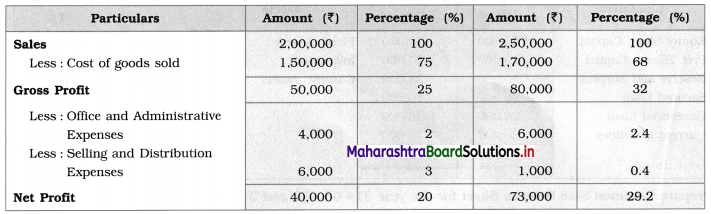
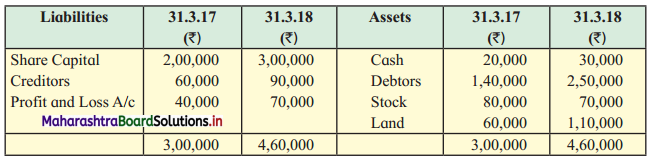
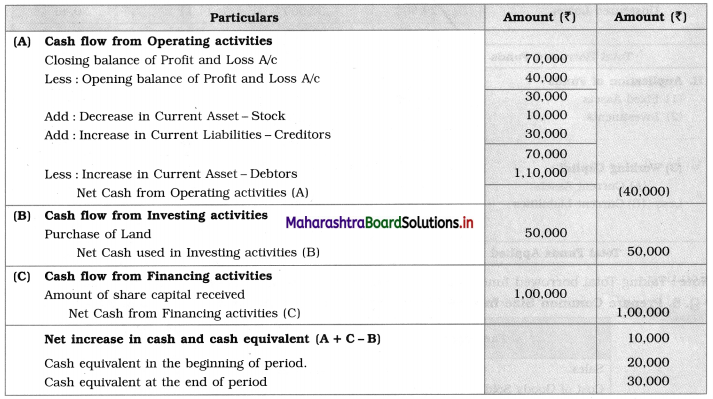
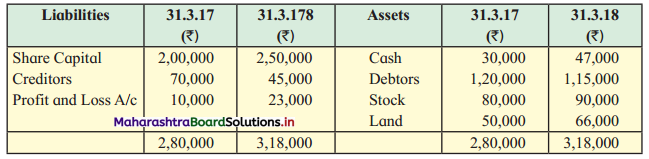
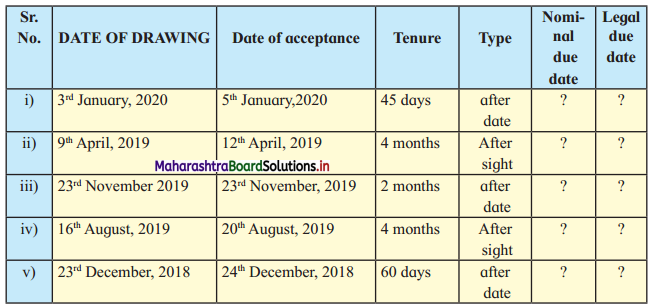
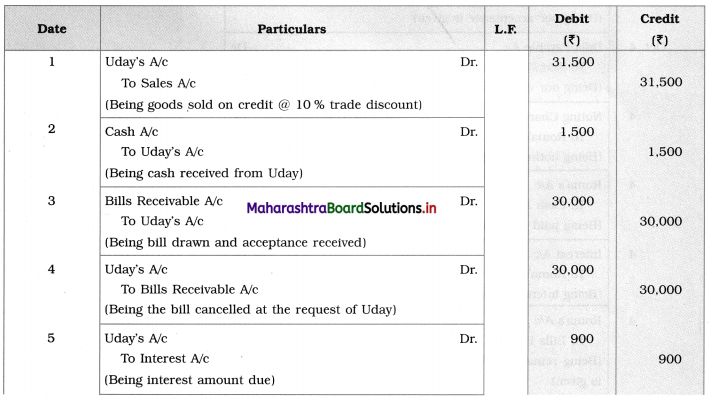
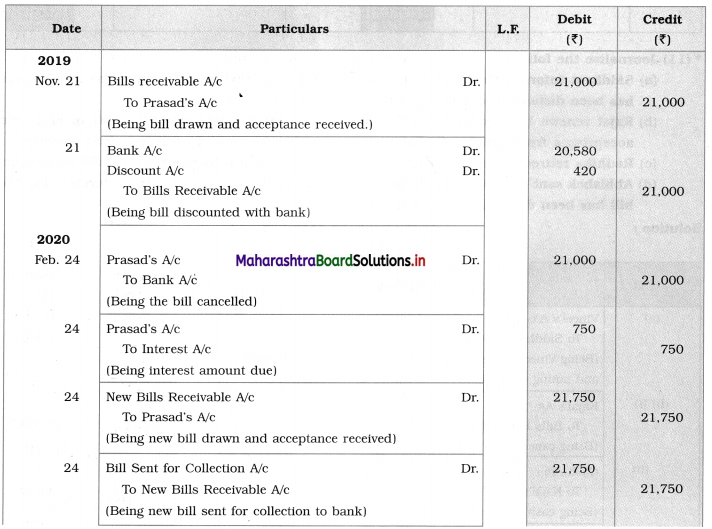
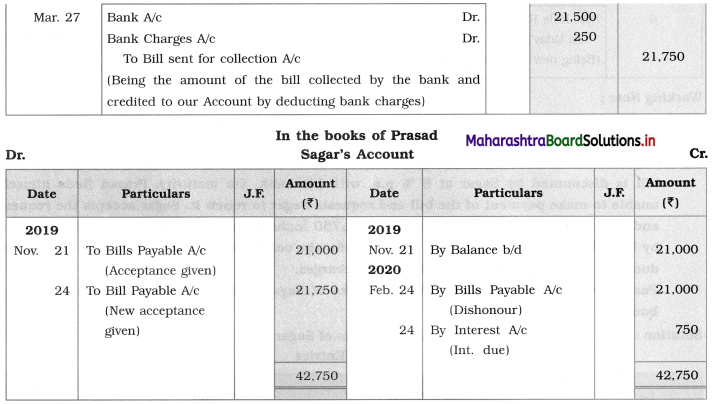
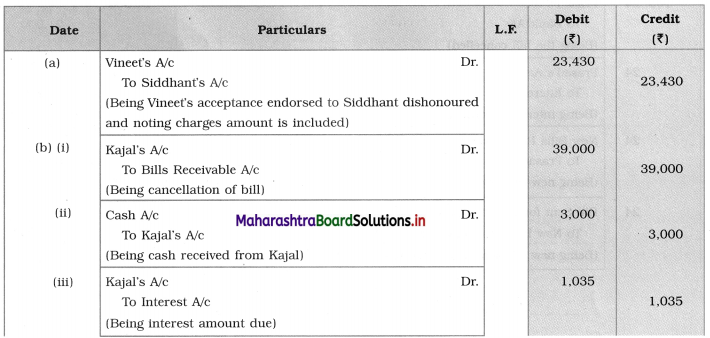
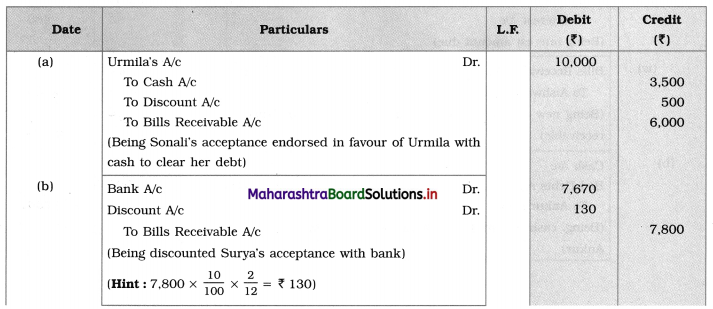
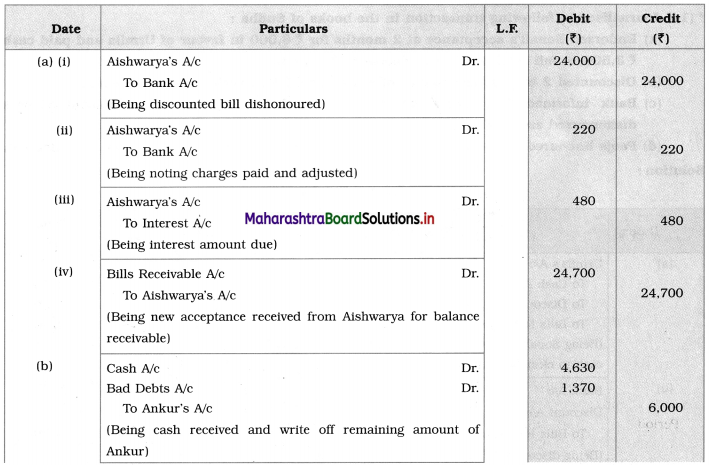
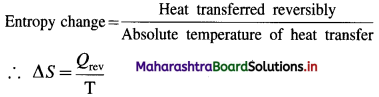
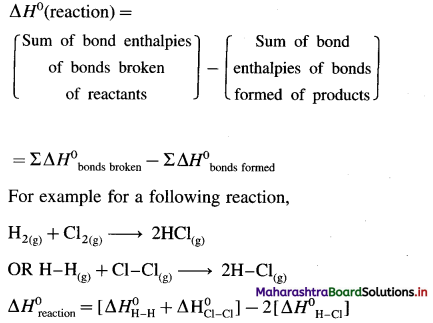
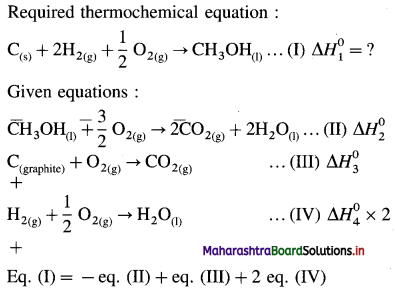
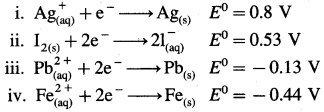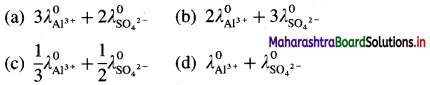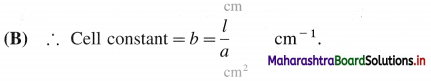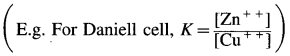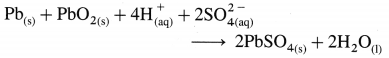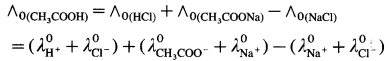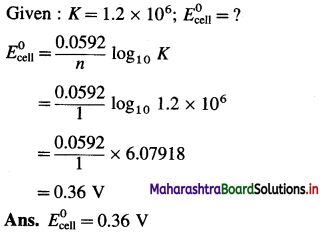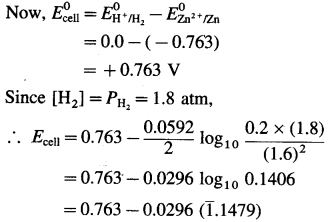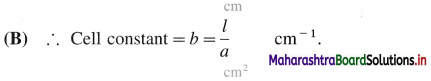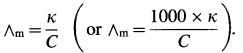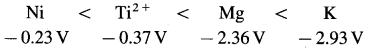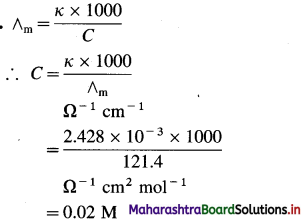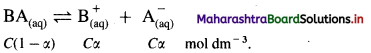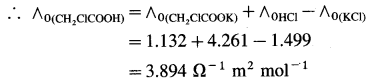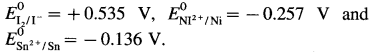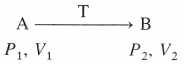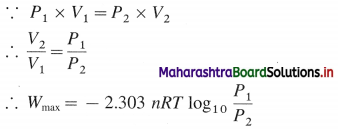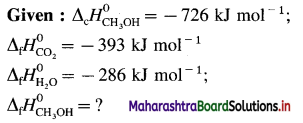Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Textbook Solutions Chapter 5 Electrochemistry Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 5 Electrochemistry
1. Choose the most correct option.
Question i.
Two solutions have the ratio of their concentrations 0.4 and ratio of their conductivities 0.216. The ratio of their molar conductivities will be
(a) 0.54
(b) 11.574
(c) 0.0864
(d) 1.852
Answer:
(a) 0.54
Question ii.
On diluting the solution of an electrolyte,
(a) both ∧ and κ increase
(b) both ∧ and κ decrease
(c) ∧ increases and κ decreases
(d) ∧ decreases and κ increases
Answer:
(c) ∧ increases and κ decreases
Question iii.
1 S m2 mol-1 is equal to
(a) 10-4 S m2 mol-1
(b) 104 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
(c) 10-2 S cm2 mol-1
(d) 102 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Answer:
(b) 104Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
Question iv.
The standard potential of the cell in which the following reaction occurs
H2+ (g, 1 atm) + Cu2+ (1 M) → 2H (1 M) + Cu(s), (\(E_{\mathrm{Cu}}^{0}\) = 0.34 V) is
(a) – 0.34 V
(b) 0.34 V
(c) 0.17 V
(d) -0.17 V
Answer:
(b) 0.34 V

