Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 15 Introduction to Polymer Chemistry Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 15 Introduction to Polymer Chemistry
Question 1.
What are polymers?
Answer:
Polymers are high molecular mass macromolecules (103 – 107 u) and consist of repeating units of monomers.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the classification of polymers based on the source. Give examples.
OR
What are natural and synthetic polymers? Give two examples of each type.
Answer:
Based on the source polymers are classified as natural, semisynthetic and synthetic polymers.
- Natural polymers : These polymers are obtained either from plants or animals, e.g., cellulose, jute, linene, rubber, silk.
- Semisynthetic polymers : The fibres obtained by giving special chemical treatment to natural fibres (cellulose) and further regenerated are called semisynthetic polymers e.g., acetate rayon, viscose rayon, cuprammonium silk.
- Synthetic polymers : The man made fibres prepared by polymerization of one monomer or copolymerization of
two or more monomers are called synthetic polymers, e.g., nylon, terylene, polythene, etc.
Question 3.
Write the classification of polymers based on structure. Give examples
OR
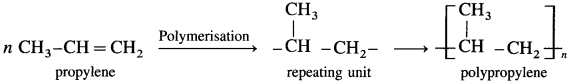
Write the reactions involved in the preparation of (1) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) (2) Polypropylene.
Answer:
Based on structure polymers are classified as linear chain polymers, branched chain polymers and network or cross linked polymers.
(1) Linear chain polymers : When the monomer molecules are joined together in a linear arrangement, the resulting polymer is straight-chain or long-chain polymer, e.g., polythene, PVC.

They have high melting points; high densities and high tensile strength.
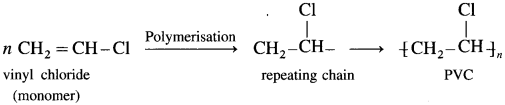
(2) Branched-chain polymers : These polymers consist of long and straight chain with smaller side chains give rise to branched-chain polymers. They have low density. They have lower melting points and tensile strength. Polypropylene having methyl groups as branches.
(3) Network or cross-linked polymers : These polymers consist of cross-linking of chains by strong covalent bonds leading to a network-like structure. Cross-linking results from polyfunctional monomers, e.g., melamine, bakelite, vulcanization of rubber. These polymers are hard rigid and brittle.

