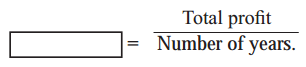Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce Book Keeping & Accountancy Solutions Chapter 6 Dissolution of Partnership Firm Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Book Keeping & Accountancy Solutions Chapter 6 Dissolution of Partnership Firm
1. Objective Questions.
A. Select the most appropriate answer from the alternatives given below and rewrite the sentences.
Question 1.
In case of dissolution assets and liabilities cire transferred to ______________ Account.
(a) Bank Account
(b) Partner’s Capital Account
(c) Realisation Account
(d) Partner’s Current Account
Answer:
(c) Realisation Account
Question 2.
Dissolution expenses are credited to ______________ Account.
(a) Realisation Account
(b) Cash/Bank Account
(c) Partner’s Capital Account
(d) Partner’s Loan Account
Answer:
(b) Cash/Bank Account
Question 3.
Deficiency of insolvent partner will be suffered by solvent partners in their ______________ ratio.
(a) capital ratio
(b) profit sharing ratio
(c) sale ratio
(d) liquidity ratio
Answer:
(b) profit sharing ratio
![]()
Question 4.
If any asset is taken over by partner from firm his Capital Account will be ______________
(a) credited
(b) debited
(c) added
(d) divided
Answer:
(b) debited
Question 5.
If any unrecorded liability is paid on dissolution of the firm ______________ account is debited.
(a) Cash/Bank Account
(b) Realisation Account
(c) Partner’s Capital Account
(d) Loan Account
Answer:
(b) Realisation Account
Question 6.
Partnership is completely dissolved when the partners of the firm become ______________
(a) solvent
(b) insolvent
(c) creditor
(d) debtors
Answer:
(b) insolvent
Question 7.
Assets and liabilities are transferred to Realisation Account at their ______________ values.
(a) market
(b) purchase
(c) sale
(d) book
Answer:
(d) book
Question 8.
If the number of partners in a firm falls below two, the firm stands ______________
(a) dissolved
(b) established
(c) realisation
(d) restructured
Answer:
(a) dissolved
![]()
Question 9.
Realisation Account is ______________ on realisation of asset.
(a) debited
(b) credited
(c) deducted
(d) closed
Answer:
(b) credited
Question 10.
All activities of partnership firm ceases on ______________ of firm.
(a) dissolution
(b) admission
(c) retirement
(d) death
Answer:
(a) dissolution
B. Write a word/phrase/term which can substitute each of the following statements.
Question 1.
Debit balance of Realisation Account.
Answer:
Realization Loss
Question 2.
Winding up of partnership business.
Answer:
Dissolution of Partnership
Question 3.
An account is opened to find out the profit or loss on sale of assets and settlement of liabilities.
Answer:
Realization A/c
Question 4.
Debit balance of an Insolvent Partner’s Capital Account.
Answer:
Capital Deficiency
![]()
Question 5.
The credit balance of the Realisation Account.
Answer:
Realization Profit
Question 6.
Conversion of asset into cash on the dissolution of the firm.
Answer:
Realisation
Question 7.
Liability is likely to arise in the future on the happening of certain events.
Answer:
Contingent Liabilities
Question 8.
Assets that are not recorded in the books of accounts.
Answer:
Unrecorded Assets
Question 9.
The account shows the realization of assets and discharge of liabilities.
Answer:
Realization A/c
![]()
Question 10.
Expenses incurred on the dissolution of the firm.
Answer:
Dissolution/Realisation Expenses
C. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons.
Question 1.
The firm must be dissolved on the retirement of a partner.
Answer:
This statement is False.
On the retirement of a partner, if the partnership agreement allows, then the remaining partner can continue the business activities. It means the firm is not to dissolve.
Question 2.
On dissolution Cash/Bank Account is closed automatically.
Answer:
This statement is True.
As the firm is dissolved, there is no question of any business activities to be carried out further and so Cash/Bank Account is also not necessary. Therefore on dissolution Cash/Bank Account is closed automatically.
Question 3.
On dissolution, Bank overdraft is transferred to Realisation Account.
Answer:
This statement is True.
As a sundry liability of the business, bank overdraft is a liability of a firm and hence, it is transferred to Realisation Account at the time of dissolution and paid a third party Liability.
Question 4.
A solvent partner having a debit balance to his Capital Account does not share the deficiency of insolvent partner Capital Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
In the partnership, the partner’s liability is unlimited so, a solvent partner having a debit balance to his Capital Account should share the deficiency of the insolvent partner capital account.
Question 5.
At the time of dissolution of the partnership, all assets should be transferred to Realisation Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
At the time of dissolution of the partnership, the cash account and Bank A/c are not transferred to Realisation A/c. Similarly, if an asset is taken over by a partner or by any creditor then that asset is transferred to the concerned person’s account and not to the Realisation Account.
![]()
Question 6.
The debit balance of an insolvent partner’s Capital Account is known as a capital deficiency.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Debit balance of Partners’ Capital Account means the excess of drawings than the capital credit balance. In the case of an insolvent partner, the debit balance of the Capital Account means liabilities which he cannot pay. It means capital deficiency.
Question 7.
At the time of dissolution, a loan from a partner will be transferred to Realisation Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
At the time of dissolution, a loan from a partner will be paid after the payment of liabilities of third parties to the firm. It is not transferred to Realisation Account. Partner’s Loan A/c is separately opened and paid accordingly.
Question 8.
Dissolution takes place when the relationship among the partners comes to an end.
Answer:
This statement is True.
As per definition, Dissolution means to wind up or to close down, and it is possible only when relations among the partners in a partnership firm come to an end.
Question 9.
The insolvency loss at the time of dissolution of the firm is shared by the solvent partners in their profit sharing ratio.
Answer:
This statement is True.
In the partnership, partners’ liability is unlimited and in case of insolvency loss, legally solvent partners are ultimately liable and are suppose to bear the loss of an insolvent partner in their profit sharing ratio.
Question 10.
Realization loss is not transferred to insolvent partner’s Capital Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
All partners of the firm are responsible for Loss on realization and hence loss on realization is supposed to be transferred to all Partners’ Capital Account, without any discrimination of solvent or insolvent.
D. Calculate the following:
Question 1.
Vinod, Vijay, and Vishal are partners in a firm sharing profit and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. Vishal becomes insolvent and his capital deficiency is ₹ 6000. Distribute the capital deficiency among the solvent partner.
Answer:
Here, capital deficiency of ₹ 6000 is to be distributed among continuing partners in their profit and loss sharing ratio, i.e. 3 : 2
Share of deficiency for Vinod = 6,000 × \(\frac{3}{5}\) = ₹ 3,600
Share of deficiency for Vijay = 6,000 × \(\frac{2}{5}\) = ₹ 2,400
Vinod and Vijay will bear ₹ 3,600 and ₹ 2,400 of Vishal’s capital deficiency.
Question 2.
Creditors ₹ 30,000, Bills Payable ₹ 20,000, and Bank Loan ₹ 10,000. Available Bank balance ₹ 40,000. What will be the amount that creditors will get in case of all partner’s insolvency?
Answer:
Ratio of creditors, Bills payable and Bank Loan = 30,000 : 20,000 : 10,000 i.e., 3 : 2 : 1
Amount received by creditors = \(\frac{3}{3+2+1}\) × 40,000
= \(\frac{3}{6}\) × 40,000
= ₹ 20,000.
![]()
Question 3.
Insolvent Partner Capital A/c debit side total is ₹ 10,000 and credit side total is ₹ 6,000. Calculate deficiency.
Answer:
Deficiency of insolvent partner = Debit side total – Credit side total
= 10,000 – 6,000
= ₹ 4,000.
Question 4.
Insolvent Partners Capital A/c debit side is ₹ 15,000 and insolvent partner brought cash ₹ 6,000. Calculate the amount of insolvency loss to be distributed among the solvent partners.
Answer:
₹ 9,000 (15,000 – 6,000) is the amount of insolvency loss to be distributed among the solvent partners.
Question 5.
The realization profit of a firm is ₹ 6,000, partners share profit and loss in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. Calculate the amount of realization profit to be credited to Partners’ Capital A/c.
Answer:
Distribution of ₹ 6,000 in 3 : 2 : 1 ratio
6,000 × \(\frac{3}{6}\) = ₹ 3,000, 6,000 × \(\frac{2}{6}\) = ₹ 2,000, 6,000 × \(\frac{1}{6}\) = ₹ 1,000
Amount of realisation profit ₹ 3,000, ₹ 2,000 and ₹ 1,000 is to be credited to Partner’s Capital A/c respectively.
E. Answer in one sentence only.
Question 1.
What is the dissolution of the partnership firm?
Answer:
Dissolution of the partnership firm means complete closure of business activities and stoppage of partnership relations among all the partners.
Question 2.
When is Realisation Account opened?
Answer:
Realisation Account is opened at the time of dissolution of the partnership firm.
Question 3.
Which accounts are not transferred to Realisation Account?
Answer:
Cash/Bank balance, Reserve funds, Profit and Loss A/c balance, Partners’ Loan accounts, etc. are not transferred to Realisation Account.
Question 4.
Who is called an insolvent person?
Answer:
Whose capital A/c shows debit balance and who is not in a position to meet his capital deficiency even from his private property is called an insolvent person.
![]()
Question 5.
What is capital deficiency?
Answer:
The debit balance of the insolvent partner’s Capital Account which the insolvent partner cannot pay is called a capital deficiency.
Question 6.
In what proportion is the balance on Realisation Account transferred to Partners Capital/Current Accounts?
Answer:
The balance on the Realisation Account is transferred to Partners Capital/Current Accounts in their profit sharing ratio.
Question 7.
Who should bear the capital deficiency of insolvent partners?
Answer:
The capital deficiency of insolvent partners should be borne by the solvent partners.
Question 8.
Which account is debited on repayment of partner’s loan?
Answer:
Partner’s Loan Account is debited on repayment of partner’s loan.
Question 9.
Which account is debited on payment of dissolution expenses?
Answer:
Realisation Account is debited on payment of dissolution expenses.
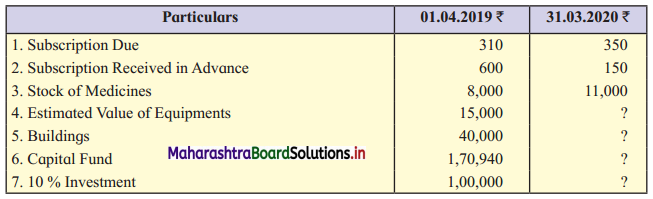
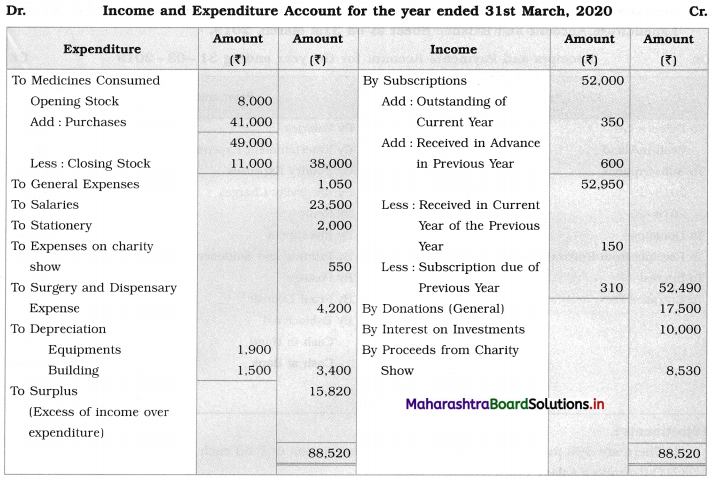
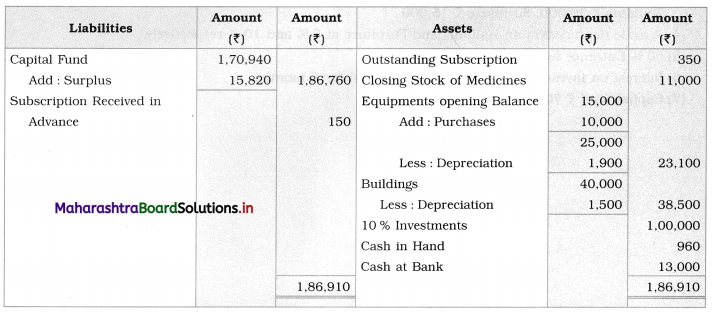
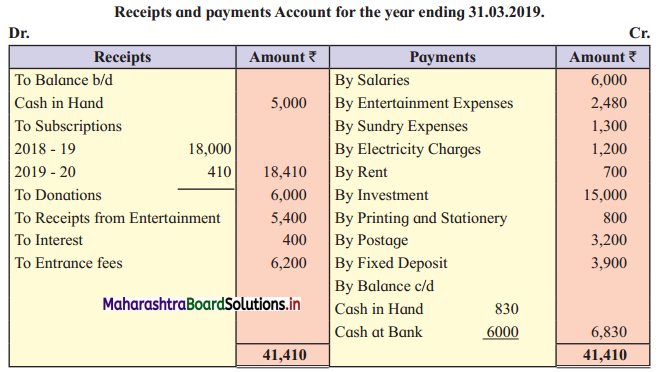
F. Complete the table.
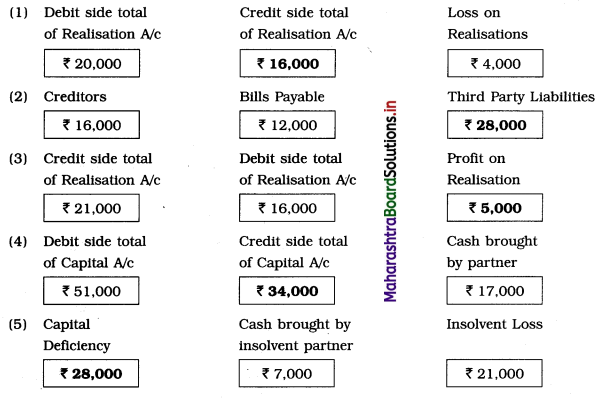
Question 1.
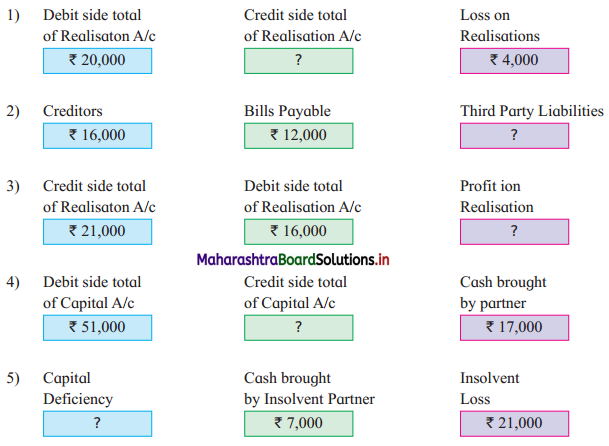
Answer:
Practical Problems
(Simple Dissolution)
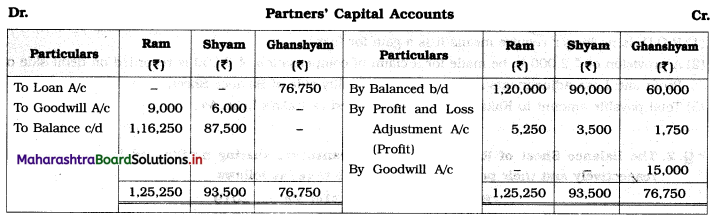
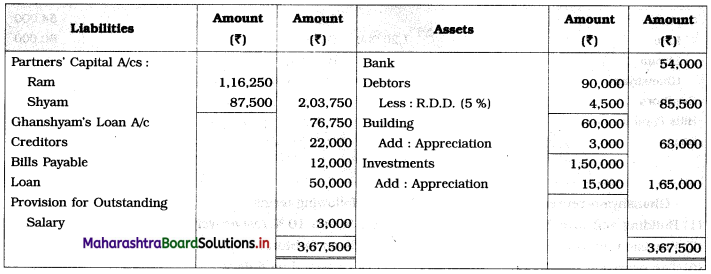
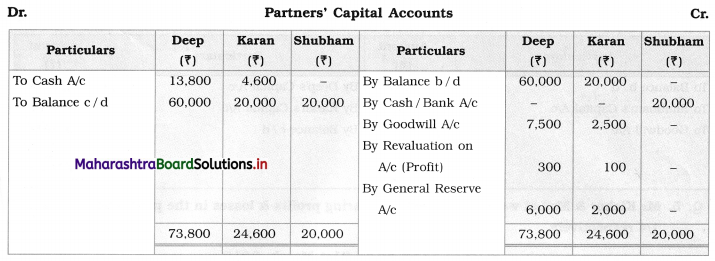
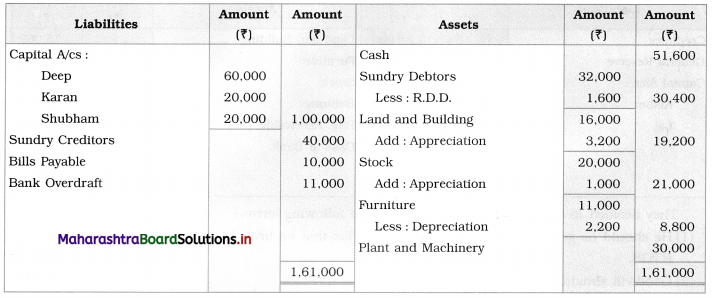
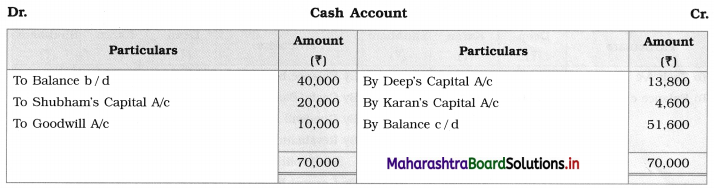
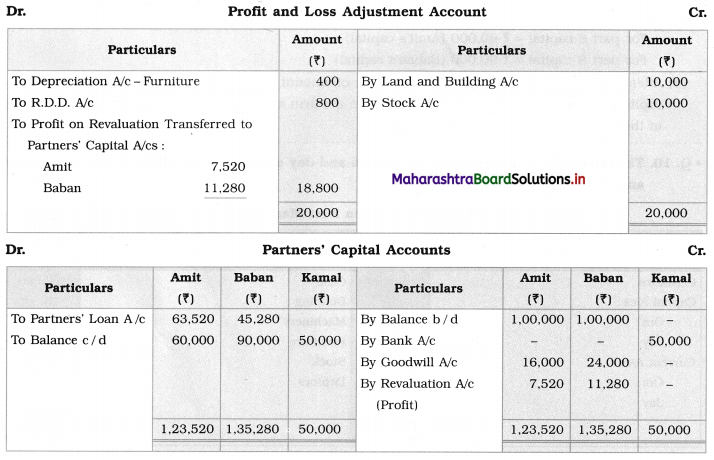
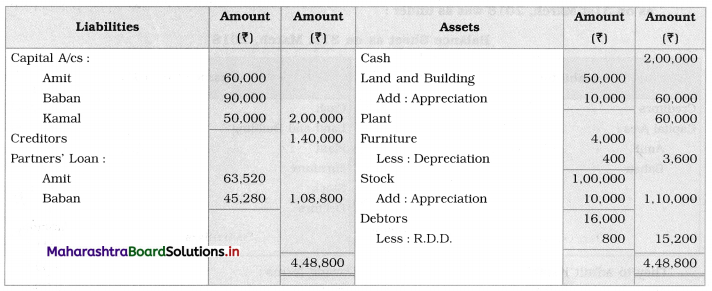
Question 1.
