Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 10 Human Health and Diseases Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 10 Human Health and Diseases
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The infectious stage of Plasmodium is …………………
(a) trophozoite
(b) sporozoite
(c) cryptozoite
(d) metacercaria
Answer:
(b) sporozoite
Question 2.
After birth, antibodies are transferred from mother to infant through …………………
(a) colostrum
(b) placenta
(c) blood
(d) tissue fluid
Answer:
(a) colostrum
![]()
Question 3.
Which cells give rise to T-lymphocytes?
(a) Thymocytes
(b) Bone marrow cells
(c) Erythrocytes
(d) Leucocytes
Answer:
(a) Thymocytes
Question 4.
Where is antigen D is present?
(a) On Rhesus factor
(b) On the surface of RBCs
(c) On A-antigen
(d) On AB-antigen
Answer:
(b) On the surface of RBCs
Question 5.
Erythroblastosis foetalis is caused when mother is …………………
(a) Rh +ve
(b) with antibody ‘a’
(c) Rh -ve
(d) with antibody ‘b’
Answer:
(c) Rh -ve
Question 6.
Which of the following is NOT a parasitic vector insect?
(a) Mosquito
(b) Housefly
(c) Honey bee
(d) Head louse
Answer:
(c) Honey bee
Question 7.
Which is the proper sequence in the developmental stages of Plasmodium?
(a) Merozoites → Sporozoite → Trophozoites → Schizonts
(b) Trophozoites → Merozoites → Sporozoite → Schizonts
(c) Sporozoite → Merozoites → Trophozoites → Schizonts
(d) Schizonts → Merozoites → Sporozoite → Trophozoites.
Answer:
(c) Sporozoite → Merozoites → Trophozoites → Schizonts
Question 8.
There is no vaccination on this disease till today.
(a) Typhoid
(b) Tuberculosis
(c) Polio
(d) AIDS
Answer:
(d) AIDS
Question 9.
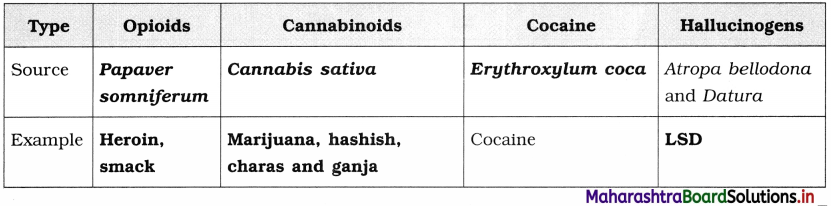
Charas, hashish, ganja are obtained from …………………
(a) Papaver somnijerum
(b) Erythroxylum coca
(c) Atropa belladorta
(d) Cannabis sativa
Answer:
(d) Cannabis sativa
Question 10.
………………. Plant is used to obtain cocaine alkaloid.
(a) Marijuana
(b) Papaver somntferum
(c) Cannabis sativa
(d) Coca
Answer:
(d) Coca
Question 11.
………………… fish is released in the waterbody to prevent the spread of Malaria and Filaria.
(a) Pomfret
(b) Tilapia
(c) Gambusia
(d) Gold fish
Answer:
(c) Gambusia
Question 12.
The carcinogen that can cause vaginal cancer is …………………
(a) Vinyl chloride
(b) Diethylstilboestrol
(c) Mustard gas
(d) Cadmium oxide
Answer:
(b) Diethylstilboestrol
Question 13.
Prostate cancer can be caused due to exposure to …………………
(a) cadmium oxide
(b) mustard gas
(c) asbestos
(d) Nickel and chromium compounds
Answer:
(a) cadmium oxide
Question 14.
Choose the correct definition of health …………………
(a) Health is not contracting any disorder or disease.
(b) State of complete physical, mental and social well-being.
(c) Health is complete absence of any disease.
(d) Health is feeling good all the time.
Answer:
(b) State of complete physical, mental and social well-being
Question 15.
The interval between infection and appearance of disease symptoms is called …………………
(a) inoculation
(b) penetration
(c) infection period
(d) incubation period
Answer:
(d) incubation period
Question 16.
What is injected in vaccination ?
(a) Half killed pathogen
(b) Dead pathogens
(c) Live pathogens
(d) Readymade antibodies
Answer:
(a) Half killed pathogen
Question 17.
Who among the following is considered as father of immunology ?
(a) Ferdinand Kohn
(b) Robert Koch
(c) Louis Pasteur
(d) Edward Jenner
Answer:
(d) Edward Jenner
Question 18.
Who coined the term antibiotics ?
(a) Charles Darwin
(b) Louis Pasteur
(c) Alexander Fleming
(d) Selman Waksman
Answer:
(d) Selman Waksman
Question 19.
Who coined the term antibody?
(a) Selman Waksman
(b) Alexander Fleming
(c) Paul Ehrlich
(d) Edward Jenner
Answer:
(c) Paul Ehrlich
Question 20.
Widal test is used for the diagnosis of …………………
(a) Malaria
(b) Typhoid
(c) Diabetes mellitus
(d) HIV/AIDS
Answer:
(b) Typhoid
Question 21.
Which bacterial genus out of the following is the common pathogen causing pneumonia ?
(a) Streptococcus sps
(b) Lactobacillus sps
(c) Pseudomonas sps
(d) Salmonella sps
Answer:
(a) Streptococcus sps
Question 22.
Given below are some statements. Which among them are symptoms of pneumonia ?
(i) Greenish, yellow sputum coughed out.
(ii) Hepatomegaly and hypoglycemia.
(iii) High fever with shaking chills.
(iv) Thickening of skin and underlying tissues.
(v) Stabbing chest pain with shortness of breath.
(vi) Mood swings and joint pains along with nausea and vomiting.
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (i), (iii), (v), (vi)
(c) (i), (ii), (iv), (vi)
(d) (ii), (iii), (iv), (v)
Answer:
(b) (i), (hi), (v), (vi)
Question 23.
Which of the following is not the common way to prevent common cold ?
(a) Using hand sanitizers
(b) Blowing nose in open
(c) Staying away from people suffering from cold
(d) Sipping warm water
Answer:
(b) Blowing nose in open
Question 24.
Common cold is not cured by antibiotics because it is …………………
(a) caused by a virus
(b) caused by a Gram-positive bacterium
(c) caused by a Gram-negative bacterium
(d) not an infectious disease
Answer:
(a) caused by a virus
Question 25.
Motile zygote of Plasmodium occurs in …………………
(a) gut of female Anopheles
(b) salivary glands of Anopheles
(c) Human RBCs
(d) Human liver
Answer:
(a) gut of female Anopheles
Question 26.
Haemozoin is …………………
(a) a precursor of haemoglobin
(b) a toxin from Streptococcus
(c) a toxin from Plasmodium
(d) a toxin from Hemophilus
Answer:
(c) a toxin from Plasmodium
Question 27.
Vaccination against malaria is not possible because …………………
(a) they produce antibodies and antitoxins
(b) they do not produce antibodies and antitoxins
(c) antibodies resistant to vaccines are produced
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) they do not produce antibodies and antitoxins
Question 28.
The active form of Entamoeba histolytica feeds upon …………………
(a) blood only
(b) erythrocytes, mucosa and submucosa of colon
(c) mucosa and submucosa of colon only
(d) food in intestine
Answer:
(b) erythrocytes, mucosa and submucosa of colon
Question 29.
Eating unwashed and raw green leafy vegetables grown along the railway tracks in Mumbai may cause …………………
(a) malaria
(b) influenza
(c) amoebic colitis
(d) ringworm
Answer:
(c) amoebic colitis
Question 30.
Which method of water purification can terminate amoebae ?
(a) Chlorination
(b) Sedimentation
(c) Filtration
(d) Boiling
Answer:
(d) Boiling
Question 31.
Which of the following measures should be taken to control amoebic dysentery ?
(A) Using insecticidal sprays to kill flies.
(B) Not allowing stagnant water to be accumulated over a long time.
(C) To avoid eating uncovered food.
(D) Drinking only boiled water.
(E) Eating plenty of fruits.
(a) (A) (C) (D)
(b) (A) (B) (D)
(c) (B) (C) (E)
(d) (A) (B) (E)
Answer:
(a) (A) (C) (D)
![]()
Question 32.
Which of the following should be avoided for endemic spread of amoebiasis ?
(a) Cleaning bathroom taps and toilet seats with disinfectants.
(b) Washing hands and using hand sanitizers.
(c) Proper sewage disposal and treatment.
(d) Eating uncovered roadside food.
Answer:
(d) Eating uncovered roadside food.
Question 33.
Name the disease in which the genital organs are grossly affected due to infective helminth.
(a) Ascariasis
(b) Ring worm
(c) Scabies
(d) Filariasis
Answer:
(d) Filariasis
Question 34.
Find the odd organism:
(a) Wuchereria bancrofti
(b) Brugia malayi
(c) Brugia timori
(d) Ascaris lumbricoides
Answer:
(d) Ascaris lumhricoides
Question 35.
When is hydrocele formed in a man ?
(a) When testis are not functioning properly.
(b) When scrotum is infected with filarial worms.
(c) When testis are injured due to accident.
(d) When there is water accumulation in testis.
Answer:
(b) When scrotum is infected with filarial worms
Question 36.
