Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
What is true about the ecosystem?
(a) Primary consumers are least dependent upon producers.
(b) Primary consumers outnumber the producers.
(c) Producers are more than primary consumers.
(d) Secondary consumers are the largest and most powerful.
Answer:
(c) Producers are more than primary consumers.
Question 2.
In an ecosystem, which shows one way passage?
(a) Free energy
(b) Carbon
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Potassium
Answer:
(a) Free energy
![]()
Question 3.
How many are biotic components from the following? Climate, carbohydrates, microbes, green plants, lipids, water, proteins, photosynthetic bacteria, chemosynthetic bacteria, herbivores, carnivores.
(a) 6
(b) 5
(c) 4
(d) 7
Answer:
(a) 6
Question 4.
From the following, which is the basic requirement for any type of ecosystem to function and sustain?
(a) Constant output of solar energy
(b) Constant input of solar energy
(c) Organic substances
(d) Organic substances dissolved in water
Answer:
(b) Constant input of solar energy
Question 5.
Which type of spatial patterns noticed in ecosystem structure?
(a) Zonation
(b) Stratification
(c) Zonation and stratification
(d) Zonation, stratification and distribution
Answer:
(c) Zonation and stratification
Question 6.
In which strata of any aquatic body there will be maximum photosynthesis?
(a) Bottom deposits
(b) Middle strata of a water body
(c) Near coastal region
(d) The depth till where sunlight can reach
Answer:
(d) The depth till where sunlight can reach
Question 7.
Which spatial pattern occurs vertically in an ecosystem?
(a) Zonation
(b) Stratification
(c) Y-shaped pattern
(d) Pyramid
Answer:
(b) Stratification
Question 8.
Which of the following is one of the characteristics of a biological community?
(a) Sex ratio
(b) Stratification
(c) Natality
(d) Mortality
Answer:
(b) Stratification
Question 9.
Identify the likely organisms (1), (2), (3) and (4) in the food web given below:
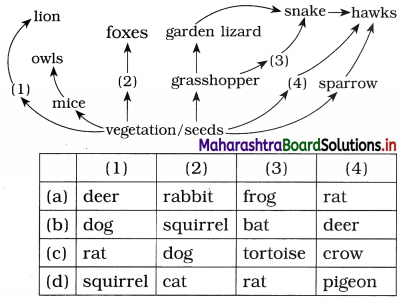
Answer:
(a) deer, rabbit, frog, rat
Question 10.
Which of the following is the basic requirement for any ecosystem to function and sustain?
(a) A constant input of solar energy
(b) Ample water availability
(c) Cool temperatures
(d) Enough winds and currents around
Answer:
(a) A constant input of solar energy
Question 11.
Which one is the most accurate definition of primary production?
(a) The amount of the food produced by plants.
(b) The amount of food available to herbivores.
(c) The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis.
(d) The amount of crop produced by farmer.
Answer:
(c) The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis.
Question 12.
Primary production is expressed in terms of
(a) kg/area
(b) weight (g-2) or energy (kcalm -2)
(c) energy in food calories
(d) calories /sq. m.
Answer:
(b) weight (g-2) or energy (kcalm-2)
Question 13.
Considerable amount of GPP is utilized by plants in
(a) metabolism
(b) respiration
(c) homeostasis
(d) excretion
Answer:
(b) respiration
Question 14.
Which one is the most appropriate definition of secondary productivity?
(a) Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
(b) Secondary productivity is the amount of food consumed by the carnivores.
(c) Secondary productivity is the amount of food consumed by the producers.
(d) Secondary productivity is the amount of energy lost in the food chain.
Answer:
(a) Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Question 15.
Choose the factor on which primary productivity does not depend.
(a) The plant species inhabiting a particular area
(b) Amount of primary consumers dependent on plants
(c) Availability of nutrients
(d) Photosynthetic capacity of plants
Answer:
(b) Amount of primary consumers dependent on plants.
Question 16.
The annual net primary productivity of the whole biosphere is approximately billion tonnes (dry weight) of organic matter.
(a) 10
(b) 50
(c) 100
(d) 170
Answer:
(d) 170
Question 17.
The rate at which light energy is changed into chemical energy of organic molecules in ecosystems is
(a) net primary productivity
(b) gross primary productivity
(c) net secondary productivity
(d) gross secondary productivity
Answer:
(b) gross primary productivity
Question 18.
What is net primary productivity?
(a) Total rate of photosynthesis
(b) Rate of energy storage by consumer
(c) Amount of organic matter stored by plants
(d) Rate of energy used
Answer:
(c) Amount of organic matter stored by plants
Question 19.
Which is the correct sequence of the steps decomposition process?
(a) Fragmentation → Mineralization → Catabolism → Humification → Leaching
(b) Leaching → Catabolism → Humification → Fragmentation → Mineralization
(c) Fragmentation → Leaching → Catabolism → Humification → Mineralization
(d) Catabolism → Humification → Fragmentation → Leaching → Mineralization
Answer:
(c) Fragmentation → Leaching → Catabolism → Humification → Mineralization
Question 20.
Match the columns:
| 1. Fragmentation | i. Release of inorganic nutrients |
| 2. Leaching | ii. Bacterial and fungal enzymes |
| 3. Catabolism | iii. Accumulation of dark amorphous substance |
| 4. Humification | iv. Precipitated as unavailable salts |
| 5. Mineralization | v. Break down into smaller pieces |
(a) 1-v, 2-ii, 3-iii, 4-i, 5-iv
(b) 1-v, 2-iv, 3-ii, 4-iii, 5-i
(c) 1-ii, 2-iii, 3-iv, 4-v, 5-i
(d) 1-iii, 2-v, 3-iv, 4-i, 5-ii
Answer:
(b) 1-v, 2-iv, 3-ii, 4-iii, 5-i
Question 21.
The slow rate of decomposition of fallen logs in nature is due to their
(a) low moisture content
(b) poor nitrogen content
(c) anaerobic environment around them
(d) low cellulose content
Answer:
(a) low moisture content
Question 22.
Small amount of energy sustains the entire living world is only ……………………… of the PAR.
(a) 20-25%
(b) 10-15%
(c) 2-10%
(d) 1-2%
Answer:
(c) 2-10%
Question 23.
Choose incorrect statement out of the following
(a) Much larger fraction of energy flows through the DFC than through the GFC.
(b) Some of the organisms of DFC are prey to the GFC animals.
(c) In an aquatic ecosystem, GFC is the major conduit for energy flow.
(d) Much less fraction of energy flows through the GFC than through the DFC.
Answer:
(d) Much less fraction of energy flows through the GFC than through the DFC
Question 24.