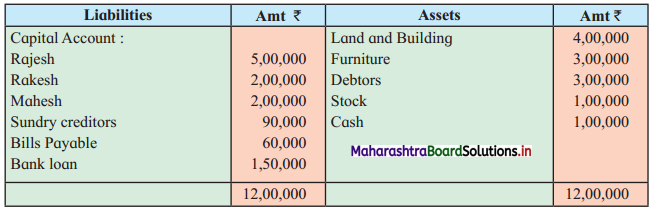
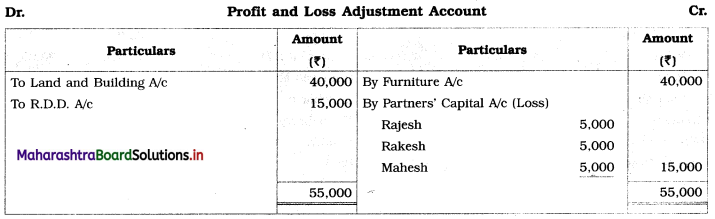
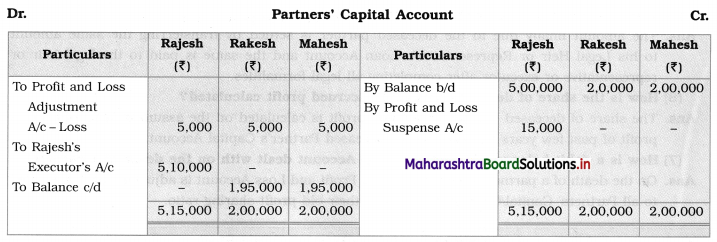
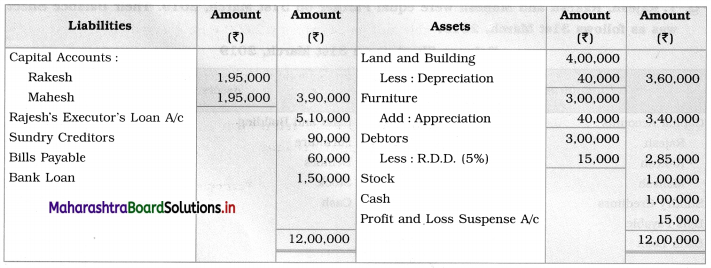
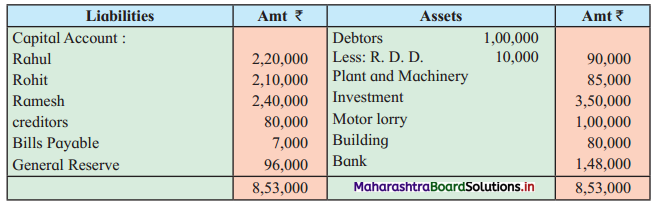
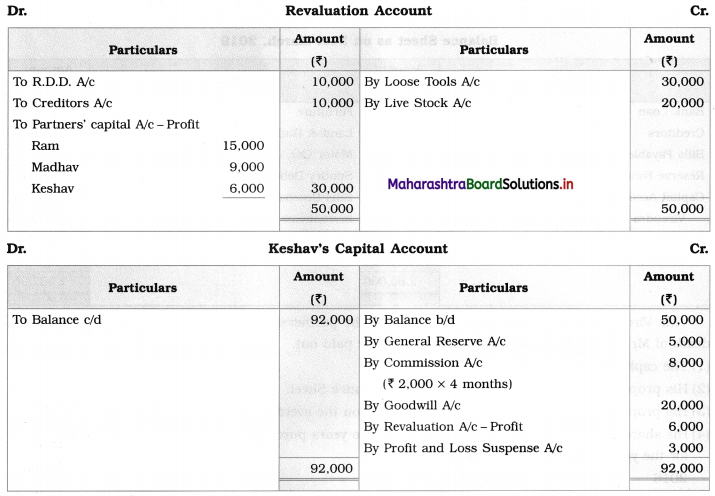
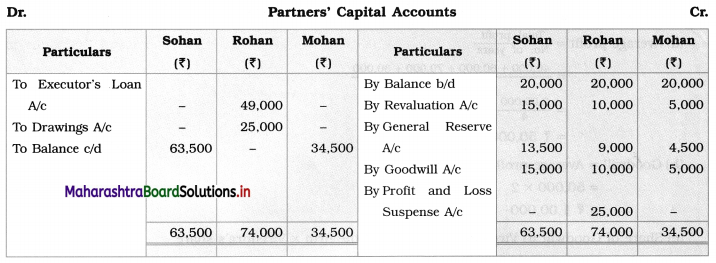
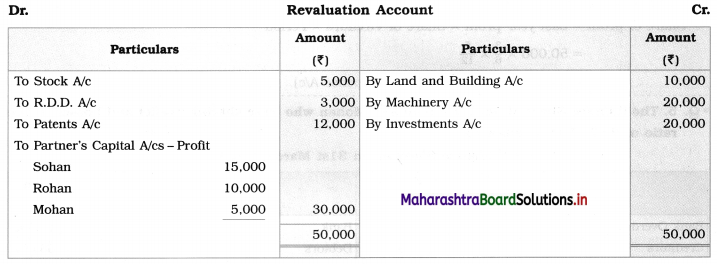
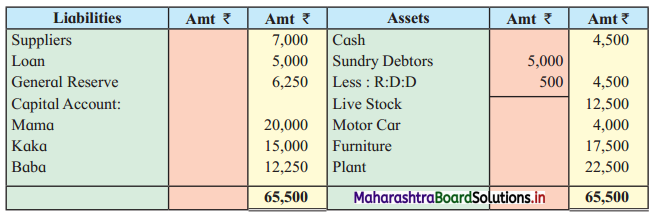
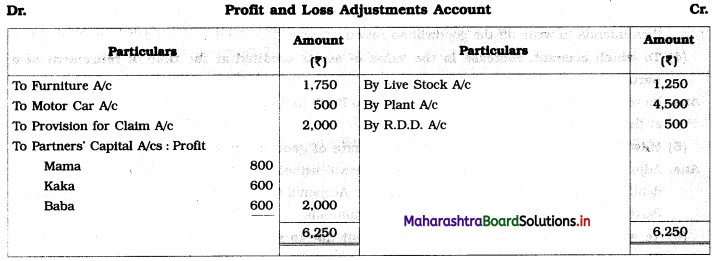
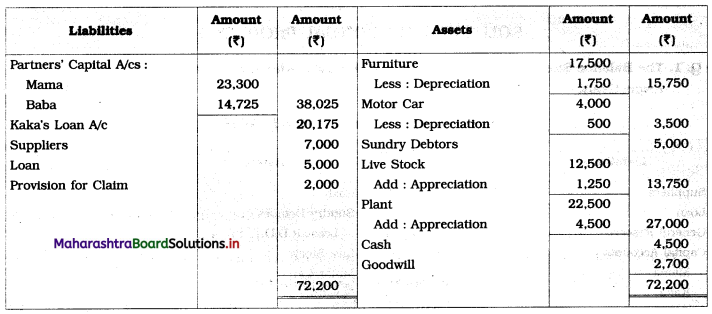
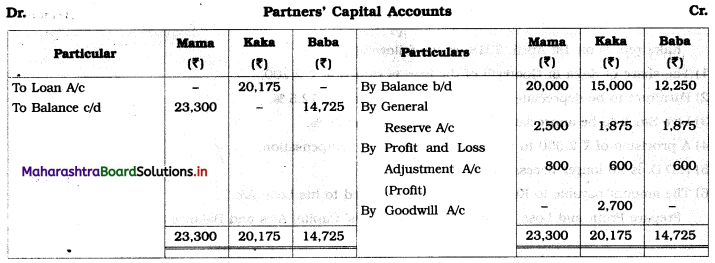
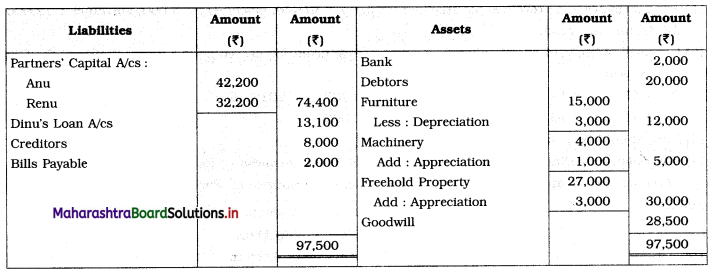
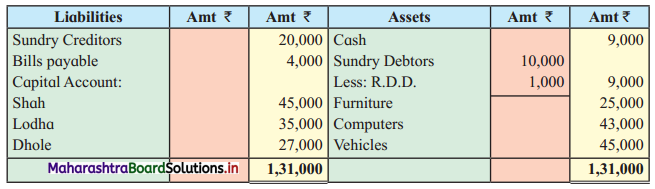
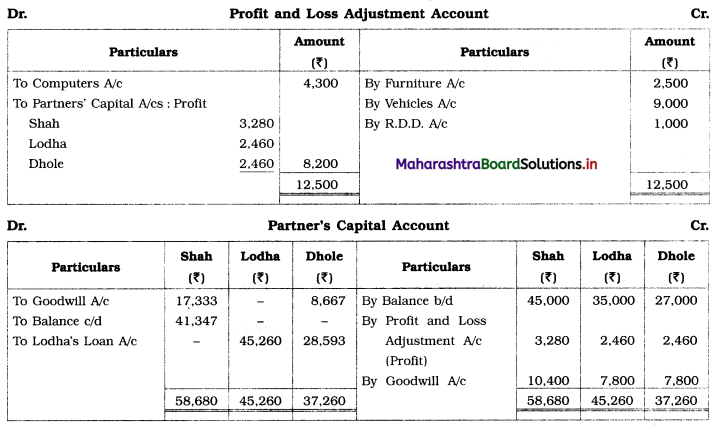
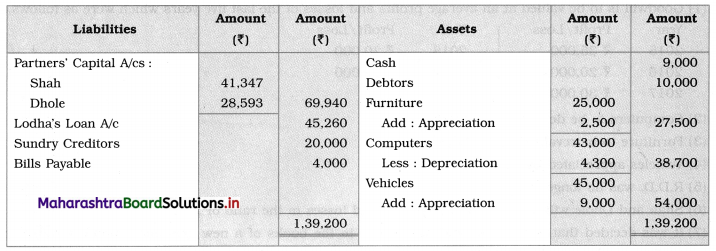
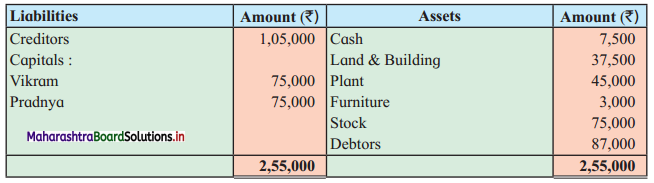
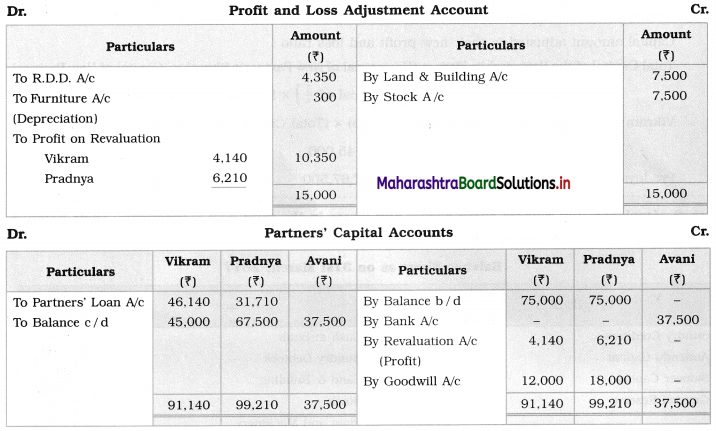
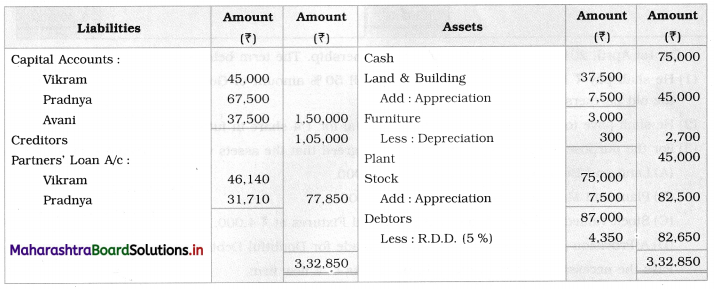
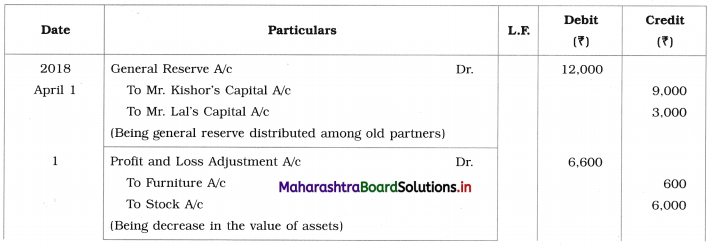
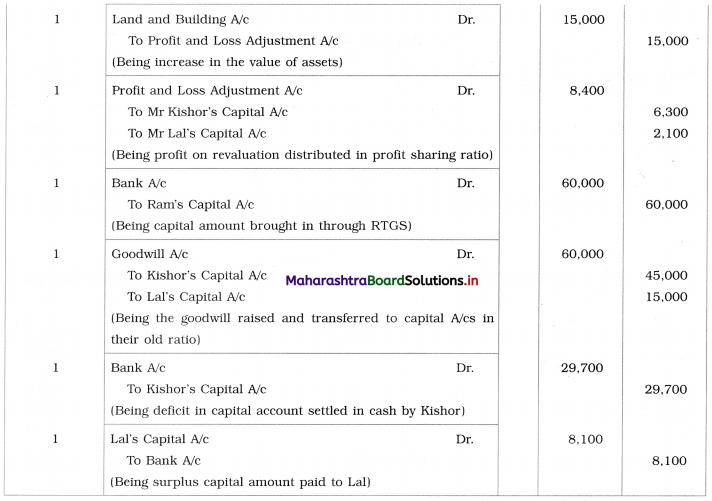
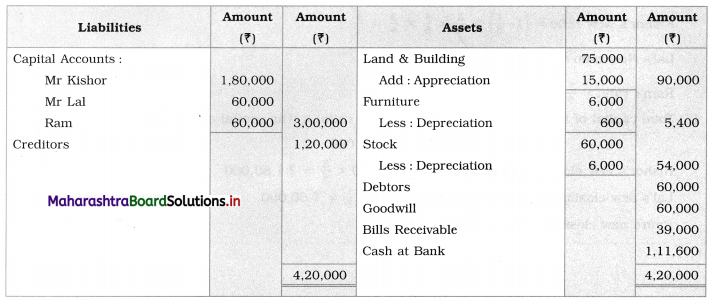
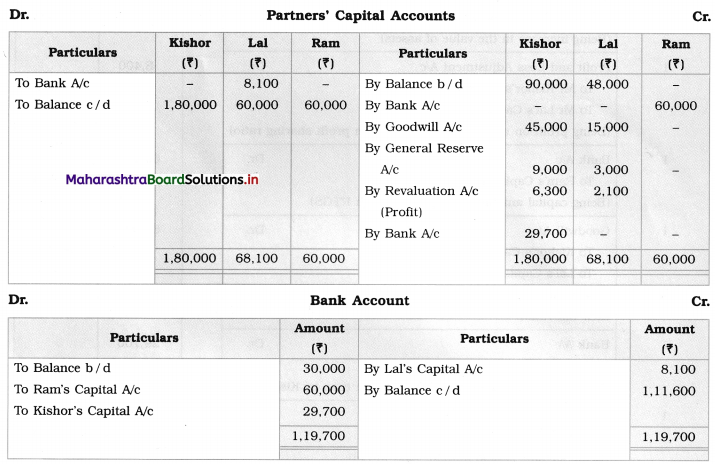
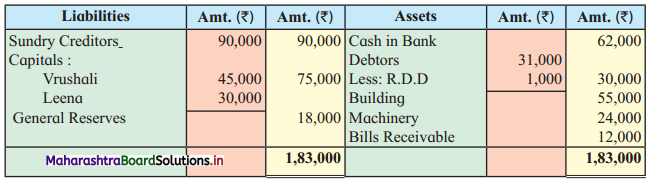
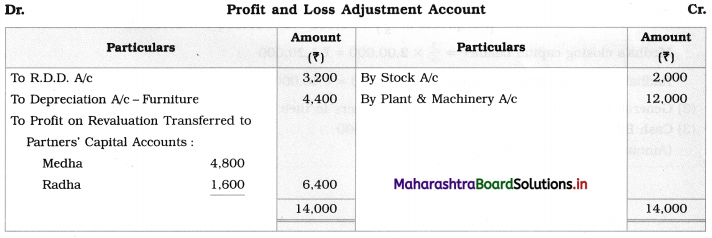
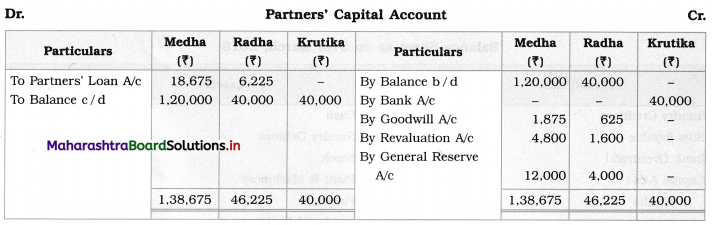
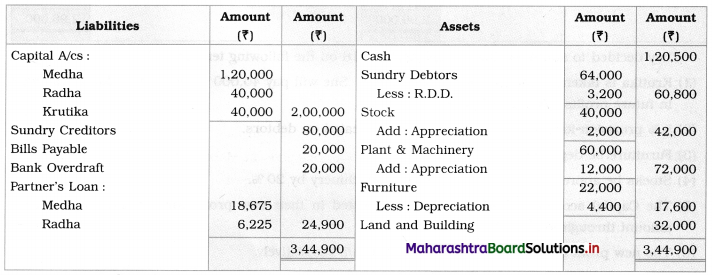
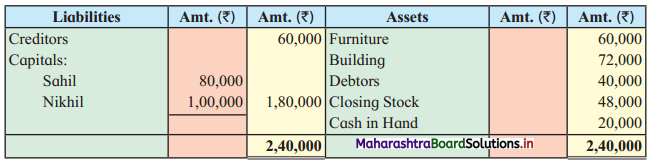
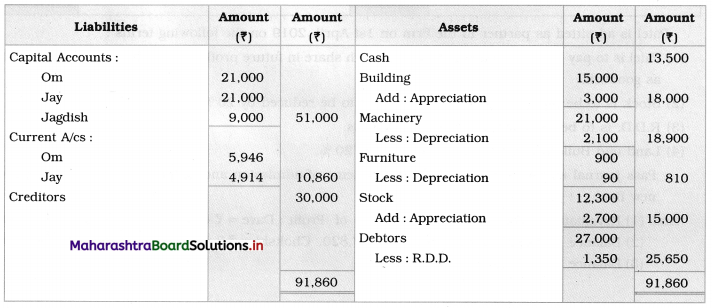