Question 3.
How are polymers classified on the basis of mode of polymerization?
OR
Write the classification of polymers based on mode of polymerization.
Answer:
There are three modes of polymerization depending upon the types of reactions taking place between the monomers.
- Addition polymerization (or chain growth polymerization)
- Condensation polymerization (or step growth polymerization)
- Ring opening polymerization
- Addition polymerization or chain growth polymerization : It is a process of polymers by the repeated addition of a large number of monomers is called addition polymerization (like alkenes) without loss of any small molecules.
Example : Formation of polyethylene from ethylene is well known example of addition polymerization. It is a chain growth polymerization. - Condensation polymerization or step growth polymerization : The process of formation of polymers from polyfunctional monomers with the elimination of some small molecules such as water, hydrochloric acid, methanol, ammonia is called condensation polymerization.
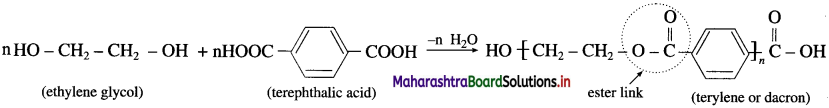
Example : The formation of terylene, a polyester polymer, from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. Condensation polymerization is a step growth polymerization. - Ring opening polymerization : The process of formation of polymers from cyclic compounds (like lactams, cyclic ethers, etc.) by ring opening is called ring opening polymerization.
Example : Polymerization of e-caprolactam.
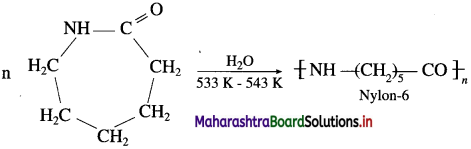 Ring opening polymerization proceeds by addition of a single monomer unit to the growing chain molecules. It is a step growth polymerization.
Ring opening polymerization proceeds by addition of a single monomer unit to the growing chain molecules. It is a step growth polymerization.
![]()
Question 4.
Classify the polymers given below as addition, condensation and ring opening polymers:
PVC, polythene, cyclic ethers, polyester, polyacrylonftrile. polystyrene.
Answer:
- Addition polymers: PVC, polythene. polyacrylonitrile. polystyrene.
- Condensation polymers: Polyester.
- Ring opening polymers : Cyclic ethers
Question 5.
Write the classification of polymers based on intermolecular forces. Give examples.
OR
In which dasses, are the polymers classified on the basis of Inter molecular forces?
Answer:
Molecular forces bind the polymer chains either by hydrogen bonds or Vander Waal’s forces. These forces are called intermolecular forces. On the basis of magnitude of intcrmolccular forces, polymers are further classified as ebstomers, fibres, thermoplastic polymers. thermosetting polymers.
(1) Elastomers: Weak van der Waals type of intermolecular forces of attraction between the polymer chains are observed in cbstomcrs. When polymer is stretched, the polymer chain stretches and when the strain is relieved the chain returns to its odginal position, Thus, polymer shows elasticity and is called elastomers. Elastomers, the elastic polymers, have weak van der Waals type of intermolecular forces which permit the polymer to be stretched. Lilastorners are soft and stretchy and used in making rubber bands. E.g.. neoprene, vulcanized rubber, buna.S, buna-N.
(2) Fibres : It consists of strong intermolecular forces of’ attraction due to hydrogen bonding and strong dipole-dipole forces. These polymers possess high tensile strength. Due to these strong intermolecular forces the fibres are crystalline in nature. They are used in textile industries, strung tyres. etc.. e.g., nylon, terylene.
(3) Thermoplastic polymers: These polymer possess moderately strong intermolecular forces of attraction between those of elastomers and fibres. These polymers arc called thermoplastic because they become soft on heating and hard on cooling. They are either linear or branched chain polymers. They can be remoulded and recycled. E.g. polyethenc, PVC, polystyrene.
(4) Thermosetting polymers: These polymers are cross linked or branched molecules and are rigid polymers. During their formation they have property of being shaped on heating. but they get hardened while hot. Once hardened these become infusible, cannot be softened by heating and therefore, cannot be remoulded and recycled.
This shows extensive cross linking by covalent bonds formed in the moulds during hardening/setting process while hot. E.g. Bakelite, urea formaldehyde resin.
Question 6.
What is meant by the term homopolymer?
Answer:
A polymer made from only one type of repeating units is called homopolymer. in some cases the repeating unit is formed by condensation of two distinct monomers. Examples. Polythene, PVC. Nylon-6.
Question 7.
What is meant by the term copolymer?
Answer:
A polymer made from two or more types of repeating units is called a copolymer. The different monomer units are randomly sequenced in the copolymer, e.g., Terylene, Nylon-6, 6, Buna-S, Buna-N.
Question 8.
Write the classification of polymers on the basis of biodegradability?
OR
(1) What are biodegradable polymers?
(2) What are nonbiodegradable polymers?
Answer:
Based un biodegradability, polymers are classified as biodegradable polymer and nonbiodegradable polymers.
(1) Biodegradable polymers: Polymers that are affected by microbes or disintegrate by themselves afler a certain period of time due to environmental degradation are called biodegradable polymers.
Examples: PHBV i.e., Polyhydroxy butyrate-CO-β-hydroxy valerate Dextron. Nylon-2-nylon-6.
(2) Non biodegradable polymers: Synthetic polymers do not disintegrate by themselves after a certain period or not affected by microbes, are called nonbiodegradhle polymers.
Examples: Bakelite, Nylon, Terylene.
Question 9.
Explain the following terms :
Answer:
- Branched chain polymer : The polymer consists of long and straight chain with smaller side chains give rise to branched chain polymers, e.g. Polypropylene
- Addition polymer : The polymer formed by the repeated addition of a large number of monomers (like alkenes) without loss of any small molecules are called addition polymers, e.g. polythene -[-CH2 – CH2-]n. It is a chain growth polymerization.
- Condensation polymer : The polymers formed by the repeated condensation reaction between polyfunctional monomers with the elimination of some molecules such as water, hydrochloric acid, methanol, ammonia are called condensation polymers, e.g. Nylon-6, 6.
- Elastomers : Polymers in which the intermolecular forces of attraction between the polymer chains are the weakest. When polymer is stretched, it has ability to stretch and when the strain is relieved it returns to its original position. Thus, polymer shows elasticity and is called elastomers, e.g. natural rubber, neoprene, vulcanized rubber.
- Homopolymer : A polymer made from only one type of repeating unit of one monomer is called homopolymer e.g. Polythene, PVC, etc.
- Biodegradable polymer : Polymers which are affected by microbes or disintegrate by themselves after a certain period of time due to environmental degradation are called biodegradable polymers.
Example : PHSV i.e. Polyhydroxy butyrate -CO-β-hydroxy valerate Dextron.
![]()
Question 10.
What is natural rubber?
Answer:
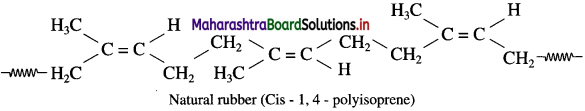
Natural rubber is a high molecular mass linear polymer of isoprene (2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene).
Question 11.
Write a note on natural rubber.
Answer:
Natural rubber is manufactured from rubber latex obtained from the rubber tree in the form of colloidal suspension. Reaction involved in the formation of natural rubber by the process of addition polymerization is as follows :
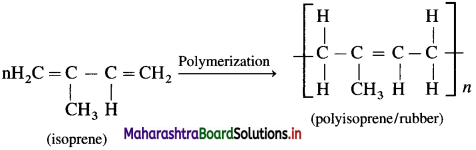
Natural rubber is -1, 4- polyisoprene. It exhibits elastic properties.
Question 12.
State properties of natural rubber.
Answer:
- Polyisoprene molecule has cis configuration of the C = C double bond. It consists of various chains held together by weak van der Waals forces and has coiled structure.
- It can be stretched like a spring and exhibits elastic property.
- Its molecular mass varies from 130,000 u to 340,000 u.
Question 13.
Write a note on vulcanization of rubber. OR Discuss the main purpose of vulcanization of rubber.
Answer:
The tensile strength, toughness and elasticity of natural rubber can be increased by adding 3 to 5% sulphur and heating at 100-150°C, resulting in cross linking of cis-1, 4-polypropene chains through disulphide bonds, (-S-S-). This process is known as vulcanization of rubber. The physical properties of rubber can be changed by controlling the amount of sulphur in the vulcanization process. Rubber made with 20-30% sulphur is hard, 3 to 10% sulphur is little harder and is used in making tyres and 1 to 3% sulphur is used in making rubber bands.
Question 14.
Write the name and structure of one of the initiators used in free radical polymerisation.
Answer:
The initiator used in free radical polymerisation is acetyl peroxide.
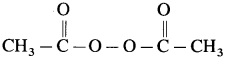
Question 15.
What is LDP? How is it prepared? Give its properties and uses.
Answer:
LDP means low-density polyethene. LDP is obtained by polymerization of ethylene under high pressure (1000 – 2000 atm) and temperature (350 – 570 K) in presence of traces of O2 or peroxide as initiator.

