c) Living on living plants or animals |
| 4. Mycorrhiza | (d) Symbiotic association of algae and fungi |
(A) i – q, ii – p, iii – r, iv – s
(B) i – q, ii – r, iii – s, iv – p
(C) i – p, ii – q, iii – r, iv – s
(D) i – r, ii – q, iii – p, iv – s
Answer:
(B) i – q, ii – r, iii – s, iv – p
Question 6.
Lowest category in the hierarchial system of classification is
(A) species
(B) order
(C) kingdom
(D) genus
Answer:
(A) species

Question 7.
Which group of fungi is called imperfect fungi?
(A) Ascomycetes
(B) Phycomycetes
(C) Deuteromycetes
(D) Basidiomycetes
Answer:
(C) Deuteromycetes
Question 8.
Which one of the following is an Incorrect pair?
(A) Three kingdom system of classification → Haeckel
(B) Three domain system of classification → Adolf Mayr
(C) Five Kingdom system of classification → R.H.Whittaker
(D) Two kingdom system of classification → Carolus Linnaeus
Hint: Three domain system of classification → Carl Woese
Answer:
(B) Three domain system of classification → Adolf Mayr
Question 9.
In the system of classification, which one of the following is NOT a category?
(A) Kingdom
(B) Series
(C) Angiospermae
(D) Genus
Hint: Angiospermae is a taxon.
Answer:
(C) Angiospermae
Question 10.
Which one of the following characteristics is NOT shown by a virus?
(A) They are acellular.
(B) They can be crystallised.
(C) Active outside the host’s body.
(D) Have genetic material.
Hint: Viruses are inert outside the host cell.
Answer:
(C) Active outside the host’s body.
Question 11.
Select the WRONG statement.
(A) Pseudopodia are locomotory and feeding structures in Sporozoans.
(B) Mushrooms belong to Basidiomycetes.
(C) Cell wall is present in members of Fungi and Plantae.
(D) Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell in all kingdoms except Monera.
Hint: Pseudopodia are locomotory and feeding structures in Protozoans.
Answer:
(A) Pseudopodia are locomotory and feeding structures in Sporozoans.

Question 12.
Which of the following are found in extreme saline conditions?
(A) Archaebacteria
(B) Eubacteria
(C) Cyanobacteria
(D) Mycobacteria
Hint: Bacteria found in extremely saline conditions are called halophiles. Archaebacteria includes bacteria that survive in most harsh habitats such as extreme salty area, hot springs and marshy area.
Answer:
(A) Archaebacteria
Question 13.
Which among the following are the smallest living cells, known without a definite cell wall, pathogenic to plants as well as animals and can survive without oxygen?
(A) Bacillus
(B) Pseudomonas
(C) Mycoplasma
(D) Nostoc
Question 14.
Viroids differ from viruses in having
(A) DNA molecules with protein coat
(B) DNA molecules without protein coat
(C) RNA molecules with protein coat
(D) RNA molecules without protein coat
Hint: Viroids are smaller than viruses. They are regarded as sub-viral agents or free RNA, without protein coat (usually found in viruses). They are infectious RNA. e.g. Potato spindle tuber disease.
Answer:
(D) RNA molecules without protein coat
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()