Which medicine is used for eradicating microfilariae from endemic areas ?
(a) Diethyle carbamacine
(b) Mebendazole
(c) Albendazole
(d) Rimfampcin
Answer:
(a) Diethyle carbamacine
Question 37.
Which of the following fungi are causative organisms of ringworm ?
(a) Microsporum
(b) Candida
(c) Thrush
(d) Tinea pedis
Answer:
(a) Microsporum
Question 38.
On which material present on the outer skin surfaces of the human body does the fungus causing infections feed on ?
(a) Melanin
(b) Keratin
(c) Lignin
(d) Suberin
Answer:
(b) Keratin
Question 39.
Which of the following statements is correct ?
(a) Fungus grows well on dry skin.
(b) Fungus cannot survive on the outside of the hair shafts.
(c) Fungus thrives well on the warm and moist skin.
(d) Nails can never show fungal infections.
Answer:
(c) Fungus thrives well on the warm and moist skin.
Question 40.
Which of the following pair is viral diseases ?
(a) Common cold, AIDS
(b) Dysentery, Common cold
(c) Typhoid, Tuberculosis
(d) Ringworm, AIDS
Answer:
(a) Common cold, AIDS
Question 41.
Which one of the following glands is often referred in relation with AIDS ?
(a) Thymus
(b) Adrenal
(c) Thyroid
(d) Pancreas
Answer:
(a) Thymus
Question 42.
The first patient of AIDS was detected in India in …………………
(a) 1980
(b) 1986
(c) 1990
(d) 1996
Answer:
(b) 1986
Question 43.
Why is it said that for AIDS prevention is the only cure ?
(a) AIDS does not have any cure, once it is contracted.
(b) By prevention AIDS cannot be cured.
(c) AIDS can be cured by proper medication and vaccination.
(d) Only prevention helps as there is no cure for AIDS.
Answer:
(d) Only prevention helps as there is no cure for AIDS.
Question 44.
After a person is detected to be having AIDS by ELISA test, which is the next confirmatory test ?
(a) Western blot
(b) Southern blot
(c) PCR
(d) Northern blot
Answer:
(a) Western blot
Question 45.
What is full form of ELISA ?
(a) Enzyme Linked Inductive Assay
(b) Enzyme Linked Iron Sorbent Assay
(c) Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Question 46.
The possible ways of transmission of AIDS are …………………
(A) Intimate sexual contact
(B) Hugging and kissing
(C) Blood transfusion without properly checking it
(D) Eating from the same plate
(E) Sharing bed linen
(F) Transplacental infection from infected mother
(G) Sharing same tattoo gun and syringes
(a) (A), (C), (F), (G)
(b) (B), (D), (E), (G)
(c) (C), (D), (E), (F)
(d) (A), (B), (C), (D)
Answer:
(a) (A), (C), (F), (G)
Question 47.
Which one of the following statements is correct ?
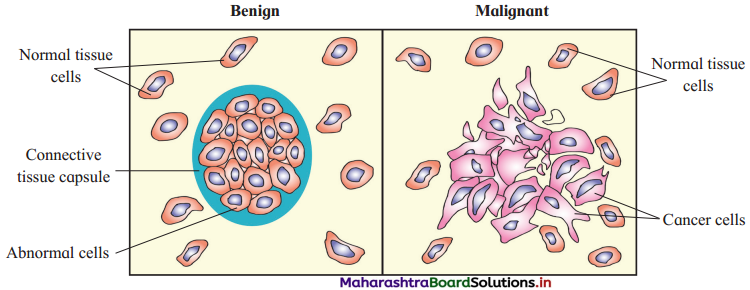
(a) Benign tumours show the property of metastasis.
(b) Heroin accelerates body functions.
(c) Malignant tumours may exhibit metastasis.
(d) Patients who have undergone surgery are given cannabinoids to relieve pain.
Answer:
(c) Malignant tumours may exhibit metastasis.
Question 48.
Heroin or smack is chemically …………………
(a) diclofenac
(b) diacetyl morphine
(c) benzodiazepine
(d) amphetamines
Answer:
(b) diacetyl morphine
Question 49.
Ecstasy is a drug that is used in most of the Rev parties which is chemically a derivative of …………………
(a) Barbiturates
(b) Amphetamines
(c) Catecholamine
(d) Morphine
Answer:
(b) Amphetamines
Question 50.
From which plant is charas obtained?
(a) Cannabis sativa
(b) Erythroxylum coca
(c) Papaver somniferum
(d) Atropa belladonna
Answer:
(a) Cannabis sativa
Question 51.
Opium is obtained from the latex of the unripe fruits of …………………
(a) Cannabis sativa
(b) Thea siensis
(c) Papaver somniferum
(d) Erythroxylon coca
Answer:
(c) Papaver somniferum
Question 52.
Use of Cannabis products results in …………………
(a) depressed brain activity and feeling of calmness
(b) suppressed brain function and relief of pain
(c) stimulation of nervous system, increased alertness and activity
(d) alteration in perception, thoughts and feelings
Answer:
(d) alteration in perception, thoughts and feelings
Question 53.
Marijuana, ganja and LSD are …………………
(a) narcotics
(b) stimulants
(c) hallucinogens
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) hallucinogens
Question 54.
What is the source of LSD ?
(a) Poppy seeds
(b) Datura plant
(c) Sugar
(d) Claviceps purpurea
Answer:
(d) Claviceps purpurea
Question 55.
Narcotics are …………………
(a) amphetamines and caffeine
(b) morphine and heroine
(c) LSD and cocaine
(d) barbiturates and benzodiazepine
Answer:
(b) morphine and heroine
Question 56.
Which is an incorrectly matched pair ?
(a) LSD – Ergot fungus
(b) Heroin – Opium
(c) Amphetamines – Depressant
(d) Benzodiazepine – Calmpose tablets
Answer:
(c) Amphetamines – Depressant
Question 57.
Choose the incorrect statement
(a) The excessive use of anabolic steroids cause severe acne.
(b) In both the sexes there is increased aggressiveness and mood swings, due to steroids.
(c) In females, anabolic steroids cause breast enlargement.
(d) In males, anabolic steroids cause enlargement of prostate gland.
Answer:
(c) In females, anabolic steroids cause breast enlargement.
Question 58.
Who are the first ones to note the danger signs of drug or alcohol abuse in the adolescents ?
(a) Alert parents and teachers
(b) Neighbours
(c) Relatives
(d) Doctors
Answer:
(a) Alert parents and teachers
Question 59.
Who can give professional help for the deaddiction?
(a) Highly qualified psychiatrist
(b) Parents
(c) Teachers
(d) Friends
Answer:
(a) Highly qualified psychiatrist
Match the columns
Question 1.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Metchnikoff | (i) ABO Blood group system |
| (b) Fleming | (ii) Concept of immunity |
| (c) Edward Jenner | (iii) Phagocytic cells |
| (d) Karl Lands teiner | (iv) Lysozyme |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Metchnikoff | (iii) Phagocytic cells |
| (b) Fleming | (iv) Lysozyme |
| (c) Edward Jenner | (ii) Concept of immunity |
| (d) Karl Lands teiner | (i) ABO Blood group system |
Question 2.
| Disease | Vector species |
| (a) Dengue | (i) Anopheles |
| (b) Malaria | (ii) Housefly |
| (c) Filaria | (iii) Culex |
| (d) Typhoid | (iv) Aedes |
Answer:
| Disease | Vector species |
| (a) Dengue | (iv) Aedes |
| (b) Malaria | (i) Anopheles |
| (c) Filaria | (iii) Culex |
| (d) Typhoid | (ii) Housefly |
Classify the following to form Column B as per the category given in Column A
Question 1.
Benzyl penicillin, Chloromycetin, Mebendazole, Levamisole, Pyrimethamine Ampicillin, Ty21a vaccine, Sulfadoxine.
| Column A (Disease) | Column B (Treatment) |
| (1) Pneumonia | ————– |
| (2) Malaria | ————– |
| (3) Ascariasis | ————– |
| (4) Typhoid | ————– |
Answer:
| Column A (Disease) | Column B (Treatment) |
| (1) Pneumonia | Benzyl penicillin, Ampicillin |
| (2) Malaria | Pyrimethamine, Sulfadoxine |
| (3) Ascariasis | Mebendazole, Levamisole |
| (4) Typhoid | Chloromycetin, Ty21a vaccine |
Question 2.
Lung cancer, Pituitary, Spleen, Skin cancer, Cancer of adipose tissue, lymph nodes, Adrenal, Bone tumour.
| Column (A Type of cancer) | Column B (Organs affected) |
| (1) Carcinoma | ————– |
| (2) Sarcoma | ————– |
| (3) Lymphoma | ————– |
| (4) Adenocarcinoma | ————– |
Answer:
| Column (A Type of cancer) | Column B (Organs affected) |
| (1) Carcinoma | Lung cancer, Skin cancer |
| (2) Sarcoma | Cancer of adipose tissue, Bone tumour |
| (3) Lymphoma | Spleen, Lymph nodes |
| (4) Adenocarcinoma | Pituitary, Adrenal |
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
By which process T-cells and B-cells are produced?