The mechanism of this reaction involves free radical addition and H-atom abstraction. The latter results in branching. As a result the chains are loosely held and the polymer has low density.
Properties of LDP :
- LDP films are extremely flexible, but tough chemically inert and moisture resistant.
- It is poor conductor of electricity with melting point 110 °C.
Uses of LDP :
- LDP is mainly used in preparation of pipes for agriculture, irrigation, domestic water line connections as well as insulation to electric cables.
- It is also used in submarine cable insulation.
- It is used in producing extruded films, sheets, mainly for packaging and household uses like in preparation of squeeze bottles, attractive containers, etc.
![]()
Question 16.
Whatis HDP ? How is it prepared ? Give its properties and uses ?
Answer:
HDP means high density polyethylene. It is a linear polymer with high density due to close packing.

HDP is obtained by polymerization of ethene in presence of Zieglar-Natta catalyst which is a combination of triethyl aluminium with titanium tetrachloride at a temperature of 333K to 343K and a pressure of 6-7 atm.
Properties of HDP :
- HDP is crystalline, melting point in the range of 144 – 150 °C.
- It is much stiffer than LDP and has high tensile strength and hardness.
- It is more resistant to chemicals than LDP.
Uses of HDP :
- HDP is used in manufacture of toys and other household articles like buckets, dustbins, bottles, pipes, etc.
- It is used to prepare laboratory wares and other objects where high tensile strength and stiffness is required.
Question 17.
How is polyacrylonitrile (PAN) prepared? Give its uses.
Answer:
Acrylonitrile (monomer) on polymerization (addition polymerization) in the presence of peroxide initiator gives polyacrylonitrile.
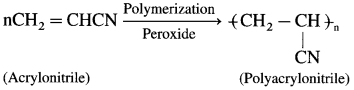
Uses : Polyacrylonitrile resembles wool and is used as wool substitute and for making orlon or acrilan.
Question 18.
How is nylon-6 prepared?
Write the reaction for the preparation of nylon 6.
Answer:
When epsilon (ε)-caprolactam is heated with water at high temperature it undergoes ring opening polymerization to form the polyamide polymer called nylon-6.

The name nylon-6 is given on the basis of six carbon atoms present in the monomer unit. Nylon-6 has high tensile strength and luster, nylon-6 fibres are used for manufacture of tyre cords, fabrics and ropes.
Question 19.
Draw the structures of polymers formed using the following monomers.


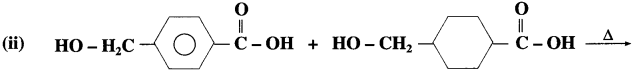
Answer:

Question 20.
How is Novolac prepared?
OR
Write the reaction to prepare Novolac polymer.
Answer:
The monomers phenol and formaldehyde undergo polymerisation in the presence of alkali or acid as catalyst.
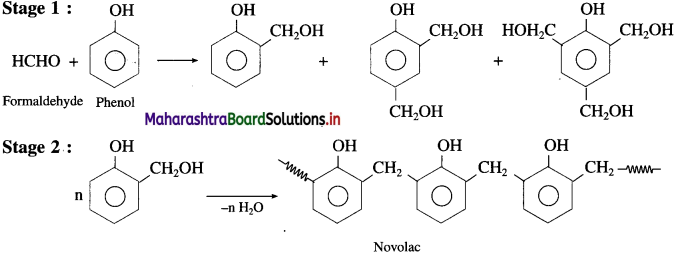
Phenol reacts with formaldehyde to form ortho or p-hydroxy methyl phenols, which further reacts with phenol to form a linear polymer called Novolac. It is used in paints.
![]()
Question 21.
How is bakelite prepared?
Answer:
In the third stage, various articles are shaped from novolac by putting it in appropriate moulds and heating at high temperature (138 °C to 176 °C) and at high pressure forms rigid polymeric material called bakelite. Bakelite is insoluble and infusible and has high tensile strength.
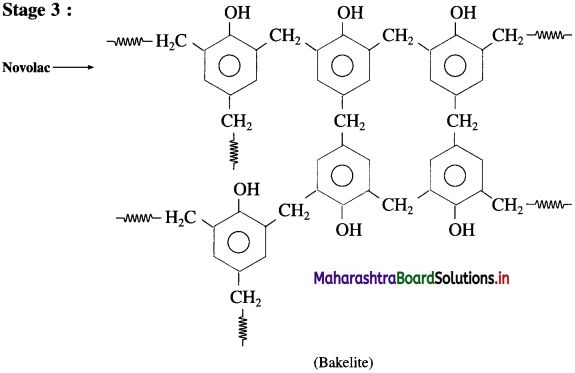
Bakelite is used in making articles like telephone instrument, kitchenware, electric insulators frying pans, etc.
Question 22.
How is a melamine-formaldehyde polymer (melamine) prepared?
Answer:
The monomers formaldehyde and melamine undergo condensation polymerisation to form cross-linked melamine formaldehyde. It is used in making crockeries, decorative table tops like formica and plastic dinner-ware.