Question v.
For the cell, Pb(s)|Pb2+ (1 M)|| Ag+ (1 M)|Ag(s), if concentration of an ion in the anode compartment is increased by a factor of 10, the emf of the cell will
(a) increase by 10 V
(b) increase by 0.0296 V
(c) decrease by 10 V
(d) decrease by 0.0296 V
Answer:
(d) decrease by 0.0296 V
Question vi.
Consider the half reactions with standard potentials
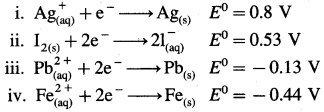
The strongest oxidising and reducing agents respectively are
(a) Ag and Fe2+
(b) Ag+ and Fe
(c) Pb2+ and I–
(d) I2 and Fe2+
Answer:
(b) Ag+ and Fe
Question vii.
For the reaction
Ni(s) + Cu2+ (1 M) → Ni2+ (1 M) + Cu(s), \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) = 0.57 V. Hence ΔG0 of the reaction is
(a) 110 kJ
(b) -110 kJ
(c) 55 kJ
(d) -55 kJ
Answer:
(b) -110 kJ
Question viii.
Which of the following is not correct ?
(a) Gibbs energy is an extensive property
(b) Electrode potential or cell potential is an intensive property.
(c) Electrical work = -ΔG
(d) If half reaction is multiplied by a numerical factor, the corresponding E0 value is also multiplied by the same factor.
Answer:
(d) If half reaction is multiplied by a numerical factor, the corresponding E0 value is also multiplied by the same factor.
Question ix.
The oxidation reaction that takes place in lead storage battery during discharge is
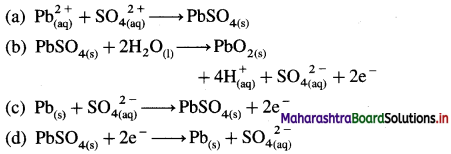
Answer:
(c) \(\mathrm{Pb}_{(\mathrm{s})}+\mathrm{SO}_{4(\mathrm{aq})}{ }^{2-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbSO}_{4(\mathrm{~s})}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-}\)
Question x.
Which of the following expressions represent molar conductivity of Al2(SO4)3 ?
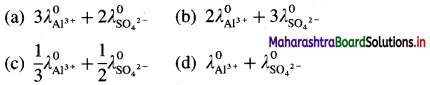
Answer:
(b) \(2 \lambda_{\mathrm{Al}^{3+}}^{0}+3 \lambda_{\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}}^{0}\)

2. Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Question i.
What is a cell constant ?
Answer:
(A) Cell constant of a conductivity cell is defined as the ratio of the distance between the electrodes divided by the area of cross section of the electrodes.
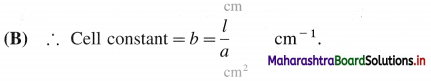
In SI units it is expressed as m-1.
Question ii.
Write the relationship between conductivity and molar conductivity and hence unit of molar conductivity.
Answer:
If k is conductivity and ∧m is molar conductivity then, ∧m = \(\frac{\kappa \times 1000}{C}\)
Unit of molar conductivity is, Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 or S cm2 mol-1.
Question iii.
Write the electrode reactions during electrolysis of molten KCl.
Answer:
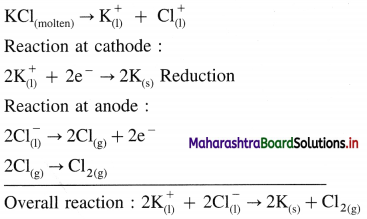
Question iv.
Write any two functions of salt bridge.
Answer:
The functions of a salt bridge are :
- It maintains the electrical contact between the two electrode solutions of the half cells.
- It prevents the mixing of electrode solutions.
- It maintains the electrical neutrality in both the solutions of two half cells by a flow of ions.
- It eliminates the liquid junction potential.

Question v.
What is standard cell potential for the reaction
3Ni(s) + 2Al3+ (1M) → 3NI2+ (1M) + 2Al(s)
if \(\boldsymbol{E}_{\mathrm{Ni}}^{0}\) = – 0.25 V and \(\boldsymbol{E}_{\mathrm{Al}}^{0}\) = -1.66V?
Solution :
Given : E0Ni2+/Ni = -0.25 V
E0Al3+/Al = – 1.66 V; E0cell = ?
Since Ni is oxidised and Al3+ is reduced,
\(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}=E_{\mathrm{Al}^{3+} / \mathrm{Al}}^{0}-E_{\mathrm{Ni}^{2+} / \mathrm{Ni}}^{0}\)
= – 1.66 – (-0.25)
= – 1.41 V
Ans. \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) = -1.41 V
[Note : Since \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) is negative, the given reaction is not possible but reverse reaction is possible.]
Question vi.
Write Nerst equation. What part of it represents the correction factor for nonstandard state conditions ?
Answer:
(1) Nernst equation for cell potential is,
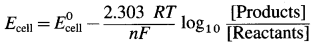
(2) The part of equation namely,
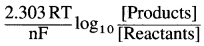
represents the correction factor for nonstandard state conditions.
Question vii.
Under what conditions the cell potential is called standard cell potential ?
Answer:
In the standard cell, the active masses of the substances taking part in the electrochemical reaction have unit value, i.e., 1 M solution or ions and 1 atm gas.
Question viii.
Formulate a cell from the following electrode reactions :
\(\mathbf{A u}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{3+}+\mathbf{3 e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathbf{A} \mathbf{u}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
\(\mathbf{M g}_{(\mathbf{s})} \longrightarrow \mathbf{M g}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+\mathbf{2 e}^{-}\)
Answer:
An electrochemical cell from above electrode reactions is,
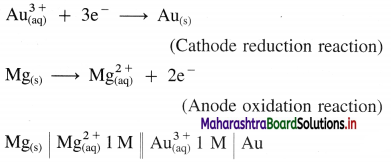
Question ix.
How many electrons would have a total charge of 1 coulomb ?
Answer:
Given : 1 Faraday = charge on 1 mol of electrons
= 6.022 × 1023 electrons and 1 Faraday = 96500 C
∵ 96500 C = 6.022 × 1023 electrons 6 022 × 1023
∴ 1 C ≡ \(\frac{6.022 \times 10^{23}}{96500}\) = 6.24 × 1018 electrons
Ans. Number of electrons = 6.24 × 1018
Question x.
What is the significance of the single vertical line and double vertical line in the formulation galvanic cell.
Answer:
(i) Consider representation of Daniell cell,
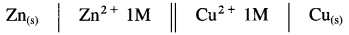
Single vertical line represents separation of two phases, solid Zn(s) and solution of ions.
(ii) Double vertical lines represent a salt bridge.

3. Answer the following in brief
Question i.
Explain the effect of dilution of solution on conductivity ?
Answer:
- The conductance of a solution is due to the presence of ions in the solution. More the ions, higher is the conductance of the solution.
- Conductivity or the specific conductance is the conductance of unit volume (1 cm3) of the electrolytic solution.
- The conductivity of the electrolytic solution always decreases with the decrease in the concentration of the electrolyte or the increase in dilution of the solution.
- On dilution, the concentration of the solution decreases, hence the number of (current carrying) ions per unit volume decreases. Therefore the conductivity of the solution decreases, with the decrease concentration or increase in dilution. (It is to be noted here that, molar conductivity increases with dilution.)
Question ii.
What is a salt bridge ?
Answer:
A salt bridge is a U-shaped glass tube containing a saturated solution of a strong electrolyte, like KCl, NH4NO3, Na2SO4 in a solidified agar-agar gel. A hot saturated solution of these electrolytes in 5% agar solution is filled in the U-shaped tube and allowed it to cool and solidify forming a gel.
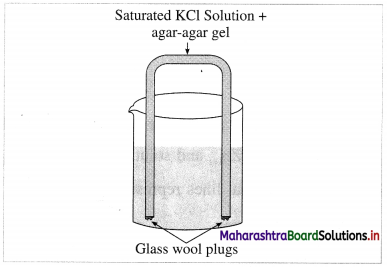
Fig. 5.9 : Salt bridge
It is used to connect two half cells or electrodes forming a galvanic or voltaic cell.
Question iii.
Write electrode reactions for the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl.
Answer:
Reactions in electrolytic cell :
(i) Reduction half reaction at cathode : There are Na+ and H+ions but since H+ are more reducible than Na+, they undergo reduction liberating hydrogen and Na+ are left in the solution.
2H2O(l) + 2e– → H2(g) + 2OH–(aq) (reduction) E0 = -0.83 V
(ii) Oxidation half reaction at anode : At anode there are Cl– and OH–. But Cl– ions are preferably oxidised due to less decomposition potential.