Answer:
T-cells and B-cells are produced from the stem cells called haemocytoblasts, in bone marrow of adults and in liver of the foetus, by the process of haematopoiesis and in the bone marrow in adult.
Question 2.
What is a hinge?
Answer:
Hinge is the region of Y-shaped structure, holding arms and stem of antibody where four polypeptide chains of antibody are held together by disulfide bonds (-s-s-) to form a ‘Y’-shaped structure.
Question 3.
What is epitope?
Answer:
Epitope is antigenic determinant, which is present on antigens.
![]()
Question 4.
What is paratope?
Answer:
Paratope is antigen binding site that is present on the antibodies.
Question 5.
Which antigen is present in Rh +ve person?
Answer:
Antigen D is present in Rh +ve person.
Question 6.
Give the role of flushing action of lachrymal secretions.
Answer:
The conjunctiva is freed from foreign particles by the flushing action of lachrymal secretions.
Question 7.
What happens when lachrymal secretion is absent in eyes?
Answer:
Eyes become susceptible to infection when lachrymal secretion is absent.
Question 8.
In tears which antibacterial substance is present?
Answer:
Lysozyme is the antibacterial substance present in the tears.
Question 9.
Which kind of immunity is provided by vaccination?
Answer:
Artificial acquired active and passive immunity is provided by vaccination.
Question 10.
Who was Edward Jenner?
Answer:
Edward Jenner was the British scientist who developed cowpox vaccine for the protection against small pox virus.
Question 11.
Mrunmayi is called universal blood acceptor. What is her blood group?
Answer:
Blood group of Mrunmayi is AB.
Question 12.
What are antigens?
Answer:
Different foreign substances that invade the body and are capable of stimulating an immune response are called antigens.
Question 13.
In which animal Rh factor was discovered at first?
Answer:
Rh factor was first discovered in Rhesus monkey for the first time.
Question 14.
What is elephantiasis?
Answer:
Elephantiasis is one of the symptoms of lymphatic filariasis, in which there is thickening of skin and underlying tissues due to presence of malarial parasite.
Question 15.
What is dermatophytosis ?
Answer:
Dermatophytosis is a clinical condition in which fungal infection of skin occur in humans, pets and cattle which is commonly called as ringworm.
Question 16.
What is sporozoite?
Answer:
Sporozoite is a developmental stage of Plasmodium produced by rupture of oocyst. Sporozoite can enter the bloodstream in human body and then infect hepatocytes or liver cells, where they multiply into merozoites.
Question 17.
Why does male mosquito not spread Malaria?
Answer:
Male mosquito feed only on plant sap and not blood of human beings; therefore it does not spread Malaria.
Question 18.
Where does Plasmodium reproduce asexually?
Answer:
Plasmodium reproduce asexually in the liver cells and red blood cells of infected human being.
Question 19.
Where does Plasmodium reproduce sexually?
Answer:
Plasmodium undergoes sexual reproduction by the process of fertilization and development in the intestine of mosquito.
Question 20.
Which fish can be used for mosquito control?
Answer:
Gambusia fish can be used for mosquito control.
Question 21.
What is arthralgia?
Answer:
Arthralgia means joint pains.
Question 22.
What do you mean by hepatomegaly?
Answer:
Hepatomegaly means enlargement of liver.
Question 23.
Which organism yields LSD?
Answer:
Ergot fungus, Claviceps purpurea yield LSD.
Question 24.
Enlist various types of barriers which prevent entry of foreign agents into the body.
Answer:
- Epithelial surface
- Antimicrobial substances in blood and tissues
- Cellular factors in innate immunity
- Fever
- Acute phase proteins (APPs).
Question 25.
Which is the gastro-intestinal disease by which 15% Indian population is affected?
Answer:
Amoebiasis or amoebic dysentery is the gastro-intestinal disease by which 15% Indian population is affected.
Question 26.
What are the anti-helminthic drugs which are used in treatment of Ascariasis?
Answer:
Anti-helminthic drugs like Piperazine, Mebendazole, Levamisole, Pyrantel are used against Ascaris lumbricoidies.
Question 27.
Which are the diseases that can be avoided by eradication of mosquitoes in your area?
Answer:
Malaria, dengue, chikungunya and filariasis or elephantiasis can be avoided by eradication of mosquitoes.
Define the following
Question 1.
Serology
Answer:
A branch of immunology which deals with the study of antigen-antibody interactions is called serology.
Question 2.
Hygiene
Answer:
Hygiene is the science of health, which aims at preserving, maintaining and improving the health of an individual or the community as a whole.
Question 3.
Disease
Answer:
Disease is a condition of disrupted or deranged functioning of one or more organs or systems of the body caused due to infection, detective diet or heredity.
Question 4.
Immune system
Answer:
The system which protects us from various infectious agents is called immune system.
Question 5.
Resistance
Answer:
Resistance is an ability to ward off damage or disease through our defence mechanism.
Question 6.
Immunity
Answer:
The immunity is defined as the general ability of a body to recognize and neutralize or destroy and eliminate foreign substances or resist a particular infection or disease.
Question 7.
Antibody
Answer:
The protective chemicals produced by immune cells in response to antigens is called antibodies.
Question 8.
Opsonisation
Answer:
The process of coating of bacteria to facilitate their subsequent phagocytosis by macrophages is called opsonisation.
Question 9.
Pathogen
Answer:
Pathogen are living agents such as viruses, ricketssia, bacteria, fungi, protozoans, helminth and certain insect larvae which are capable of causing diseases.
Question 10.
Parasite
Answer:
An organism that lives in or on another organism called host and takes its nourishment from it (host) is called parasite.
Question 11.
Pathogenicity
Answer:
The ability of an organism to enter a host and cause a disease is called pathogenicity.
Question 12.
Infectious disease
Answer:
The disease which is transmitted from infected person to another healthy person either directly or indirectly is called infectious disease or communicable disease.
Question 13.
Non-infectious disease
Answer:
The disease that cannot be transmitted from one infected person to another healthy person, either directly or indirectly is called non infectious or non-communicable disease.
Question 14.
Innate immunity
Answer:
Innate immunity is defined as the resistance to infections that an individual possesses due to his or her genetic make-up and thus it is inborn defence mechanism present naturally in the body.
Question 15.
Acquired immunity
Answer:
The resistance developed during lifetime is called acquired immunity.
Question 16.
APP proteins
Answer:
APP proteins or acute phase proteins are certain collection of plasma proteins which are suddenly increased by the infection caused after injury.
Question 17.
Incubation period
Answer:
Incubation period is the time interval from the invasion of a pathogen to the development of clinical manifestations or symptoms.
Name the following
Question 1.
Name the cell that produces lymphokines.
Answer:
Helper T-cells
Question 2.
Blood group systems in human beings.
Answer:
ABO, Rh, Duffy, Kidd, Lewis, P MNS, Bombay blood group.
![]()
Question 3.
Types of sarcoma.
Answer:
- Osteosarcoma (bone)
- Myosarcoma (muscle)
- Chondrosarcoma (cartilage)
- Liposarcoma (adipose tissue)
Question 4.
Therapies used for treatment of cancer.
Answer:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Supportive therapy
Question 5.
Name the term for the transmission of HIV from pregnant mother to foetus.
Answer:
Transplacental.
Question 6.
Factors that maintain good health.
Answer:
- Balanced diet
- Personal hygiene
- Regular exercise
- Right attitude of mind
- Good habits.
Question 7.
Two examples of ascaricides.
Answer:
Mebendazole and Albendazole, etc.
Question 8.
Two vaccines for typhoid.
Answer:
- Oral Ty21a
- Injectable Typhoid polysaccharide vaccine or Typhium vi/ Typherix.
Question 9.
Parasites causing lymphatic filariasis.
Answer:
- Wuchereria bancrojti
- Brugiamalayi
- Brugia timori.
Question 10.
Parasites causing Subcutaneous Filariasis.
Answer:
- Loa loa
- Mansonella spp.
Question 11.
Name the scientists who discovered AB blood group?
Answer:
Decastallo and Sturti
Distinguish between the following
Question 1.
Inborn immunity and acquired immunity.
Answer:
| Inborn Immunity | Acquired Immunity |
| 1. Inborn immunity or innate immunity is also called natural immunity. | 1. Acquired immunity is also called adaptive immunity. |
| 2. Innate immunity is present right from the birth. | 2. Acquired immunity is not present at birth, but is acquired during lifetime of the individual. |
| 3. Inborn immunity does not depend upon the previous exposure to a pathogen or foreign substance. | 3. Acquired immunity always depends upon the previous exposure to a pathogen or foreign substance. |
| 4. It is non-specific immunity as it can offer resistance to any pathogen. | 4. It is specific immunity as it can offer resistance only to a particular pathogen. |
| 5. Innate immunity consists of various types of barriers for defence against the pathogens. | 5. Acquired immunity consists of various types of cells which are able to produce antibodies. |
| 6. Inborn immunity shows immediate effect in the body. | 6. Acquired immunity requires several days to become activated. |
| 7. Inborn immunity is seen in all animals. | 7. Acquired immunity is seen only in vertebrates. |
| 8. Inborn immunity is genetic in nature and is heritable. | 8. Acquired immunity is non-genetic in nature and is non-heritable. |
Question 2.
Communicable and non-communicable diseases.