Question 23.
Write the preparation of the following synthetic rubbers and give their uses :
(1) Buna-S or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) (2) Neoprene rubber
Answer:
(1) Buna-S rubber : Its trade name is SBR (Styrene-butadiene rubber) Buna-S is a copolymer of styrene and 1, 3-butadiene. When 75 parts of butadiene and 25 parts of styrene subjected to addition polymerization by the action of sodium.
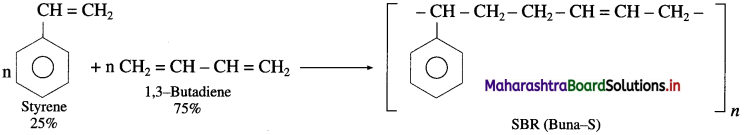
Uses : Buna-S is superior to natural rubber with regard to mechanical strength and has abrasion resistance. Hence, it is used in tyre industry.
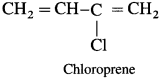
(2) Neoprene : Neoprene, a synthetic rubber, is a condensation polymer of chloroprene (2-chloro-l, 3-butadiene), Chloroprene polymerizes rapidly in presence of oxygen.

Vulcanization of neoprene takes place in presence of magnesium oxide.

Uses : Neoprene is resistant to petroleum, vegetable oils, light as well as heat. It is used in making hose pipes for transport of gasoline and making gaskets. It is used for manufacturing insulator cable, jackets, belts for power transmission and conveying.
![]()
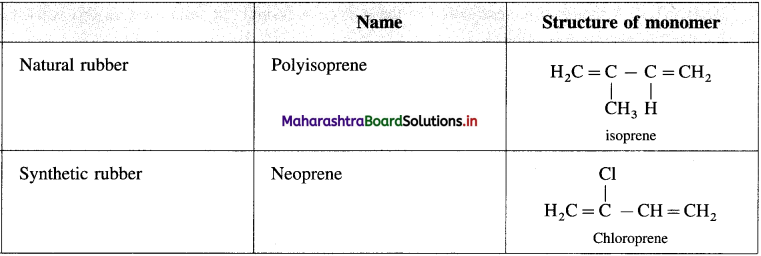
Question 24.
Write structure of natural rubber and neoprene rubber along with the name and structure of their monomers.
Answer:
Question 25.
Write the preparation of viscose rayon.
Answer:
Viscose rayon is a semisynthetic fibre. It is a regenerated cellulose. The molecular formula of cellulose is (C6H10O5)n. A modified representation of the molecular formula of cellulose Cell-OH is used in the reactions involved in viscose formation.
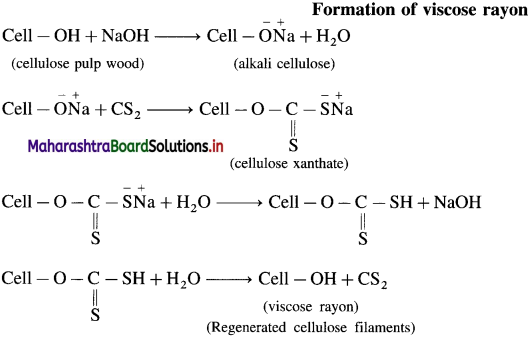
Cellulose (wood pulp) is treated with the concentrated NaOH to form alkali cellulose. It is then converted to xanthate by treating with CS2. Further xanthate is mixed with dilute NaOH to form viscose solution which is extruted through spinnerates of spinning machine into acid bath, when regenerated cellulose fibres precipitate, i.e. viscose rayon.
Question 26.
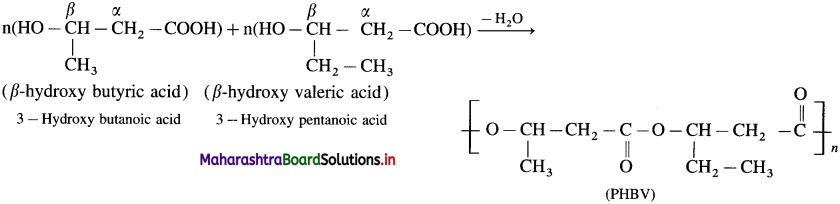
How is PHBV polymer prepared?
Answer:
It is a copolymer. The monomers β-hydroxy butyric acid (3-hydroxy butanoic acid) and β-hydroxy valeric acid (3-hydroxy pentanoic acid) undergo polymerization to form PHBV polymer. It has an ester linkage. Hydroxyl group of one monomer forms ester link by reacting with carboxyl group of the other. Thus PHBV is an aliphatic polyester i.e. poly β-hydroxybutyrate-co-β-hydroxy valerate (PHBV). It is a biodegradable polymer.
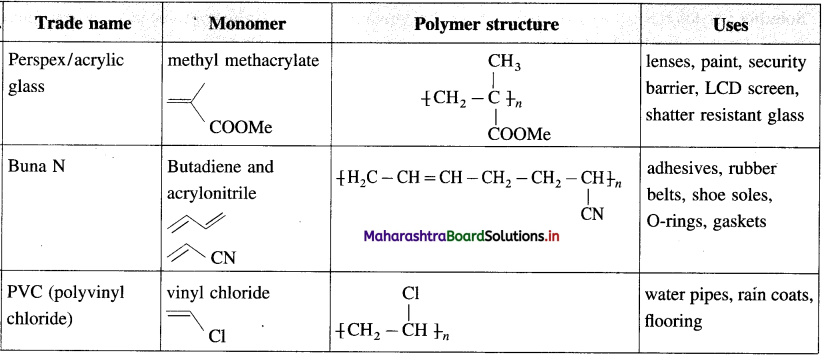
Question 27.
Write the name/s of monomer/s, polymer structure and one use of each of the following polymers (trade name) :
Answer:

![]()
Question 28.
Write the names of monomers used in preparing following polymers :
(1) Dacron.
Answer:
Monomers : Ethylene glycol and Dmiethyl terephthalate (DMT)
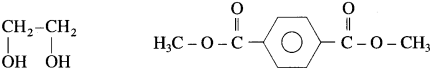
(2) Bakelite.
Answer:
Monomers : o-hydroxy methyl phenol and formaldehyde.
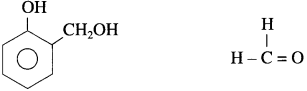
(3) Nylon-6, 8.
Answer:
Monomers : Hexamethylene diamine and Hexamethylene dicarboxylic acid.
H2N-(CH2)6-NH2 HOOC-(CH2)6-COOH
(4) Melamine.
Answer:
Monomers : Melamine and Formaldehyde

(5) Buna-S.
Answer:
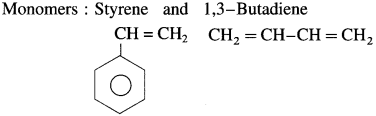
(6) Buna-N.
Answer:

(7) Butyl rubber.
Answer:

(8) Teflon.
Answer:
Monomers : F2C = CF2 Tetrafluoroethene
(9) Natural rubber.
Answer:
Monomers : 1,3-Butadiene
CH2 = CH – CH = CH2
(10) Neoprene.
Answer:
Monomers : Chloroprene or 2-Chloro-l,3-butadiene
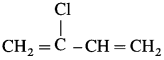
Question 29.
Write the structures of monomers used in the preparation of following polymers.
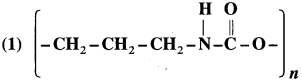
Answer:
The monomers used in the preparation of above polymer are :
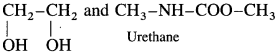
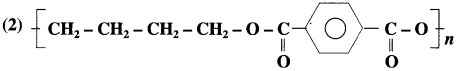
Answer:
The monomers used in the preparation of above polymer are :
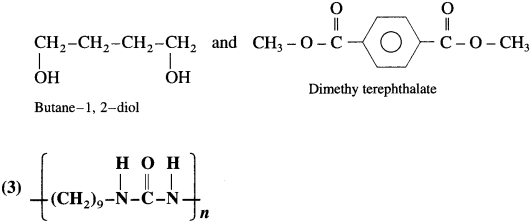
Answer:
The monomer used in the preparation of above polymer are :
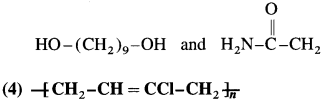
Answer:
The monomer used in the preparation of above polymer is
![]()
Question 30.
Following monomers are used to prepare polymers. Predict the structures of polymers:
(1) Ethylene glycol.
Answer:
Ethylene glycol  is used in the preparation of polyester (terylene or dacron).
is used in the preparation of polyester (terylene or dacron).
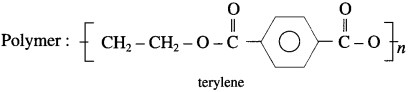
Terylene is polyester fibre formed by the polymerization of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol.
Terylene is obtained by condensation polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid in presence of catalyst zinc acetate and antimony trioxide at high temperature.
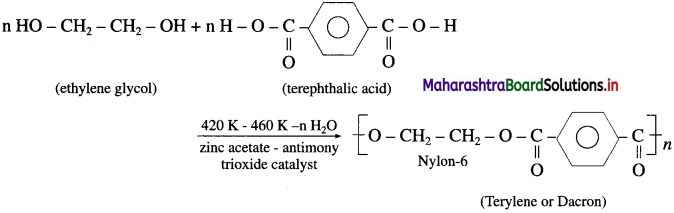
Properties :
- Terylene has relatively high melting point (265 °C)
- It is resistant to chemicals and water.
Uses :
- It is used for making wrinkle-free fabrics by blending with cotton (terycot) and wool (terywool), and also as glass reinforcing materials in safety helmets.
- PET is the most common thermoplastic which is another trade name of the polyester polyethylenetereph- thalate.
- It is used for making many articles like bottles, jams, packaging containers.
(2) ε-Caprolactam.
Answer:
ε-caprolactam is used in the preparation of nylon-6.
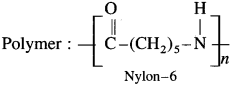
When epsilon (ε)-caprolactam is heated with water at high temperature it undergoes ring opening polymerization to form the polyamide polymer called nylon-6.

The name nylon-6 is given on the basis of six carbon atoms present in the monomer unit. Nylon-6 has high tensile strength and luster, nylon-6 fibres are used for manufacture of tyre cords, fabrics and ropes.
(3) Ethene.
Answer:
Ethene is used in the preparation of polythene
Polymer: ![]()
Linear chain polymers : When the monomer molecules are joined together in a linear arrangement, the resulting polymer is straight-chain or long-chain polymer, e.g., polythene, PVC.

They have high melting points; high densities and high tensile strength.

![]()
(4) Formaldehyde.
Answer:
Formaldehye is used in the preparation of bakelite.
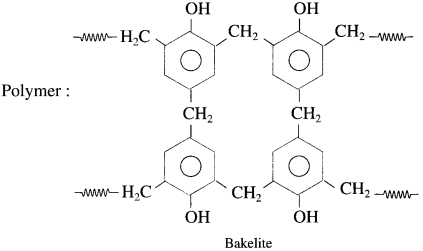
The monomers phenol and formaldehyde undergo polymerisation in the presence of alkali or acid as catalyst.

Phenol reacts with formaldehyde to form ortho or p-hydroxy methyl phenols, which further reacts with phenol to form a linear polymer called Novolac. It is used in paints.
In the third stage, various articles are shaped from novolac by putting it in appropriate moulds and heating at high temperature (138 °C to 176 °C) and at high pressure forms rigid polymeric material called bakelite. Bakelite is insoluble and infusible and has high tensile strength.