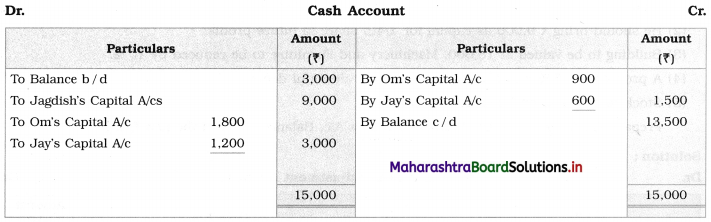
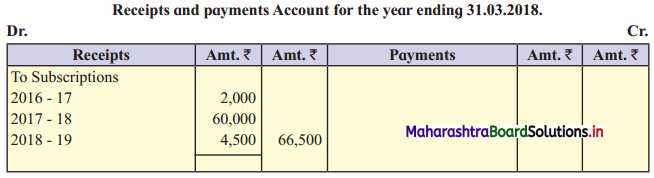
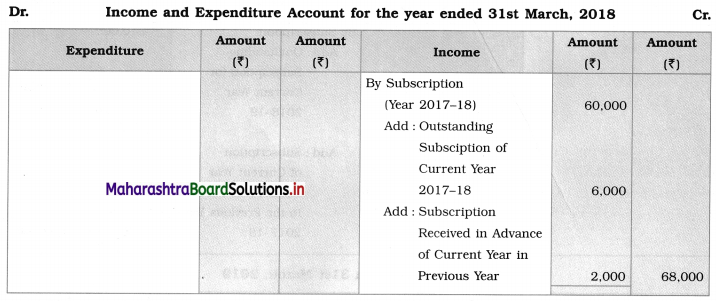
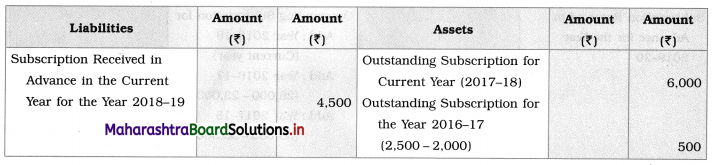
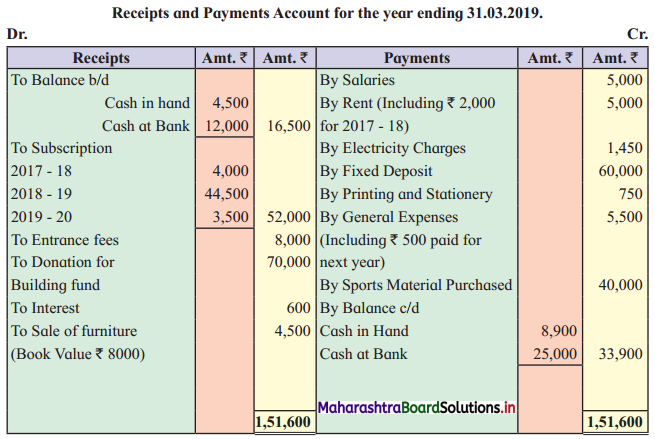
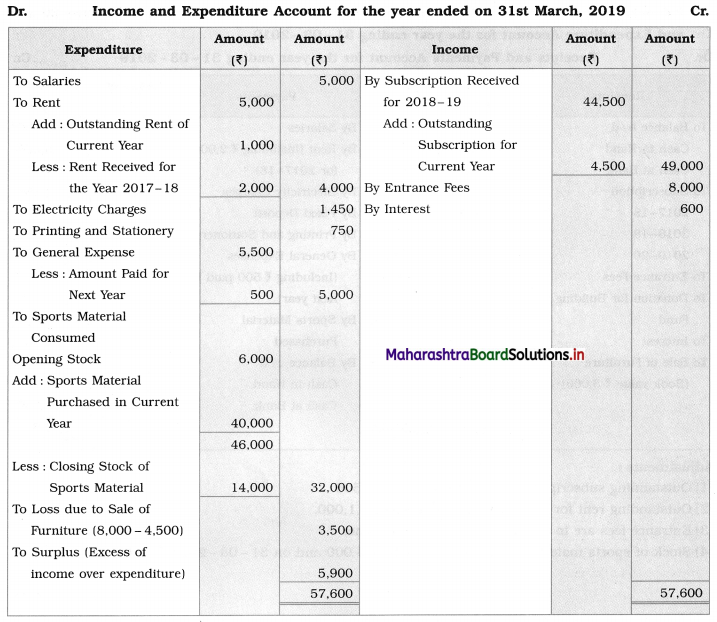
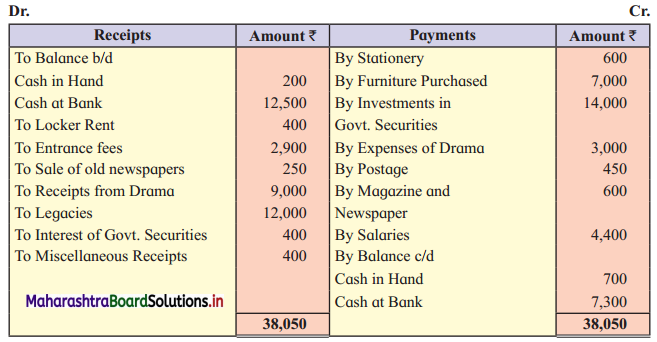
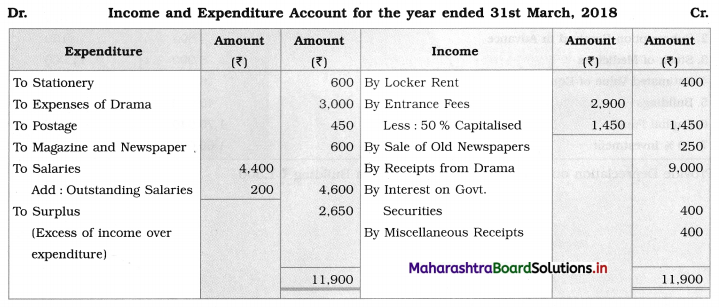
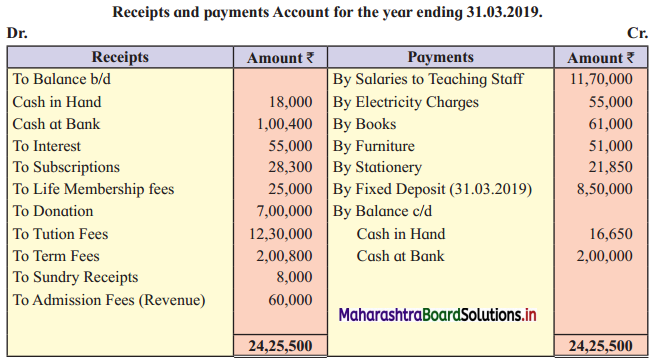
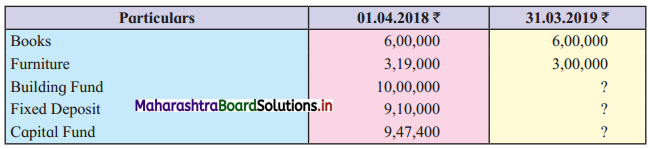
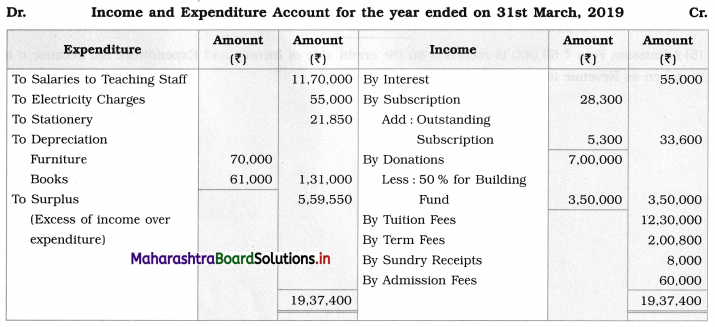
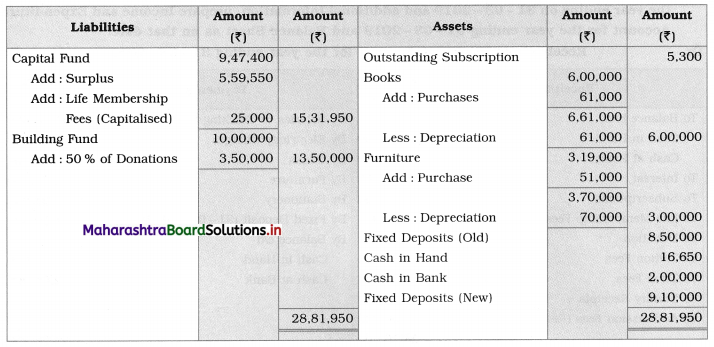
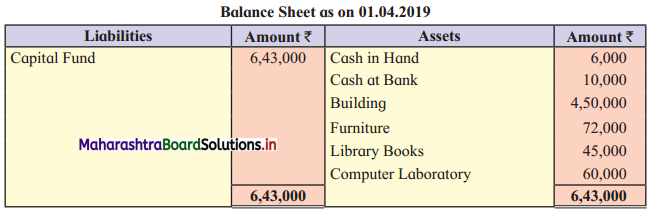
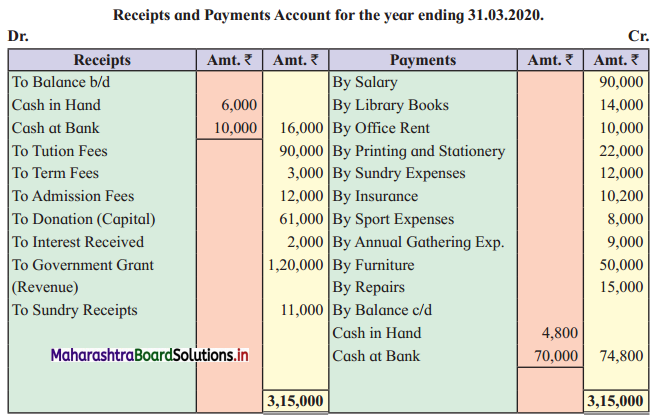
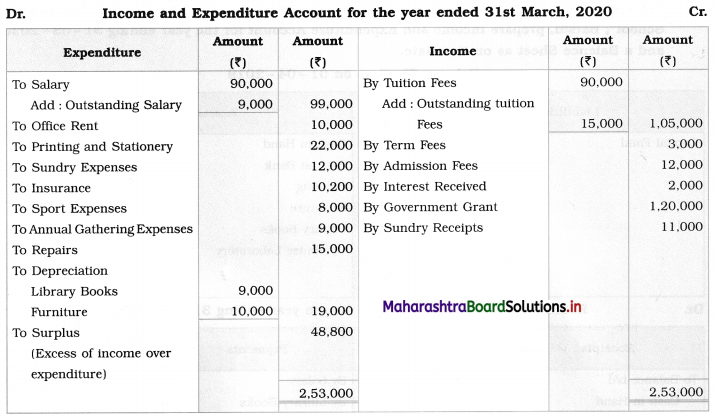
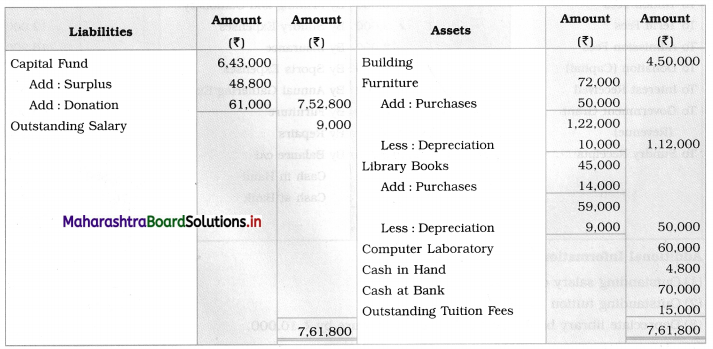
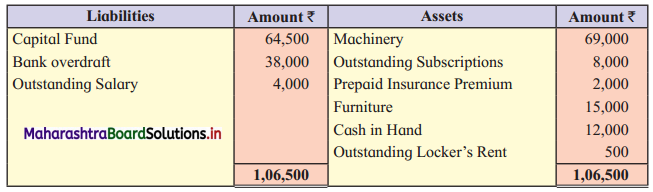
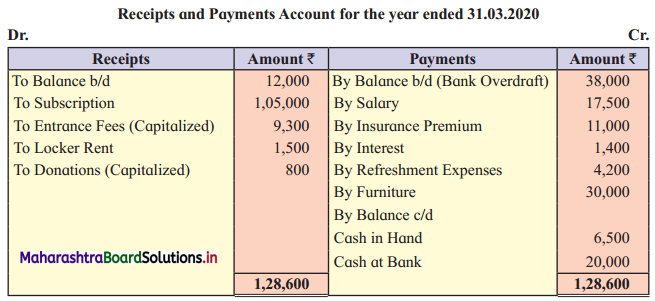
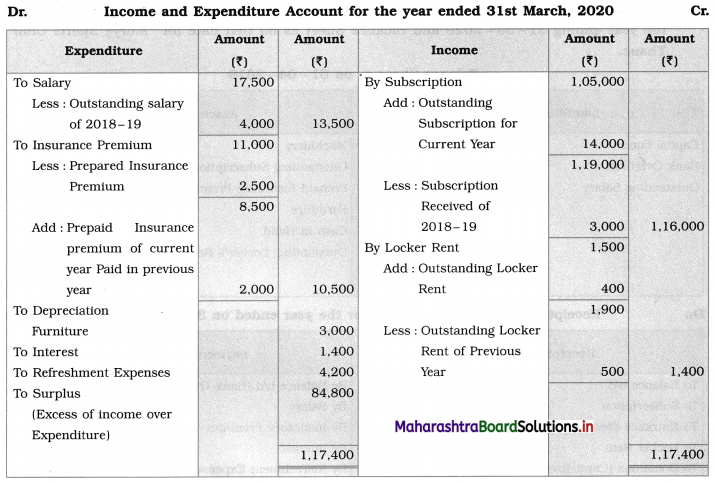
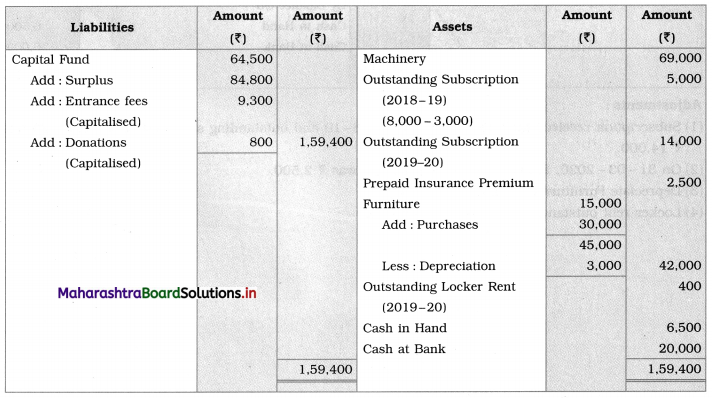
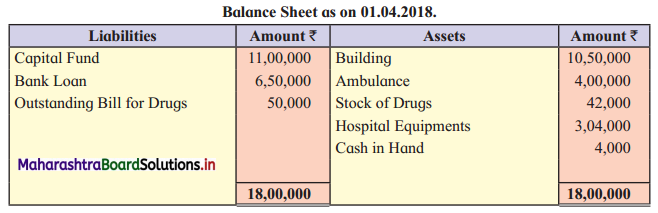
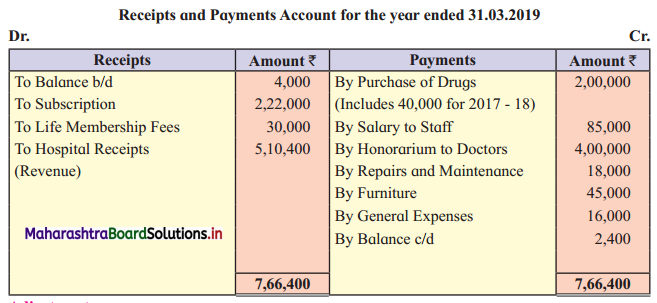
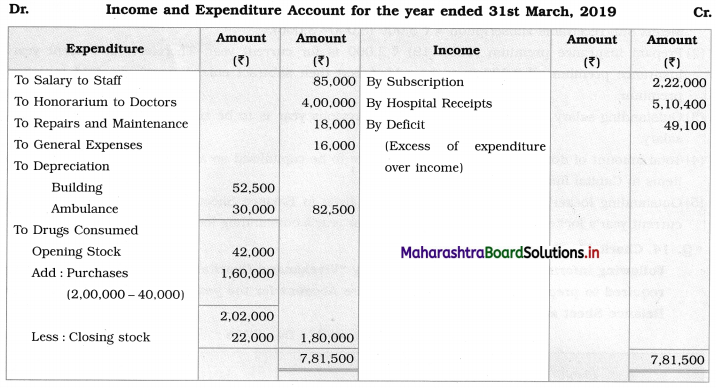
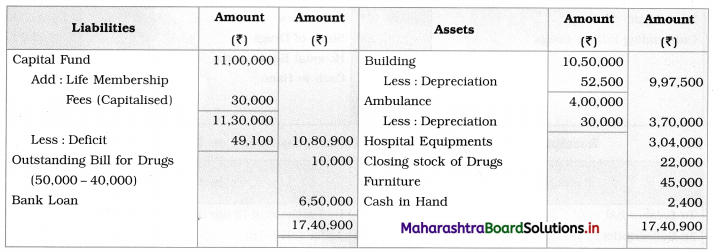
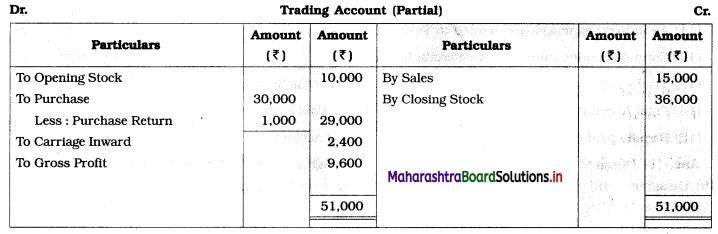
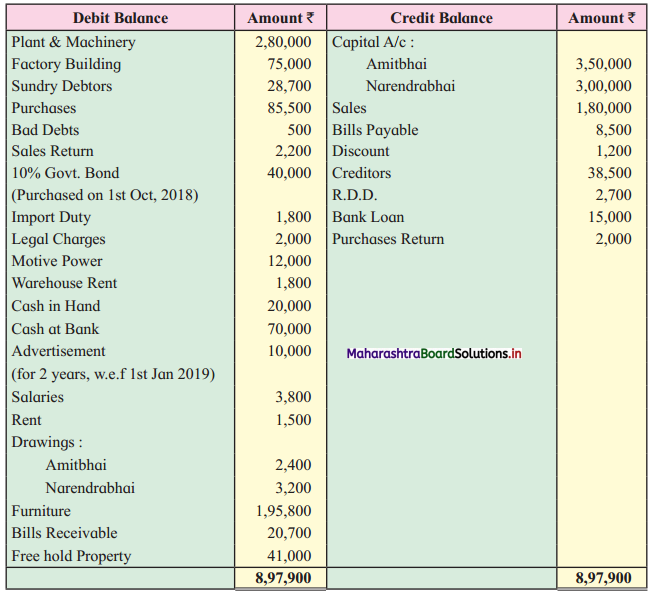
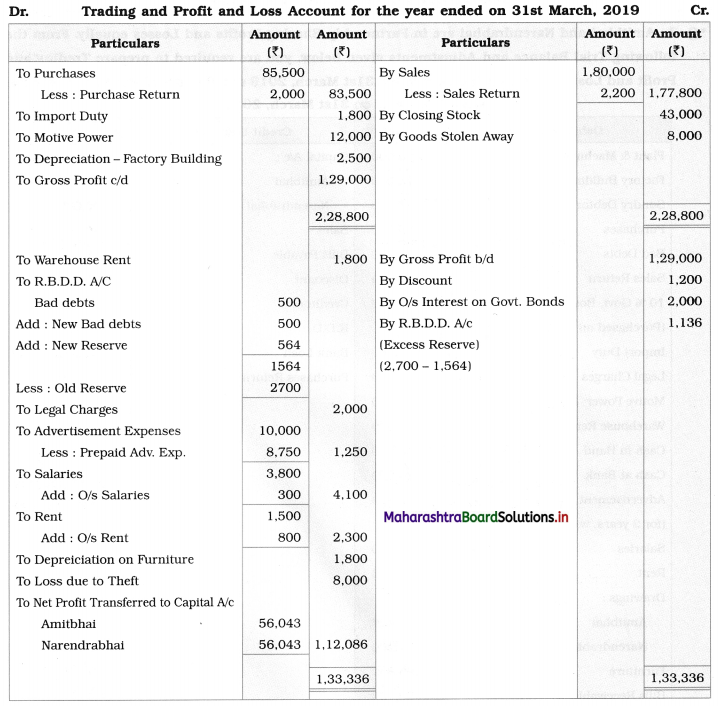
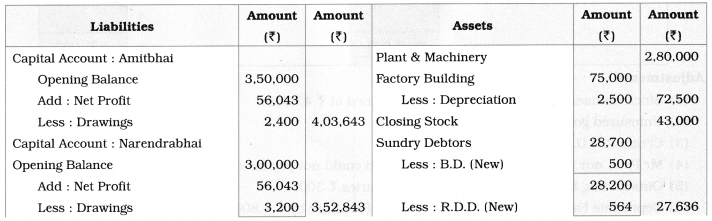
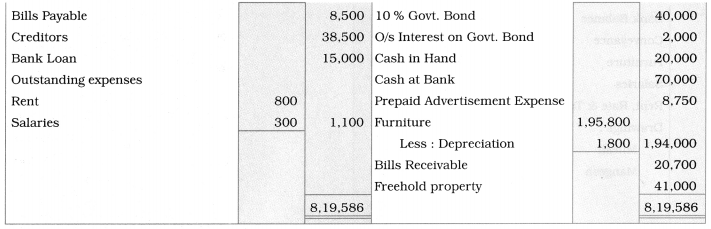