Net cell reaction : Since two electrons are gained at cathode and two electrons are released at anode for each redox step, the electrical neutrality is maintained. Hence we can write,
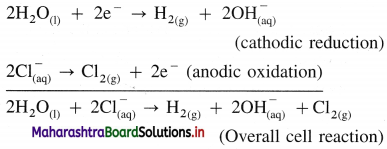
Since Na+ and OH– are left in the solution, they form NaOH(aq).
Question iv.
How many moles of electrons are passed when 0.8 ampere current is passed for 1 hour through molten CaCl2 ?
Answer:
Given : I = 0.8 A; t = 1 × 60 × 60 = 3600 s
Number of moles of electrons = ?
Q = I × t
= 0.8 × 3600
= 2880 C
1 Faraday = 1 mol electrons
1 Faraday = 96500 C
∵ 96500 C = 1 mol electrons
∴ 2880 C ≡ \(\frac{2880}{96500}\)
= 0.02984 mol electrons
Ans. Number of moles of electrons = 0.02984

Question v.
Construct a galvanic cell from the electrodes Co3+|Co and Mn2+|Mn. \(\boldsymbol{E}_{\mathrm{Co}}^{0}\) = 1.82 V,
\(\boldsymbol{E}_{\mathrm{Mn}}^{0}\) = – 1.18V. Calculate \(\boldsymbol{E}_{\text {cell }}^{0}\).
Answer:

Question vi.
Using the relationsip between ∆G0 of cell reaction and the standard potential associated with it, how will you show that the electrical potential is an intensive property ?
Answer:
(1) For an electrochemical cell involving n number of electrons in the overall cell reaction,
ΔG0 = -nF\(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\)
where ΔG0 is standard Gibbs energy change and \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) is a standard cell potential.
(2) ∴ \(E_{\mathrm{cell}}^{0}=\frac{-\Delta G^{0}}{n F}\)
Since ΔG0 changes according to number of moles of electrons involved in the cell reaction, the ratio, ΔG0/nF remains constant.
(3) Therefore \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) is independent of the amount of substance and it represents the intensive property.
Question vii.
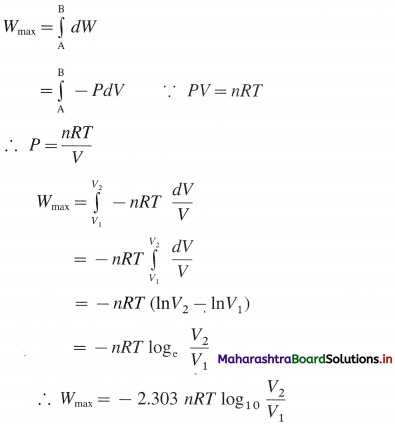
Derive the relationship between standard cell potential and equilibrium constant of cell reaction.
Answer:
For any galvanic cell, the overall cell reaction at equilibrium can be represented as,
Reactants ⇌ Products.
[For example for Daniell cell,
\(\mathrm{Zn}_{(s)}+\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{s})}\) ]
The equilibrium constant, K for the reversible reaction will be, \(K=\frac{[\text { Products }]}{[\text { Reactants }]}\)
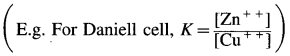
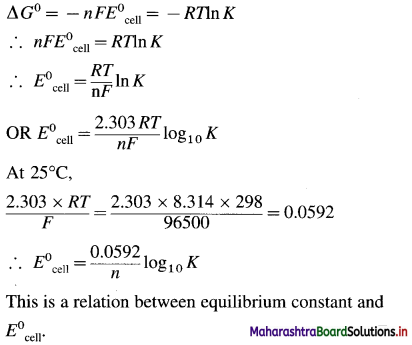
The equilibrium constant is related to the stan-dard free energy change Δ G0, as follows,
ΔG0 = -RTlnK
If \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) is the standard cell potential (or emf) of the galvanic cell, then ΔG0 = -nFE0cell
By comparing above equations,
Question viii.
It is impossible to measure the potential of a single electrode. Comment.
Answer:
(1)
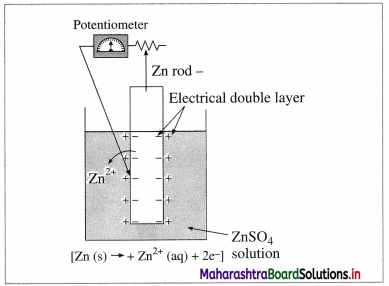
Fig 5.12(a) : Measurement of single electrode potential
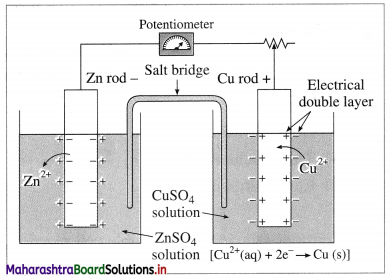
Fig 5.12(b) : Measurement of cell potential
According to Nemst theory, electrode potential is the potential difference between the metal and ionic layer around it at equilibrium, i.e. the potential across the electric double layer.
(2) For measuring the single electrode potential, one part of the double layer, that is metallic layer can be connected to the potentiometer but not the ionic layer. Hence, single electrode potential can’t be measured experimentally.
(3) When an electrochemical cell is developed by combining two half cells or electrodes, they can be connected to the potentiometer and the potential difference or cell potential can be measured.
Ecell = E2 – E1
where E1 and E2 are reduction potentials of two electrodes.

Question ix.
Why do the cell potential of lead accumulators decrease when it generates electricity ? How the cell potential can be increased ?
Answer:
Working of a lead accumulator :
(1) Discharging : When the electric current is withdrawn from lead accumulator, the following reactions take place :
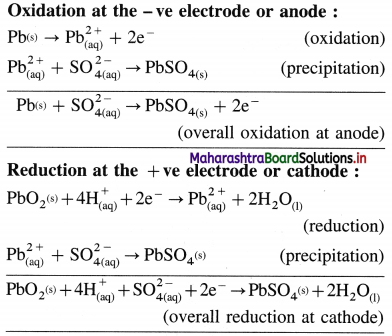
(2) Net cell reaction :
(i) Thus, the overall cell reaction during discharging is
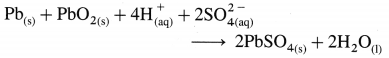
OR
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
The cell potential or emf of the cell depends upon the concentration of sulphuric acid. During the operation, the acid is consumed and its concentration decreases and specific gravity decreases from 1.28 to 1.17. As a result, the emf of the cell decreases. The emf of a fully charged cell is about 2.0 V.
(ii) Recharging of the cell : When the discharged battery is connected to external electric source and a higher external potential is applied the cell reaction gets reversed generating H2SO4.
Reduction at the -ve electrode or cathode :
PbSO4(s) + 2e– → Pb(s) + \(\mathrm{SO}_{4(\mathrm{aq})}^{2-}\)
Oxidation at the + ve electrode or anode :

The emf of the accumulator depends only on the concentration of H2SO4.
Question x.
Write the electrode reactions and net cell reaction in NICAD battery.
Answer:
Reactions in the cell :
(i) Oxidation at cadmium anode :
Cd(s) + 2OH–(aq) → Cd(OH)2(s) + 2e–
(ii) Reduction at NiO2(s) cathode :
NiO2(s) + 2H2O(l) + 2e– → Ni(OH)2(s) + 2OH–(aq)
The overall cell reaction is the combination of above two reactions.
Cd(s) + NiO2(s) + 2H2O(l) → Cd(OH)2(s) + Ni(OH)2(s)