Answer:
| Communicable diseases | Non-communicable diseases |
| 1. Diseases transmitted from infected person to healthy person are called communicable or infectious diseases. | 1. Diseases that are not passed from one person to other are non-communicable or non-infectious diseases. |
| 2. Communicable diseases spread through pathogens. | 2. Non-communicable diseases do not spread through pathogens. |
| 3. Communicable diseases are not inherited from parental generation to offspring. | 3. Non-communicable diseases like cancer can be from parental generation to offspring. |
| 4. Vectors play the major role in spreading disease from one person to another. | 4. Caused due to allergy, illness, malnutrition or abnormalities in cell proliferation, changes in lifestyle, environment play a significant role. |
| 5. Treated by conventional methods using antibiotics and other drugs. | 5. Treated conservatively for a long time or surgically. |
| 6. Diseases are acute which develop suddenly due to infections. E.g. Pneumonia, Tuberculosis, AIDS, Typhoid, Cholera, Malaria. | 6. Diseases are chronic which develop and persist for a long time. E.g. Cancer, Rickets, Allergies, Kwashiorkor, Diabetes, Heart disease, etc. |
Question 3.
Ascariasis and Filariasis.
Answer:
| Ascariasis | Filariasis |
| 1. Only one species Ascaris lumbricoid.es cause ascariasis. | 1. There are many species of nematode that can cause filariasis. |
| 2. Ascaris causes the infection of alimentary canal. | 2. Wuchereria bancrofti causes the infection of lymphatic system. |
| 3. Ascaris does not cause swellings of upper and lower limbs. | 3. Filariasis cause swellings of extremities. |
| 4. Ascaris is caused due to faeco-oral transmission. | 4. Filariasis is caused due to vector transmission (Culex mosquito). |
| 5. Medicines for treatment of Ascariasis are Piperazine, Mebendazole, Levamisole, Pyrantel. | 5. Medicines for treatment of filariasis are diethyl- carbamazine citrate. |
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Despite constant exposure to variety of pathogens, why do most of us remain healthy?
Answer:
- All human beings are exposed to various foreign bodies, including infectious agents like bacteria, viruses, etc. which are called pathogens.
- But human body can resist almost all types of these pathogens.
- For this purpose, there is immune system which protects us from various infectious agents.
- There is resistance and prevention of the damage or disease, through our defence mechanisms.
- Thus, despite constant exposure to variety of pathogens, most of us remain healthy.
Question 2.
What are the unique features of acquired immunity?
Answer:
Following are the unique features of acquired immunity:
- Specificity : Production of specific antibody or T-lymphocyte against a particular antigen/ pathogen is called specificity.
- Diversity : Ability to recognize vast variety of diverse pathogens or foreign molecules by immunity is called diversity.
- Discrimination between self and non¬self : Acquired immunity can differentiate between own body cells (self) and foreign (non-self) molecules.
- Memory : The first immune response upon encounter of a specific foreign agent and its elimination is retained as a memory. This results in quicker and stronger immune response when the same pathogen is encountered again.
Question 3.
Describe the polypeptide chains seen in the structure of an antibody.
Answer:
- There are four polypeptide chains which make the antibody.
- There are two heavy or H-chains and two light or L-chains.
- Each chain has two distinct regions, the variable region and the constant region.
- Variable regions carry the antigen binding site or paratope.
- This part of antibody recognizes and bindsto the specific antigen to form an antigen- antibody complex.
Question 4.
Which are the antimicrobial substances in blood and tissues?
Answer:
- There are more than 30 serum proteins, circulating in the blood in an inactive state, which forms the complement system.
- ‘Complement cascade’ is activated by presence of pathogens and thus they eliminate pathogens.
- Cells which are affected by viruses secrete interferons which are a class of cytokines. These soluble proteins attack the pathogens.
- Some leucocytes stimulate other cells to protect themselves from viral infection.
Question 5.
Is developing fever a bad sign or a good action? Explain.
Answer:
- Fever is the innate immunity mechanism. When there is fever, the body rises.
- This is in response to infection in a natural way.
- Developing fever is a natural defence mechanism.
- Fever helps to accelerate the physiological processes by which the invading pathogens are destroyed.
- Fever stimulates the production of interferon and helps in recovery from viral infections.
- Taking all these points into consideration, getting fever is a good action that innate immunity is working properly, however, entry of pathogen in the body causing illness is a bad sign.
Question 6.
With the help of a chart explain the compatibility of human blood groups.
Answer:
Different types of blood groups:
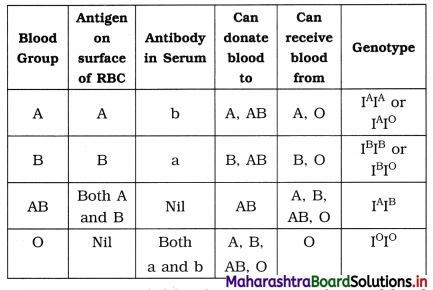
- Person with blood group A can donate blood to persons having blood group A or AB and receive blood from A or O.
- Person with blood group B can donate blood to persons having blood group B or AB and receive blood from B or O.
- Person with blood group O can donate blood to all the persons having blood group either A, B, AB or O, because blood group O is universal donor. But can receive blood only from person having blood group O.
- Person with blood group AB can donate blood to only AB but can receive blood from all the persons having blood group either, A, B, O or AB because AB is universal recipient.
Question 7.
The blood group of Krutika is O Rh +ve. What would be the possible blood groups of her parents?
Answer:
- Krutika has O blood group, therefore her genotype is I°I°.
- Her parents can be of following combinations.
- They may be having blood group A or B with heterozygous genotype respectively, i.e. IAI° and IBI°. If both of them are heterozygous, having either A or B blood group, Krutika can be of O type.
- Other possibility is both the parents have to be O.
- For being Rh positive, her at least one parent should be Rh positive. Rh negative is a recessive phenotype and hence needs double dose of these genes.
Question 8.
Can a person with blood group O Rh+ve donate blood to a patient with blood group O Rh-ve? Why?
Answer:
No. blood group O may be common to both donor and recipient but their Rh factor is different. A person with RH+ve blood cannot donate to a patient with Rh-ve blood group. In Rh+ve blood there is antigen D. This antigen D when enters the body of recipient, there are production of anti-RH antibodies in his or her body. These anitibodies with cause agglutination of the Rh +ve blood which will be given to the patient. This agglutination will cause clots inside the vital organ of the recipient and the death may follow.
Question 9.
Why do we suffer from common cold repetitively in our life, but other viral diseases like Influenza or Small pox only once?
Answer:
Influenza infection causes production of antibodies in our body, once the virus attacks us. Therefore, second encounter with the virus may not cause effect. But in case of common cold, large number of different virus families are responsible for developing infection of common cold. Many a times different allergens are also inducing agents for common cold. Thus we may suffer from common cold again and again.
Question 10.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Answer:
- Main symptoms of infectious pneumonia are cough producing greenish or yellow sputum or phlegm and a high fever with chills.
- Shortness of breath, stabbing chest pain, coughing up blood, headaches, sweaty and clammy skin, loss of appetite, fatigue, blueness of the skin, nausea, vomiting, mood swings and joint pains or muscle aches are some other symptoms.
Question 11.
What is the diagnosis and treatment of filariasis? How can we control this disease ?
Answer:
I. Diagnosis and Treatment : For the patient, diethyl-carbamazine citrate is the drug used for twice a day for three weeks. Thereafter for five days every six months the same treatment is repeated. This becomes effective against filarial worms.
II. Prevention and Control:
- Mosquito eradication should be done for controlling filariasis.
- In the areas with mosquitoes, avoid mosquito bite by using mosquito nets and insect repellents.
Question 12.
What are the signs and symptoms of filariasis?
Answer:
Signs and symptoms of filariasis:
- As the lymphatic drainage does not take place, there is oedema with thickening of skin and underlying tissue.
- Extremities like legs, arms, breasts, scrotum, etc. are affected by nematode causing lymphatic filariasis, i. e. Wuchereria bancrofti.
- Lymph vessels and lymph nodes are enlarged and swollen.
- Elephantiasis is seen in which limbs are swollen like legs of elephant.
- Lymphoedema, i.e. accumulation of lymph fluid is seen in tissue causing swelling.
- Hydrocele condition develops in which testis are enlarged due to accumulation of lymphatic fluid in testis.
Question 13.
What are the various ways in which mosquitoes can be eradicated from any area?
Answer:
Eradication of mosquitoes:
- Removal of all stagnant water pools around the houses.
- If such water bodies are there, they should be sprayed with insecticides.
- But better option which is eco-friendly is releasing mosquito eating fish like Gambusia or Tilapia.
- Use of mosquito repellent plants like Citronella. Use of coils and repellent creams.
- Fumigation of the area to kill the mosquito.
- Aedes sps. breed in man-made containers, especially plastic and cement tanks. Care should therefore be taken to dispose such containers properly. Water should not be accumulated in them.
Question 14.
What precautions will you take if you are travelling in an area which has lot of mosquitoes?
Answer:
- Avoiding areas where mosquitoes are in more concentration.
- Carrying mosquito repellent creams or coils.
- Use of mosquito nets and other fumigation devices.
- Wearing full clothing in light colours.