In an ecosystem, bacteria are considered as
(a) primary consumers
(b) microconsumers
(c) macroconsumers
(d) secondary consumers
Answer:
(b) microconsumers
Question 25.
Which of the following can be a top carnivore of marine ecosystem?
(a) Zooplankton
(b) Sea cucumber
(c) Sea horse
(d) Kingfisher
Answer:
(d) Kingfisher
Question 26.
Identify the possible link ‘A’ in the following food chain.
Plant → Insect → Frog → A’ → Eagle
(a) Rabbit
(b) Wolf
(c) Cobra
(d) Parrot
Answer:
(c) Cobra
Question 27.
Why is the pyramid of biomass inverted in sea?
(a) Because plants are absent.
(b) Because fishes have less biomass.
(c) Because phytoplankton which are primary producers have less biomass.
(d) Because primary producers have more biomass.
Answer:
(c) Because phytoplankton which are primary producers have less biomass.
Question 28.
Identify the wrong statement in relation to concept of pyramids.
(a) Pyramid of energy is always upright, can never be inverted.
(b) In most ecosystems, all the pyramids of number of energy and biomass are upright.
(c) Inverted pyramid of biomass is observed in pond ecosystem as small standing crop of phytoplankton supports larger zooplanktons.
(d) Pyramid of biomass in sea is upright because fishes feed on standing crop of planktons.
Answer:
(d) Pyramid of biomass in sea is upright because fishes feed on standing crop of planktons.
Question 29.
Identify A, B, C and D in the following simplified model of phosphorus cycling in a terrestrial ecosystem.
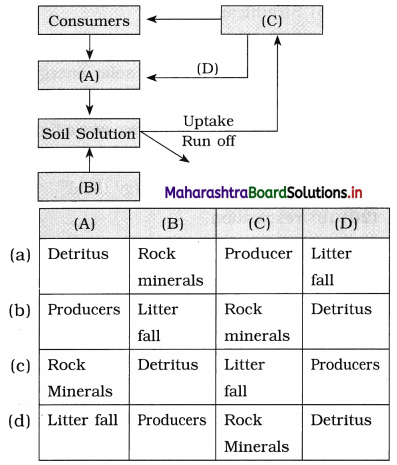
Answer:
(a) Detritus, Rock minerals, producer, litter fall
Question 30.
From the following, which is not a fate of carbon in plants?
(a) Released in transpiration. atmosphere through
(b) Liberated in respiration. atmosphere through
(c) Consumed by animal in the form of food.
(d) Remains as it is as organic matter when plant dies.
Answer:
(a) Released in atmosphere through transpiration.
Question 31.
Bacterial role in carbon cycle is ………………
(a) photosynthesis
(b) chemosynthesis
(c) assimilation
(d) breakdown of organic matter
Answer:
(d) breakdown of organic matter
Question 32.
Which out of the following is the major reservoir of carbon?
(a) Animal bodies
(b) Fruits
(c) Ocean
(d) Coal mines
Answer:
(c) Ocean
![]()
Question 33.
Which act of human beings has great impact on carbon cycle?
(a) Breaking of limestone
(b) Building up of limestone reefs
(c) Burning of fossil fuels
(d) Volcanic eruption
Answer:
(c) Burning of fossil fuels
Question 34.
Rock phosphates are brought into circulation by the process of ………………….
(a) combustion
(b) sedimentation
(c) weathering
(d) absorption
Answer:
(c) weathering
Question 35.
In animals this structure is not containing phosphorus.
(a) Bones
(b) Shells
(c) Teeth
(d) Hairs
Answer:
(d) Hairs
Question 36.
Phosphorus is not a major constituent of
(a) DNA
(b) Proteins
(c) RNA
(d) ATP
Answer:
(b) Proteins
Question 37.
Secondary Succession takes place on/in
(a) Newly cooled lava
(b) Bare rock
(c) Degraded forest
(d) Newly created pond
Answer:
(c) Degraded forest
Question 38.
Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in a biotic community is known as
(a) Pyramid
(b) Divergence
(c) Stratification
(d) Zonation
Answer:
(c) Stratification
Question 39.
The developmental stages of ecological succession are called
(a) serial stages
(b) serai stages
(c) cereal stages
(d) trophic levels
Answer:
(b) serai stages
Question 40.
What is the peculiarity of pioneers in succession?
(a) They are always heterotrophic components.
(b) They always face favourable growth conditions.
(c) They are the most successful terminal occupants of the area.
(d) They face adverse conditions and get established there.
Answer:
(d) They face adverse conditions and get established there.
Question 41.
What are pioneers?
(a) First serai stage
(b) Heterotrophic serai stage
(c) Terminal (last) serai stage
(d) Final climax community
Answer:
(a) First serai stage
Question 42.
The stable community established in an area is known as
(a) pioneer community
(b) climax community
(c) equilibrium community
(d) autotrophic community
Answer:
(b) climax community
Question 43.
The entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area are called
(a) climax
(b) sere
(c) pioneer
(d) standing population
Answer:
(b) sere
Question 44.
The primary succession refers to the development of communities on a ………………….
(a) freshly cleared crop field
(b) forest clearing after devastating fire
(c) pond, freshly filled with water after a dry phase
(d) Newly-exposed habitat with no record of earlier vegetation
Answer:
(d) Newly-exposed habitat with no record of earlier vegetation
Question 45.
Which is the most important service provided by environment?
(a) Release of oxygen
(b) Formation of ozone layer
(c) Carbon assimilation in photosynthesis
(d) Agents of pollination
Answer:
(c) Carbon assimilation in photosynthesis
Match the columns
Question 1.
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Tansley | (a) 10% law |
| (2) C. Elton | (b) Ecosystem services |
| (3) R. Lindemann | (c) Ecological pyramids |
| (4) Millennium Ecosystem Assessment report | (d) Ecosystem |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Tansley | (d) Ecosystem |
| (2) C. Elton | (b) Ecosystem services |
| (3) R. Lindemann | (a) 10% law |
| (4) Millennium Ecosystem Assessment report | (c) Ecological pyramids |
Question 2.
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Rooted floating angiosperm | (a) Cyperus |
| (2) Free-floating plant | (b) Typha |
| (3) Reed swamp | (c) Pistia |
| (4) Marsh-meadow | (d) Lotus |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Rooted floating angiosperm | (d) Lotus |
| (2) Free-floating plant | (c) Pistia |
| (3) Reed swamp | (b) Typha |
| (4) Marsh-meadow | (a) Cyperus |
Question 3.