Bakelite is used in making articles like telephone instrument, kitchenware, electric insulators frying pans, etc.
Question 31.
Classify the following polymers as step growth or chain growth polymers :
(1) Nylon-6,6
(2) Terylene
(3) Polyethene (4) PVC.
Answer:
Step growth polymers : Nylon-6,6, terylene
Chain growth polymers : Polythene, PVC.
Question 32.
Classify the following as linear, branched or cross linked polymers :
(1) Bakelite
(2) Starch
(3) Polythene
(4) Nylon.
Answer:
Linear polymers : Polythene, nylon.
Cross-linked polymers : Bakelite, starch.
Question 33.
Classify the following as addition and condensation polymers :
(1) Bakelite
(2) polyvinyl chloride
(3) polythene
(4) terylene.
Answer:
Addition polymers : Polyvinyl chloride, polythene
Condensation polymers : Bakelite, terylene.
![]()
Question 34.
Arrange the polymers in increasing order of their intermolecular forces :
Nylon-6,6, Polythene, Buna-S.
Answer:
The increasing order of their intermolecular forces of attraction follows the order :
Buna-S, Polythene, Nylon-6,6.
Question 35.
Classify the following as natural, synthetic and semisynthetic polymers :
Terylene, cuprammonium silk, jute, melamine
Answer:
Natural polymers : Jute
Synthetic polymers : Terylene, melamine
Semisynthetic polymers : Cuprammonium silk
Question 36.
Complete the following statements :
(1) Chemically teflon is …………………………. .
(2) …………………………. is the catalyst used to obtain HDP by polymerisation of ethene.
(3) Viscose rayon is a …………………………. .
Answer:
(1) polytetrafluoroethylene
(2) Zieglar-Natta
(3) semisynthetic fibre (regenerated fibre).
Question 37.
Answer the following in one sentence each.
(1) Name a polymer used for making LCD screen?
Answer:
The polymer used for making LCD screen is Perspex.
(2) Which of the two is a condensation polymer? Bakelite or Polythene?
Answer:
The condensation polymer is bakelite.
(3) Which of the two is a linear polymer? Nylon or Starch.
Answer:
The linear polymer is nylon.
(4) Which of the two is a step growth polymer? Nylon-6,6 or PVC.
Answer:
The step growth polymer is Nylon-6,6.
(5) Write the use of polyacrylamide gel.
Answer:
Polyacrylamide gel is used in electrophoresis.
(6) Write the use of urea formaldehyde resin.
Answer:
Urea formaldehyde resin is used in making unbreakable dinnerware and decorative laminates.
(7) Give an example of semisynthetic polymer.
Answer:
Semisynthetic polymer : Viscose rayon, cuprammonium silk.
(8) Write the monomer unit of teflon.
Answer:
Monomer unit of teflon : Tetrafluoroethene (F2C = CF2).
(9) Write the equation for the preparation of polypropylene.
Answer:
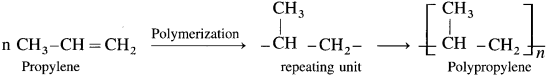
(10) Name a synthetic polymer which contains amide linkage.
Answer:
Polymer that contains amide linkage : Nylon-6; Nylon 6,6.
(11) Name a synthetic polymer which contains ester linkage.
Answer:
Polymer that contains ester linkage : Terylene or Dacron.
![]()
(12) Name one thermosetting and one thermoplastic polymer.
Answer:
Thermosetting polymer : Bakelite.
Thermoplastic polymer : Polythene, polystyrene.
(13) State the uses of biodegradable polymers.
Answer:
Biodegradable polymers are used as orthopaedic devices, implants, sutures and drug release matrices.
(14) Name a copolymer which is used for making nonbreakable crockeries.
Answer:
The polymer used in making nonbreakable crockeries : Melamine formaldehyde polymer.
(15) Write the structure of monomer used in the preparation of 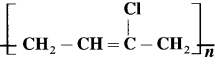
Answer:
The structure of monomer : 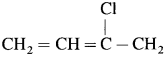
(16) Write the structure of melamine.
Answer:
The monomers formaldehyde and melamine undergo condensation polymerisation to form cross-linked melamine formaldehyde. It is used in making crockeries, decorative table tops like formica and plastic dinner-ware.

(17) What does SBR stand for?
Answer:
SBR stand for styrene(S)butadiene (B) rubber (R).
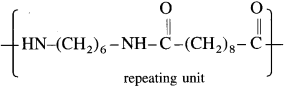
(18) Draw the structure of repeating unit in nylon-6,10.
Answer:
The structure of repeating unit in nylon-6,10 is
(19) What are the monomers used to prepare nylon given below?