- Staying indoors when mosquitoes are swarming, especially in the evening.
- Taking anti-malarial pills as a precautionary measure.
![]()
Question 15.
Deaddiction may be difficult but not impossible. Collect information about NGOs, working in the field of deaddiction.
Answer:
There are many NGOs that work in the field of deaddiction. In different cities, there are different organizations. Even the central Government has started helpline number 1800-11-0031 for those drug and alcohol addicts who need help to come out of these addictions. Muktangan in Pune is one such reputed organization which does the great work in the field of deaddiction.
Question 16.
What are the most common warning signs of drug and alcohol abuse among youth ?
Answer:
The most warning signs of addictions are as follows:
- Drop in academic performance, absenteeism from school or college.
- No interest in personal hygiene and hobbies.
- Withdrawal from the society, increased tendency of isolation and depression.
- Aggressive and rebellious behaviour resulting into strained relationships with family and friends.
- Fatigue and change in sleeping and eating habits.
- Fluctuations in weight, appetite, deteriorating health, etc.
Question 17.
What are the preventive measures for malaria?
Answer:
Preventive measures of malaria :
- Transmission of malarial parasite can be reduced by preventing mosquito bites. Therefore, mosquitoes should be controlled or totally eradicated.
- This can be done by using of mosquito nets and insect repellents.
- Mosquito control measures such as spraying insecticides inside houses and draining stagnant water where mosquitoes lay their eggs.
- The mosquito larvae can be eradicated by releasing Gambusia fish which can feed upon these larvae.
- Vaccine against malaria is also under preparation.
Question 18.
How does Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebiosis ?
Answer:
- Amoebiosis is spread through ingestion of the cyst form of Entamoeba histolytica. This is a commensal organism.
- Cyst is a semi-dormant and hardy structure found in faeces of infected person.
- Non-encysted amoebae are called trophozoites. The trophozoites die quickly after leaving the body but may also be present in faeces.
- Trophozoites are rarely the source of new infections.
- The infection may remain asymptomatic for many days as Amoeba can remain latent in the gastrointestinal tract.
Question 19.
Describe the signs and symptoms of amoebiasis.
Answer:
Amoebiasis shows following common symptoms:
- Diarrhoea, flatulence, stool with mucus and abdominal pains (cramps) are common.
- Stool sticky with mucus and blood.
- Amoebae form cysts in the liver, in such case there is hepatomegaly, i.e. enlargement of liver.
- Liver shows amoebic liver abscess accompanied with fever and pain in right side of the abdomen.
Question 20.
How can amoebiasis be prevented?
Answer:
Prevention of amoebiasis is to be done at two levels, viz. at home and at endemic level.
1. Prevention of the spread of amoebiasis at the home level:
- Washing hands with soap and water after using the toilet or changing a baby’s diaper and before handling and eating food.
- Cleaning bathrooms and toilets properly with germicides.
- Avoiding raw vegetables when in endemic areas where they are grown in soil fertilized by human faeces.
- Boiling and purifying the drinking water.
2. Prevention of the spread of amoebiasis at endemic level:
- Avoiding consumption of street foods especially in public places.
- Following good sanitary practice, as well as using proper sewage disposal or treatment.
- E. histolytica cysts are usually resistant to chlorination; therefore sedimentation and filtration of water supplies are necessary to reduce the incidence of infection.
- Avoiding shared towels or face washers.
Question 21.
Describe the symptoms of ascariasis.
Answer:
- After infection by Ascaris lumbricoides, there is appearance of eggs in stools in 60 – 70 days.
- In larval ascariasis, symptoms are seen in 4-16 days after infection.
- The final symptoms are gastrointestinal discomfort, colic and vomiting, fever and appearance of live worms in faeces.
- Some patients may have pulmonary symptoms. Inflammation of alveolar walls is seen. This is known as pneumonitis.
- Some may show neurological disorders during migration of the larvae.
- Loss of appetite which reflects in weight loss.
- A bolus of worms may obstruct the intestine.
- Larvae that migrate may also cause eosinophilia, i.e. increase in number of eosinophils.
Question 22.
What are the preventive measures against ascariasis?
Answer:
- Prevention of ascariasis can be done by adopting the following measures :
- Use of proper toilet facilities.
- Safe disposal of excreta.
- Protection of food from dirt and soil.
- Washing of vegetables before cooking and avoiding eating raw, unwashed vegetables and fruits.
- Hand washing and use of safe food. Observing personal hygiene.
- Use of pharmaceutical drugs such as Mebendazole and Albendazole can kill Ascaris.
Question 23.
Discuss the clinical manifestation of AIDS.
Answer:
There are four stages of clinical manifestations or symptoms of AIDS.
- Stage I : This is initial infection with the virus and formation of antibodies, usually 2-8 weeks after initial infection.
- Stage II : In this stage the person is asymptomatic carrier. Incubation takes place with a period ranging for 6 months to 10 years.
- Stage III : This is called AIDS related complex (ARC). In this stage, one or more of the following clinical signs are seen. E.g. Recurrent fever for longer than one month, fatigue, unexplained diarrhoea, night sweats, shortness of breath, loss of more than 10 per cent body weight, etc.
- Stage IV : This is the end stage in which patient shows full blown AIDS. Thus it is called the end stage of HIV infection. Life threatening opportunistic infections (like pneumonia, tuberculosis, Kaposi sarcoma, etc.) are easily caught during this period.
Question 24.
Through which modes HIV infection does not spread?
Answer:
- HIV does not spread through casual contact such as hugging, etc.
- Insect bite such as mosquito bites does not transmit HIV.
- Participation in sports is not the mode by which HIV transmits.
- Contact between articles used by AIDS patient, a hand shake with him or her does not transmit HIV
- HIV infections do not occur through swimming pool or by sharing clothes, utensils, etc.
Question 25.
Write about laboratory diagnosis and treatment of AIDS.
Answer:
I. Laboratory diagnosis :
- There are two tests for diagnosis of AIDS.
- First test is ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) which is used to detect the HIV antibodies.
- The second confirmatory test is Western Blot, which is used to weed out any false positive results. It is a highly specific test.
- It is based on detecting specific antibody to viral core protein and envelope glycoprotein.
II. Treatment of AIDS:
- AIDS cannot be cured.
- Antiretroviral drugs are used to reduce the viral load and prolong the life of HIV patient. E.g. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) uses drugs such as TDF (tenofovir), EFV (Efavirenz), Lamivudine (3TC), etc.
Question 26.
Describe the structure of HIV with a suitable diagram.
Answer:
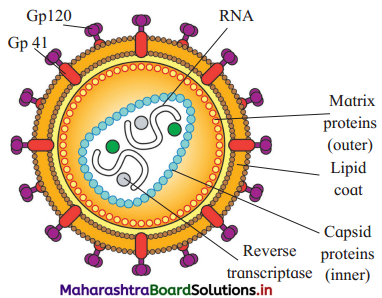
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus or HIV is spherical and 100 to 140 nm in diameter.
- It has centrally located two ss RNA molecules along with reverse transcriptase enzymes.
- There are coverings of two layers of proteins. The outer layer formed by matrix protein (pi7) while in inner layer is of capsid protein (p24).
- An additional layer of lipids is seen over the matrix protein layers. This layer is impregnated with glycoprotein GP120 and GP41.
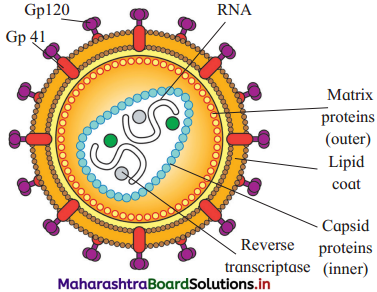
Question 27.
What are the modes of transmission of HIV or AIDS?
Answer:
The transmission of HIV occurs through following routes:
- Sexual relations, mainly unsafe sexual contact including oral, vaginal and anal sex.
- Through blood and blood products either by blood transfusions or sharing needles and syringes.
- Transplacental From pregnant mother to her foetus through placenta. Nursing mother can also transmit HIV to her baby through lactation.
- Spreading the virus is very rare in case of accidental needle injury, artificial insemination with infected donated semen and transplantation with infected organs.
- HIV is seen in urine, tears, saliva, breast milk and vaginal secretions but unless these body fluids enter the injuries and wounds, transmission is not easy.
Question 28.
What are the measures of prevention and control of AIDS ?
Answer:
- Preventive measures : AIDS has no cure, hence prevention is the best choice. The
following steps help in preventing this dreadful disease. - High risk group people should be educated about HIV transmission. They should never donate blood.
- Use of disposable needles and syringes should be done with proper disposal.
- Risky sexual habits should be avoided.
- Tooth brushes, razors, other articles that can become contaminated with blood should not be shared.
- Blood should be screened before receiving it.
- Routine screening of blood and semen donors, organ donors (kidney, liver, lung, cornea), and patients undergoing haemodialysis must be done.
- Pregnant women or those women who are contemplating pregnancy should be regularly screened.
Question 29.
Explain the ill-effects of opioids and cannabinoids on health.
OR
What are harmful effects of drug abuse?
Answer:
- Opioids bind to specific opioid receptors which are present in central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. Some opioids e.g. heroin act like depressants and slow down all the body functions.