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Pioneer species | (a) Entire gradient of communities |
| (2) Climax species | (b) Spatial pattern |
| (3) Succession | (c) Quercus |
| (4) Sere | (d) Crustose lichen |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Pioneer species | (d) Crustose lichen |
| (2) Climax species | (c) Quercus |
| (3) Succession | (b) Spatial pattern |
| (4) Sere | (a) Entire gradient of communities |
Classify the following to form Column B as per the category given in Column A.
Question 1.
Estuarine waters, Taiga, Aquarium tank, Lake, Evergreen forest, Flower garden.
| Types of ecosystems | Examples |
| (1) Aquatic | ————– |
| (2) Terrestrial | ————— |
| (3) Artificial | ————– |
Answer:
| Types of ecosystems | Examples |
| (1) Aquatic | (a) Estuarine waters, Lake |
| (2) Terrestrial | (b) Taiga, Evergreen forest |
| (3) Artificial | (c) Aquarium tank, Flower garden |
Question 2.
Xerarch, Epipelagic, Hydrosere, Sublittotral, Intertidal, Benthic.
| Phenomena | Examples |
| (1) Stratification | ————– |
| (2) Zonation | ————— |
| (3) Succession | ————– |
Answer:
| Phenomena | Examples |
| (1) Stratification | (a) Epipelagic, Benthic |
| (2) Zonation | (b) Sublittotral, Intertidal |
| (3) Succession | (c) Xerarch, Hydrosere |
Question 3.
Nature trails, Pollination, Sea food, Carbon sequestration, Animal therapy, Pest control, Health care, Nutrient cycling.
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Supporting services | ————– |
| (2) Provisioning services | ————— |
| (3) Regulating services | ————– |
| (4) Cultured services | ————— |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Supporting services | (a) Pollination, Nutrient services cycling |
| (2) Provisioning services | (b) Sea food, Health care |
| (3) Regulating services | (c) Carbon sequestration, services Pest control |
| (4) Cultured services | (d) Nature trails, Animal services therapy |
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What forms the physical structure of the ecosystems?
Answer:
Interaction of biotic and abiotic components, results in a physical structure of ecosystems.
Question 2.
How is species composition of an ecosystem decided?
Answer:
By identification and enumeration of plant and animal species of a given ecosystem, its species composition can be decided.
Question 3.
What does base of each pyramid represent?
Answer:
The base of each pyramid represents the first trophic level of producers.
Question 4.
How is stratification seen in the forested land?
Answer:
Stratification seen in forested land is as follows trees occupying top vertical strata or layer of a forest, shrubs the second strata and herbs and grasses occupying the bottom layer.
Question 5.
What is meant by nutrient cycling?
Answer:
The cyclic movement of nutrient elements through the various components of an ecosystem, is called nutrient cycling.
Question 6.
Why nutrient cycling is called biogeochemical cycle?
Answer:
The nutrients are cycled from biotic organisms (bio) to abiotic components in the earth (geo) and all these nutrients are in the form of chemicals, therefore, nutrient cycling is called biogeochemical cycle.
Question 7.
What is the function of reservoirs in nutrient cycling?
Answer:
The function of the reservoir is to meet with the deficit, which occurs due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux in any ecosystem.
Question 8.
Till what time does the climax community remain stable?
Answer:
The climax community remains stable as long as the environment remains unchanged.
Question 9.
Which are the pioneers in the aquatic habitat during primary succession?
Answer:
Small phytoplankton are the pioneers in the aquatic habitat during primary succession.
![]()
Question 10.
What are serai communities?
Answer:
The individual transitional communities formed during succession are termed serai communities.
Question 11.
What are the benefits given by the healthy ecosystems?
Answer:
Healthy ecosystems give the benefits from wide range of economic, environmental and aesthetic goods and services.
Question 12.
Which are the major producers in a terrestrial ecosystem?
Answer:
The major producers in a terrestrial ecosystem are herbaceous and woody plants.
Question 13.
Which are the major producers in an aquatic ecosystem?
Answer:
Major producers in an aquatic ecosystem are phytoplankton and algae.
Question 14.
Which event is the beginning of the detritus food chain or web?
Answer:
Death of any organism is the beginning of the detritus food chain or web.
Question 15.
State the 10% law. Who gave this law?
Answer:
R. Lindermann gave the 10% law which states that only 10% of the energy is transferred to each trophic level as net energy, from the previous trophic level. B
Give definitions of the following
Question 1.
Ecosystem
Answer:
A self-regulatory and self-sustaining structural and functional unit of biosphere in which there are interacting biotic and abiotic components is called an ecosystem.
Question 2.
Stratification
Answer:
Vertical distribution of different species of plants and animals occupying different levels, is known as stratification.
Question 3.
Zonation
Answer:
Horizontal distribution of plants and animals on land or in water, is called zonation.
Question 4.
Productivity
Answer:
Conversion of inorganic chemicals into organic material with the help of the radiant energy of the sun by the autotrophs and consumption of the autotrophs by heterotrophs.
Question 5.
Decomposition
Answer:
Decomposition is the break-down of dead organic material and mineralization of the dead matter.
Question 6.
Energy flow
Answer:
Energy flow is the unidirectional flow of energy from producers to consumers and finally dissipation and loss as heat.
Question 7.
Saprotrophs
Answer:
Organisms which can degrade the detritus and obtain their energy and nutrient requirements are called saprotrophs
Question 8.
Trophic level
Answer:
A specific place occupied by the organisms in the food chain is called their trophic level.
Question 9.
Ecological pyramid
Answer:
Ecological pyramid is the graphic representation showing relationship between the organisms of different successive trophic levels with respect to energy, biomass and number.
Question 10.
Leaching
Answer:
The precipitation of water-soluble inorganic nutrients into the soil horizon in the form of salts is called leaching.
Question 11.
Humification
The formation of humus is humification.
Question 12.
Mineralization
Answer:
The process in which humus is degraded by some microbes to release inorganic nutrients is called mineralization.
Question 13.
Eutrophication
Answer:
Eutrophication is the sudden influx of phosphorus in water bodies due to agricultural runoff or industrial effluents which are rich in phosphate content.
Question 14.
Ecological succession
Answer:
The gradual and predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession.
Question 15.
Sere
Answer:
The entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area is called a sere.
Name the following
Question 1.
Functional aspects of ecosystem.
Answer:
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Nutrient cycling
- Energy flow.
Question 2.
Two types of spatial patterns.
Answer:
- Stratification
- Zonation.
Question 3.
Stratification seen in open seas.
Answer:
Epipelagic, mesopelagic, bathy-pelagic and benthic zones.
Question 4.