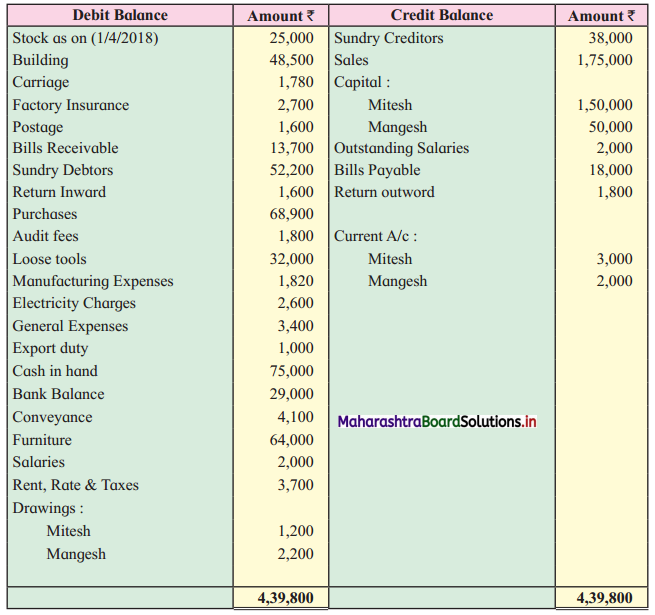
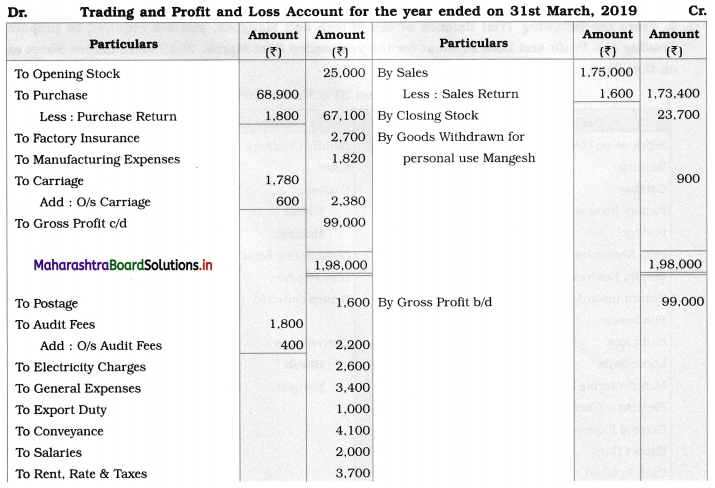
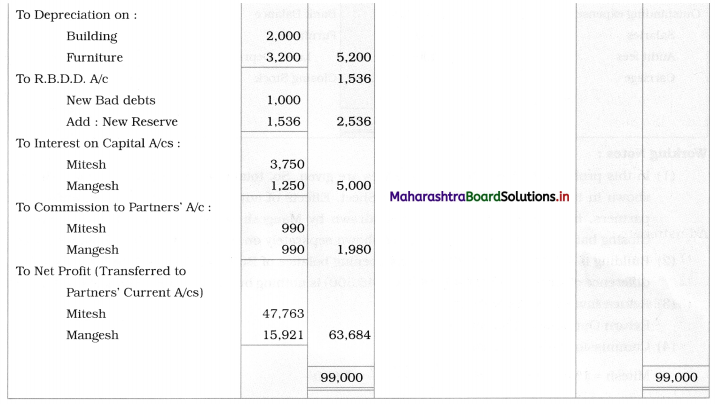
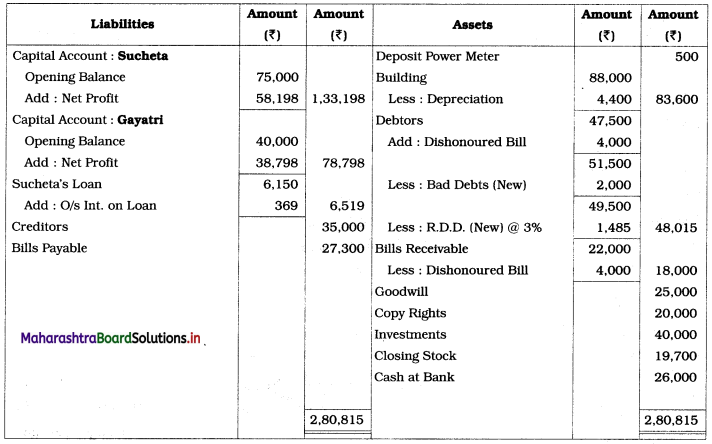
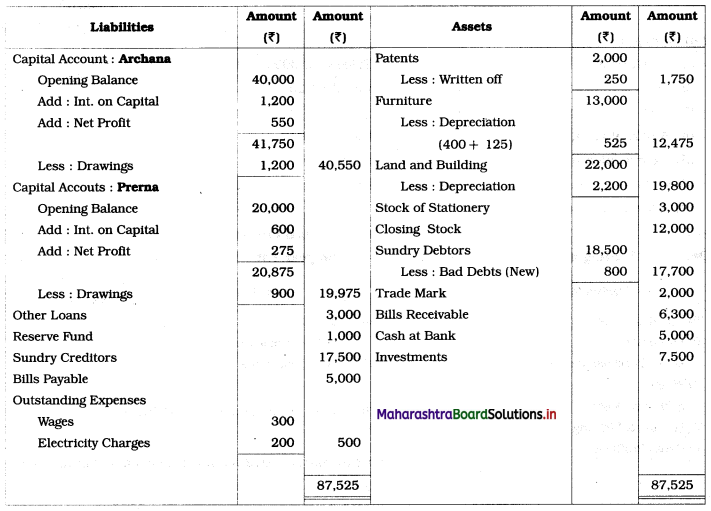
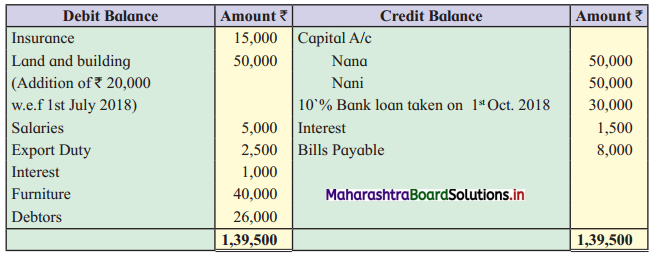
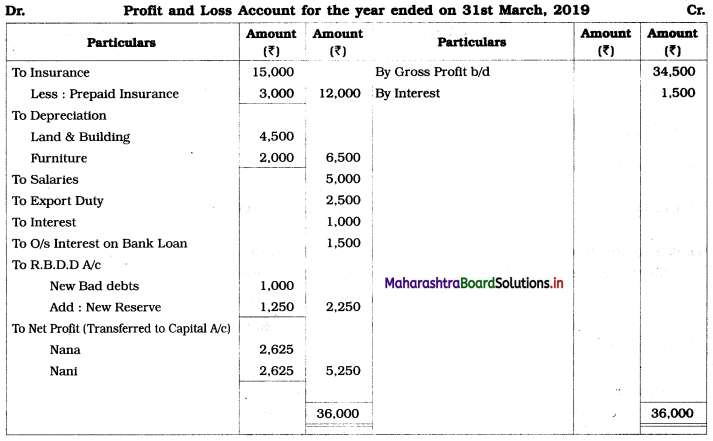
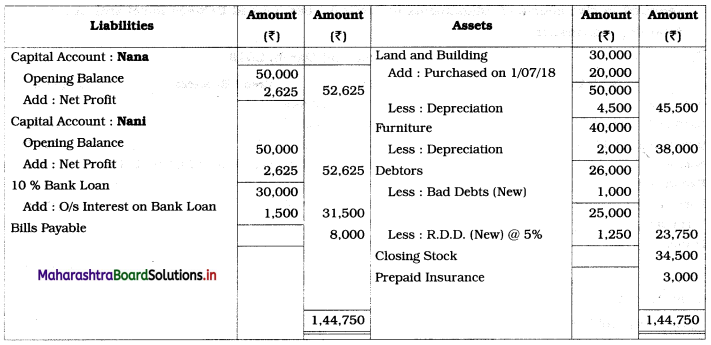
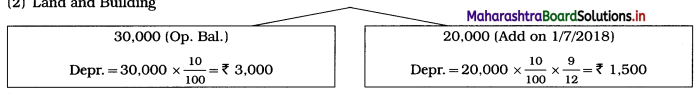
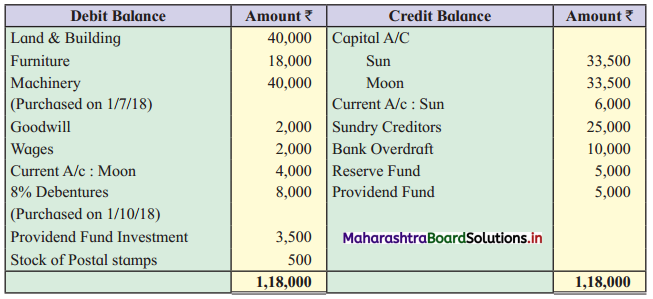
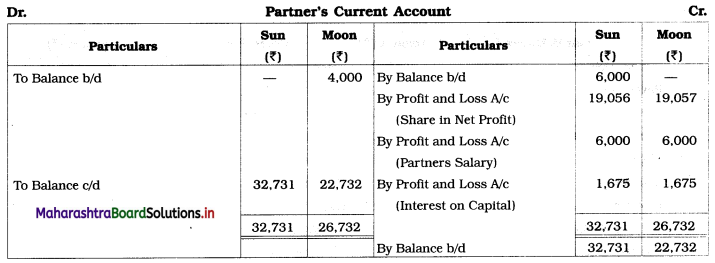
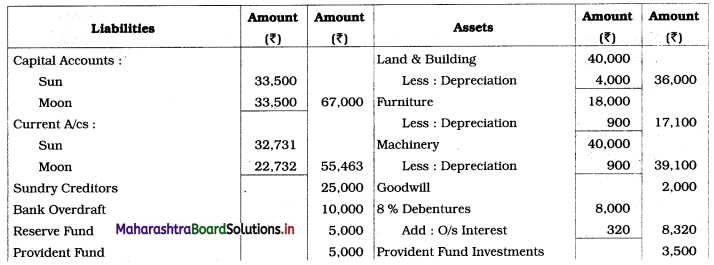
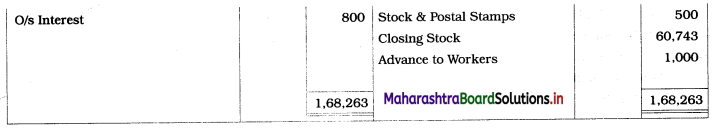
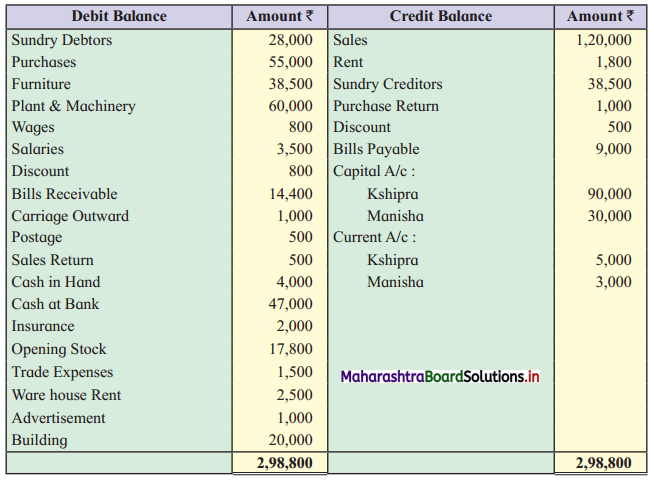
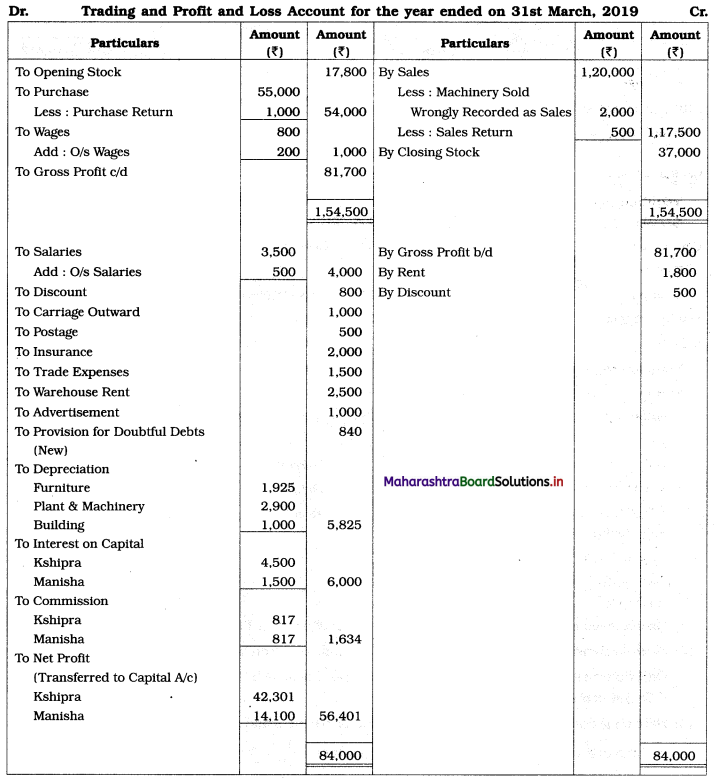
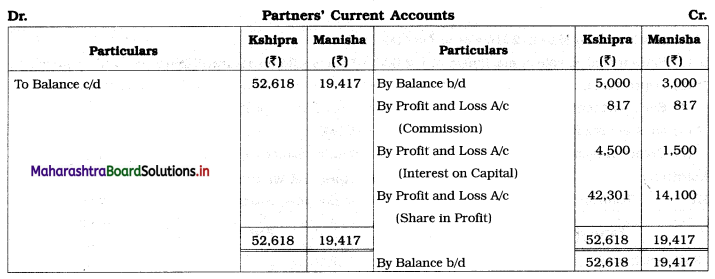
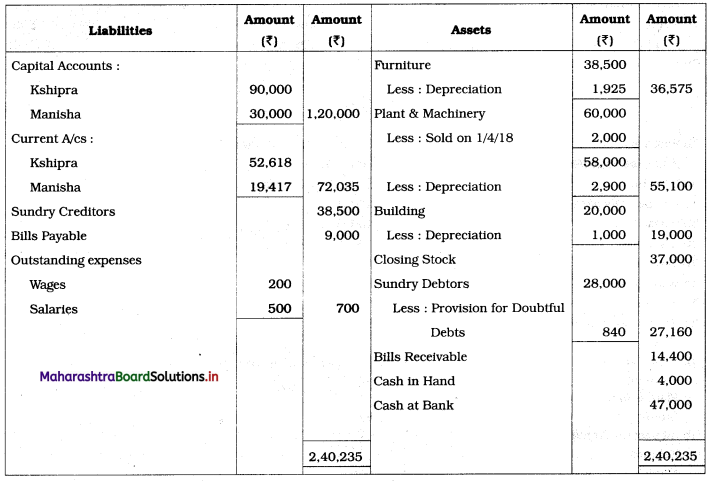
Ganesh and Kartik are partners sharing profits and losses equally. They decided to dissolve the firm on 31st March 2018. Their Balance Sheet was as under:
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2018
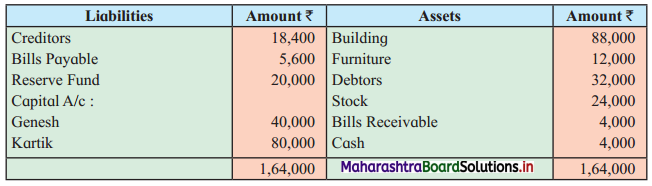
Assets were realised as under:
Building ₹ 82,000, Debtors ₹ 22,000, Stock ₹ 20,000. Bills Receivable ₹ 3,200 and Ganesh agreed to take over Furniture for ₹ 10,000. Realisation Expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000.