Answer:
Monomers used in the preparation of nylon are

(20) Write the monomers used to prepare nylon given below :
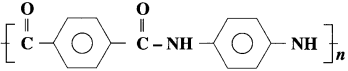
Answer:
Monomers used in the preparation of nylon are
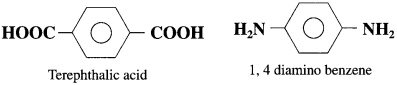
![]()
(21) Name the catalyst which is formed from titanium chloride and triethyl aluminium.
Answer:
The catalyst Zieglar Natta is formed from titanium chloride and triethyl aluminium.
(22) Define molecular mass of polymer.
Answer:
Molecular mass of a polymer is an average of the molecular masses of the constituent molecules.
(23) Which factor determines the molecular mass of polymer.
Answer:
Molecular mass of polymer depends upon the degree of polymerization (DP). DP is the number of monomer units in a polymer molecule.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 38.
Select and write the most appropriate answer from the given alternatives for each subquestion :
1. Which one is the natural polyamide polymer?
(a) Cuprammonium silk
(b) Wool
(c) Perlon-L
(d) Jute
Answer:
(b) Wool
2. The synthetic fibres are prepared from
(a) cellulose
(b) starch
(c) chemical compounds
(d) polymers
Answer:
(c) chemical compounds
3. Which of the following is NOT a vegetable fibre?
(a) Hemp
(b) Jute
(c) Cotton
(d) Keratin
Answer:
(d) Keratin
4. Which of the following fibres are made up of polyamides?
(a) Dacron
(b) Rayon
(c) Nylon
(d) Terylene
Answer:
(c) Nylon
5. An example of natural cellulose fibre is
(a) cotton
(b) wool
(c) silk
(d) rayon
Answer:
(a) cotton
6. Cellulose is the main constituent of
(a) nylon-6
(b) cotton
(c) terylene
(d) wool
Answer:
(b) cotton
7. Of the following, which group contains two cellulosic fibres and one protein fibre?
(a) Cotton, keratin, wool
(b) Linen, keratin, wool
(c) Cotton, linen, rayon
(d) Cotton, keratin, linen
Answer:
(d) Cotton, keratin, linen
8. Which of the following is not a vegetable fibres?
(a) Hemp
(b) Jute
(c) Cotton
(d) Keratin
Answer:
(d) Keratin
![]()
9. Which of the following is polyamide?
(a) Teflon
(b) Nylon 6, 6
(c) Terylene
(d) Bakelite
Answer:
(b) Nylon 6, 6
10. The monomer of e-caprolactam is
(a) styrene
(b) amino acid
(c) aminocaproic acid
(d) adipic acid O
Answer:
(c) aminocaproic acid
11.  is the formula of _ Jn
is the formula of _ Jn
(a) Nylon-66 salt
(b) Nylon-66
(c) DMT
(d) Nylon-6
Answer:
(d) Nylon-6
12. Nylon-6 is a
(a) polyester fibre
(b) protein fibre
(c) poly caprolactum fibre
(d) poly amine fibre
Answer:
(c) poly caprolactum fibre
13. The condensation product of e-caprolactum is
(a) teflon
(b) nylon-6
(c) nylon-66
(d) bakelite
Answer:
(b) nylon-6
14. \(\left[\overline{\mathrm{O}} \mathrm{OC}-\left(\mathrm{CH}_{2}\right)_{4}-\mathrm{COO}-\mathrm{N} \mathrm{H}_{3}-\left(\mathrm{CH}_{2}\right)_{6}-\mathrm{N} \mathrm{H}_{3}\right]\) is the formula of
(a) nylon-6
(b) nylon-6 salt
(c) nylon-66 salt
(d) nylon-66
Answer:
(b) nylon-6 salt
15. The starting material required for the preparation of Nylon-66 is
(a) glycol
(b) α-amino acid
(c) adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine
(d) dimethyl terephthalate and ethylene glycol
Answer:
(c) adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine
16. Terylene is also known as
(a) styrene
(b) butadiene
(c) dacron
(d) teflon
Answer:
(c) dacron
![]()
17. Terylene is
(a) vegetable fibre
(b) protein fibre
(c) polyester fibre
(d) polyamide fibre
Answer:
(c) polyester fibre
18. Terylene polymer is formed in
(a) the presence of nitrogen
(b) the presence of hydrogen
(c) the presence of oxygen
(d) the vacuum
Answer:
(d) the vacuum
19. The by-product formed during the preparation of terylene fibre is
(a) glycerol
(b) propylene glycol
(c) ethylene glycol
(d) ethyl alcohol
Answer:
(c) ethylene glycol
20. Nylon polymer cannot be used for making
(a) tyre cords
(b) films
(c) dress materials
(d) fishing nets
Answer:
(b) films
21. Glycol is an important constituent of
(a) nylon-6
(b) nylon-66
(c) terylene
(d) hexamethylene diammonium adipate
Answer:
(c) terylene
22. Terylene is prepared by the process of
(a) halogenation
(b) condensation
(c) esterification
(d) hydrogenation
Answer:
(b) condensation
23. What are the steps during polymerisation to form terylene?
(a) Terephthalic acid is condensed with ethylene glycol at 420 K-460 K.
(b) Ethylene glycol displaces methanol to form dihydroxy diethyl terephthalic acid
(c) Zinc acetate – antimony trioxide is used as catalyst
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
24. During polymerisation of nylon salt to nylon-66, the conditions are