Zonation seen at the junction of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Answer:
Inter-tidal, Littoral, Sub-littoral zones.
Question 5.
Common herbivores in terrestrial ecosystem.
Answer:
Insects (grasshopper, aphids), birds (parrot) and some mammals (sheep, cattle, goat, donkey).
![]()
Question 6.
Secondary consumers.
Answer:
All carnivorous animals such as frogs, lizards, birds of prey, hunting animals like tiger, lion, wolf, etc.
Question 7.
Three types of food chains.
Answer:
- Grazing
- Detritus
- Arasitic.
Question 8.
Different trophic levels.
Answer:
Producer, herbivore, primary carnivore, secondary carnivore, tertiary carnivore and ultimate carnivore are different trophic levels.
Question 9.
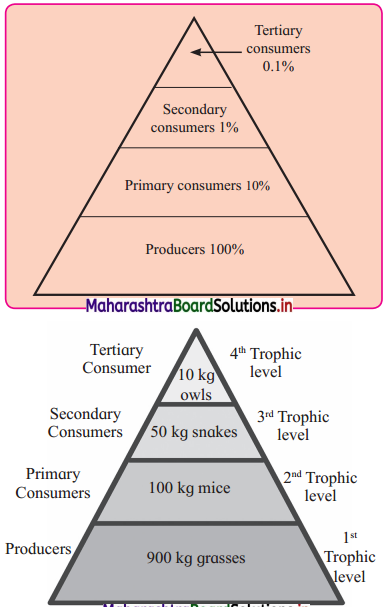
Three types of ecological pyramids.
Answer:
- Pyramid of biomass
- Pyramid of numbers
- Pyramid of energy
Question 10.
The important steps in the process of decomposition.
Answer:
- Fragmentation
- Leaching
- Catabolism
- Humification
- Mineralization
Question 11.
Sequential steps in process of succession.
Answer:
- Nudation
- Invasion
- Ecesis
- Aggregation
- Competition and co-action
- Reaction and stabilization
Question 12.
Types of Nutrient cycles.
Answer:
- Gaseous and
- Sedimentary.
Question 13.
Reservoir for the sedimentary cycle.
Answer:
Earth’s crust.
Question 14.
Reservoir for gaseous cycles.
Answer:
Atmosphere.
Distinguish between the following
Question 1.
Natural ecosystem and artificial ecosystem.
Answer:
| Natural ecosystem | Artificial ecosystem |
| 1. Natural ecosystems are naturally formed. | 1. Artificial ecosystems are man made. |
| 2. There are no human inputs in natural ecosystems. | 2. Artificial ecosystem is based on all human inputs. |
| 3. Natural ecosystems are self-sustainable. | 3. Artificial ecosystems are not self-sustainable. |
| 4. In natural ecosystem, energy and materials are used and reused in cyclic manner. E.g. Ocean, forest, wetlands, estuary. | 4. In artificial ecosystem, Energy and materials have to be given by human intervention which requires constant inputs. E.g. Farm land, aquaculture ponds, aquarium in the house. |
Question 2.
Primary and secondary succession.
Answer:
| Primary succession | Secondary succession |
| 1. The primary succession starts in the area where no living organisms ever existed. | 1. The secondary succession starts in an area which has lost all the living organisms once existed. |
| 2. Areas where primary succession starts are bare rock, newly formed pond, newly cooled lava, etc. | 2. Abandoned farm, cut or burnt forest, flooded land’, etc. are areas where secondary succession begins. |
| 3. Primary succession is a very slow process. | 3. Secondary succession is comparatively a faster process. |
Question 3.
Carbon cycle and phosphorus cycle.
Answer:
| Carbon cycle | Phosphorus cycle |
| 1. Carbon cycle is a gaseous cycle. | 1. Phosphorus cycle is a sedimentary cycle. |
| 2. Carbon cycle has higher speed. | 2. Phosphorus cycle is very slow. |
| 3. There is respiratory release of CO2 in carbon cycle. | 3. There is no respiratory release of phosphorus. |
| 4. Atmospheric inputs of carbon through rainfall are larger. | 4. Atmospheric inputs of phosphorus through rainfall are much smaller. |
| 5. Exchanges of phosphorus between organism and environment are negligible in carbon cycle due to photosynthesis and respiration. | 5. Exchanges of phosphorus between organism and environment are negligible in phosphorus cycle. |
Given reasons
Question 1.
All animals are called consumers.
Answer:
- All animals depend on plants for food either directly as in case of herbivorous animals or indirectly as in case of carnivorous animals.
- Animals cannot perform photosynthesis as they are not autotrophic.
- They are heterotrophic and hence all are called consumers.
Question 2.
Food chains do not exist in isolation, but are always interconnected to form food web.
Answer:
- Food chains start from producers and end with consumers.
- But beyond secondary carnivores, the amount of energy available is too less.
- Thus, there is no tertiary carnivore that feeds exclusively on secondary carnivore.
- The secondary carnivore, however, many times will feed on herbivores directly.
- Therefore, food chains do not exist in isolation, but are always interconnected to form food web, so that the stability of ecosystem is maintained.
Question 3.
The pyramid of biomass in the sea is inverted.
Answer:
- The food chain in the sea is dependent on producers i.e. phytoplankton.
- The biomass of phytoplankton is always. lesser to the biomass of fishes which are dependent upon these phytoplankton.
- The pyramid of biomass, therefore, in the sea is inverted.
Question 4.
The pyramid of energy is always upright.
Answer:
- When the energy is moving from one trophic level to the next one, there is loss of some energy in the form of heat.
- Therefore, the energy is always more on the lower trophic levels as compared to the higher trophic levels.
- Due to this reason, the pyramid of energy is always upright and never inverted.
![]()
Question 5.
Only a fraction of sunlight is used for photosynthesis.
Answer:
- When sunlight falls on the earth surface about 34% of this is reflected back.
- About 10% is held by the ozone layer, water vapour and other atmospheric gases.
- Out of the total solar energy, about 56% reaches to the earth’s atmosphere.
- Only 0.02% of the sunlight is used for photosynthesis. This shows that only a fraction of sunlight is used for photosynthesis.
Question 6.
Usually crustose lichens form a pioneer species.
Answer:
- The pioneer species is the one which invades a bare area.
- When primary succession occurs it takes place on rocks.
- The crustose lichens can secrete acids which can dissolve rocks. This starts weathering of rocks and soil formation.
- Further, bryophytes and mosses can take hold of such soil. Therefore, as a pioneer on the barren rocks only crustose lichens can grow.
Write short notes
Question 1.
Zonation in wetland.