4. Answer the following :
Question i.
What is Kohrausch law of independent migration of ions? How is it useful in obtaining molar conductivity at zero concentration of a weak electrolyte ? Explain with an example.
Answer:
(A) Statement of Kohlrausch’s law : This states that at infinite dilution of the solution, each ion of an electrolyte migrates independently of its co-ions and contributes independently to the total molar conductivity of the electrolyte, irrespective of the nature of other ions present in the solution.
(B) Explanation : Both the ions, cation and anion of the electrolyte make a definite contribution to the molar conductivity of the electrolyte at infinite dilution or zero concentration (∧0).
If \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) and \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\) are the molar ionic conductivities of cation and anion respectively at infinite dilution, then
∧0 = \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) + \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\).
This is known as Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
For an electrolyte, BxAy giving x number of cations and y number of anions,
∧0 = x\(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) + y\(\lambda_{-}^{0}\).
(C) Applications of Kohlrausch’s law :
(1) With this law, the molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte at zero concentration can be determined. For example,
\(\wedge_{0(\mathrm{KCl})}=\lambda_{\mathrm{K}^{+}}^{0}-\lambda_{\mathrm{Cl}^{-}}^{0}\)
(2) ∧0 values of weak electrolyte with those of strong electrolytes can be obtained. For example,
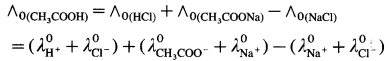
Molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte at infinite dilution or zero concentration cannot be measured experimentally.
Consider the molar conductivity (∧0) of a weak acid, CH3COOH at zero concentration. By Kohlrausch s law,
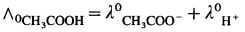
where λ0CH3COO– and λ0H+ are the molar ionic conductivities of CH3COO– and H+ ions respectively.
If ∧0CH3COONa, ∧0HCl and ∧0NaCl are molar conductivities of CH3COONa, HCl and NaCl respectively at zero concentration, then by
Kohlrausch’s law,
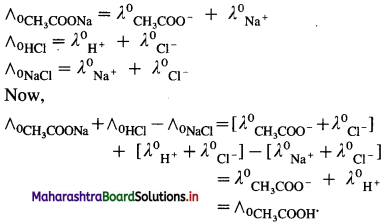
Hence, from ∧0 values of strong electrolytes, ∧0 of a weak electrolyte CH3COOH, at infinite dilution can be calculated.
Question ii.
Explain electrolysis of molten NaCl.
Answer:
(1) Construction of an electrolytic cell : It consists of a vessel containing molten (fused) NaCl. Two graphite (carbon) inert electrodes are dipped in it, and connected to an external source of direct electric current (battery). The electrode connected to a negative terminal of the battery is a cathode and that connected to a positive terminal is an anode.
(2) Working of the cell :
(A) In the external circuit, the electrons flow through the wires from anode to cathode of the cell.
(B) The fused NaCl dissociates to form cations (Na+) and anions (Cl–).
\(\mathrm{NaCl}_{\text {(fused) }} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_{(\mathrm{l})}^{+}+\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{l})}^{-}\)
Na+ migrate towards cathode and Cl– migrate towards anode.
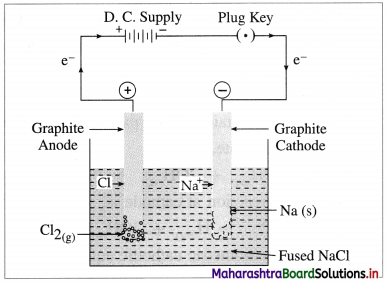
Fig. 5.7 : Electrolysis of fused sodium chloride
(C) Reactions in electrolytic cell :
(i) Reduction half reaction at cathode : The Na+ ions get reduced by accepting electrons from a cathode supplied by a battery and form metallic sodium.
\(\mathrm{Na}^{+}+\mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_{(\mathrm{s})} \text { (reduction) }\)
(ii) Oxidation half reaction at anode : The Cl– ions get oxidised by giving up electrons to the anode forming neutral Cl atoms in the primary process, and these Cl atoms combine forming Cl2 gas in the secondary process.

The released electrons in the anodic oxidation half reaction return to battery through the metallic wires.
Net cell reaction : In order to maintain the electrical neutrality, the number of electrons gained at cathode must be equal to the number of electrons released at anode. Hence the reduction half reaction is multiplied by 2 and both reactions, oxidation half reaction and reduction half reaction are added to obtain a net cell reaction.
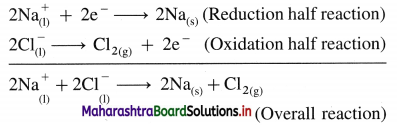
Results of electrolysis :
- A molten silvery white Na is formed at cathode which floats on the surface of molten NaCl.
- A pale green Cl2 gas is liberated at anode.

Question iii.
What current strength in amperes will be required to produce 2.4g of Cu from CuSO4 solution in 1 hour ? Molar mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol-1.
Answer:
Given : WCu = 2.4 g; t = 1 hr = 1 × 60 × 60 s
MCu = 63.5 g mol-1; I = ?
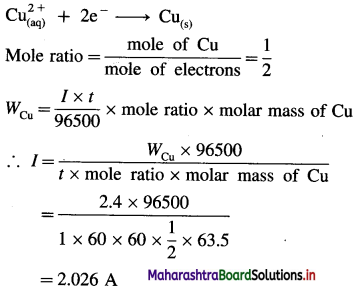
Ans. Current strength = I = 2.026 A
Question iv.
Equilibrium constant of the reaction,
2Cu+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + Cu(s)
is 1.2 × 106. What is the standard potential of the cell in which the reaction takes place ?
Answer:
For the cell reaction, n = 1
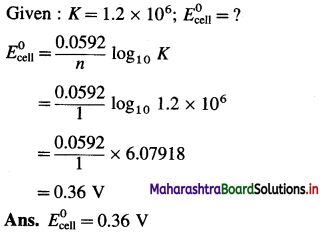
Question v.
Calculate emf of the cell
Zn(s)|Zn2+ (0.2M)||H+(1.6M)|H2(g, 1.8 atm)|Pt at 25°C.
Answer:
Given : Zn(s)|Zn2+(0.2M)||H+(1.6M)|H2(g, 1.8 atm)|Pt
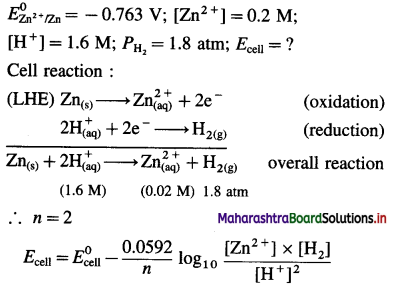
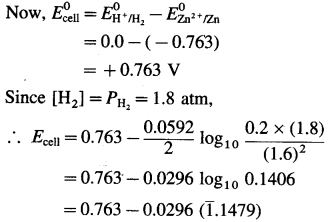
= 0.763 – 0.0296 × (- 0.8521)
= 0.763 + 0.02522
= 0.7882
Ans. \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) = 0.7882 V
Question vi.
Calculate emf of the following cell at 25°C.
Zn(s)| Zn2+(0.08M)||Cr3+(0.1M)|Cr
E0Zn = – 0.76 V, E0Cr = – 0.74 V
Answer:
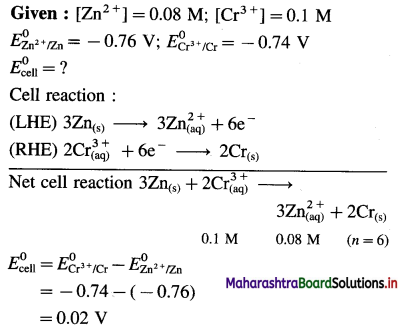
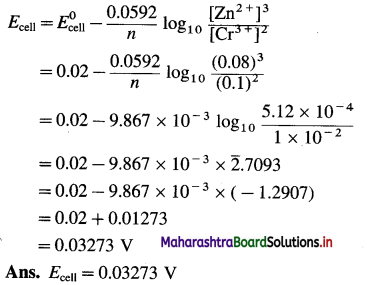
Question vii.
What is a cell constant ? What are its units? How is it determined experimentally?
Answer:
(A) Cell constant of a conductivity cell is defined as the ratio of the distance between the electrodes divided by the area of cross section of the electrodes.
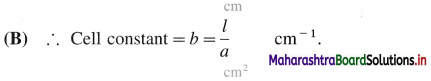
In SI units it is expected as m-1.
The resistance of an electrolytic solution is measured by using a conductivity cell and Wheatstone
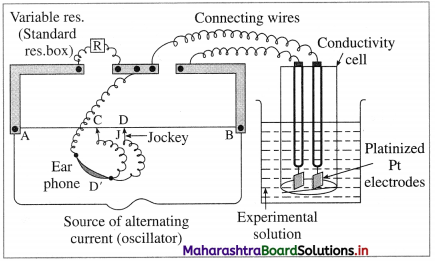
Fig. 5.6 : Measurement of conductance
The measurement of molar conductivity of a solution involves two steps as follows :
Step I : Determination of cell constant of the conductivity cell :
KCl solution (0.01 M) whose conductivity is accurately known (κ = 0.00141 Ω-1 cm-1) is taken in a beaker and the conductivity cell is dipped. The two electrodes of the cell are connected to one arm while the variable known resistance (R) is placed in another arm of Wheatstone bridge.
A current detector D’ which is a head phone or a magic eye is used. J is the sliding jockey (contact) that slides on the arm AB which is a wire of uniform cross section. A source of A.C. power (alternating power) is used to avoid electrolysis of the solution.
By sliding the jockey on wire AB, a balance point (null point) is obtained at C. Let AC and BC be the lengths of wire.
If Rsolution is the resistance of KCl solution and Rx is the known resistance then by Wheatstone’s bridge principle,
\(\frac{R_{\text {solution }}}{\mathrm{BC}}=\frac{R_{x}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
∴ \(R_{\text {solution }}=\mathrm{BC} \times \frac{R_{x}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
Then the cell constant ‘ b ’ of the conductivity cell is obtained by, b = κKcl × Rsolution.
Step II : Determination of conductivity of the given solution :
KCl solution is replaced by the given electrolytic solution and its resistance (Rs) is measured by Wheatstone bridge method by similar manner by obtaining a null point at D.
The conductivity (κ) of the given solution is,
κ = \(\frac{\text { cell constant }}{R_{\mathrm{s}}}=\frac{b}{R_{\mathrm{s}}}\)
Step III: Calculation of molar conductivity :
The molar conductivity (∧m) is given by,
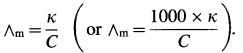
Since the concentration of the solution is known, ∧m can be calculated.