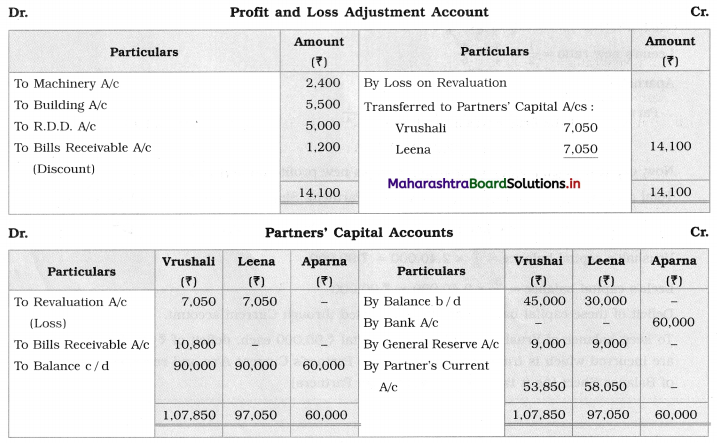
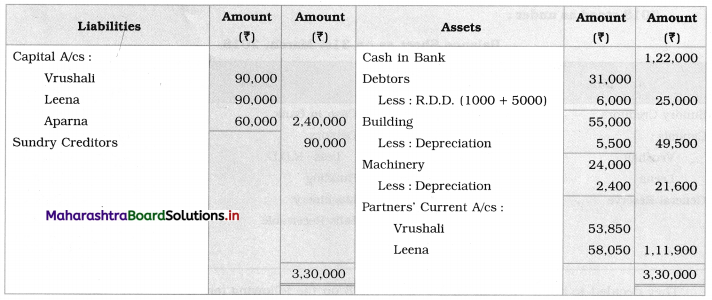
Show Realisation A/c, Partners’ Capital A/c, and Cash A/c.
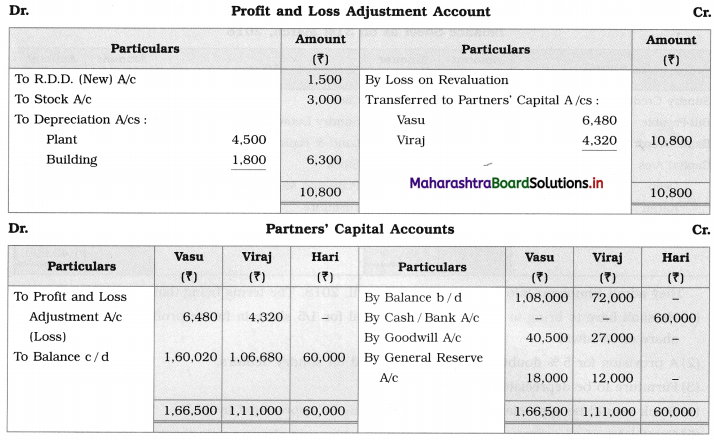
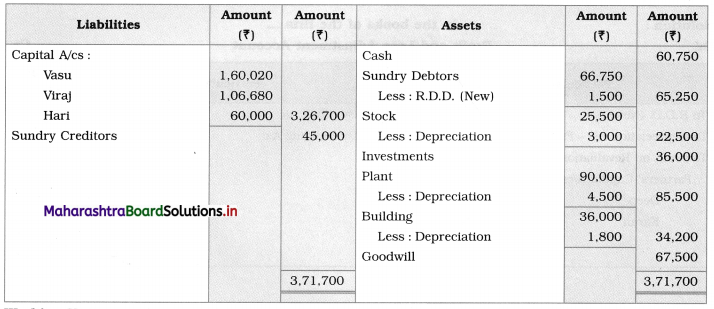
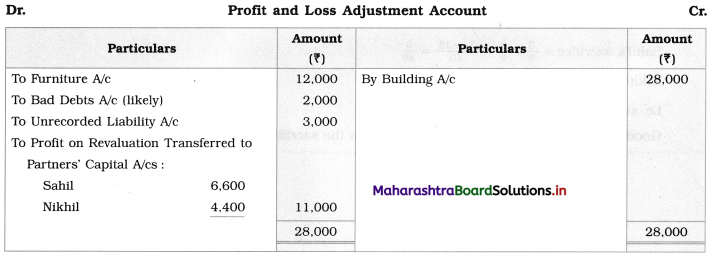
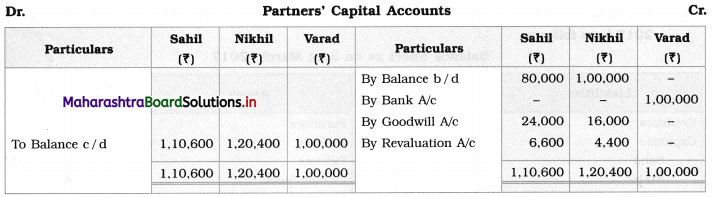
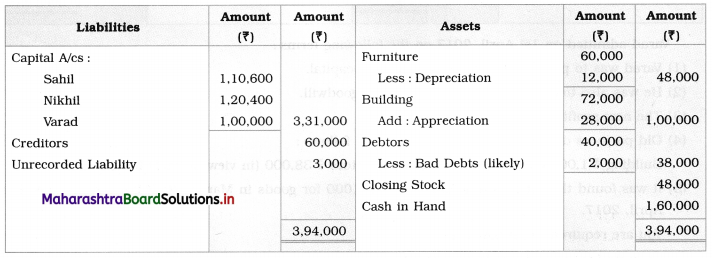
Solution:
In the books of Ganesh and Kartik
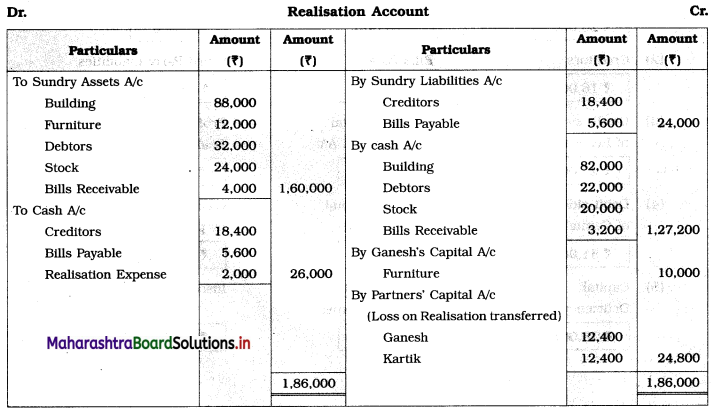
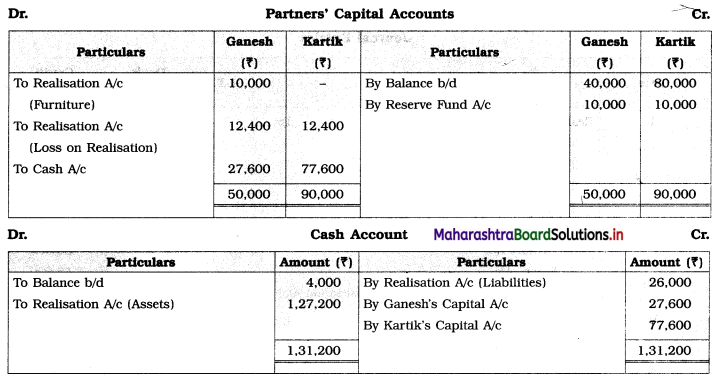
Working Notes:
1. Amount paid to Ganesh and Kartik are ₹ 27,600 and ₹ 77,600 respectively.
2. Loss on Realisation and Reserve fund amounts are equally distributed.
3. Furniture is taken over by Ganesh so his Capital A/c is debited.
![]()
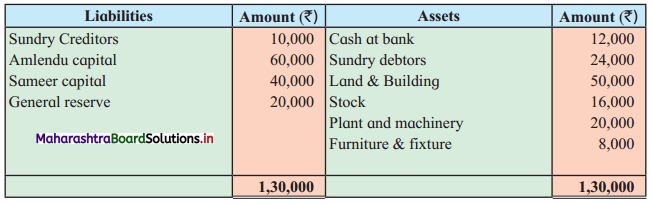
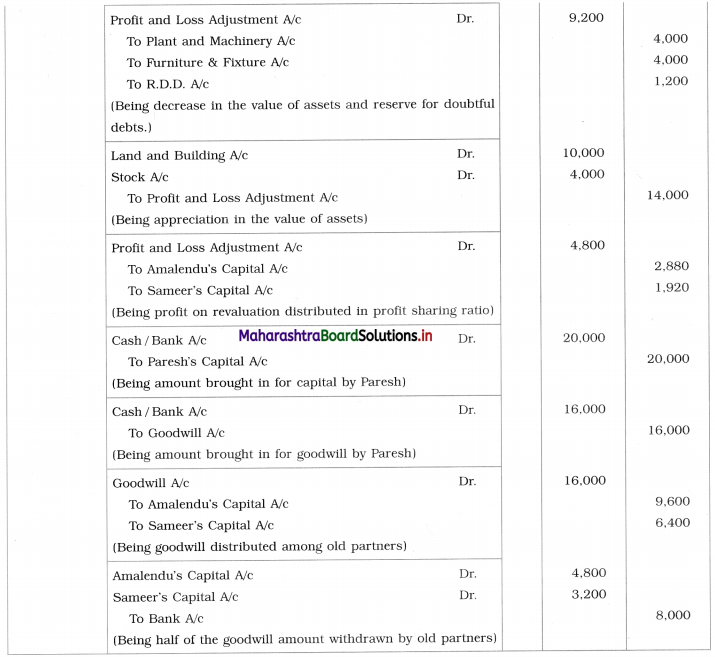
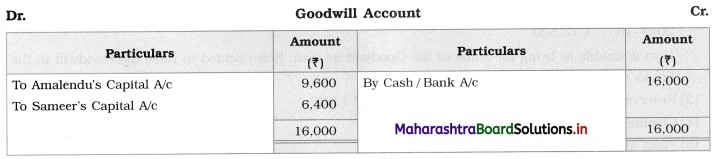
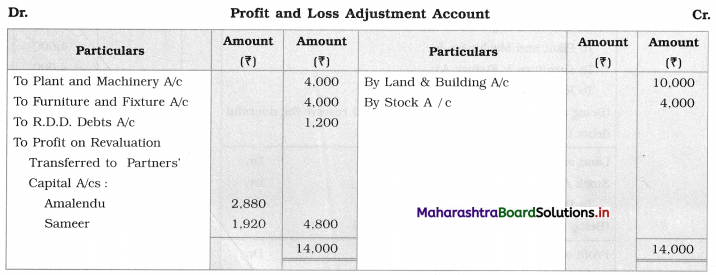
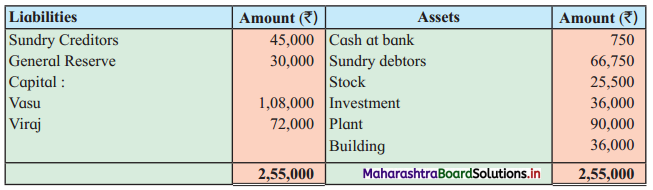
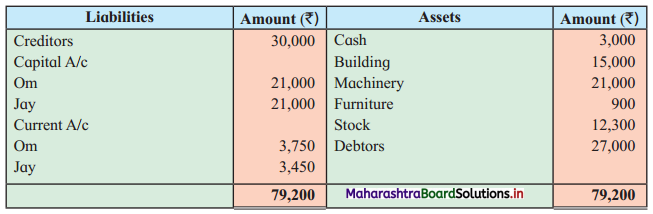
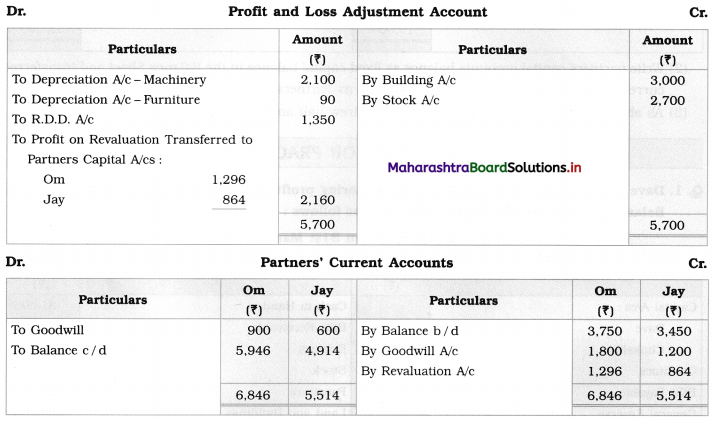
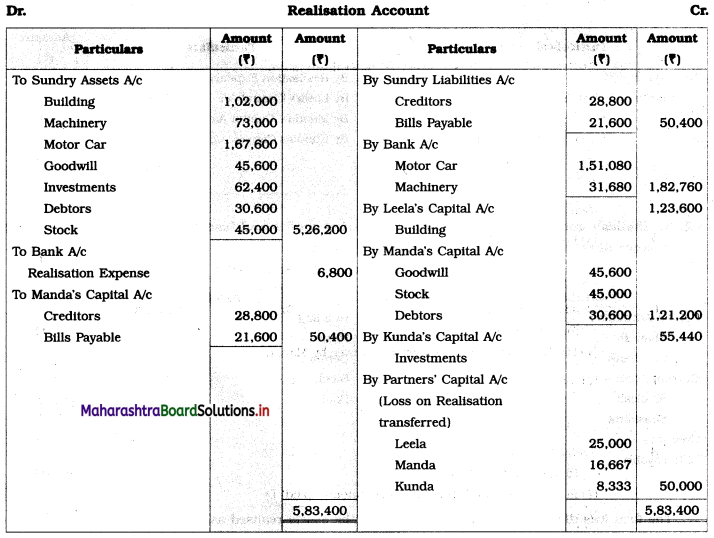
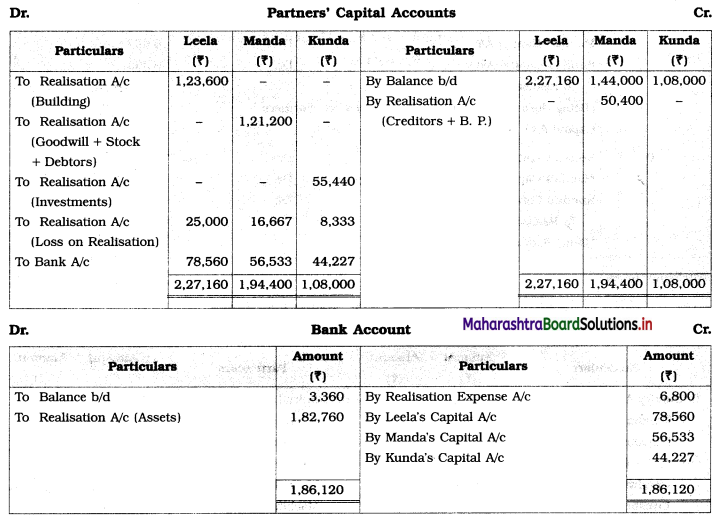
Question 2.
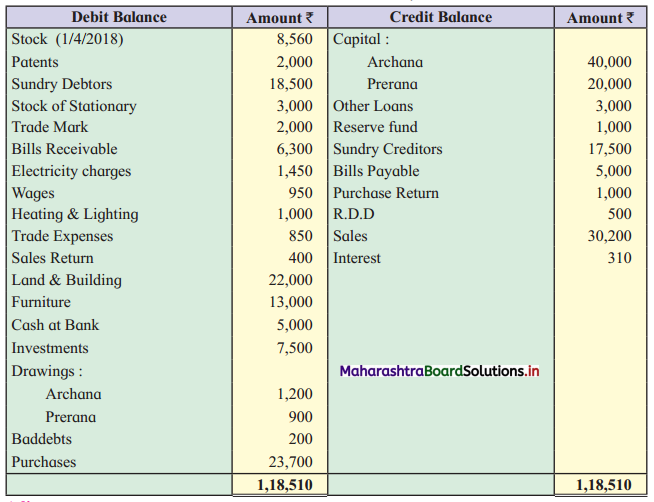
Leela, Manda, and Kunda are partners in the firm ‘Janki Stores’ sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1 respectively. On 31st March 2018, they decided to dissolve the firm when their Balance Sheet was as under.