(a) room temperature and pressure
(b) temperature 503 K
(c) temperature 553 K in presence of Nitrogen
(d) heating in an autoclave at 373 K
Answer:
(c) temperature 553 K in presence of Nitrogen
25. Which one of the following is a condensation polymer?
(a) Nylon
(b) Polythene
(c) PVC
(d) Teflon
Answer:
(a) Nylon
![]()
26. Which one of the following is an addition polymer?
(a) Bakelite
(b) Nylon-6,6
(c) Polystyrene
(d) Terylene
Answer:
(c) Polystyrene
27. A polymer of butadiene and Acrylonitrile is called
(a) Buna-S
(b) Buna-N
(c) Buna-B
(d) Buna-A
Answer:
(b) Buna-N
28. Natural rubber is a polymer of
(a) Styrene
(b) Butadiene
(c) Vinyl chloride
(d) Isoprene
Answer:
(d) Isoprene
29. In which of the following pairs both are copolymers?
(a) PHBV, bakelite
(b) Polythene, terylene
(c) Polyacrylonitrile, nylon-6,6
(d) Polystyrene, melamine
Answer:
(a) PHBV, bakelite
30. The polymer used in paints is
(a) Nylon
(b) Glyptal
(c) Neoprene
(d) Terylene
Answer:
(b) Glyptal
31. Which of the following contains biodegradable polymers only?
(a) Cellulose, dextron, PHBV
(b) Starch, PHBV, PVC
(c) Bakelite, nylon-2-nylon-6, nylon-6,6
(d) Cellulose, starch, terylene
Answer:
(a) Cellulose, dextron, PHBV
32. Thermosetting polymer is
(a) Nylon-6
(b) Nylon-6,6
(c) Bakelite
(d) SBR
Answer:
(c) Bakelite
33. Nylon thread contains the polymer
(a) Polyamide
(b) Polyvinyl
(c) Polyester
(d) Polyethylene
Answer:
(a) Polyamide
34. Polythene, PVC, teflon and neoprene are all
(a) Monomers
(b) Homopolymers
(c) Copolymers
(d) Condensation polymers
Answer:
(b) Homopolymers
![]()
35. Which one of the following is NOT a biodegrad¬able polymer?
(a) Starch
(b) Cellulose
(c) Dextron
(d) Decron
Answer:
(d) Decron
36. The polymer used in making blankets (artificial wool) is
(a) Polyester
(b) Polyacrylonitrile
(c) Polythene
(d) Polystyrene
Answer:
(b) Polyacrylonitrile
37. Which one of the following is a linear polymer?
(a) Bakelite
(b) LDP
(c) Nylon
(d) Formaldehyde melamine polymer
Answer:
(c) Nylon
38. Which one of the following is a branched polymer?
(a) PVC
(b) Polyester
(c) Nylon
(d) Polypropylene
Answer:
(d) Polypropylene
39. The polymer used to make non-stick cookware is
(a) Polyethene
(b) Polystyrene
(c) Polytetrafluoroethylene
(d) Polyvinyl chloride
Answer:
(c) Polytetrafluoroethylene
40. The monomer used to prepare orlon is
(a) CH2 = CH-CN
(b) CH2 = CHCl
(c) CH2 = CH-F
(d) CH2 = CF2
Answer:
(a) CH2 = CH-CN
41. Buna-N rubber is a copolymer of
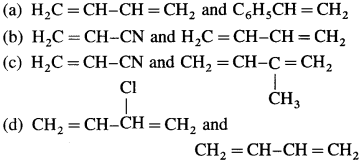
Answer:
(b)
42. Bakelite is a polymer of
(a) Formaldehyde and phenol
(b) Benzaldehyde and phenol
(c) Formaldehyde and benzyl alcohol
(d) Acetaldehyde and phenol
Answer:
(a) Formaldehyde and phenol
![]()
43. The process involving heating of natural rubber with sulphur is known as
(a) Sulphonation
(b) Vulcanisation
(c) Galvanisation
(d) Calcination
Answer:
(b) Vulcanisation
44. A polymer of bisphenol and phosgene is called
(a) Polyamide
(b) Glyptal
(c) Polycarbonate
(d) Polystyrene
Answer:
(c) Polycarbonate
45. Thermocol is a homopolymer of
(a) terephthalic acid
(b) acrylonitrile
(c) methyl a-cyanoacrylate
(d) styrene
Answer:
(d) styrene
46. The polymer is used to prepare shatter resistant glass is called
(a) Perspex/acrylic glass
(b) Soda glass
(c) Buna N
(d) Polyacrylamide
Answer:
(a) Perspex/acrylic glass
47. A polymer used in making shoe soles is
(a) Glyptal
(b) Buna-N
(c) Buna-S
(d) Poly carbonate
Answer:
(b) Buna-N
48. The Zieglar-Natta catalyst is used in the preparation of
(a) LDPE
(b) PHBV
(c) PAN
(d) HDPE
Answer:
(d) HDPE
49. Which of the following is natural rubber?
(a) cis-1, 4-polyisoprene
(b) neoprene
(c) Trans-1. 4-polyisoprene
(d) Butyl rubber
Answer:
(a) cis-1, 4-polyisoprene
50. Which one from the following is the Terylene polymer?
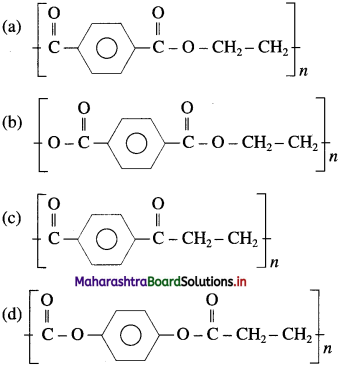
Answer:
(b)
![]()
51. Equivalent amount of Hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid on complete neutralization produces :
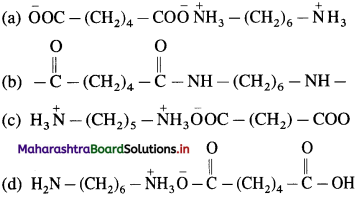
Answer:
(a)
52. Polyhydroxy butyrate-CO-β-hydroxy valerate represents
(a) Dextron
(b) Nylon-6, 6
(c) Nylon-2-nylon-6
(d) PHBV
Answer:
(d) PHBV
53. Among the following, the biodegradable polymer is
(a) PVC
(b) Nylon-6, 6
(c) Nylon-2-nylon-6
(d) Neoprene
Answer:
(c) Nylon-2-nylon-6
54. The monomers of Nylon-2-nylon-6 are
(a) glycine and ω-amino caproic acid
(b) lactic acid and glycolic acid
(c) glycolic acid and co-amino caproic acid
(d) isobutylene and isoprene
Answer:
(a) glycine and ω-amino caproic acid