- Cannabinoids have the capacity to interact with receptors present in the brain. Inhalation or ingestion of cannabinoids such as marijuana, hashish, charas and ganja have adverse effect on cardiovascular system.
- Cannabinoid like LSD causes hallucinations.
- All these substances are addictive and hence cause adverse effects on the body and health.
Question 30.
Give the adverse effects of opioids, cannabinoids and morphine on human health.
Answer:
1. Opioids:
- Opioids bind to specific opioid receptors present in the central nervous system and in gastrointestinal tract.
- They are depressants and slow down the body functions.
2. Cannabinoids:
- Cannabinoids interact with receptors in the brain.
- They affect cardiovascular system of the body.
3. Morphine:
- Morphine is an effective sedative and pain killer when used for medicinal purpose.
- When abused it affects physical, physiological and psychological functions.
Give reasons
Question 1.
Vaccines are safe.
Answer:
During their manufacture, vaccines are rigorously tested. Many rounds of study, examination and research are carried out before they are used for general public. Extensive research and evidences are gathered to check their safety. Sometimes, some vaccines produce side effects but these are rare and mild. Hence vaccines are considered to be safe.
Question 2.
Innate immunity is also known as non-specific immunity.
Answer:
Innate immunity is non-specific because it does not depend on previous exposure to foreign substances. It is inborn capacity of the body to resist the pathogen that causes the disease. It is natural immunity and hence it remains non-specific, trying to protect the body in case of any invasion of foreign body.
Question 3.
Vaccination is important for preventing pneumonia.
Answer:
Vaccinations for pneumonia are available against Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. If given earlier in life, they reduce the chances of catching pneumococcal infections. The deaths can be prevented which are common due to lung infections. Since it is a common and chronic j disease for all age groups, for the prevention one must take vaccination.
![]()
Question 4.
Common cold is the most frequent ! infectious disease in humans.
Answer:
Common cold is caused by virus which is abundantly present in congested city environments. The upper respiratory tract is infected due to these rhinoviruses and corona viruses. Average adult contracts such infections 2 to 4 times in a year while children capture it 6 to 12 times in a year. Therefore, it is said to be the most frequent infectious disease of human beings.
Question 5.
Typhoid is food and water-borne disease.
Answer:
Typhoid is caused due to Salmonella typhi which isa Gram-negative bacterium, transmitted from a patient or carrier to another healthy person through contaminated food or water. Flying insects, mostly houseflies transmit the bacteria from faeces to the food. Poor hygienic habits and improper public sanitation system spreads typhoid. Therefore, it is said to be food and water-borne disease.
Question 6.
Malignant tumour is more dangerous than benign tumour.
Answer:
Malignant tumour cells can show metastasis and hence can spread far and wide in the body, affecting other healthy cells and tissues. They are difficult to cure by any therapy as one does not know exact location of the cancerous cells. They also produce variety of symptoms depending on their i location. On the contrary, benign tumours can be treated surgically. Since they are covered by a cyst like membrane, the cancerous cells do not spread from them. Thus malignant tumour can be lethal as against the benign tumour.
Question 7.
Prevention is better than cure for AIDS.
Answer:
Till this time, there is no preventive vaccination for AIDS. There is also no cure for AIDS. The medicines are also costly and may not give complete cure. The only way to remain away from AIDS is the complete awareness about it. Thus it should be prevented by not allowing HIV to enter our body. Once HIV finds the entrance, the cure is impossible. Therefore, it is said that prevention is better them cure for AIDS.
Write short notes
Question 1.
Cellular factors in innate immunity.
Answer:
- Phagocytic cells ingest and destroy the pathogens.
- This is natural defence against the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms and other foreign particles in blood and tissues.
- Phagocytic cells are of two types, viz. microphages and macrophages. They can remove foreign particles that enter the body.
- Natural killer (NK) cells is a class of lymphocytes which carry out important and non-specific defence against viral infections and tumours.
Question 2.
Acute phase proteins (APPs).
Answer:
- Acute phase proteins are involved in innate immune mechanism.
- When there is an infection or injury, it leads to a sudden increase in concentration of certain plasma proteins, which are called acute phase proteins or APPs.
- These include C Reactive Protein (CRP), Mannose binding protein, Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein, Serum Amyloid P etc.
- APPs enhance host resistance, prevent tissue injury and promote repair of inflammatory lesions.
Question 3.
Rh factor.
Answer:
Rh factor:
- Rh factor is the term adapted from Rhesus monkey.
- In rhesus monkey, there is antigen D on the surface of their RBCs.
- Landsteiner and Wiener discovered this antigen and termed it as Rh factor.
- Persons having Rh factor or D antigen are called Rh positive while those lacking D antigen or Rh factor are called Rh negative.
Question 4.
Erythroblastosis foetalis.
Answer:
- Erythroblastosis foetalis is condition in which there is destruction of the erythrocytes of the foetus. It is the haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
- This is caused in foetus, if mother is Rh -ve and father is Rh +ve. Rh +ve is the dominant allele, the foetus becomes Rh +ve, when its father is RH +ve.
- Rh +ve blood groups have D antigen which induces a strong immunogenic response when introduced into Rh -ve individuals.
- During foetal life, there is connection between mother and foetus through placenta, therefore Rh +ve antigen D from the foetus enters maternal circulation.
- This triggers formation of anti-Rh antibodies in mother. Subsequently Rh+ve foetus receives anti-Rh antibodies produced by mother.
- This causes agglutination reaction resulting into haemolysis in foetus. In order to prevent HDN, Rh -ve mother is injected with the anti-Rh antibody during all her pregnancies if her husband is Rh +ve.
Question 5.
Common cold.
Answer:
- The common cold (nasopharyngitis or rhinopharyngitis) is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory system. The causative organisms are rhinoviruses and coronaviruses.
- Symptoms include cough, sore throat, runny nose and fever.
- There is no known treatment, however, symptoms usually resolve spontaneously in 7 to 10 days.
- The best prevention for the common cold is to stay away from infected people and places where infected individuals have been.
- Hand washing with plain soap and water is recommended. Also alcohol-based hand sanitizers provide very little protection.
Question 6.
Life cycle of Plasmodium.
Answer:
- Anopheles Female mosquito which is a carrier carries sporozoites. When it bites the human, these sporozoites enter human circulation.
- Sporozoites undergo asexual reproduction through fission or schizogony in the liver cells or erythrocytes of the human.
- It forms merozoites. The cells formed within erythrocytes function as gametocytes. They undergo gamogony.
- Upon biting such person, the gametocytes enter into female Anopheles, fertilization occurs in its gut.
- Diploid zygote transforms into oocyst. Oocyst forms large number of haploid sporozoites through meiosis (sporogony).
- Sporozoites migrate to salivary glands and are ready to infect new human host.
- Again Sporozoite → Merozoite → Trophozoite → Schizont sequence is carried on for plasmodial stages in human body.
- The sexual life cycle of Plasmodium occurs in mosquito body which acts as a vector. While its asexual phase takes place in human body.
Question 7.
Pneumonia.
Answer:
- Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of alveoli in the lungs causing formation of fluid in the lungs. This condition is called consolidation and exudation.
- Causes of pneumonia are infection due to bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites, chemical burns or physical injury to the lungs.
- Influenza virus, adenovirus, para influenza and Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) are some viruses that can cause pneumonia. Bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae and fungal pathogens e.g. Pneumocystis jirovecii and Pneumocystis carinii can also spread infection of pneumonia. Chemical burns of physical injury to lungs also cause similar infection.
- Main symptoms of infectious pneumonia are cough producing greenish or yellow sputum or phlegm and a high fever with chills.
- Shortness of breath or dyspnea, stabbing chest pain, coughing up blood, headaches, sweaty and clammy skin, loss of appetite, fatigue, blueness of the skin, nausea, vomiting, mood swings and joint pains or muscle aches are some other symptoms.
- Preventive vaccination against pneumonia is available. Medicines such as Benzyl penicillin, Ampicillin and Chloramphenicol are effective to prevent pneumonia.
Question 8.
Ringworm.
Answer:
- Ringworm or Dermatophytosis is a clinical condition caused by Trichophyton and Microsporum fungal infection of the skin. This infection is seen in humans and pets.
- Dermatophytes are the fungi that feed on keratin. Keratin is the material found in the outer layer of skin, hair and nails.
- These fungi attack various parts of the body. Infections on the body forms enlarged raised red rings. These patches have intense itching. Infection on the skin of the feet may cause athlete’s foot and jock itch.
- When the nails are infected it causes onychomycosis. During this the nails thicken, discolour and finally crumble and fall off.
- Prevention of ringworm infection is to be done by avoiding sharing of clothing, sports equipment, towels or sheets. Clothes should be washed in hot water with fungicidal soap after suspected exposure to ringworm. One should not walk barefoot but use appropriate footwear.
- Diagnosis of ringworm is done by physical examination and treatment is done with uses drugs like nystatin, fluconazole, itraconazole, etc.
Question 9.
Dengue.
Answer:
- Dengue is a viral disease causing high fever. It is a painful, debilitating vector-borne disease.
- There are four closely related dengue viruses that cause infection.
- Vector of Dengue virus is female Aedes mosquito. The mosquito takes up the dengue virus when it sucks blood of a person suffering from dengue.