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2018
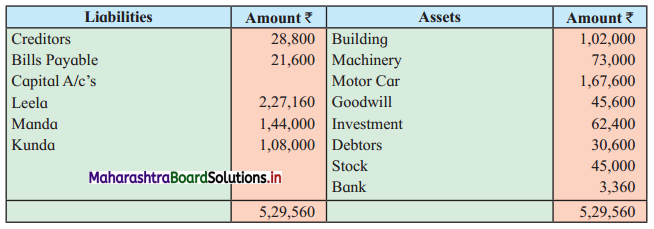
Leela agreed to take over the Building at ₹ 1,23,600. Manda took over Goodwill, Stock, and Debtors at book values and agreed to pay Creditors and Bills payable. Motor car and Machinery realized ₹ 1,51,080 and ₹ 31,680 respectively. Investments were taken by Kunda at an agreed value of ₹ 55,440. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 6,800.
Pass necessary entries in the books of ‘Janki Stores’.
Solution:
In the books of ‘Janki Stores’
Journal Entries
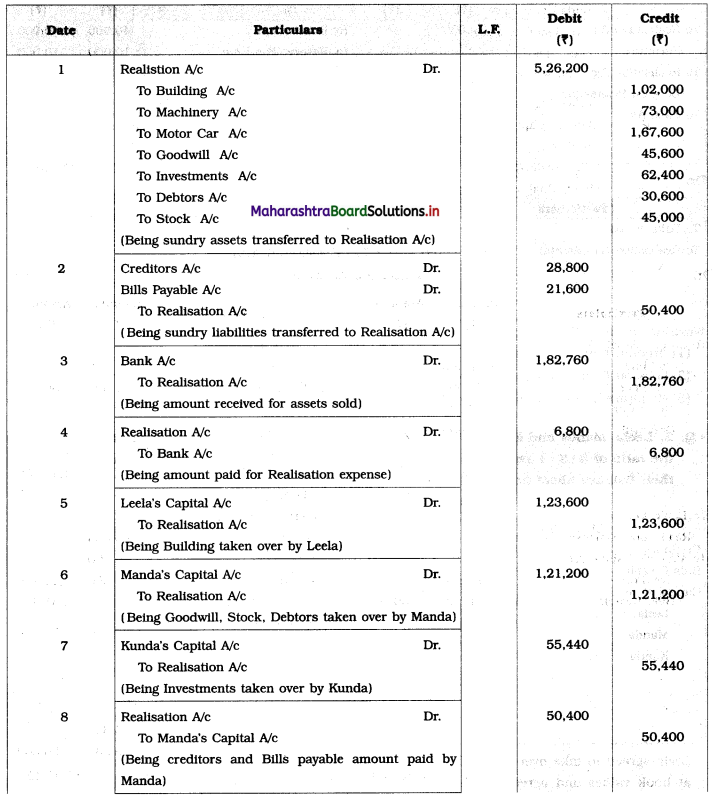
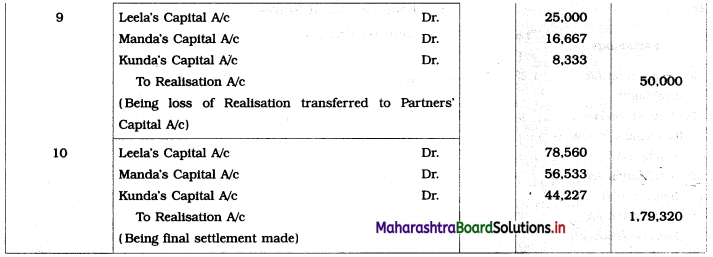
Working Notes:
In the books of Leela, Manda, and Kunda
Question 3.
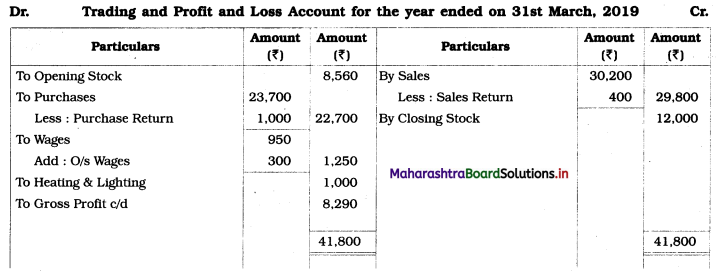
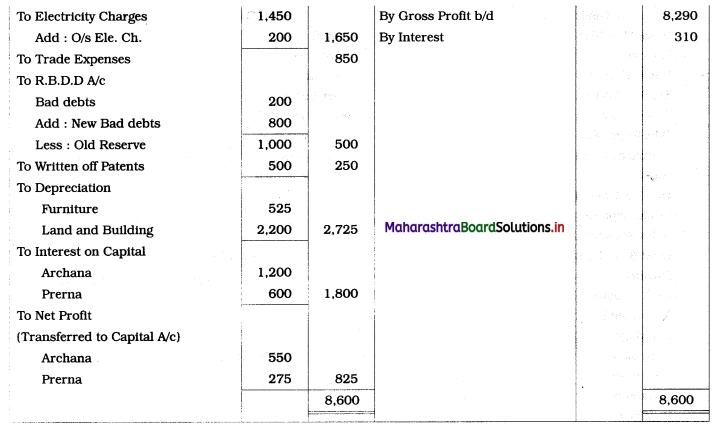
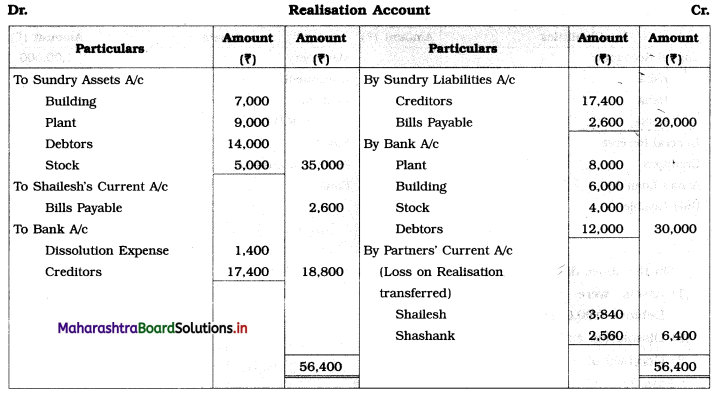
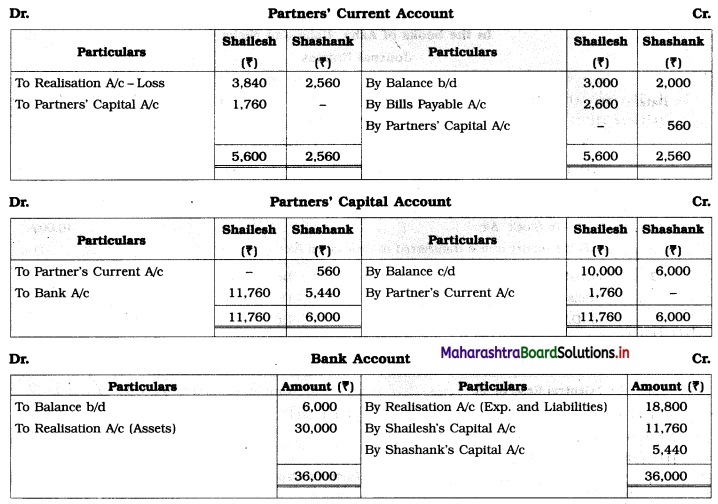
Shailesh and Shashank were partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. Their Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019 was as follows:
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
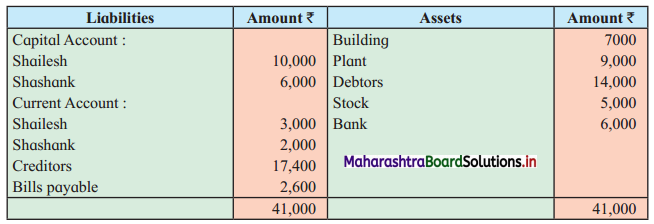
The firm was dissolved on the above date and the assets realised as under:
1. Plant ₹ 8,000, Building ₹ 6,000, Stock ₹ 4,000 and Debtors ₹ 12,000.
2. Shailesh agreed to pay off the Bills Payable.
3. Creditors were paid in full.
4. Dissolution expenses were ₹ 1,400.
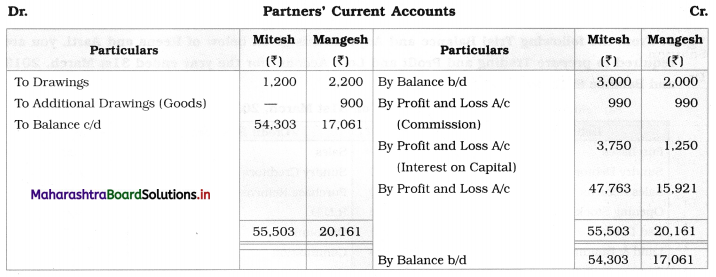
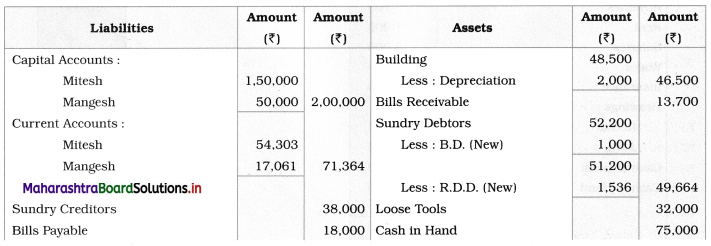
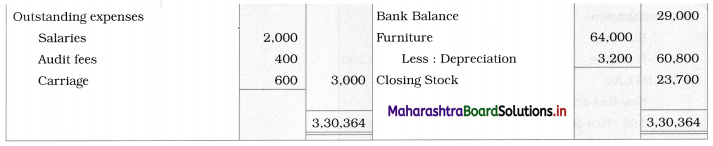
Prepare Realisation A/c, Partners’ Current A/c, Partners’ Capital A/c, and Bank A/c.
Solution:
In the books of Shailesh and Shashank
![]()
Question 4.
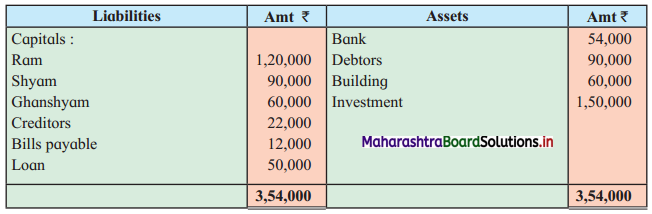
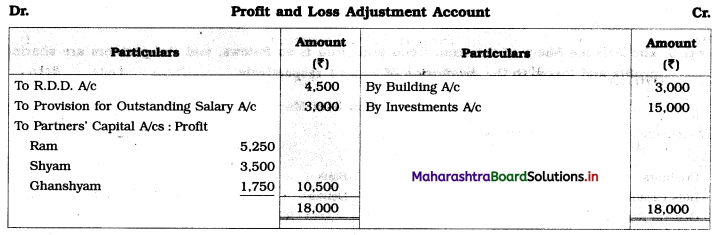
Asha, Usha, and Nisha were partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. The following is the Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019.
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
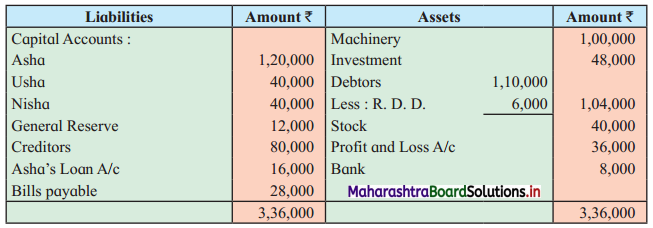
On the above date, the partners decided to dissolve the firm.
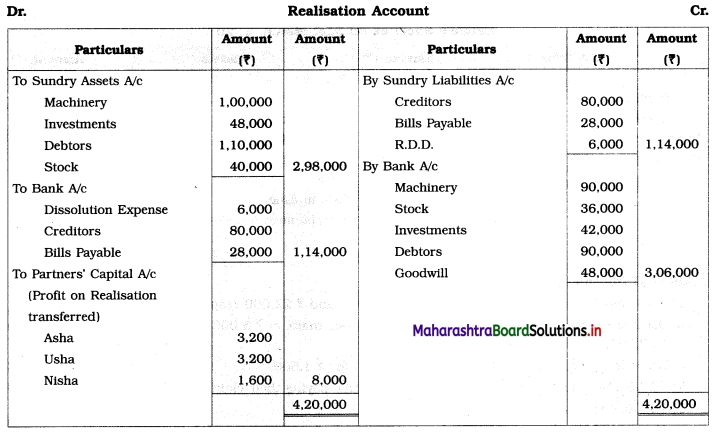
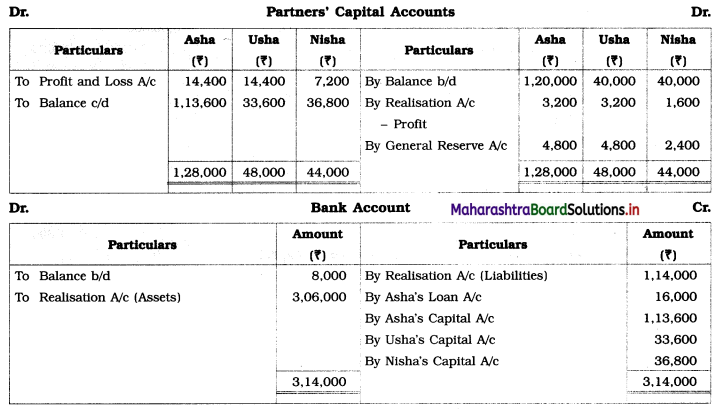
1. Assets were realised at: Machinery ₹ 90,000, Stock ₹ 36,000, Investment ₹ 42,000 and Debtors ₹ 90,000.
2. Dissolution expenses were ₹ 6,000.
3. Goodwill of the firm realized ₹ 48,000.
Pass Journal Entries to close the books of the firm.
Solution:
In the books of Asha, Usha, and Nisha
Journal Entries
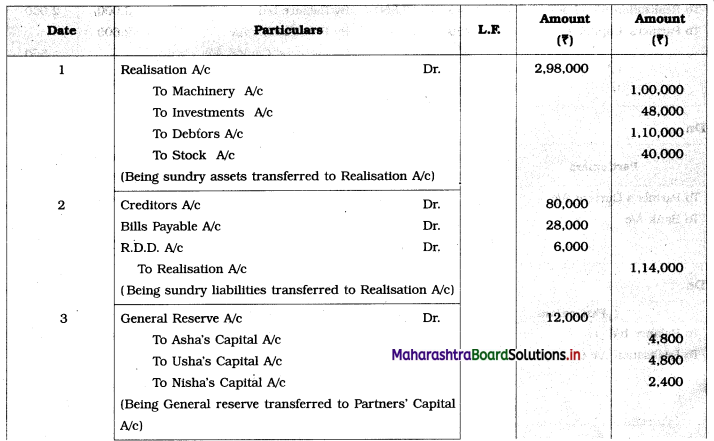
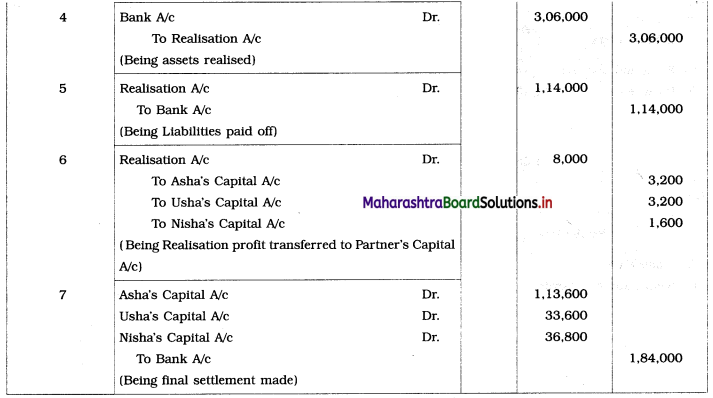
Working Notes:
In the books of Asha, Usha, and Nisha
Question 5.
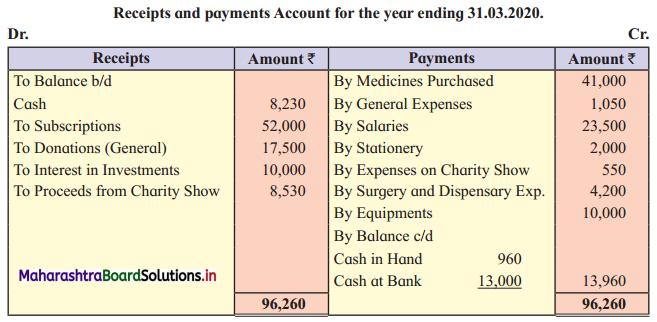
Seeta and Geeta are partners in the firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 1. They decided to dissolve the partnership on 31st March 2020 on which date their Balance Sheet stood as follows:
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2020
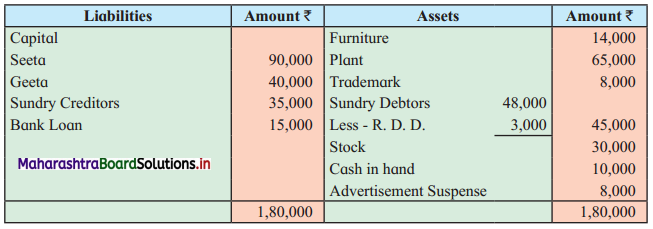
Additional Information:
1. Plant and Stock took over by Seeta at ₹ 78,000 and ₹ 22,000 respectively.
2. Debtors realised 90% of the book value and Trademark at ₹ 5,000 and Goodwill was realised for ₹ 27,000.
3. Unrecorded assets estimated at ₹ 4,500 were sold for ₹ 1,500.
4. ₹ 1,000 Discounts were allowed by creditors while paying their claim.
5. The Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 3,500.
You are required to prepare Realisation A/c, Cash A/c, and Partners’ Capital A/c.