Question viii.
How will you calculate the moles of electrons passed and mass of the substance produced during electrolysis of a salt solution using reaction stoichiometry.
Answer:
Calculation of moles of electrons passed : The charge carried by one mole of electrons is referred to as one faraday (F). If total charge passed is Q C, then moles of electrons passed = \(\frac{Q(\mathrm{C})}{F\left(\mathrm{C} / \mathrm{mol} \mathrm{e}^{-}\right)}\)
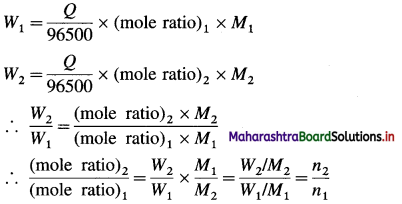
Calculation of mass of product : Mass, W of product formed is given by,
W = moles of product × molar mass of product (M)
= \(\frac{Q}{96500}\) × mole ratio × M
= \(\frac{I \times t}{96500}\) × mole ratio × M 96500
When two electrolytic cells containing different electrolytes are connected in series so that same quantity of electricity is passed through them, then the masses W1 and W2 of products produced are given by,
Question ix.
Write the electrode reactions when lead storage cell generates electricity. What are the anode and cathode and the electrode reactions during its recharging?
Answer:
Recharging of the cell : When the discharged battery is connected to external electric source and a higher external potential is applied the cell reaction gets reversed generating H2SO4.
Reduction at the – ve electrode or cathode :
\(\mathrm{PbSO}_{4(\mathrm{~s})}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Pb}^{(s)}+\mathrm{SO}_{4(\mathrm{aq})}^{2-}\)
Oxidation at the + ve electrode or anode :

The emf of the accumulator depends only on the concentration of H2SO4.
Question x.
What are anode and cathode of H2-O2 fuel cell ? Name the electrolyte used in it. Write electrode reactions and net cell reaction taking place in the fuel cell.
Answer:
Construction :
(i) In fuel cell the anode and cathode are porous electrodes with suitable catalyst like finely divided platinum.
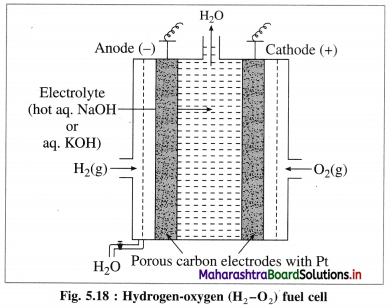
(iii) H2 is continuously bubbled through anode while O, gas is bubbled through cathode.
Working (cell reactions) :
(i) Oxidation at anode : At anode, hydrogen gas is oxidised to H2O.
2H2(g) + 4OH–(aq) → 4H2O(l) + 4e– (oxidation half reaction)
(ii) Reduction at cathode : The electrons released at anode travel to cathode through external circuit and reduce oxygen gas to OH–.
O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e– → 4OH–(aq) (reduction half reaction)
(iii) Net cell reaction: Addition of both the above reactions at anode and cathode gives a net cell reaction.
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) (overall cell reaction)
Question xi.
What are anode and cathode for Leclanche’ dry cell ? Write electrode reactions and overall cell reaction when it generates electricity.
Answer:
A dry cell has zinc vessel as anode and graphite rod as cathode and moist paste of ZnCl2, MnO2, NH4Cl as electrolytes.
At anode :
Zn(s) → \(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\) + 2e– (Oxidation half reaction)
At graphite (c) cathode :
\(2 \mathrm{NH}_{4(\mathrm{e})}^{+}\) + 2e– → 2NH3(aq) + H2(g) (Reduction half reaction)
2MnO2(s) + H2 → Mn2O3(s) + H2O(l)
There is a side reaction inside the cell, between Zn2+ ions and aqueous NH3.
\(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+4 \mathrm{NH}_{3(\mathrm{aq})} \longrightarrow\left[\mathrm{Zn}\left(\mathrm{NH}_{3}\right)_{4}\right]_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}\)
Question xii.
Identify oxidising agents and arrange them in order of increasing strength under standard state conditions. The standard potentials are given in parenthesis.
Al(- 1.66 V), Cl2 (1.36 V), Cd2+ (-0.4 V), Fe (-0.44 V), I2 (0.54 V), Br– (1.09 V).
Answer:
The oxidising agents are I2, Br– and Cl2. The increasing strength is
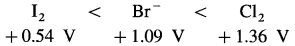
(Note : Actually Br2 acts as an oxidising agent but not Br–.)