- The spread of dengue is not directly from one person to another person.
Question 10.
Performance enhancers.
Answer:
- Performance enhancers are certain drugs used by sportspersons to enhance their performance during competitions.
- Narcotic analgesics, anabolic steroids, diuretics and certain hormones are misused by such sportspersons to increase muscle strength and bulk. It also promotes aggressiveness and improve overall performance.
- Use of anabolic steroids cause side effects.
- Females show masculinization, increased aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, abnormal menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth on the face and body, enlargement of clitoris, deepening of voice.
- Males show acne, increased aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, and reduction of size of the testicles, decreased sperm production, kidney and liver dysfunction, breast enlargement, premature baldness, enlargement of the prostate gland.
- These effects may be permanent with prolonged use. Using such drugs is illegal and punishable.
Chart Based Questions
Question 1.
Complete the chart of ABO blood group system and answer the questions given below:
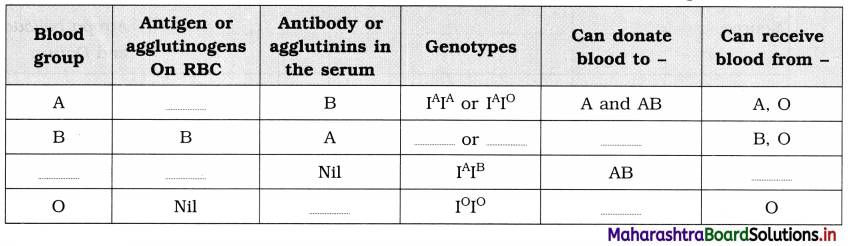
Questions:
(i) Which blood group from the above table is called universal acceptor?
(ii) Which blood group from the above table is called universal donor?
Answer:
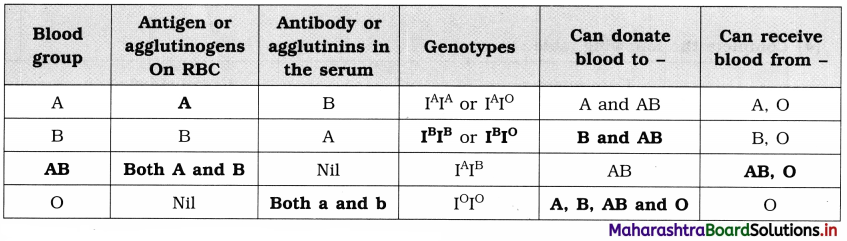
(i) Blood group AB is called universal acceptor.
(ii) Blood group O is called universal donor.
Question 2.
Complete the table
| Plasmodium species | Incubation period | Pattern of fever |
| ———— | ————– | High fever after 48 hours. |
| ————– | 28 days | ————– |
| ————– | 17 days | ————- |
| ———— | ————- | High fever at irregular intervals between 22 to 48 hours. |
Answer:
| Plasmodium species | Incubation period | Pattern of fever |
| P. vivax | 14 days | High fever after 48 hours. |
| P. malariae | 28 days | High fever after 72 hours interval |
| P. ovale | 17 days | High fever after 48 hours interval |
| P. falciparum | 12 days | High fever at irregular intervals between 22 to 48 hours. |
Question 3.
Complete the following table
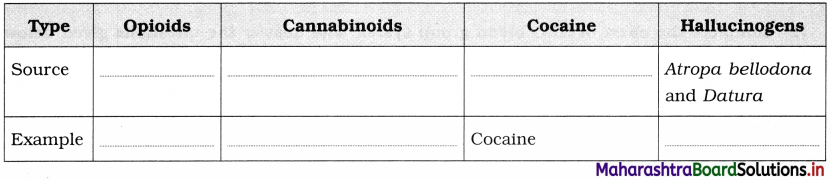
Answer:
Question 4.
Complete the following table:
| Carcinogen | Organ affected |
| N-nitrosodimethlene | ————– |
| Aflatoxin | ———- |
| ————– | Vagina |
| ————– | Urinary bladder |
| ————– | Prostate |
| ————– | Skin and lungs |
Answer:
| Carcinogen | Organ affected |
| N-nitrosodimethlene | Lungs |
| Aflatoxin | Liver |
| Diethylstilboestrol | Vagina |
| 2-naphthylamine and 4-aminobiphenyl | Urinary bladder |
| Cadmium oxide | Prostate |
| Soot, coal tar (2-4 benzopyrene) | Skin and lungs |
Diagram Based Questions
Question 1.
Label the given diagram
Img 7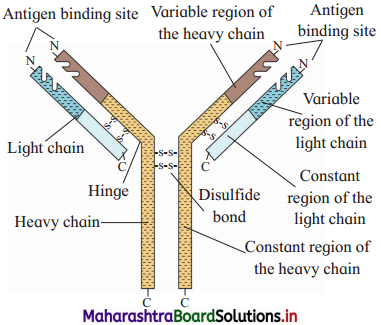
Answer:
- Antigen binding site.
- Variable region of heavy chain
- Varible region of light chain
- Constant region of light chain
- Constant region of heavy chain
- Disulphide bond
- Hinge
- Light chain
- Heavy chain
Question 2.
Observe the given diagram and answer the following questions:
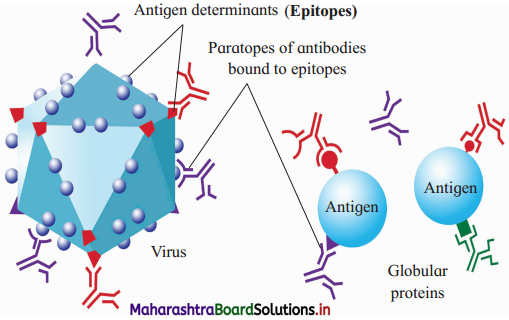
(1) What is I and II in the above diagram?
Answer:
I is a virus which is trying to cause infection, II are two antigen molecules which are trying to attack the virus.
(2) What structures are responsible for antigen and antibody complex? Identify them in the above diagram.
Answer:
(a) is epitope which is antigen determinant and
(b) is a paratope which is part of the antibody. Epitope and paratope are specific to each other and hence they form a complex.
(3) What is the study of antigen-antibody interactions called?
Answer:
The study of antigen-antibody interactions is called serology.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks after observing the diagram.
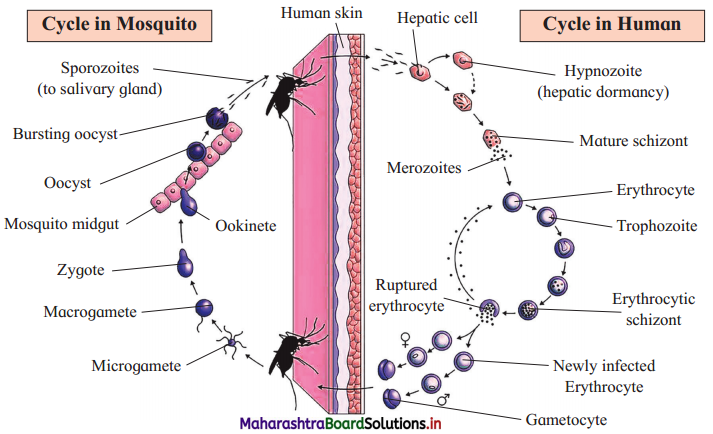
On the right side of the diagram, the stages of plasmodium are passed in the body of ……………….. Whereas on the left side of the diagram, those take place in the body of ………………, ………………. is the stage that is dormant in the liver of human host. From this ………………… and then ………………… is the stage in the erythrocytes, which rupture and gives rise to …………….. Microgamete and macrogamete fuse with each other to form …………………… which later gives rise to ookinete which forms ………………… This enters the salivary glands of mosquito …………………. phase of Plasmodium occurs in mosquito body, whereas …………………… phase is in human body.
Answer:
On the right side of the diagram, the stages of plasmodium are passed in the body of human. Whereas on the left side of the diagram, those take place in the body of mosquito. Hypnozoite is the stage that is dormant in the liver of human host. From this schizont and then merozoites Trophozoite is the stage in the erythrocytes, which rupture and gives rise to gamerocyte. Microgamete and macrogamete fuse with each other to form zygote which later gives rise to ookinete which forms sporozoites. This enters the salivary glands of mosquito. Sexual phase of Plasmodium occurs in mosquito body, whereas asexual phase is in human body.
Question 4.
Observe the given diagram and answer the following questions
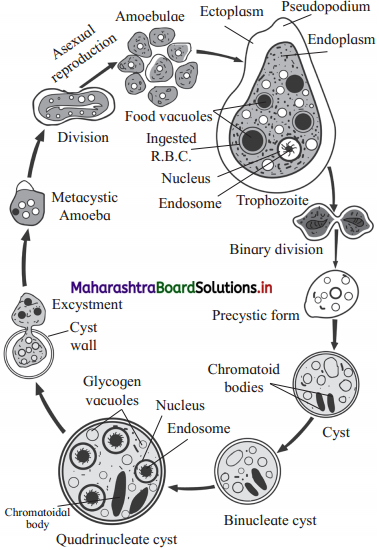
(1) Enlist the stages of Entamoeba histolytica you see in the above diagram.