Answer:
There are four zones in wetland, viz. subtidal channels, mudflats, low marsh and high marsh. High marsh is more in terrestrial ecosystem while the subtidal channels are more of aquatic nature.
- Subtidal channels : These are important habitat for fish during low tide. This region allows good drainage and flooding in mudflats.
- Mudflats : This area is very rich in invertebrate life. Therefore, many wading birds are dependent for food in this area. Algal mat is also observed on mud flats.
- Low marsh : This area is a good habitat for cordgrass, insects, herons and egrets and the clapper rails.
- High marsh : This region supports pickleweed and patches of cordgrass. Sparrow and clapper rails are seen here.
Question 2.
Pond as a small ecosystem.
Answer:
- For every ecosystem there are four important functional aspects viz. productivity, decomposition, nutrient cycling and energy flow.
- In a small pond ecosystem, too, there are complex interactions.
- Pond is a shallow water body in which all the above four basic processes of an ecosystem are observed.
- The abiotic component is water along with dissolved inorganic and organic substances and rich soil deposit at the bottom of the pond.
- The sunlight acts as a source of solar energy, the cycle of temperature, day-length and other climatic conditions regulate the rate of function of the entire pond.
- Phytoplankton are the main producers along with algae and other aquatic plants.
- Zooplankton, aquatic insects and fish are the consumers.
- The decomposers are the fungi and bacteria present in the bottom soil.
Question 3.
Primary succession.
Answer:
- Primary succession means the initial development of life on barren piece of land.
- Primary succession occurs on newly cooled lava, rocks and newly created pond or reservoir. In a newly formed volcanic island, the life starts and takes up millions of years to develop the whole biomass.
- In the successive serai stages, there is a change in the diversity of species of organisms, increase in the number of species and organisms as well as an increase in the total biomass.
- The establishment of a new biotic community is generally very slow and takes millions of years.
- Primary succession depends on climatic condition, soil characteristics and natural processes.
Question 4.
Secondary succession.
Answer:
- Secondary succession begins in areas where previously natural biotic communities were present. But later were destroyed due to causes such as abandoned farm lands, burnt or cut forests, flooded lands, etc.
- Secondary succession is faster than primary succession because already there is some soil or sediment present.
- It occurs in the form of changed vegetation. But due to changed vegetation, there is also change in the resident animals that depend for food and shelter.
- Thus, with secondary succession, the numbers and types of animals and decomposers also change.
- During succession, natural or human induced disturbances (fire, deforestation, etc.), can convert a particular serai stage of succession to an earlier previous / preceding stage.
- Sometimes, disturbances like this can create new conditions that encourage some species and eliminate other species.
Question 5.
Succession of Plants.
Answer:
- Succession of plants is of two types based on the nature of the habitat. These are hydrarch or hydrosere which is based on water or very wetland areas and xerarch or xerosere based on very dry areas.
- In wetter areas hydrarch succession begins and then successional series progress from hydric to the mesic conditions.
- Xerarch succession starts in dry areas and the series progress from xeric to mesic conditions.
- Both hydrarch and xerarch successions lead to mesic or medium water condition which is neither too xeric nor too hydric.
Question 6.
Pioneer species.
Answer:
- Pioneer species are the ones that invade a bare area during primary succession.
- Crustose lichens which are able to secrete acids to dissolve rock usually start as pioneer species. They bring about weathering of rocks and soil formation.
- Later here bryophytes, mosses are settled as they can take hold in the small amount of soil. They are then followed by herbaceous plants, and after several more stages, ultimately a stable climax forest community is formed.
Question 7.
Succession in aquatic habitat.
Answer:
- In aquatic habitats the pioneer species in primary succession are the small phytoplankton.
- Phytoplankton are replaced by rooted- submerged plants (e.g. Hydrilla), rooted- floating angiosperms (e.g. Lotus) followed by free-floating plants (e.g.Pistia), then reed swamp (e.g. Typha), marsh-meadow (e.g. Cyperus), scrub (e.g. Alnus) and finally the trees (e.g. Quercus) in a very systematic and gradual way.
- The climax again would be a forest. With passage of time, the water body is converted into land.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe the functions of the ecosystem.
Answer:
Functions of an ecosystem:
- Biological energy flow.
- Productivity of the ecosystem.
- Photosynthesis and respiration that take place in the ecosystem.
- Nutrient cycles operating in the ecosystem.
- Regulation of the environment by the organisms and the regulation of the organisms by the environment in turn.
- Interactions of biotic and abiotic components of the ecosystem.
Question 2.
What are the types of ecosystems? Give their suitable examples.
Answer:
Ecosystems are of two types, viz. natural ecosystem and artificial ecosystem.
(1) Natural ecosystems : The ecosystems which operate under natural conditions without any much major interference by man are called natural ecosystems. E.g. terrestrial ecosystems such as grasslands, forests, deserts, etc. or aquatic ecosystems such as lakes, river, wetland, etc.
(2) Artificial ecosystems : The man engineered ecosystems which are maintained artificially by man by the addition of energy are called artificial ecosystems. These ecosystems are dependent upon manipulations from human beings. E.g. croplands, aquarium, aquaculture, etc. are the types of artificial ecosystems.
Question 3.
What are the different components of ecosystem?
Answer:
(1) There are two main components of the ecosystem, viz. abiotic components and biotic components.
(2) Abiotic components include all the inorganic substances such as B S, C, N, H, etc., their distribution and amount available in an ecosystem and the organic compounds such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, etc. along with the climate of that region.
(3) Biotic components include all the living organisms living in an ecosystem. The living organisms may be autotrophic or producers and converters or transducers. These are either green plants having photosynthetic abilities or chemosynthetic microorganisms. The heterotrophic organisms are called consumers.
They can either be macroconsumers or microconsumers.
- Macroconsumers are herbivores, carnivores or omnivores as per the order in which they appear in the food chain.
- Herbivores are primary consumers while the carnivores are secondary consumers.
- Omnivores can be secondary or tertiary consumers.
- Microconsumers are decomposing organisms and hence they are also called decomposers. They have saprophytic mode of nutrition. Bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi are some of the microconsumers.
- Microconsumers decompose complex organic compounds from dead and living protoplasm and release the inorganic nutrients obtained from them, back to the environment.
Question 4.
What are the two spatial patterns in an ecosystem? Describe them briefly.
Answer:
- There are two spatial patterns recognized in an ecosystem, viz. zonation and stratification.
- Zonation is the spatial pattern which occurs horizontally along the ground. Along a horizontal gradient, the density and distribution of the species keep on varying.