Question xiii.
Which of the following species are reducing agents? Arrange them in order of increasing strength under standard state conditions. The standard potentials are given in parenthesis.
K (-2.93V), Br2(1.09V), Mg(-2.36V), Co3+(1.61V), Ti2+(-0.37V), Ag+(0.8V), Ni (-0.23V).
Answer:
Lower the standard reduction potential, higher is reducing power. The reducing agents are Ni, Mg and K. Their increasing strength is,
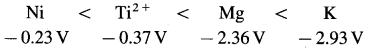
(Note : Cations don’t act as reducing agent since they are already in oxidised state.)
Question xiv.
Predict whether the following
reactions would occur spontaneously
under standard state conditions.
a. Ca(s) + Cd2+(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + Cd(s)
b. 2 Br-(s) + Sn2+(aq) → Br2(l) + Sn(s)
c. 2Ag(s) + Ni2+(aq) → 2 Ag+(aq) + Ni(s)
(use information of Table 5.1)
Answer:

12th Chemistry Digest Chapter 5 Electrochemistry Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
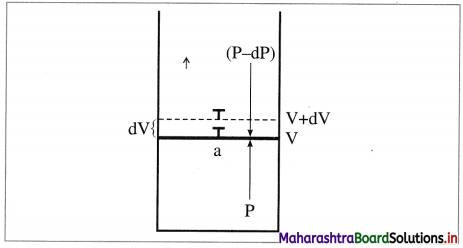
How does electrical resistance depend on the dimensions of an electronic (metallic) conductor?
Answer:
The electrical resistance of an electronic conductor is linearly proportional to its length (l) and inversely proportional to its cross section area a.
Fig. 5.3 : Electronic conductor
Thus, R ∝ l; R ∝ \(\frac{1}{a}\)
∴ R ∝ \(\frac{l}{a}\) or R = ρ × \(\frac{l}{a}\)
where the proportionality constant p is called specific resistance. IUPAC recommends the term resistivity for specific resistance.
Question 2.
What are the units of resistivity ?
Answer:
For an electronic conductor of length l, and cross section area a, the resistance R is represented as
R = ρ × \(\frac{l}{a}\)
where ρ is the resistivity of the conductor.
∴ ρ = R × \(\frac{a}{l}\)
If l = 1 m, a = 1 m2, ρ = R
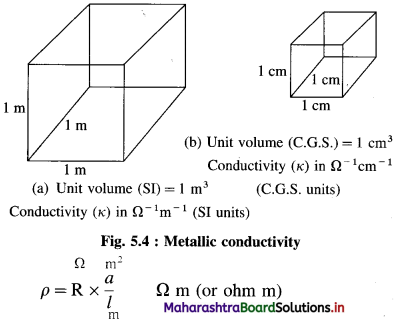
Hence, resistivity is the resistance of a conductor of volume of 1 m3.
(In C.G.S. units, the units of ρ are ohm cm. Hence, ρ is the resistance of a conductor of unit volume or 1 cm3.)

Question 3.
Define resistivity. What are its units ?
Answer:
Resistivity (or specific resistance) : It is the resistance of a conductor that is 1 m in length and 1 m2 in cross section area in SI units. (In C.G.S. units, it is the resistance of a conductor that is 1 cm in length and 1 cm2 in cross section area.) Hence, the resistivity is the resistance of a conductor of unit volume. (In case of electrolytic solution, ρ is the resistivity i.e., resistance of a solution of unit volume.)
It has SI units, ohm m and C.G.S. units, ohm cm.
Question 4.
Why is alternating current used in the measurement of conductivity of the solution ?
Answer:
If direct current (D.C.) by battery is used, there will be electrolysis and the concentration of the solution is changed. Hence alternating current (A.C.) with high frequency is used.
Try this… (Textbook page No. 93)
Question 1.
What must be the concentration of a solution of silver nitrate to have the molar conductivity of 121.4 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 and the conductivity of 2.428 × 10-3 Ω-1 cm-1 at 25 °C ?
Answer:
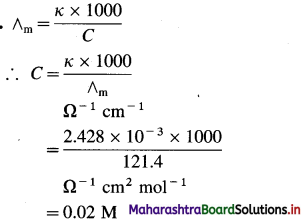
∴ Concentration of a Solution = 0.02 M
Try this… (Textbook page No. 96)
Question 1.
Obtain the expression for dissociation constant in terms of ∧c and ∧0 using Ostwald’s dilution law.
Answer:
Consider a solution of a weak electrolyte, BA having concentration C mol dm-3. If α is the degree of dissociation, then by Ostwald’s theory of weak electrolytes,
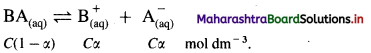
If K is the dissociation constant of the weak electrolyte, then by Ostwald’s dilution law,
K = \(\frac{\alpha^{2} C}{(1-\alpha)}\)
If ∧m is the molar conductivity of the electrolyte BA at the concentration C and ∧0 is the molar conductivity at zero concentration or infinite dilution, then
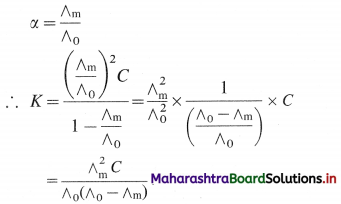
Hence by measuring ∧m at the concentration C and knowing ∧0, the dissociation constant can be calculated.
If \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) and \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\) are the ionic conductivities, then by Kohlrauseh’s law, ∧0 = \(\lambda_{+}^{0}\) + \(\lambda_{-}^{0}\).

Learn this as well…
Question 1.
How is the cell constant of a conductivity cell determined?
Answer:
The cell constant of a given conductivity cell is obtained by measuring the resistance (R) (or the conductance) of a standard solution whose conductivity (fc) is accurately known by using Wheatstone’s bridge (discussed in Q. 37). For this purpose, KCl solution of accurately known conductivity is used.
\(\kappa_{\mathrm{KCl}}=\frac{1}{R_{\mathrm{KCl}}} \times \frac{l}{a}\) where \(\frac{l}{a}\) is a cell constant, represented by b.
∴ \(\kappa_{\mathrm{KCl}}=\frac{b}{R_{\mathrm{KCl}}}\)
or b = κKCl × RKCl
For example, the conductivity of 0.01 M KCl is 0.00141 Ω-1 cm-1 (S cm-1). Hence by measuring R KCl the cell constant b can be obtained.
Try this… (Textbook page No. 95)
Question 1.
Calculate ∧0 (CH2ClCOOH) if ∧0 values for HCl, KCl and CH2ClCOOK are respectively, 4.261, 1.499 and 1.132 Ω-1 m2 mol-1.
Solution :

Adding equations (i) and (ii) and subtracting equation (iii) we get equation (I).
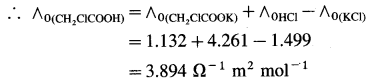
Can you tell ? (Textbook page No. 103)
Question 1.
You have learnt Daniel cell in XIth standard. Write notations for anode and cathode. Write the cell formula.
Answer:
Daniel cell is represented as,