Answer:
Trophozoite, pre-cystic form, cyst, binucleate cyst, quadrinucleate cyst, Metacycstic amoeba, amoebulae are the different stage of Entamoeba histolytica that are seen in the above diagram.
(2) Where are these stages passed?
Answer:
These stages are passed in the lumen of intestine of the host human being.
(3) How does Entamoeba come out of the body of the host?
Answer:
Encysted Entamoeba pass out with the faecal matter of the host.
![]()
Question 5.
Observe the given diagram and answer the following questions:
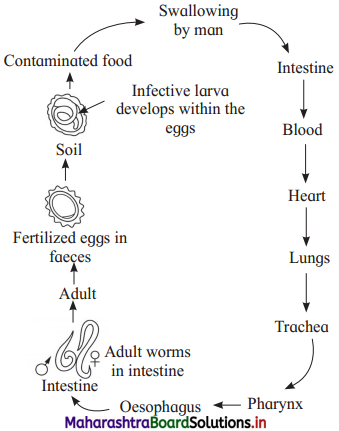
(1) In life cycle of Ascaris at what stage do they enter the human body?
Answer:
When there is development of infective larva inside the egg of Ascaris, it enters the human body.
(2) How do they enter the human body and through which organ do they enter?
Answer:
Ascaris eggs are deposited in the faeces. They mix in the soil, if faeces is exposed in open. From there, it can enter into nearby water body or it may contaminate vegetables or other food stuffs. Such unhygienic food or unclean hands pass these eggs in the body of human through the mouth.
(3) What are the vital organs affected by the Ascaris during its development within the body of host human ?
Answer:
Ascaris can affect trachea, lungs, heart, brain and eyes too.
(4) In which organ do they copulate and produce fertilized eggs?
Answer:
Adult male and female copulate in the intestine of the host human.
Question 6.
Observe the given diagram and answer the following questions:
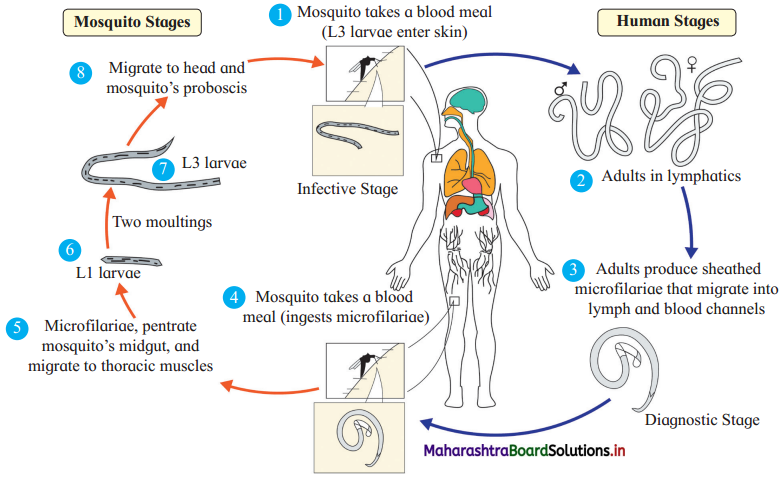
(1) In which host stage II is completed?
Answer:
Stage II is completed in human.
(2) What happens in step 1 and step 2?
Answer:
Humans are infected at step 1 when mosquito bites human and larvae enter blood stream. In step 2 adult Wuchereria worms are formed in lymphatics.
(3) Describe the events in step 3.
Answer:
Mosquito carries the blood as it bites the human in step 4 and ingests microfilariae in human blood. Later the microfilariae start growing in the midgut of mosquito.
(4) In which host stage I is completed?
Answer:
Stage I is completed in mosquito.
Question 7.
Sketch and label the diagram of pathogen that causes typhoid.
Answer:
Pathogen of typhoid is Salmonella typhi.
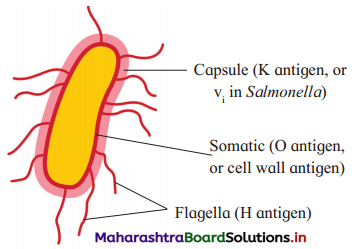
Question 8.
Sketch and label disease causing agents of pneumonia.
Answer:
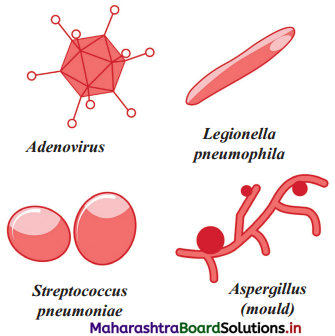
Question 9.
Sketch and label benign and malignant tumours.
Answer:
Question 10.
Sketch and label structure of HIV.
Answer:
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Describe different ways in which epithelial surface offers the innate immunity.
Answer:
- Skin and mucous covering, when intact protects the body against the invasion by pathogens. The healthy skin has bactericidal activity due to the salts present in drying sweat.
- Sebaceous glands in the skin produce secretions and long chain of fatty acids. These are bactericidal and fungicidal.
- Respiratory tract is provided with mucosa which prevents entry of microorganisms to a large extent.
- The inhaled particles are arrested through hair in the nasal passage. The particles that pass beyond nasal passage are caught by mucus lining the epithelium. They are swept back to pharynx. Then they are either swallowed or coughed out.
- The cough reflex is an important defence mechanism of respiratory tract.
- There is saliva in the mouth which has inhibitory effect on microorganisms. Gastric secretions has acidity and hence microorganisms are destroyed in stomach.
- The flushing action of urine eliminates bacteria from the urethra. Semen too has antibacterial substances, e.g. Spermine and zinc.
Question 2.
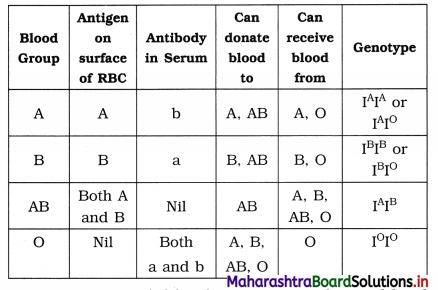
Explain ABO blood group system in human being with a suitable chart.
Answer:
- In ABO system, the blood groups are determined by the antigen present on the surface of red blood cells.
- The blood groups are of four types, viz. A. B, AB and O.
- In person with blood group A there is antigen ‘A’ on the surface of their red blood cells (RBCs) and antibodies ‘b’ in their plasma.
- In person with blood group B there is antigen ‘B’ on the surface of their red blood cells (RBCs) and antibodies ‘a’ in their plasma.
- In person with blood group AB there are both antigens ‘A’ and ‘B’ on the surface of their RBCs and no antibodies in their plasma.
- In person with blood group ‘O’ there are no antigens ‘A’ and ‘B’ on the surface of their RBCs but have both ‘a’ and ‘b’ antibodies in their plasma.
- During blood transfusion compatibility of blood has to be taken into consideration.
- Person with ‘O’ blood group is called universal donor while the person with ‘AB’ blood group is called universal recipient. Individuals with blood group O can donate blood to anyone, while those individuals with blood group AB can receive blood from any person.
Question 3.
What are the main causes of cancer?
Answer:
Causes of Cancer : Following carcinogenic factors are responsible for causing cancer.
- Chemicals : Many induce development of cancer. E.g. nicotine, caffeine, polycyclic hydrocarbons and products of combustion of coal and oil. Sex hormone and steroids, if given or secreted in excess, can cause cancer. E.g. Breast cancer.
- Radiation : Radiations such as X-rays, gamma-rays, cosmic rays, ultra-violet rays are carcinogenic.
- Viruses : Virus possessing oncogenes (v-onc genes) are carcinogenic. E.g. EBV (Epstein-barr virus), HPV (Human papiloma virus) are oncogenic viruses.
- Oncogenes : Cellular oncogenes (c-onc genes) or proto-oncogenes can cause cancer. They are present in normal cells but if activated they lead to oncogenic transformation of cells.
- Addiction : Addictive substances like cigarette smoke, tobacco lead to cancer of mouth, lips and lungs. Alcohol can cause cancer of oesophagus, stomach, intestine and liver. Drugs like marijuana or anaerobic steroids can also cause cancer.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the different ways of treating cancer?
Answer:
Cancer treatment consists of combination of a number of therapies which are follows:
(1) Chemotherapy : Chemotherapy means giving certain anticancer drugs. These drugs check cell division by inhibiting DNA synthesis. But these are more toxic to cancerous cell than to normal cells. Chemotherapy shows side effects such as hair loss or anaemia.
(2) Radiotherapy : In addition to chemotherapy, radiations are given. The cancer cells are bombarded with the radiations from radioactive materials such as cobalt, iridium and iodine. The X-rays, gamma rays and charge particles are used to destroy the cancerous tissue or cells. They cause minimum damage to the surrounding normal tissue or cells.
(3) Surgery : Entire cancerous tissue or cells are removed surgically. E.g. breast tumour or uterine tumour. After removing the cancerous tissue, additionally other treatments are also given.
(4) Immunotherapy : For tackling with tumour, patients are given biological response modifiers such as a-interferon which activates their immune system to destroy the tumour.
(5) Supportive therapy : With supportive therapy, patient’s quality of life is increased. To treat symptoms of cancer and side effects of cancer treatments, this therapy is used. This therapy varies depending upon condition of individual patient.