Solution:
In the books of Seeta and Geeta
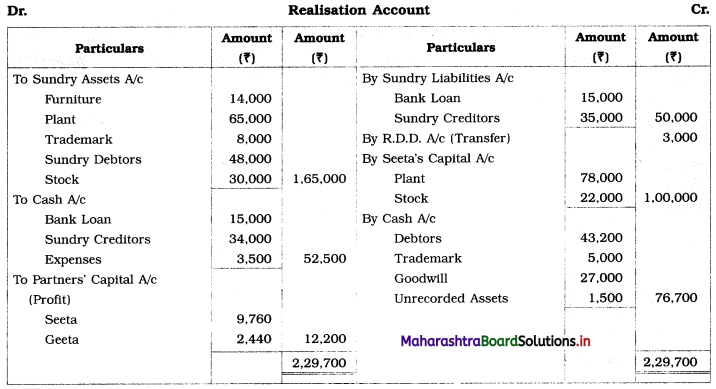
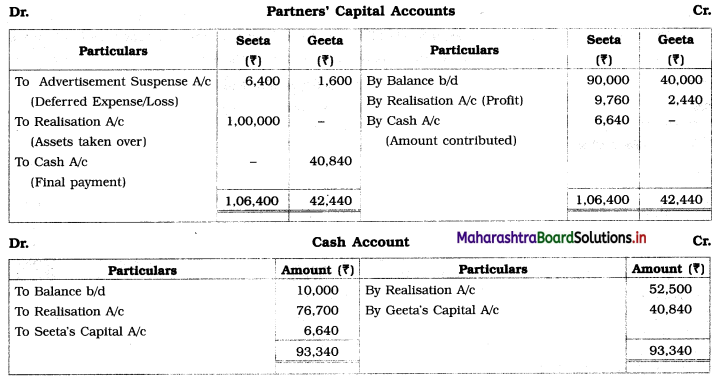
Working Notes:
1. Bank Loan is an external liability of the firm and therefore it is transferred to Realisation A/c.
2. Amount recovered from Debtors = 90% of Gross Debtors = \(\frac {90}{100}\) × 48,000 = ₹ 43,200.
3. Amount paid to creditors = Value of Creditors – Discount given = 35,000 – 1,000 = ₹ 34,000.
4. Sale of unrecorded assets for ₹ 1,500 is recorded on the credit side of Realisation A/c and debit side of Cash A/c.
5. It is presumed that Furniture realised nothing.
![]()
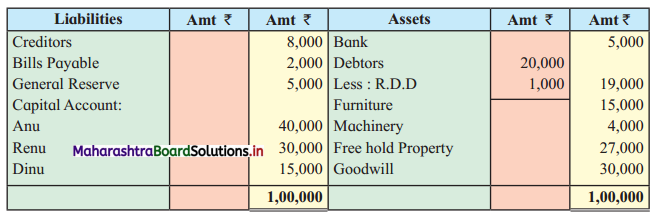
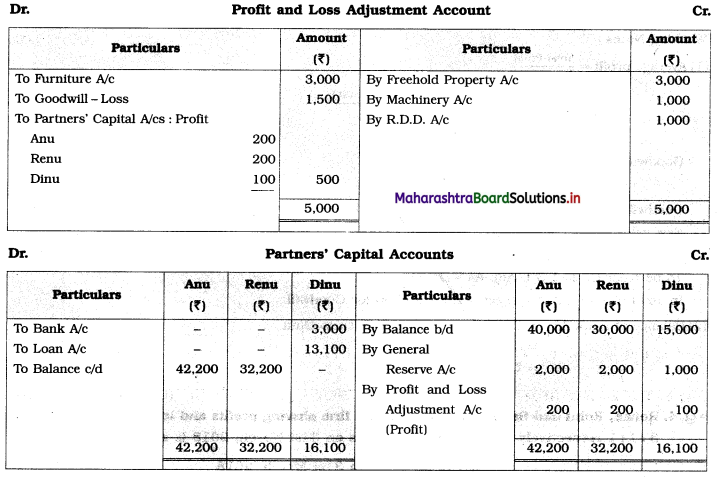
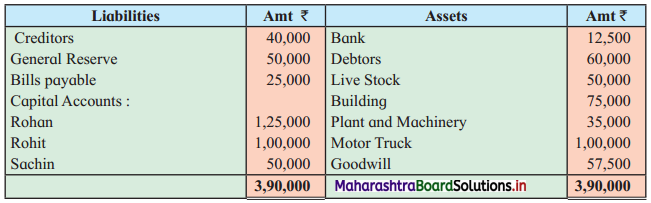
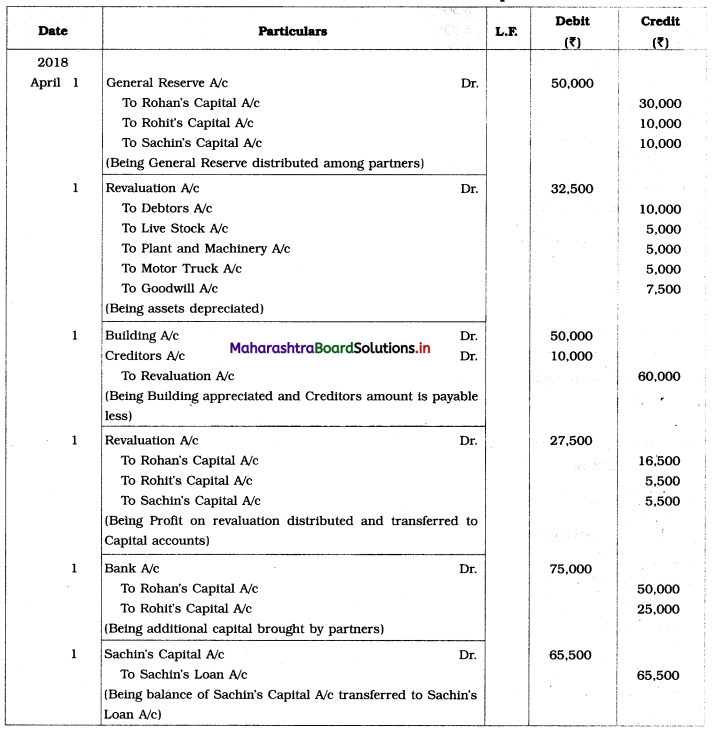
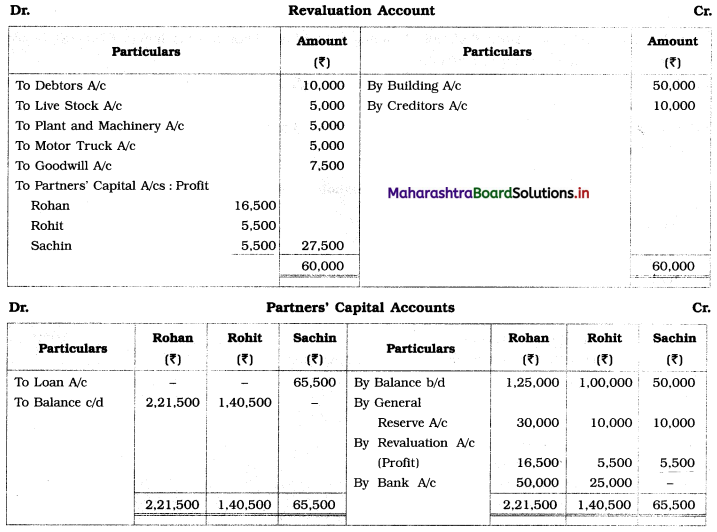
Question 6.
Sangeeta, Anita, and Smita were in partnership sharing profits and losses in the ratio 2 : 2 : 1. Their Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019 was as under:
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
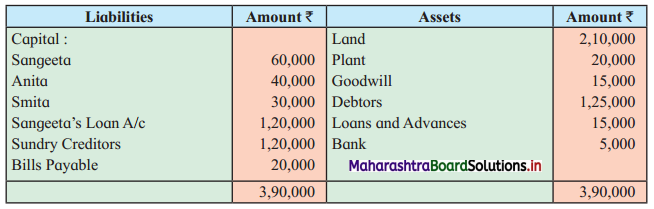
They decided to dissolve the firm as follows:
1. Assets realised as; Land recovered ₹ 1,80,000; Goodwill for ₹ 75,000; Loans and Advance realised ₹ 12,000; 10% of the Debts proved bad.
2. Sangeeta took Plant at book value.
3. Creditors and Bills payable paid at 5% discount.
4. Sandhya’s loan was discharged along with ₹ 6,000 as interest.
5. There was a contingent liability in respect of bills of ₹ 1,00,000 which was under discount. Out of them, a holder of one bill of ₹ 20,000 became insolvent.
Show Realisation Account, Partners’ Capital Account, and Bank Account.
Solution:
In the books of Sangeeta, Anita, and Smita
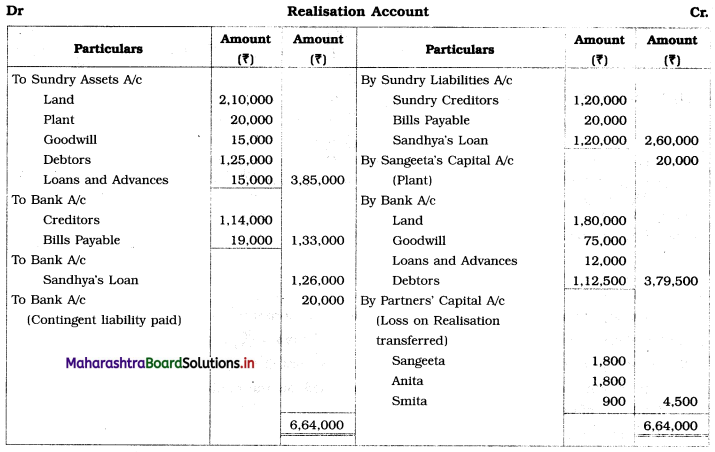
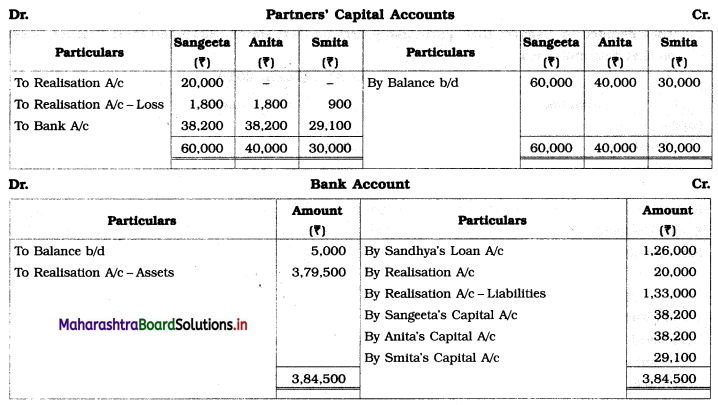
Working Notes:
1. Amount paid towards Sandhya’s Loan = Loan amount + Interest due on loan
= 1,20,000 + 6,000
= ₹ 1,26,000
2. Amount received from Debtors = Debtors – Bad debts
= 1,25,000 – 10% of 1,25,000
= 1,25,000 – 12,500
= ₹ 1,12,500
3. Amount paid to Creditors = Creditor – 5% discount
= 1,20,000 – 5% on 1,20,000
= 1,20,000 – 6,000
= ₹ 1,14,000
4. Amount paid towards Bills payable = Bills payable – 5% discount
= 20,000 – 5% on 20,000
= 20,000 – 1,000
= ₹ 19,000
5. Bill of ₹ 1,00,000 was discounted with the Bank. On the due date, bank could not recover ₹ 20,000 from one bill holder as he was declared insolvent. Therefore, we are required to settle that contingent liability of ₹ 20,000.
![]()
Question 7.
Saiesh, Sumit, and Hemant were in partnership sharing Profits and Losses in the ratio 2 : 2 : 1. They decided to dissolve their partnership firm on 31st March 2019 and their Balance Sheet on that date stood as;
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
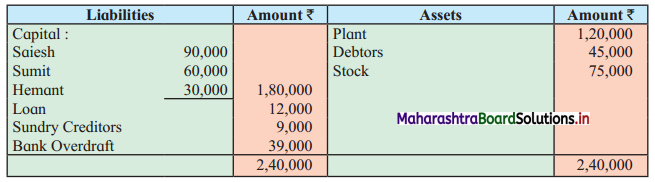
It was agreed that;
1. Sailesh to discharge Loan and to take Debtors at book value.
2. Plant realised ₹ 1,35,000.
3. Stock realised ₹ 72,000.
4. Creditors were paid off at a discount of ₹ 45.
Show Realisation Account, Partners’ Capital Account, and Bank Account.
Solution:
In the books of Sailesh, Sumit, and Hemant
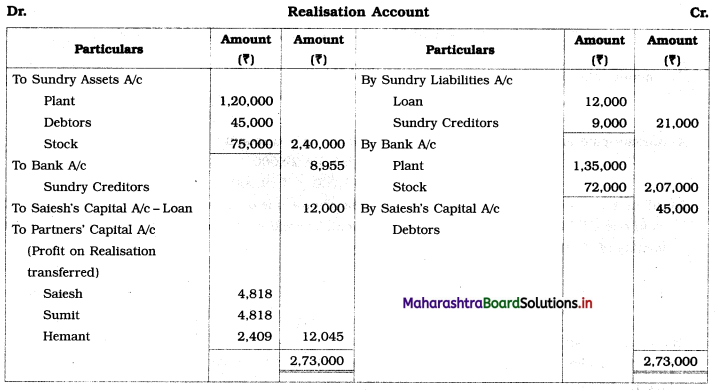
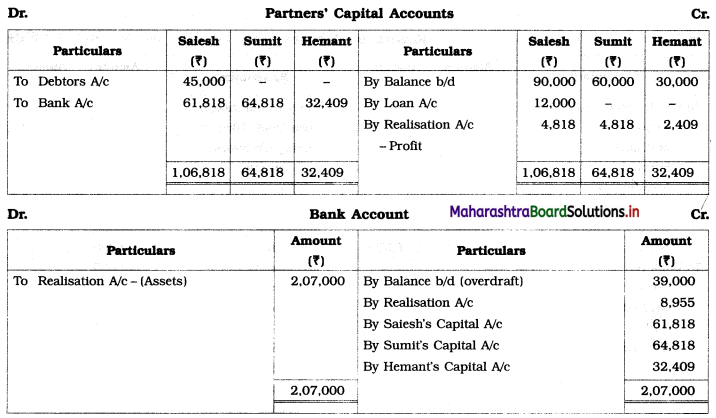
(When one partner become Insolvent)
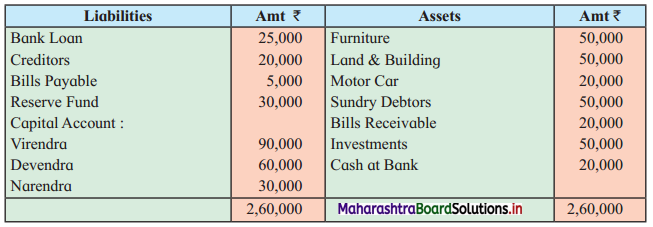
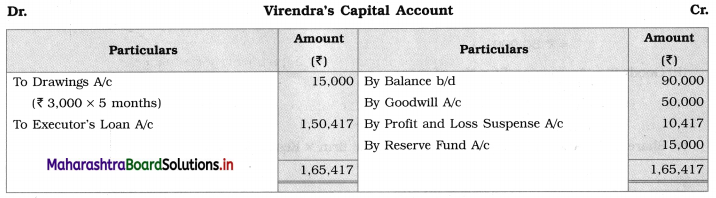
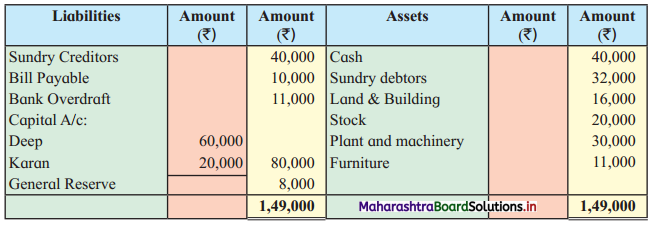
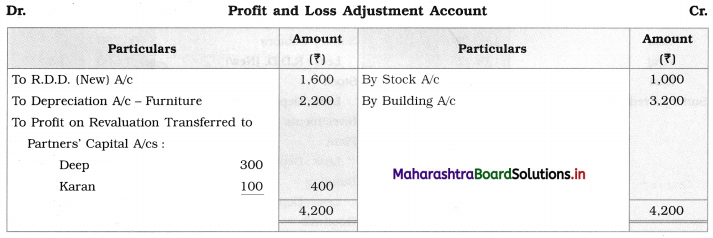
Question 8.
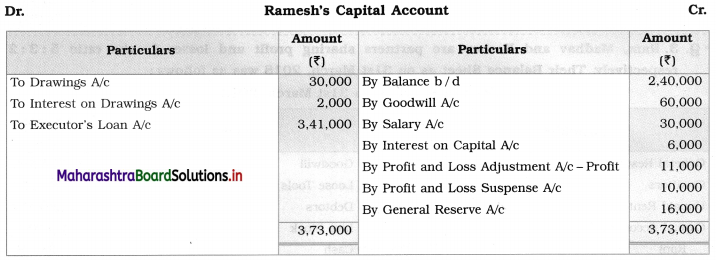
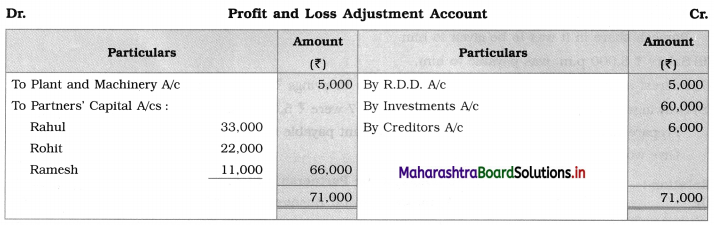
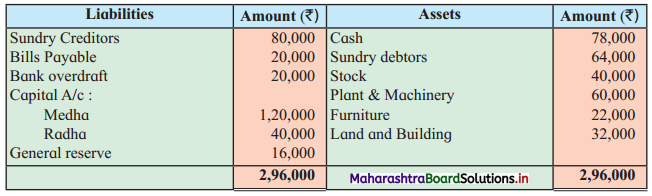
Sitaram, Gangaram, and Rajaram are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 2 : 3. On 1st April 2019 they agreed to dissolve the partnership, their Balance Sheet was as follows:
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
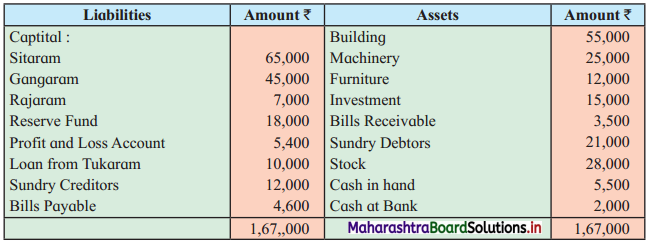
The assets realised: Building ₹ 46,750; Machinery ₹ 18,550; Furniture ₹ 9,600; Investment ₹ 10,650; Bill Receivable and Debtors ₹ 20,750. All the liabilities were paid off. The cost of realisation was ₹ 800. Rajaram becomes bankrupt and ₹ 1,100 only was recovered from his estate.