- Stratification is the spatial pattern which occurs vertically. This is determined by the height of organisms. Such stratification is seen in forest community where trees of different species grow to different heights.
Question 5.
Describe the concept of energy flow.
OR
In an ecosystem the flow of energy is unidirectional. Explain.
Answer:
(1) For considering the energy flow in an ecosystem the following aspects have to be taken into account:
- The efficiency of the producers in the absorption and conversion of the solar energy.
- The quantity of converted energy is used by the consumers.
- The total input of energy in the form of food and its efficiency of assimilation by the consumers.
- The amount of energy is lost through respiration, heat, excretion, etc.
- The ultimate gross net production.
(2) The energy captured by autotrophs never returns back to the sun. The energy obtained by the herbivores will never go back to autotrophs. Hence energy flow is always unidirectional.
(3) The energy flow through different trophic levels is progressive and hence previous trophic level cannot get this back.
(4) The amount of energy keeps on decreasing as it travels to further trophic level. This loss of energy is due to dissipation as heat formed during various metabolic activities of the organism. The energy loss is measured as respiration coupled with unutilized energy.
(5) If the food chain is shorter there is greater amount of available food energy. When the length of food chain increases, there is corresponding more loss of energy.
Question 6.
What could be the reason for the low productivity of ocean?
Answer:
- The conditions of land and in ocean are not same. Primary productivity which is the biomass or dry weight produced by the plants per unit area during the photosynthesis is different for oceanic ecosystem.
- In ocean, sunlight does not penetrate uniformly at all depths. It is thus the main limiting factor which decreases the rate- of photosynthesis.
- Decrease in rate of photosynthesis decreases the growth of phytoplankton and then that of the zooplankton. Aquatic plants such as algae are also affected due to lack of sunlight.
- Minerals and nutrients is also a limiting factor based on location of the oceans.
- Therefore, there is less productivity of the oceans to about 55 billion tons as compared to productivity on land which is about 170 billion tonnes.
Question 7.
What could be the connecting points between the GFC and DFC?
Answer:
- In grazing food chain, the energy is transferred from producers to consumers.
- The autotrophs convert inorganic matter into organic compounds which is then transferred in food chain or food web.
- In detritus food chain energy is obtained from organic matter or detritus generated in trophic levels of the grazing food chain.
- Detritus such as dead bodies of animals or fallen leaves, which are then eaten by decomposers or detritivores.
- These detritivores can also be consumed in grazing food chain by secondary consumers or predators.
- When decomposers convert organic matter back into inorganic substances, the autotrophs use these minerals again.
- In this way GFC and DFC are connected to each other in cyclic and mutual exchanges.
![]()
Question 8.
How will you classify man as carnivore (primary/ secondary) or omnivore? Why?
Answer:
Autotrophic producers or plants make the first trophic level. They synthesize their own food. Herbivores are primary consumers. They eat producers. Carnivores are secondary consumers. They eat primary consumers. The trophic level of man is omnivore as he eats both plants and animals. Non vegetarian person can be called carnivore while totally vegetarian person can be herbivore. However, the most appropriate placement of man is omnivorous.
Question 9.
How many trophic levels human beings function in a food chain?
Answer:
(1) All food chains and webs have at least two dr three trophic levels. Generally, there are a maximum of four tropic levels. Many consumers feed at more than one tropic level.
(2) Man is a primary consumer when he eat plants such as vegetables. Vegans and vegetarians who do not consume any animal product, fish or meat of any kind are primary consumers. They belong to the second trophic level.
(3) But some humans have different dietary choices. Many humans are omnivores, meaning they consume both plant and animal material. Thus, they may be on the third or even fourth tropic level.
(4) For example, if man consumes goat meat he is a part of the third tropic level.
(5) But when he eats bigger fish (and considering fish eats smellier fish) he becomes tertiary consumer on the fourth tropic level.
Question 10.
What is climax community? What leads to such a community?
Answer:
- Climax community is the community which is near equilibrium with the environment.
- The sequential changes in the structure and composition of the community, to adjust with the changing environment is called a climax community.
Question 11.
From algae to forest, explain in relation with the succession.
Answer:
- When there is a succession from algae to forest, it depends upon the amount of water available.
- The succession begins with small phyto-planktons followed by submerged and free floating and then rooted hydrophytes, sages, grasses and finally the trees.
- Similarly, there is also a transformation from a pool of water to swamp then marsh and then mesic which means neither too dry nor too wet conditions.
- Then small plants like mosses can inhabit followed by herbs, shrubs and then trees. Such succession ultimately leads to a stable climax forest community.
Question 12.
Explain the following terms with reference to ecological succession.
(1) Serai stages.
Answer:
The developmental stages of the ecological succession are known as serai stages.
(2) Pioneers.
Answer:
The organisms belonging to first serai stage in the ecological succession are known as pioneers.
(3) Hydrosere.
Answer:
Hydrosere or hydrarch succession is a type of ecological succession which is determined by the amount of water available during succession. Hydrosere occurs when there is abundant water available in the area where organisms reside.
(4) Xerosere.
Answer:
Xerosere or xerarch succession is a type of ecological succession which is determined by the amount of water available during succession. Xerosere occurs when there is very little water available in the area where organisms reside. Such succession is observed in desert regions.
Question 13.
Why is zonation more pronounced at the edges of habitat?
Answer:
- Edge of the habitat is an abruptly changing region. E.g. the shore or littoral zone is the edge between aquatic and terrestrial habitats.
- At such places there is variety of environmental factors, such as temperature, wind exposure, light intensity, wave action, and salinity, etc.
- These abiotic factors are never constant in such areas and they show tremendous variation.
- Therefore, the intertidal communities show differences in regions that are occupied by them. In this way zonation is more pronounced in such areas when edges of habitat are present.
Question 14.
What is the maximum number of trophic levels in a food chain?
Answer:
- There are maximum four trophic levels in an ecosystem.
- Rarely five levels are seen where it is occupied by apex consumer.
- But as the trophic levels are moving from producers to consumers, lesser and lesser energy remains.
- Through heat loss, lot of amount of energy is dissipated, therefore no ecosystem can sustain fifth trophic level.
Question 15.
How would you explain inverted pyramid of biomass in oceanic ecosystem?
Answer:
- Pyramid of biomass is inverted in an oceanic ecosystem because in oceans the biomass of fishes is much more than the biomass of phytoplanktons.
- The biomass of phytoplanktons which are the producers in the ocean is smaller than that of zooplanktons.
- Zooplankton are primary consumers in oceans. The biomass of zooplanktons is smaller than that of secondary consumers which are fish.
- This results in the inverted pyramid of biomass is an oceanic ecosystem.