Try this… (Textbook page No. 104)
Question 1.
Write electrode reactions and overall cell reaction for Daniel cell you learnt in standard XI.
Answer:
Reactions for Daniell cell:
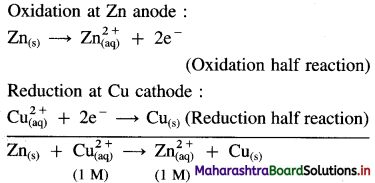
Question 1.
Describe different types of reversible electrodes with examples. (1 mark for each type)
Answer:
A reversible electrochemical cell or a galvanic cell consists of two reversible half cells or electrodes. There are four types of reversible electrodes according to their compositions.
(1) Metal-metal ion electrode : This electrode is set up by dipping a metal in a solution containing its own ions, e.g. Zn rod dipped into ZnSO4 solution containing Zn++ ions of concentration C.
It is represented as,
\(\mathrm{Zn}^{2+}{ }_{(\mathrm{aq})} \mid \mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{s})}\)
The reduction reaction at the electrode is,
Zn++(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s)
(2) Metal-sparingly soluble salt electrode : This electrode consists of a metal coated with one of its sparingly soluble salts and immersed in a solution containing an electrolyte having a common anion as that of the salt. For example, silver electrode coated with sparingly soluble AgCl dipped in KCl solution with common anion Cl–. This electrode is represented as,
Cl–(aq) | AgCl(s) | Ag(s)
The reduction reaction is,
AgCl(s) + e → Ag(s) + Cl–(aq)
(3) Gas electrode : This is developed by bubbling pure and dry gas around a platinised platinum foil dipped in the solution containing ions (of the gas) reversible with respect to the gas bubbled.
The gas is adsorbed on the surface of platinum foil and establishes an equilibrium with its ions in the solution. Pt electrode provides electrical contact and also acts as a catalyst.
Some of the gas electrodes are represented as follows :
(i) Hydrogen gas electrode :
H+(aq) | H2(g, PH2) | Pt
Reduction reaction : H+(aq) + e– → \(\frac {1}{2}\)H2(g)
(ii) Chlorine gas electrode :
Cl–(aq) | Cl2(g, PCl2) | Pt
Reduction reaction : \(\frac {1}{2}\)Cl2(g) + e- → Cl–(aq)
(4) Redox electrode (Oxidation reduction electrode) : This electrode consists of a platinum wire dipped in a solution containing the ions of the same metal (or a substance) in two different oxidation states, like Fe2+ – Fe3+, Sn2+ – Sn4+, Mn++ – MnO–4, etc.
A platinum electrode which provides an electrical contact and acts as catalyst aquires an equilibrium between two ions in the solution, due to their tendency to undergo a change from one oxidation state to another. The electrodes are represented as,
Fe2+(aq), Fe3+(aq) | Pt
Reduction reaction : Fe3+(aq) + e– → Fe2+(aq)
SnCl2(aq), SnCl4(aq) | Pt
Reduction reaction : Sn4+(aq) + 2e– →Sn2+(aq)

Use your brain power! (Textbook page No. 98)
Question 1.
Distinguish between electrolytic and galvanic cells.
Answer:
Electrolytic cell:
- This device is used to bring about a non-spontaneous chemical reaction by passing an electric current.
- It is used to bring about a chemical reaction generally for the dissociation (electrolysis) of compounds.
- In this cell, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
- In this cell, the cathode is negative and the anode is positive.
- Electrolytic cells are irreversible.
- Oxidation takes place at the positive electrode and reduction at the negative electrode.
- The electrons are supplied by the external source and enter through cathode and come out through anode.
- It is used for electroplating, electrorefining, etc.
Electrochemical cell (Galvanic cell or Voltaic cell):
- This device is used to produce electrical energy by a spontaneous chemical reaction.
- It is used to generate electricity.
- In this cell, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
- In this cell, the cathode is positive and the anode is negative.
- Electrochernical cells are reversible.
- Oxidation takes place at the negative electrode and reduction at the positive electrode.
- The electrons move from anode to cathode in the external circuit.
- It is used as a source of electric current.
Try this… (Textbook page No. 107)
Question 1.
Write expressions to calculate equilibrium constant from
i. Concentration data
ii. Thermochemical data
iii. Electrochemical data
Answer:
(i) Consider following a reversible cell reaction.
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
If [A], [B], [C] and [D] represent concentrations of reactants and products then the equilibrium constant K is,
K = \(\frac{[\mathrm{C}]^{c} \times[\mathrm{D}]^{d}}{[\mathrm{~A}]^{a} \times[\mathrm{B}]^{b}}\)
(ii) If ΔG0 is the standard Gibbs free energy change at temperature T then,
ΔG0 = – RTlnK = – 2.303 RTlog10K
(iii) From electrochemical data,
if \(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}\) is the standard cell potential and K is the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction at a temperature T, then,
\(E_{\text {cell }}^{0}=\frac{0.0592}{n} \log _{10} K\)

Learn this as well…
Question 1.
The construction and working of the calomel electrode.
Answer:
(1) Since standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is not convenient for experimental use, a secondary reference electrode like calomel electrode is used.
(2) Construction : It consists of a glass vessel with side arm B for dipping in a desired solution of another electrode like, ZnSO4(aq) for an electric contact. The vessel is filled with mercury, a paste of Hg and Hg2Cl2 (calomel) and saturated KCl solution.
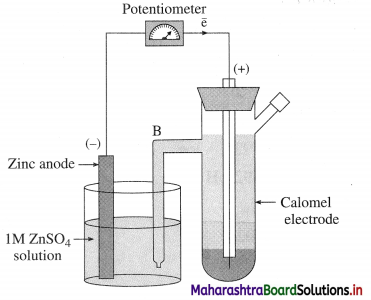
Fig. 5.15 : Determination of standard electrode potential using calomel electrode
(3) The potential developed depends upon the concentration of Cl– or KCl solution. When saturated KCl solution is used, its reduction potential is 0.242 V.
(4) Consider following cell :
Zn(s) | ZnSO4(aq) || KCl(aq) | Hg2Cl2(s) | Hg
OR Zn(s) | ZnSO4(aq) || Calomel electrode
Reduction reaction for calomel electrode :
Hg2Cl2(s) + 2e– → 2Hg(l) + 2Cl–(aq)
Hence potential of calomel electrode depends on the concentration of Cl– or KCl solution.
Can you tell ? (Textbook page No. 114)
Question 1.
In what ways are fuel cells and galvanic cells similar and in what ways are they different ?
Answer:
Similarity between fuel cells and galvanic cells :
- In both the cells, there is oxidation at anode and j reduction at cathode.
- The cell potential is developed due to net redox reactions.
- Both are galvanic cells.
Difference in fuel cells and galvanic cells :
- Fuel cells involve electrodes with large surface area while galvanic cells involve electrodes with j compact surface area.
- Fuel cells involve gaseous materials on a large scale while galvanic cells involve gaseous materials at a definite pressures along with electrolytes or there may not be gases.
- In fuel cells, the cell potential is developed due to exothermic combustion reactions while in galvanic cell, cell potential is developed due to normal redox reactions.
- In fuel cells gaseous electrode materials are continuously supplied from outside while in galvanic cells electrode materials have constant concentration or may change due to reactions.
Use your brain power (Textbook page No. 114)
Question 1.
Indentify the strongest and the weakest oxidizing agents from the electrochemical series.
Answer:
From the electrochemical series,
(a) The strongest oxidising agent is fluorine since it has the highest standard reduction potential (\(E_{\mathrm{F}_{2} / \mathrm{F}^{-}}^{0}\) = + 2.87 V).
(b) The weakest oxidising agent (or the strongest reducing agent) is lithium since it has the lowest standard reduction potential, (\(E_{\mathrm{Li}^{+} / \mathrm{Li}}^{0}\) = -3.045 V).

Use your brainpower (Textbook page No. 115)
Question 1.
Identify the strongest and the weakest reducing agents from the electrochemical series.
Answer:
(a) From the electrochemical series, the strongest reducing agent is lithium since it has the lowest standard reduction potential (\(E_{\mathrm{Li}^{+} / \mathrm{Li}}^{0}\) = -3.045 V).
(b) The weakest reducing agent is fluorine since it has the highest standard reduction potential,
(\(E_{\mathrm{F}_{2} / \mathrm{F}^{-}}^{0}\) = +2.87 V).
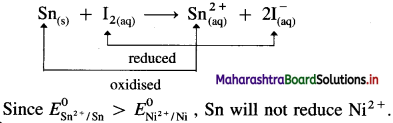
Question 2.
From E° values given in Table 5.1, predict whether Sn can reduce I2 or Ni2+.
Answer:
From the electrochemical series,
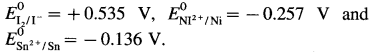








![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()





![]()
![]()