Show Realisation Account, Bank Account, and Capital Account of the partners.
Solution:
In the books of Sitaram, Gangaram and Rajaram
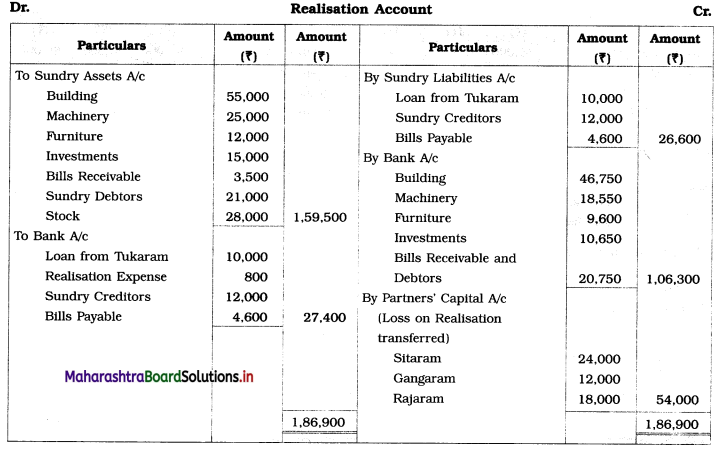
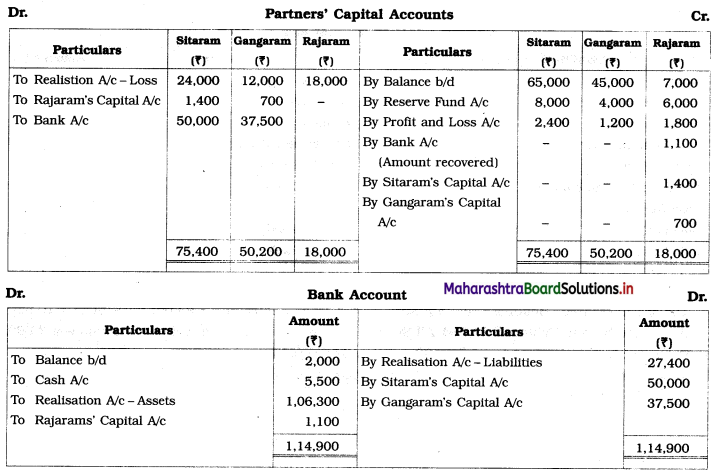
Working Notes:
1. ₹ 1,100 is recovered from Rajaram’s estate which is recorded on the credit side of Rajaram’s Capital Account and on the debit side of Bank A/c.
2. Capital deficiency of Rajaram = Debit total of Capital A/c – Credit total of Capital A/c
= 18,000 – 15,900
= ₹ 2,100
The deficit amount of Rajaram A/c ₹ 2,100 is distributed among continuing partners’ in 2 : 1 ratio.
![]()
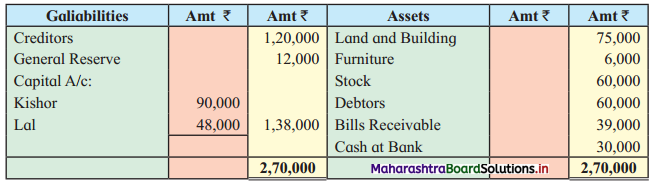
Question 9.
Following is the Balance Sheet of Vaibhav, Sanjay, and Santosh
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
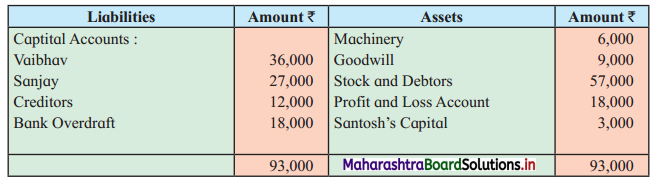
Santosh is declared insolvent so the firm is dissolved and assets realised as follows:
1. Stock and Debtors ₹ 54,000, Goodwill – NIL, Machinery at book value.
2. Creditors allowed a discount of 10%.
3. Santosh could pay only 25 paise in the rupee of the balance due.
4. Profit sharing ratio was 8 : 4 : 3.
5. A contingent liability against the firm ₹ 9,000 is cleared.
Give Ledger Account to close to books of the firm.
Solution:
In the books of Vaibhav, Sanjay, and Santosh
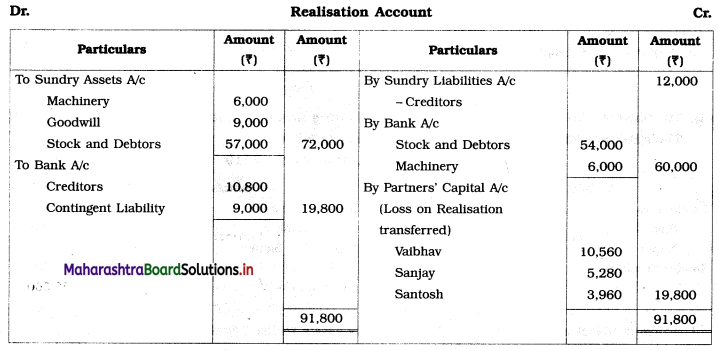
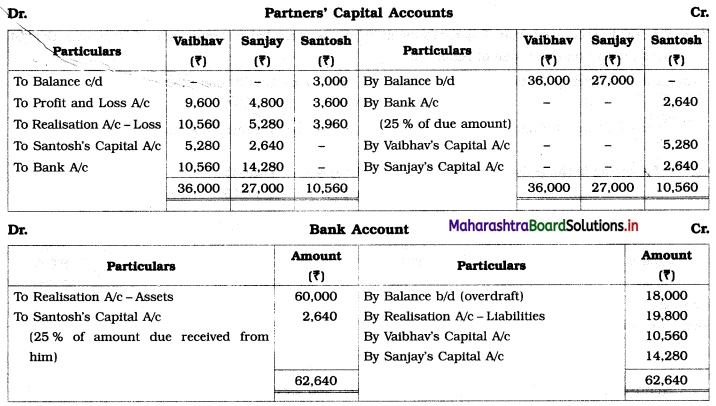
Working Notes:
1. Contingent liability paid, so Realisation A/c is debited and Bank A/c is credited.
2. Santosh could pay only 25 paise in a rupee of the balance due i.e.
Balance due from Santosh (Debit side of Partners Capital A/c) = ₹ 10,560
25% of ₹ 10,560 = ₹ 2,640 (Amount recorded on debit side of Bank A/c)
Capital deficiency of Santosh = 10,560 – 2,640 = ₹ 7,920
₹ 7,920 to be distributed among continuing partner in their profit-loss ratio = 8 : 4 i.e. 2 : 1.
7,920 × \(\frac{2}{3}\) = ₹ 5,280
7,920 × \(\frac{1}{3}\) = ₹ 2,640
(When Two Partners become Insolvent)
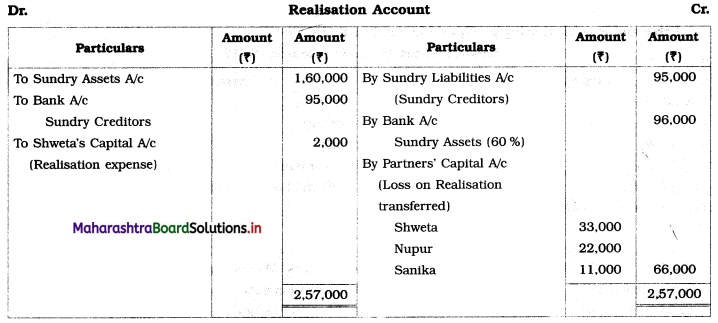
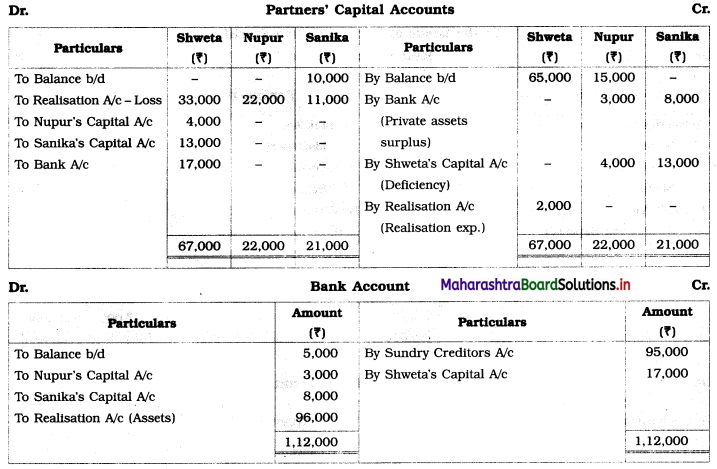
Question 10.
Shweta, Nupur, and Sanika are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. Their Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019 was as follows:
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
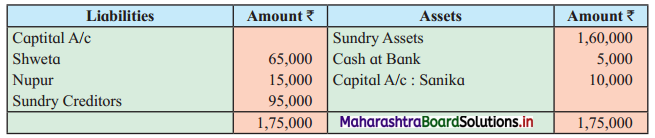
The firm is dissolved on 31st March 2019. Sundry assets realised @ 60% of its book value. Realisation expenses ₹ 2,000 paid by Shweta. Nupur and Sanika both are insolvent.
Nupur’s private estate has got a surplus of ₹ 3,000 and that of Sanika ₹ 8,000.
Show necessary Ledger Accounts to close the books of the firm.
Solution:
In the books of Shweta, Nupur and Sanika
![]()
(When All Partners become Insolvent)
Question 11.
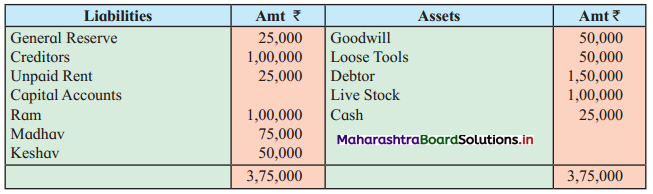
Following is the Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019 of a firm having three partners Priti, Priya, and Prachi.
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
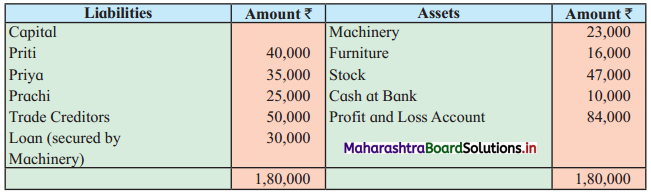
The firm was dissolved due to the insolvency of all the partners. Machinery was sold for ₹ 18,000, while Furniture fetched ₹ 14,000, Stock realized ₹ 35,000. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 2,000. Nothing could be recovered from Priya and Prachi, but ₹ 3,400 could be collected from Priti’s private estate.
Close the books of accounts of the firm.
Solution:
In the books of Priti, Priya, and Prachi
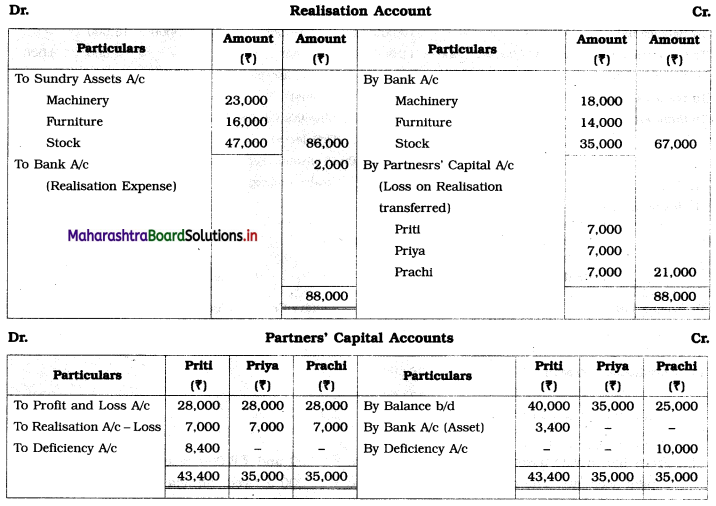
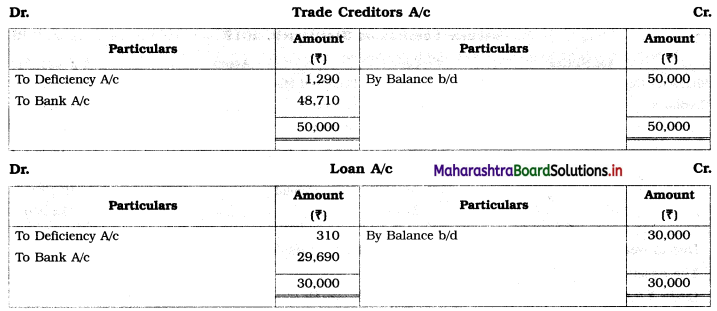
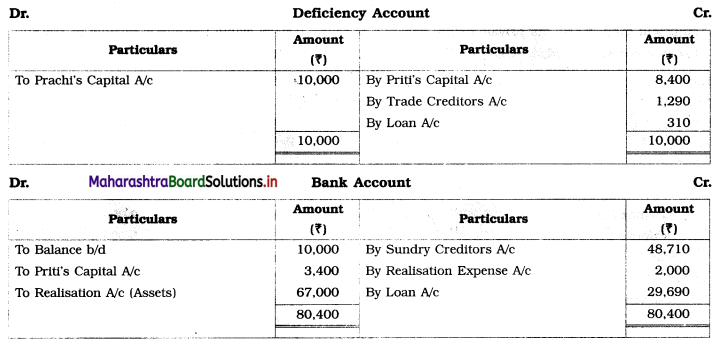
Working Notes:
1. Amount paid to loan from sale of machinery = ₹ 18,000
Balance of Loan 30,000 – 18,000 = ₹ 12,000
2. Ratio of Trade creditors and Loan = 50,000 : 12,000
= 50 : 12
= 25 : 6
3. Balance of cash available = 10,000 + 67,000 + 3,400 – 18,000 – 2,000
= 80,400 – 20,000
= ₹ 60,400
Amount paid towards loan = \(\frac{6}{31} \times \frac{60,400}{1}\) = ₹ 11,690
Amount paid to Trade creditors = \(\frac {25}{31}\) × 60,400 = ₹ 48,710
Amount paid towards loan = 18,000 + 11,690 = ₹ 29,690.
Question 12.
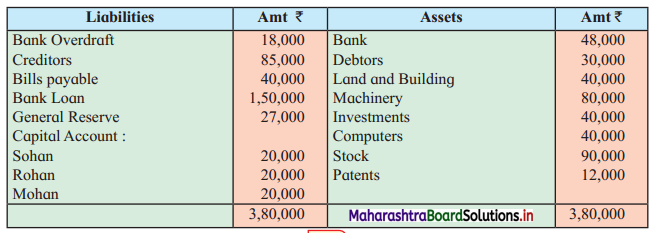
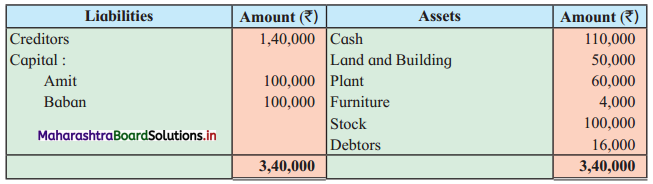
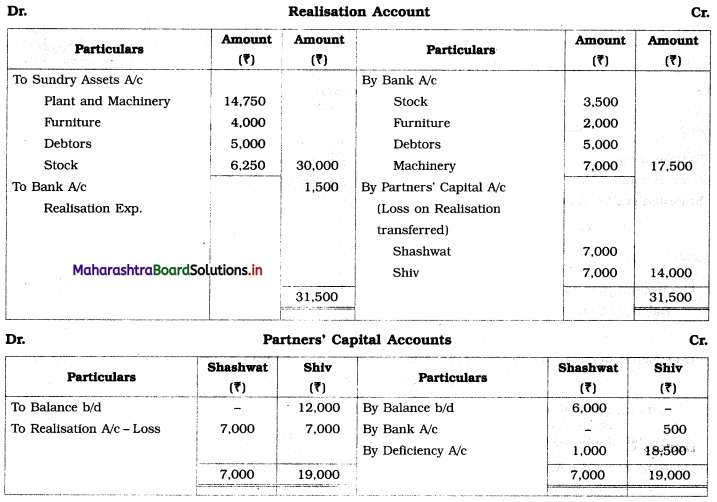
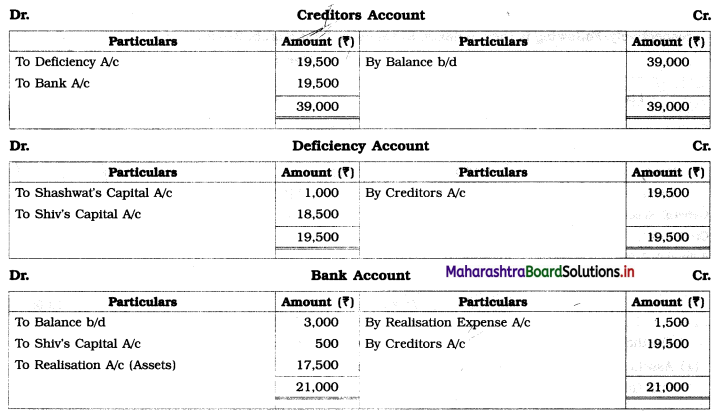
Shashwat and Shiv are equal partners. Their Balance Sheet stood as under:
Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2019
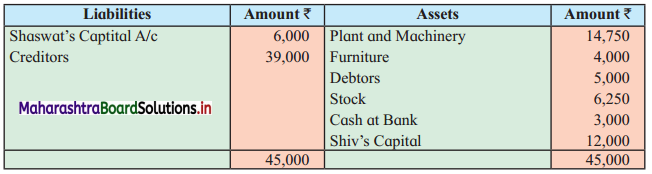
Due to weak financial position, all partners were declared bankrupt.
The Assets were realised as follows:
Stock ₹ 3,500, Furniture ₹ 2,000, Debtors ₹ 5,000 and Machinery ₹ 7,000.
The cost of collection and distributing the estate amounted to ₹ 1,500. Shashwat’s private estate is not sufficient even to pay his private debts, whereas in Shiv’s private estate there is a surplus of ₹ 500.
Prepare necessary Ledger Accounts to close the books of the firm.
Solution:
In the books of Shashwat and Shiv
Working Note:
As partners we’re not able to pay their loss amount, a difference of amount is considered as deficiency of partners.