- Also the life span of phytoplankton is very small, which are consumed almost as rapidly as they are formed.
- The phytoplankton have high reproductive potential by which they reproduce rapidly. All these facts make the pyramid inverted in case of oceanic ecosystem.
Question 16.
What is secondary productivity? What is annual net primary productivity of biosphere?
Answer:
- Secondary productivity is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
- It is the rate of assimilation of food energy by the consumers.
- This amount of energy available to consumer for transfer to the next trophic level.
- The annual net primary productivity of the whole biosphere is approximately 170 billion tonnes (dry weight) of organic matter. Of 170 billion tonnes, the oceans create about 55 billion tonnes, and rest is by land ecosystems.
Complete the given chart
| Trophic levels | Type of organisms | Status | Example |
| …………….…. | …………………….. | Secondary consumer | …………………….. |
| ……………..… | Herbivore, Heterotrophs | …………………….. | ……………………. |
| ……………..… | Autotrophs | ……………………. | Phytoplankton, grass, trees |
Answer:
| Trophic levels | Type of organisms | Status | Example |
| Third trophic level | Carnivore, Heterotrophs | Secondary consumer | Lion, Frog |
| Second trophic level | Herbivore, Heterotrophs | Primary consumer | Cattle, Sheep, Deer |
| First trophic level | Autotrophs | Producer | Phytoplankton, grass, trees |
Diagram based questions
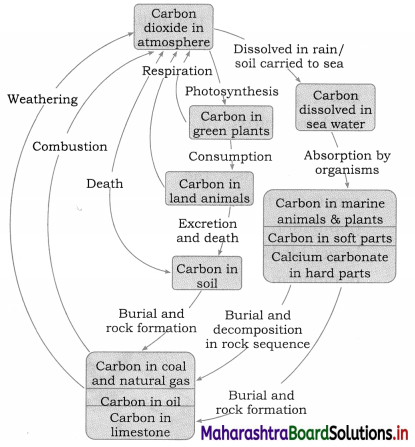
Question 1.
Sketch and label Carbon cycle
Answer:
Question 2.
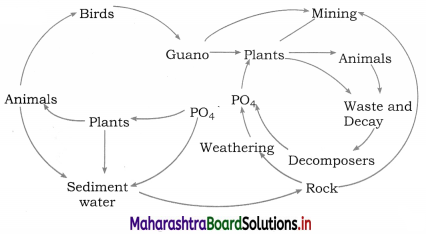
Sketch and label phosphorus cycle
Answer:
Question 3.
Sketch and label decomposition cycle
Answer:
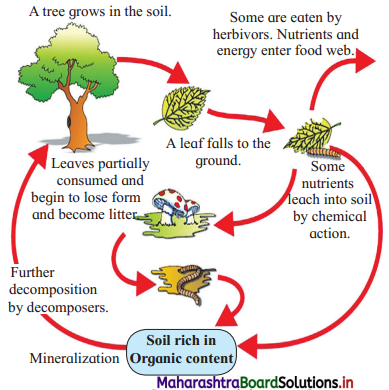
Question 4.
Sketch and label simple grazing food chain
Answer:

![]()
Question 5.
Sketch and label ecological pyramids of energy and pyramid of biomass
Answer:
Question 6.
Observe pyramids of numbers and answer the questions below
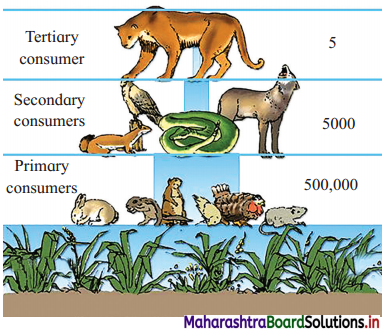
Questions:
1. In the above pyramid of numbers how many primary consumers are supporting secondary consumers? What will happen if the numbers are reversed?
2. When does pyramid of numbers get inverted in case of a single tree ecosystem ?
3. What will happen, if in the above example, we substitute larger bird of prey feeding on small insect eating birds?
Answer:
(1) 500,000 primary consumers are supporting 5000 secondary consumers. If the numbers are reversed, i.e. if primary consumers are lesser than secondary consumers, then the secondary consumers will have fierce competition and will lead to decline in their number too. The pyramid of numbers will get inverted in such case.
(2) If we plot the number of insects on a single tree, smaller birds feeding on insects, and parasites on those birds, we get an inverted pyramid.
(3) If large birds are feeding on smaller insect eating birds, their population will decrease. This will result into increased number of insects as there will be no check on the insect population due to loss of smaller predator birds. If larger birds keep on feeding constantly and unchecked on smaller birds, the smaller ones will eventually become lesser and lesser in their population and this in turn will starve the larger birds too, leading in decrease of their population too.
Question 7.
Observe the given food web and answer the questions
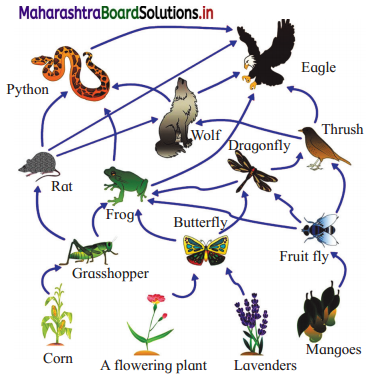
Questions
1. Name the producers in the above web.
2. Name the primary consumers in the above web.
3. Which is an omnivore animal in the above web? Why?
4. Why frog is occupying an important ecological position in this web?
5. From the given food web diagram, give the trophic levels where the eagle is present.
Answer:
1. Corn crop, flowering plant, lavender plant, mango tree
2. Grasshopper, butterfly, fruit fly
3. Rat, because it feeds on grains of corn as well as on insects.
4. Frog feeds on insects and keeps the insect population under check. It also falls prey to snakes and birds of prey like eagle. Thus, supports their population by providing food.
5. (1) Eagle is apex consumer in the following cases : Lavender/Producer → Butterfly/ Primary consumer → Dragon fly /Secondary consumer → Thrush/Tertiary consumer → Eagle/Apex consumer
Or
Corn/Producer → grasshopper/Primary consumer → frog/Secondary consumer → python/Tertiary consumer → eagle/Apex consumer.
(2) Eagle is tertiary consumer in the following case : Rat/Primary consumer → python/ Secondary consumer → eagle/Tertiary consumer
(3) Secondary consumer in the following case : Rat/Primary consumer → eagle/ Secondary consumer
Question 8.
Observe the given figure and answer the questions:
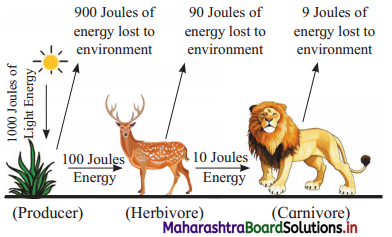
Questions:
1. Which trophic level has maximum energy?
2. Why carnivores have least energy shown in this diagram?
Answer:
1. Producers which form first trophic level has maximum energy.
2. When energy flows from one trophic level to the next, some amount is lost as heat. As it can be seen that producers had 1000 joules of energy, out of which 900 joules are lost when energy flowed from producers to primary consumers. Further, it was lost again by 90 joules while herbivore to carnivore energy flow was taking place. Therefore, the carnivore gets least energy as it is the higher trophic level.
Question 9.
Identify A, B, C, D and E given in sketch of carbon cycle
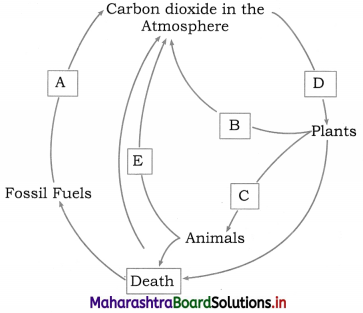
Answer:
A : Combustion
B : Respiration by plants
C : Respiration by animals
D : Photosynthesis
E : Decomposition.
Question 10.
Observe the diagram and answer the questions
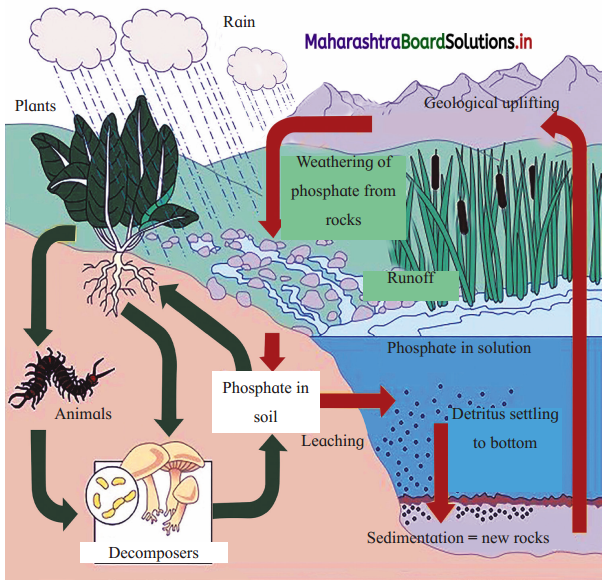
1. Fill in the empty boxes with proper words in the above figure.
2. Which cycle is it depicting?
3. What kind of cycle is it?
Answer:
1. A : geological uplifting, B : Weathering of phosphate from rocks, C : Phophaste in solution. D : Detritus settling at bottom, E : Sedimentation forming New rocks, F : Phosphate in soil, G : Leaching
2. Phosphorus cycle
3. Sedimentary cycle
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Describe the pathway followed by phosphorus in an ecosystem.
Answer:
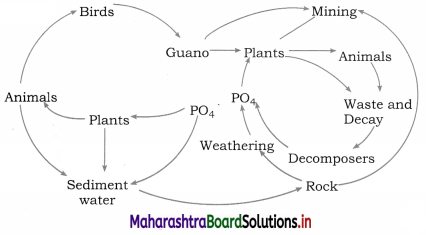
(1) The phosphorus cycle is the simplest of all the nutrient cycles, which is a type of sedimentary cycle. It constitutes cyclic movement of phosphorus through hydrosphere, lithosphere and biosphere.
(2) Since phosphorus is a heavy molecule it never goes into the atmosphere. Phosphorus remains in the bodies of organisms, dissolved in water or in the form of rock. The natural reservoir of phosphorus is rock in which phosphorus is present in the form of phophates.
(3) Upon weathering of the rock due to action of mildly acidic water, the phosphates in the rock go into the solution.
(4) Plants take up phosphorus in the form of phosphate. The roots of plants can absorb phosphate ions from the soil. Animals obtain phosphorus through food which they consume. Thus autotrophs supply phosphorus to heterotrophs. Phosphorus is a major biological constituent of all the living organisms.
It is found in biological membranes, nucleic acids e.g. DNA, RNA, cellular energy transfer systems such as ATE Phosphorus is thus an essential element.
(5) The requirement of phosphorus in animals is much more as it is the component of bones, hooves, teeth, shells.
(6) The waste products formed through defecation and the dead organisms are decomposed by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria releasing phosphorus. This in turn is used up by other growing plants. Phosphorus is always in short supply and hence acts as limiting factor for the plant growth.
Sudden influx of phosphorus in the form of agricultural runoff or industrial effluents rich in phosphate content, leads to eutrophication in water bodies. Eutrophication is due to overgrowth of algae at the instance of high phosphorus dissolved in water. The overgrowth of algae kills or harms the aquatic life.
Question 2.
What are the most important ecological services whose value cannot be determined?
Answer:
(1) The main ecological services are fixation of atmospheric CO2 and release of O2 are the most important services provided by an ecosystem.
(2) Photosynthetic activity of photoautotrophs helps in carbon sequestration in the form of CO2 from the atmosphere. At the same time it releases O2 as a by-product.
(3) O2 is needed for respiration by all aerobic organisms. Oxygen also purifies air.
(4) For human consumption, crops and fruits are continuously required. These can be produced only after pollination of plants. Wind, water or other biotic agent such as insects therefore play an important role as ecosystem service. Without pollination there would be no crops and no fruits.
Question 3.
What are the four categories of ecosystem services as given by Millennium Ecosystem Assessment Report in 2005? What are the services included in each?
Answer:
Ecosystem services are of following four categories:
(1) Supporting services : Support to the life on earth such as nutrient cycling, primary production, soil formation, habitat provision, pollination and overall maintenance of balance of ecosystem.
(2) Provisioning services : Provides necessities such as food in the form of crops, fruits and seafood, raw materials such as timber, skins, fuel wood, genetic resources in the form of seeds, crop improvement genes, and health care, other resources such as water, medicinal resources in the form of test and assay organisms and ornamental resources such as furs, feathers, ivory, orchids, butterflies, etc.
![]()
(3) Regulating services : Regulation of processes on the earth such as carbon sequestration, prey-predation regulation, waste decomposition and detoxification, purification of water and air and pest control.
(4) Cultural services : Under this category, humans get services from nature in the form of cultural, spiritual and historical, recreational experiences, opportunity to learn science and indulge in education, and pets and animal therapy.